Слайд 2
Mist – a suspension of small water droplets or moist
hygroscopic particles that slightly obscures visibility. Mist is reported when
visibility exceeds 1 km; below that limit the obscuration would be classed as fog.
Fog – a visible suspension of water droplets in the atmosphere near the surface, and defined by international agreement as reducing visibility to less than 1 km. There is no physical distinction between fog and cloud, other than the fact that the base of clouds is above the surface of the ground.
Haze is reported when visibility decreases to values from 1 to 10 km (dry haze: relative humidity is less 100%).
Слайд 3Condensation and fog
Properties of water
Formation of dew, frost, rime
Types of
fog
formation
clearance
Synoptic situations
Слайд 4Water
Three phases … solid, liquid, gas (vapour)
Latent heat
heat absorbed or
emitted to change state.
Relative humidity
amount of water vapour the air
holds as a percentage of amount it could hold when saturated.
Dew-point temperature
temperature at which air just becomes saturated w.r.t water when cooled at constant pressure.
Слайд 5
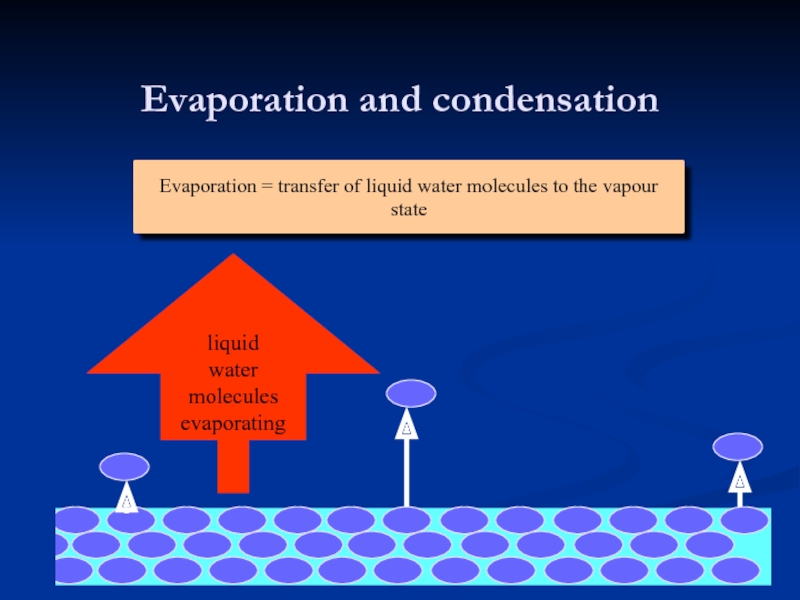
Evaporation = transfer of liquid water molecules to the vapour
state
Evaporation and condensation
Слайд 6
water
vapour
molecules
condensing
Condensation = transfer of water vapour molecules to the
liquid state
Evaporation and condensation
Слайд 7
water
vapour
molecules
condensing
=
Dynamic equilibrium for a plane surface of pure water
occurs when ... no. of molecules transferring to vapour state
= no. transferring to liquid state - Saturation
Evaporation and condensation
Слайд 8Dew
What do you need?
Moisture, cooling, condensation surface
Clear skies at night
(loss of long wave radiation)
Light/calm winds to prevent mixing
Moisture source
What
is it?
Condensation of water vapour onto surface whose temperature is < Td
small water drops D < 1mm
Слайд 9Dew
Ground cools
Air near ground is cooled to dew point
Water condenses
onto ground
Latent heat given out during condensation
slows temperature fall
Air near
the ground becomes drier
∴ Dew point falls
Temperature must fall further for condensation to continue.
Слайд 10For sub-zero temperatures
Frost occurs when T < 0°C
ground frost
for ground temp < 0°C
air frost for screen temp
< 0°C
Classified as slight, moderate, severe, very severe (temperature and wind)
Ice deposits onto cooled surfaces are hoar frost (terminology: deposition/sublimation)
Слайд 11Hoar frost or rime?
Super cooled droplets required
Deposits of ice when
drops meet a sub-zero surface.
Rime builds up on windward sides
of objects (fence posts).
Слайд 12Fog
What is it?
A suspension of microscopic water droplets in the
air reducing visibility at the earth’s surface to:
< 1000m for
met. observations, aviation
and shipping.
< 200m for public service purposes
Слайд 13Freezing fog
Super-cooled fog drops which freeze on impact with a
surface
Ice fog
Tiny suspended ice particles
Usually requires T= -30°C
Very rare in
the UK but often in Siberia!
Fog
Слайд 14Why does fog form?
Water vapour condenses onto atmospheric particles.
For condensation
we need saturation.
How do we turn unsaturated air into saturated
air?
Слайд 15Condensation
Vapour
Pressure
Temperature
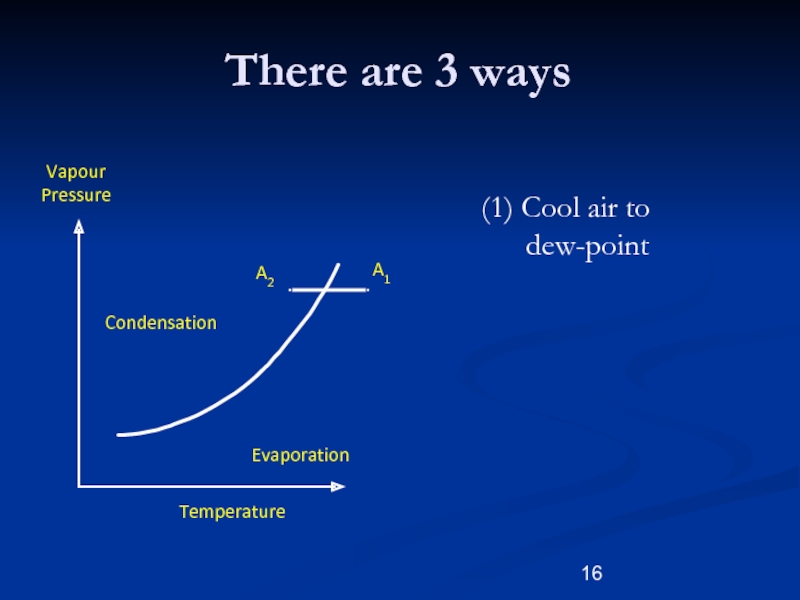
There are 3 ways
Evaporation
Слайд 16(1) Cool air to
dew-point
A2
A1
Vapour
Pressure
Temperature
There are 3
ways
Evaporation
Condensation
Слайд 17(1) Cool air to
dewpoint
(2) Add water
vapour
A2
A1
B2
B1
Vapour
Pressure
Temperature
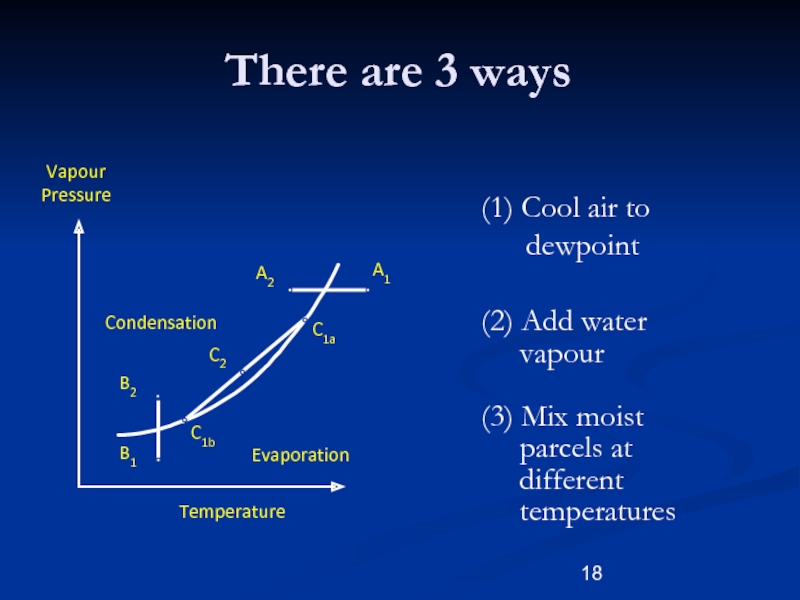
There are 3 ways
Evaporation
Condensation
Слайд 18(1) Cool air to
dewpoint
(2) Add water
vapour
(3) Mix moist
parcels at
different
temperatures
A2
A1
B2
B1
C1b
C1a
C2
Vapour
Pressure
Temperature
There are 3 ways
Evaporation
Condensation
Слайд 19Fog Classification
There are four main types:
Radiation - cooling of ground
by radiation
Advection - (warm advection) cooling of air by conduction
Upslope
- cooling of air by adiabatic expansion
Frontal - increasing moisture by evaporation
Also:
Steam - (cold advection) increasing moisture by evaporation
Слайд 201. Radiation fog
Favourable conditions
Clear sky or thin, high cloud
Moist air
in lowest 100m
Moist ground
Light surface wind
Favourable local topography
When are these
conditions likely?
Слайд 21Stage 1. Dew deposition
Clear night, strong radiative cooling
Light winds
Rapid fall
in surface temperature
Cools to dew point
Dew deposition
Air dries, dew point
falls but … mixing maintains condensation
Heat
Temperature
Td
T
Cooling
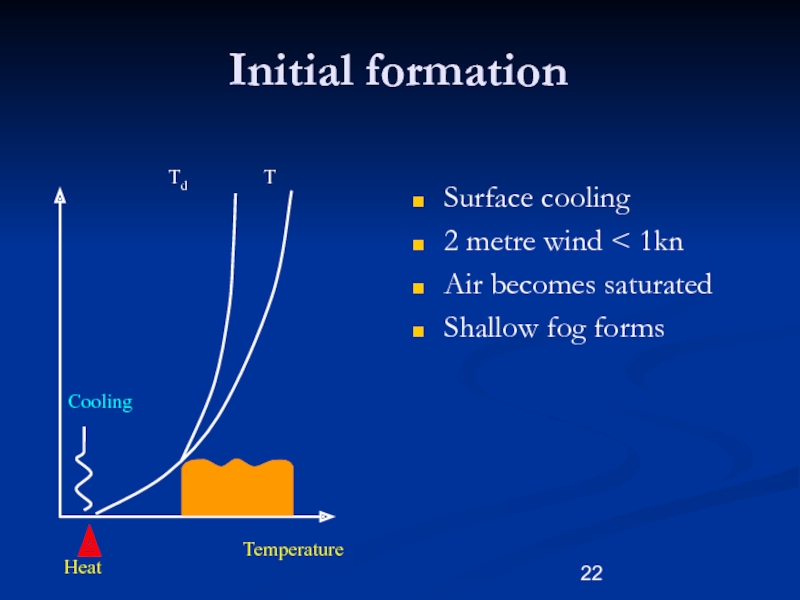
Слайд 22Initial formation
Surface cooling
2 metre wind < 1kn
Air becomes saturated
Shallow
fog forms
Heat
Temperature
Td
T
Cooling
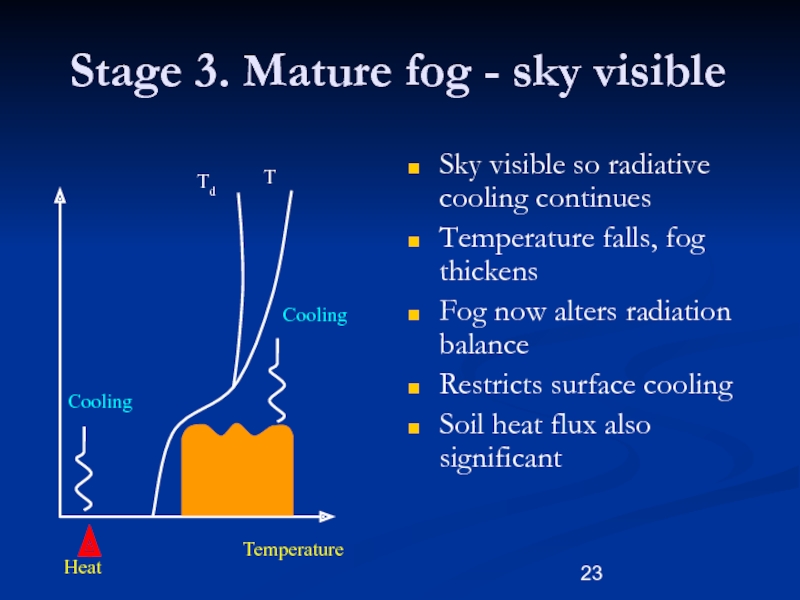
Слайд 23Stage 3. Mature fog - sky visible
Sky visible so radiative
cooling continues
Temperature falls, fog thickens
Fog now alters radiation balance
Restricts surface
cooling
Soil heat flux also significant
Heat
Temperature
Td
T
Cooling
Cooling
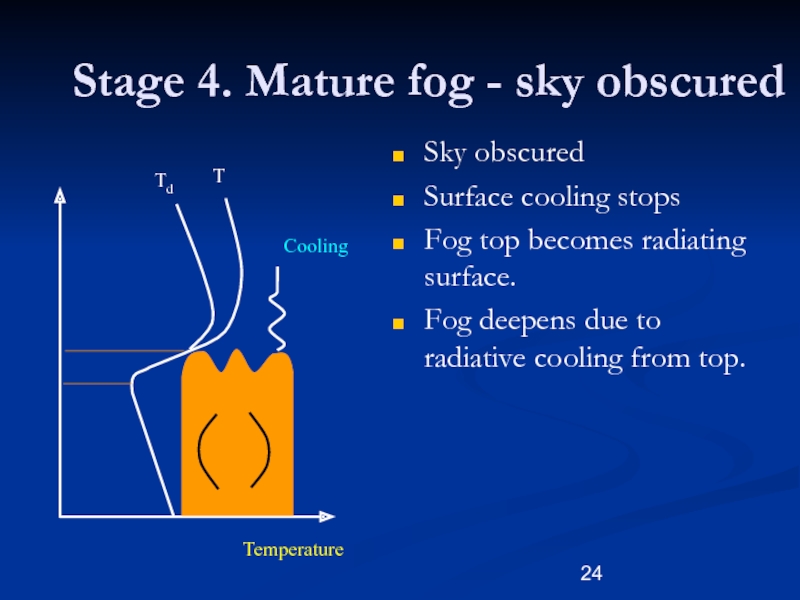
Слайд 24Stage 4. Mature fog - sky obscured
Sky obscured
Surface cooling stops
Fog top becomes radiating surface.
Fog deepens due to radiative cooling
from top.
Temperature
Td
T
Cooling
Слайд 25Additional processes...
Lowering of stratus to the ground
Advective Effects
Fog upwind
Air mass change
Upslope motion
Sunrise
Turbulence
Dew evaporating
Pollution
Smog
Слайд 26Clearance mechanisms
Solar radiation – raises air temperature above dew point.
Increase
in gradient wind – turbulence
Advection of cloud over the fog
– radiation warms the fog top (most efficient method)
Advection of drier air – lowers surface dew point
Слайд 272. Advection Fog
Warm advection fog:
Warm moist air moving over cold
land or sea.
Cooling to dew point from below.
Mostly sea fog
Over
land, stratus
Cold advection fog:
Cold air moving over warm water.
Moisture evaporates then condenses again.
Arctic Sea Smoke.
Слайд 283. Upslope fog
Formed by
Warm, moist air forced to rise over
hills.
Air cools adiabatically on ascent
Very common in western and northern
Britain
Tropical maritime airmass
Слайд 294. Frontal fog
Formed by:
Ahead of warm front … rain from
warm air falling into very cold, stable air.
Rain evaporates
Layer eventually
becomes saturated and fog develops
Often produces stratus not fog.
How do you clear it?
Слайд 31A more concrete example
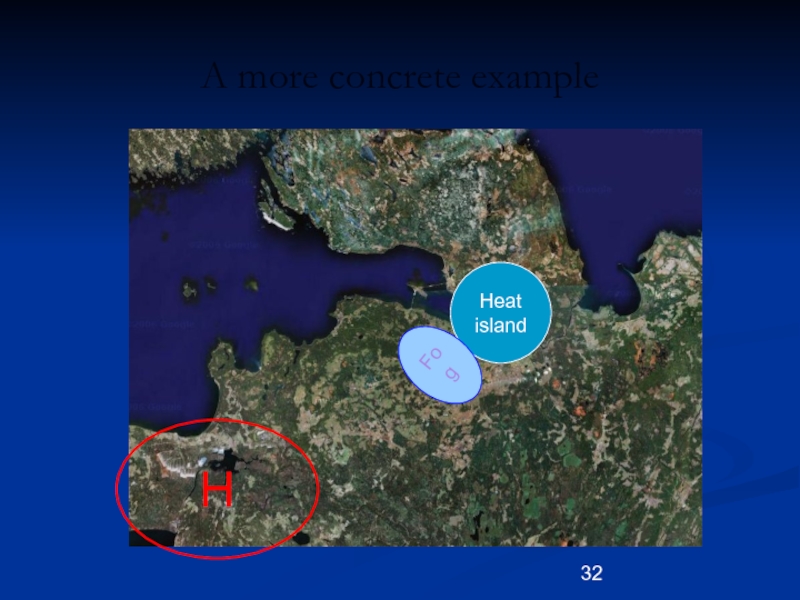
St. Petersburg, end of October–beginning of November.
Here lakes, rivers, and swamps that make the air to
be very humid cover for a large area.
A huge anticyclone occupies almost whole Europe. Its center is found to SW from St. Petersburg. Short days and long nights make the air mass colder and colder from day to day.
Cold and stable air mass and clear sky at nighttime plus very humid air (due to local condition) facilitates formation of a fog. However, within the town “warm island” (here the air temperature is about 20 C higher) no fog may appear, while over colder suburbs the fog forms.
As result, over airport Pulkovo the fog can be formed, over St. Petersburg cannot. That is the local weather.
Слайд 32A more concrete example
H
Heat
island
Fog
Слайд 33Types of fogs.
Radiation fog
Advection fog
Evaporation fog
Mixing fog
Слайд 34Could you name more fog types?
Upslope Fog
Ice Fog
Freezing Fog
Слайд 35Weather Sayings
It's raining cats and dogs.
Clear moon frost soon
When ants scatter everywhere, the weather is going to be
hot.