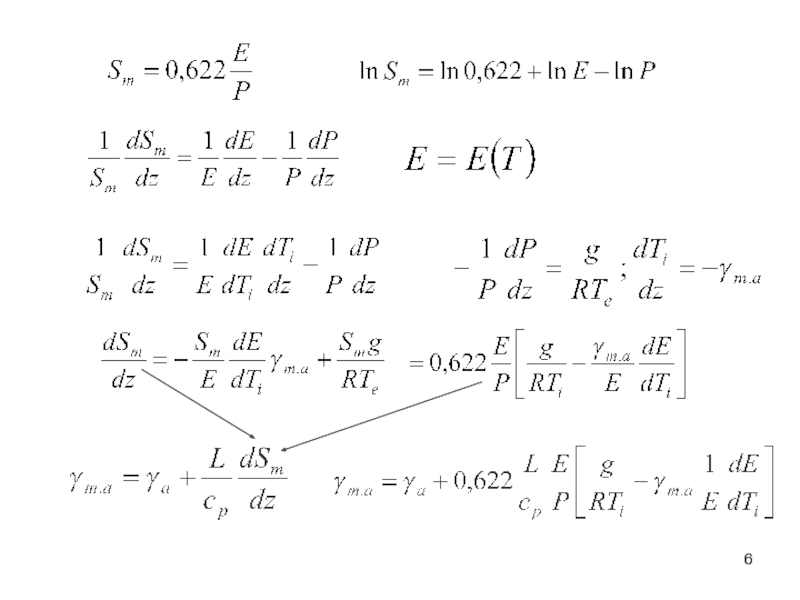Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Moist adiabatic processes
Содержание
- 1. Moist adiabatic processes
- 2. So, Ti0, RH
- 3. From the above reasoning it follows:Temperature of
- 4. First law of thermodynamics for the moist,
- 5. For adiabatic processAccounting for static equation, we
- 6. Слайд 6
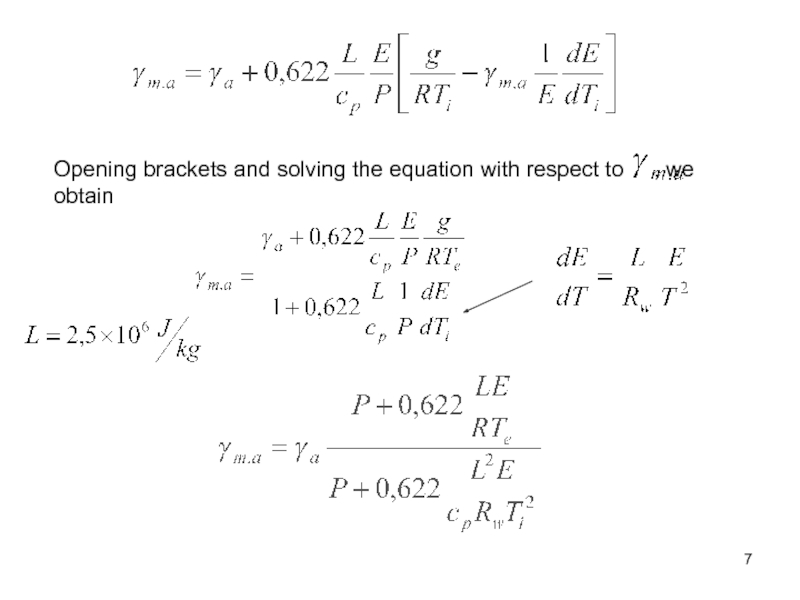
- 7. Opening brackets and solving the equation with respect to , we obtain
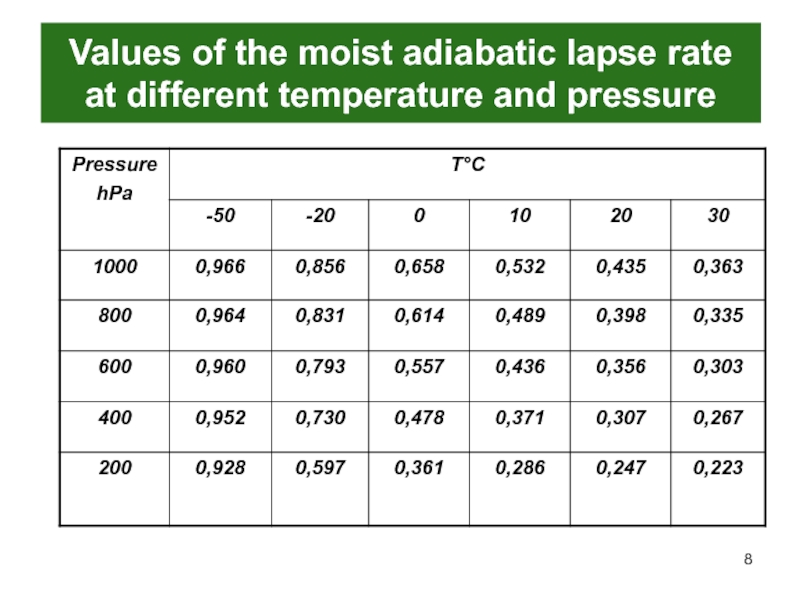
- 8. Values of the moist adiabatic lapse rate at different temperature and pressure
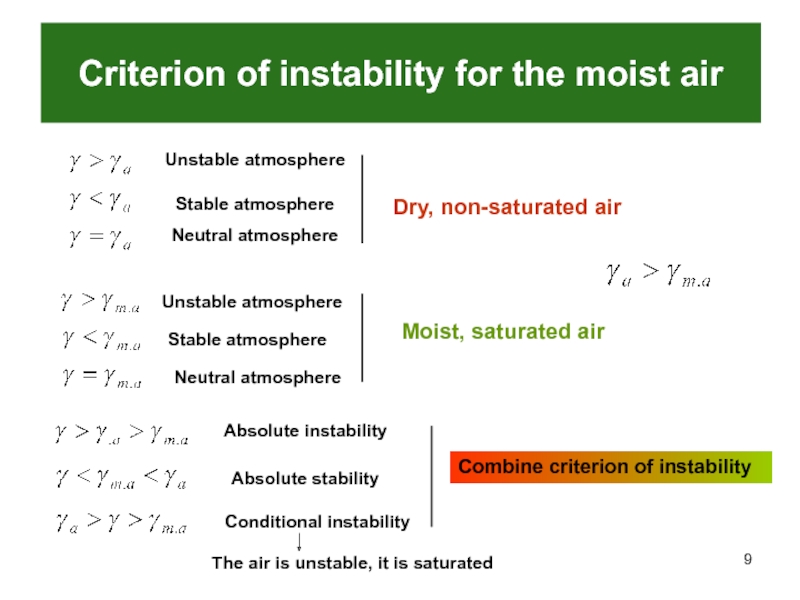
- 9. Criterion of instability for the moist airUnstable
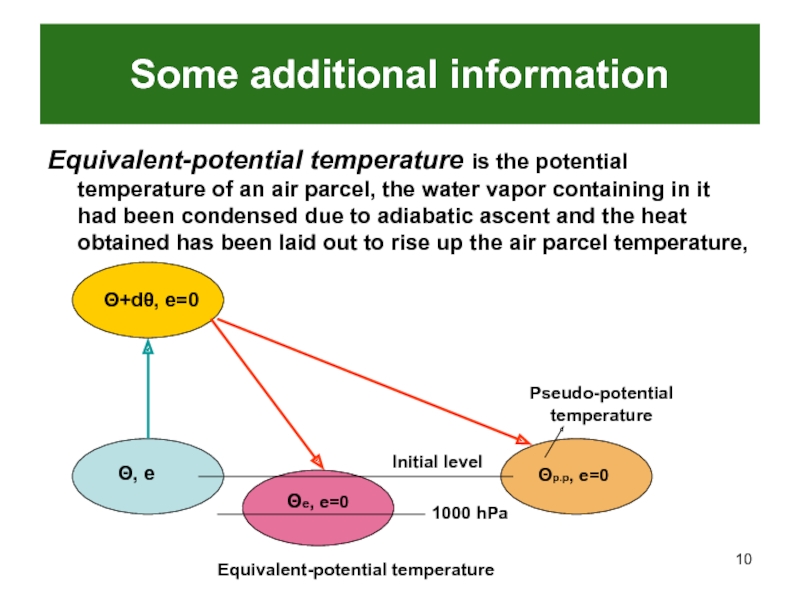
- 10. Some additional informationEquivalent-potential temperature is the potential
- 11. Some additional informationThe pseudopotential temperature(Θp.p) is a
- 12. If we have a convergence in an
- 13. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Moist adiabatic processes
An adiabatic process in moist, saturated air is
called
in the dry or non-saturated airСлайд 2
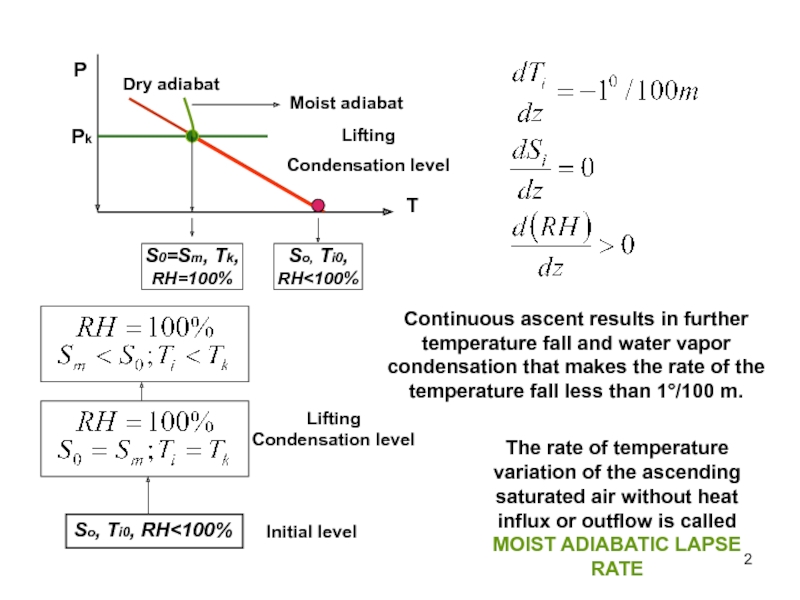
So, Ti0, RH
further temperature fall and water vapor condensation that makes the
rate of the temperature fall less than 1°/100 m.So, Ti0, RH<100%
Initial level
Lifting Condensation level
The rate of temperature variation of the ascending saturated air without heat influx or outflow is called MOIST ADIABATIC LAPSE RATE
Слайд 3From the above reasoning it follows:
Temperature of an ascending parcel
of air decreases with height, but slower that at dry
adiabatic process ( ).Due to condensation, the particle specific humidity Sm decreases with height
Relative humidity remains equal to 100%.
Adiabatic ascent of the moist air till attaining saturated state is called DRY STAGE.
Further ascending of the saturated air above the condensation level is called MOIST STAGE
Condensation level
Dry stage
Moist stage
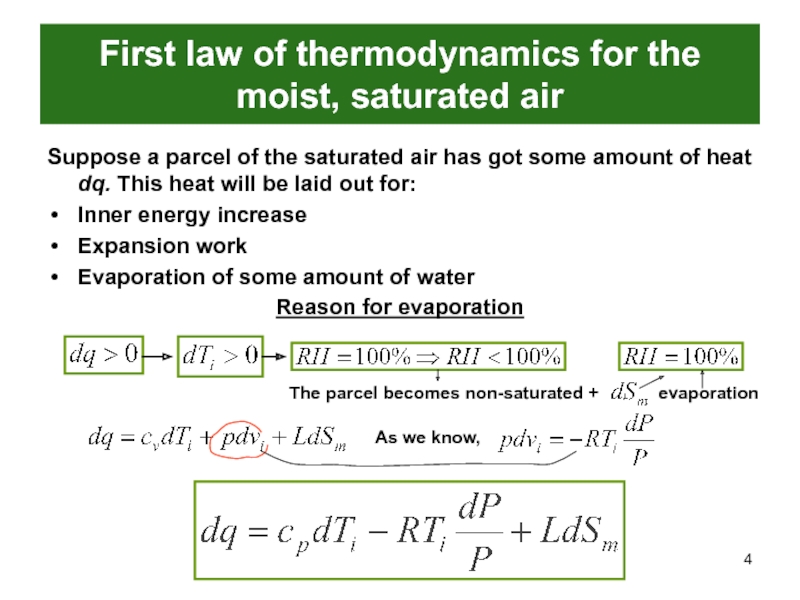
Слайд 4First law of thermodynamics for the moist, saturated air
Suppose a
parcel of the saturated air has got some amount of
heat dq. This heat will be laid out for:Inner energy increase
Expansion work
Evaporation of some amount of water
Reason for evaporation
The parcel becomes non-saturated +
evaporation
As we know,
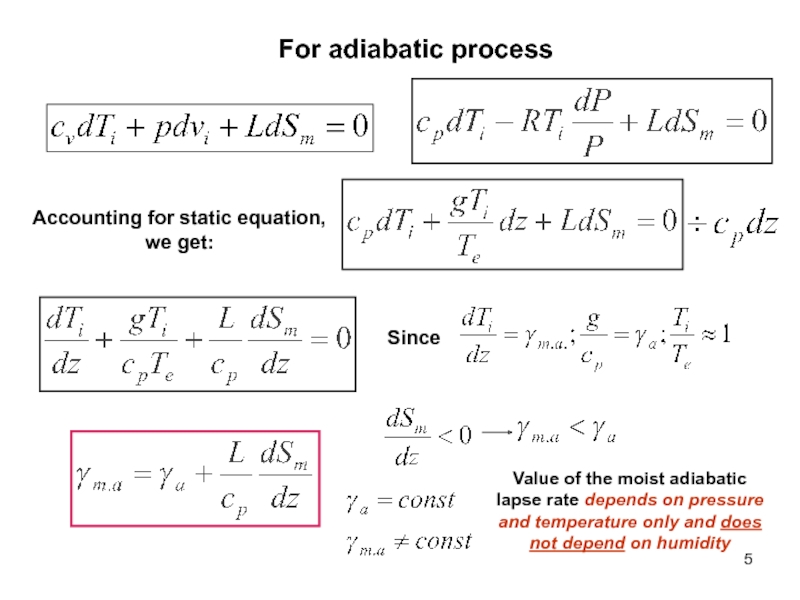
Слайд 5For adiabatic process
Accounting for static equation, we get:
Since
Value of the
moist adiabatic lapse rate depends on pressure and temperature only
and does not depend on humidityСлайд 9Criterion of instability for the moist air
Unstable atmosphere
Stable atmosphere
Neutral atmosphere
Dry,
non-saturated air
Unstable atmosphere
Stable atmosphere
Neutral atmosphere
Moist, saturated air
Absolute instability
Absolute stability
Conditional instability
The
air is unstable, it is saturatedCombine criterion of instability
Слайд 10Some additional information
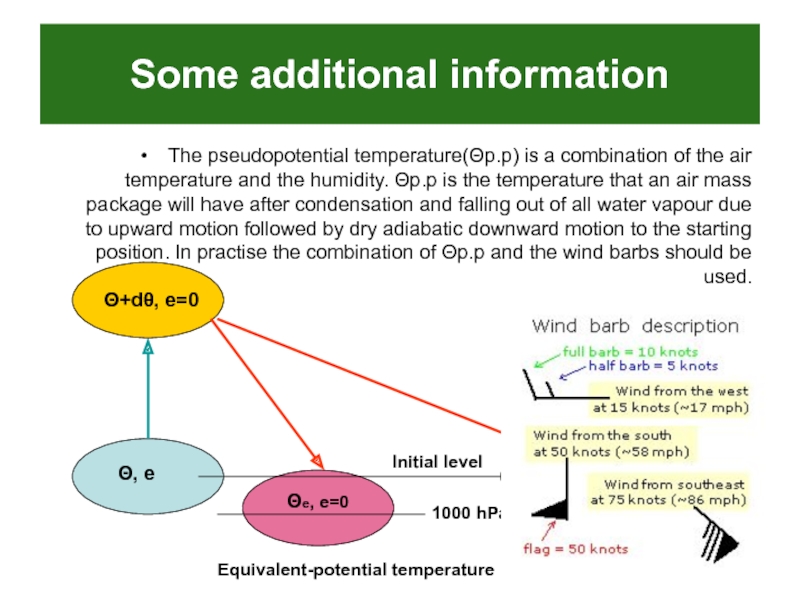
Equivalent-potential temperature is the potential temperature of an
air parcel, the water vapor containing in it had been
condensed due to adiabatic ascent and the heat obtained has been laid out to rise up the air parcel temperature,Θ, e
Θ+dθ, e=0
Θe, e=0
1000 hPa
Equivalent-potential temperature
Θp.p, e=0
Initial level
Pseudo-potential temperature
Слайд 11Some additional information
The pseudopotential temperature(Θp.p) is a combination of the
air temperature and the humidity. Θp.p is the temperature that
an air mass package will have after condensation and falling out of all water vapour due to upward motion followed by dry adiabatic downward motion to the starting position. In practise the combination of Θp.p and the wind barbs should be used.Θ, e
Θ+dθ, e=0
Θe, e=0
1000 hPa
Equivalent-potential temperature
Θp.p, e=0
Initial level
Pseudo-potential temperature
Слайд 12
If we have a convergence in an area with relatively
high tpspot we should be aware to convection or even
severe thunderstorms.Although we have that parameter only for 2m-values the following thresholds can be used as guidlines:- tpspot < 50°C: thunderstorms not likely, - 50°C > tpspot < 60°C: thunderstorms possible, - 60°C > tpspot < 70°C: thunderstorms likely (partly severe), - 70°C > tpspot < 80°C: severe thunderstorms, - tpsopot > 80°C: extreme thunderstorms