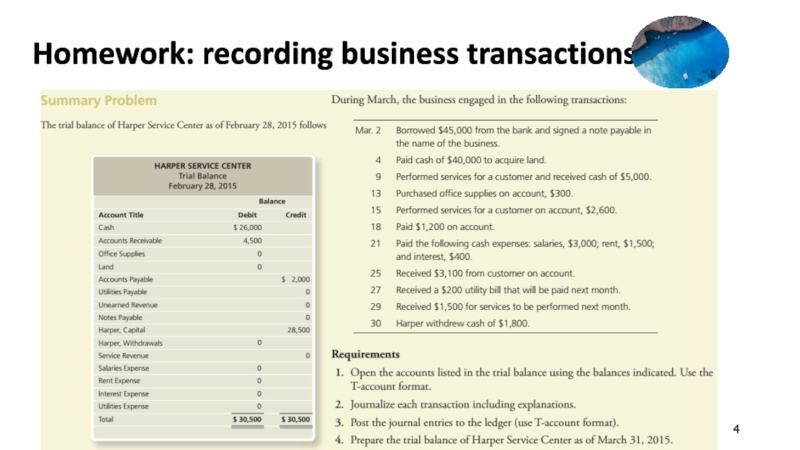
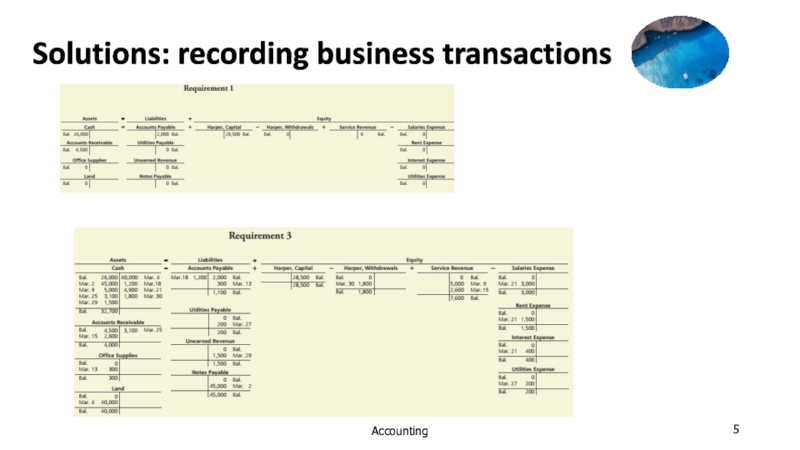
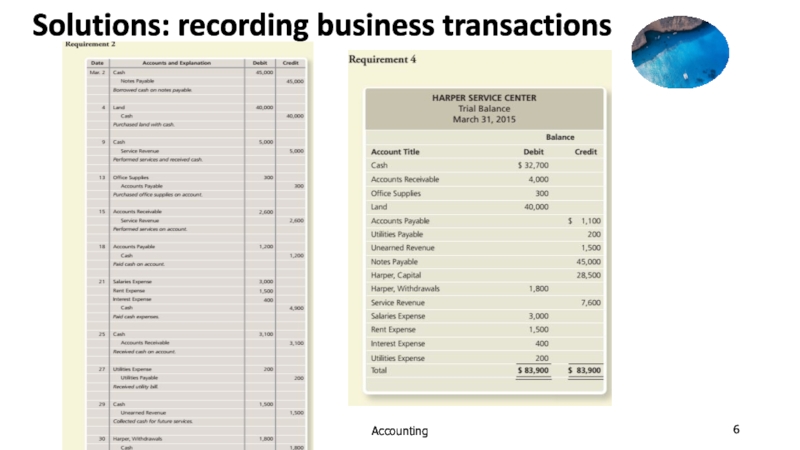
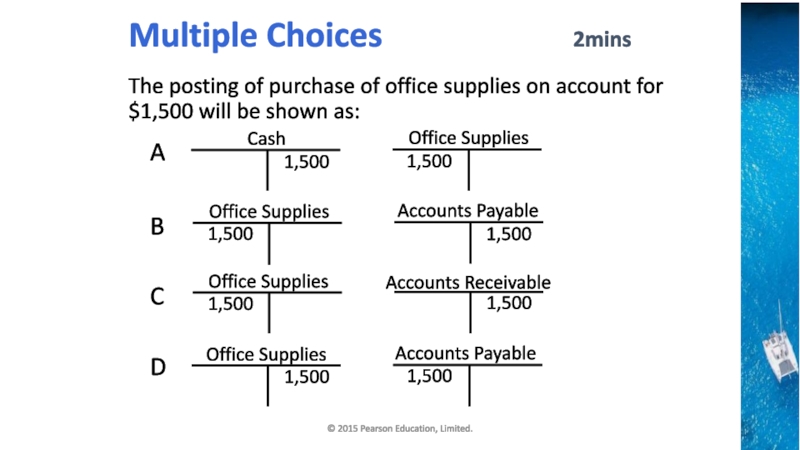
a trader by paying $10,000 into bank account.
2. April 2,
Abdul buys a motor vehicle for the business, and pay$2,000.
3. April 3,Abdul buy goods which he will re-sell in the normal course of trade for $3,000.
4. April 4, Abdul sells a quantity of the goods for $800,and pay the money into the bank.
5. April 7, a customer returns some goods and receives a refund of $40.
6. April 8, Abdul return some goods costing $100 to a supplier and receives a refund.
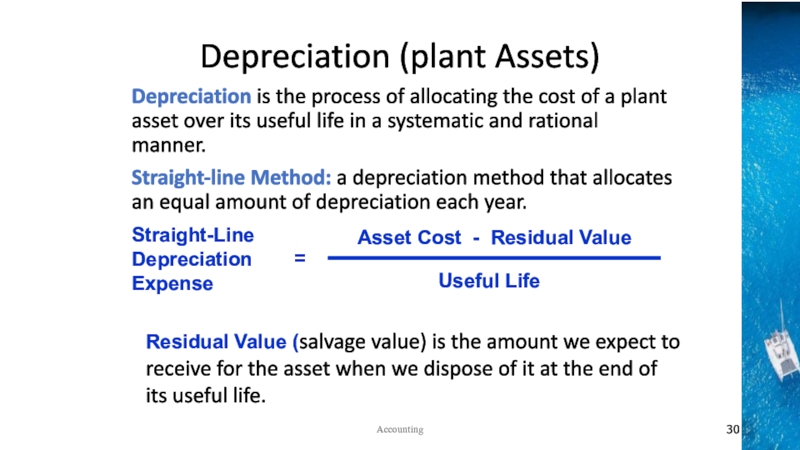
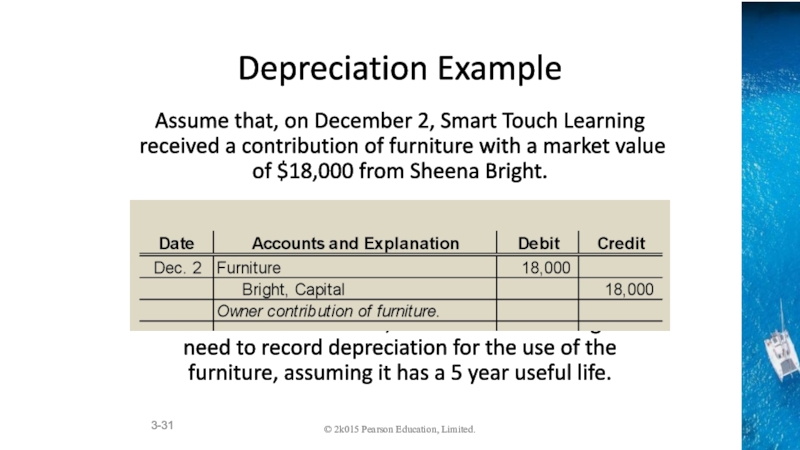
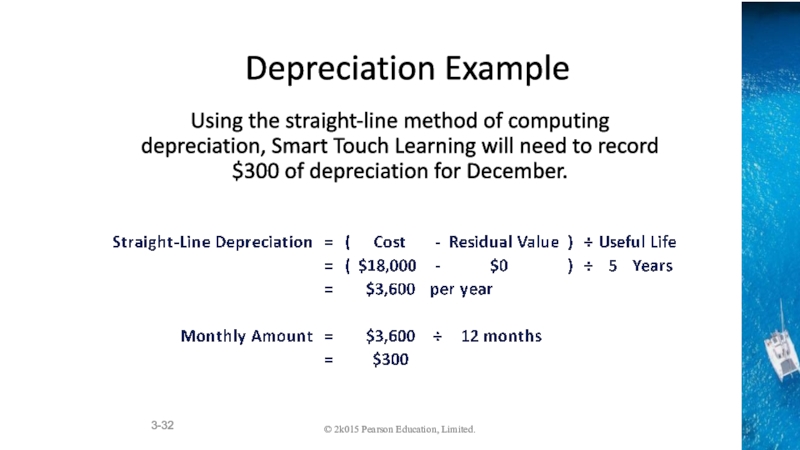
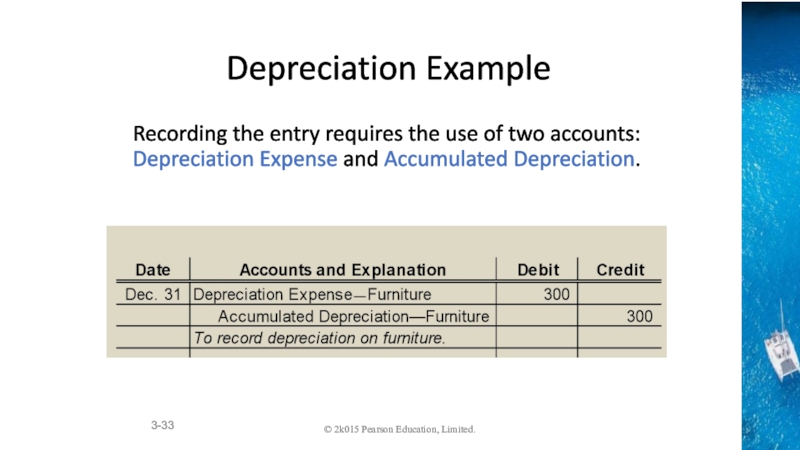
Accounting
7. April 10, Abdul buys another motor vehicle for the business and pay $4,000.
8. April 11, Tania lends the business $5,000,Abdul put the money into the bank account.
9. April 12, Abdul pays rent on a warehouse by cheque, $1,000.
10. April 14, Abdul subsets part of the warehouse and receives a cheque for $300 for the rent .this is paid into the bank.
11. April 15, Abdul pays wages by cheque,$1,200.
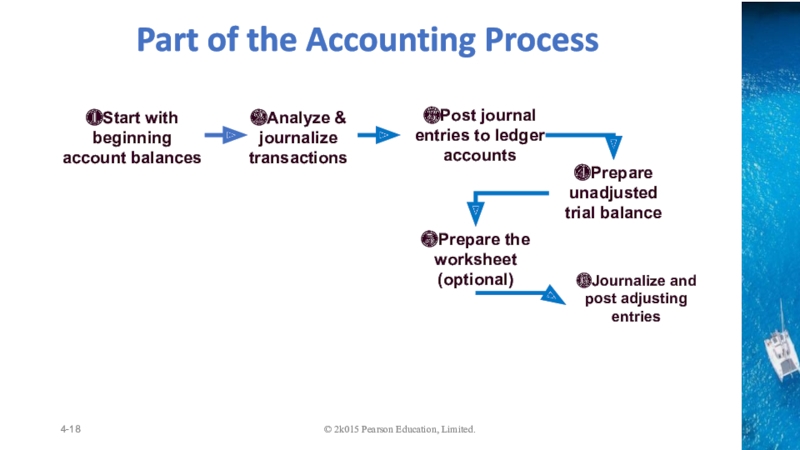
Identifying 11 transactions and Classifying different accounts
Recording the transaction into journals
Posting into the Ledger accounts