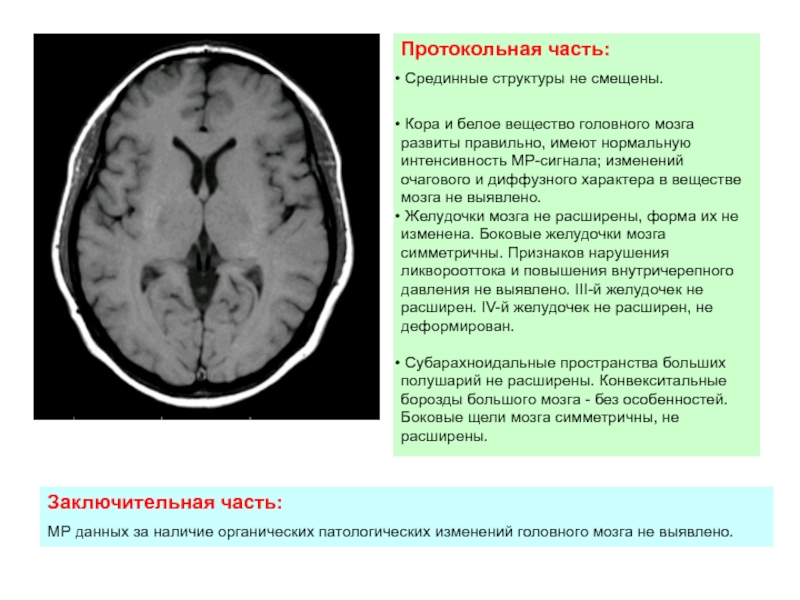
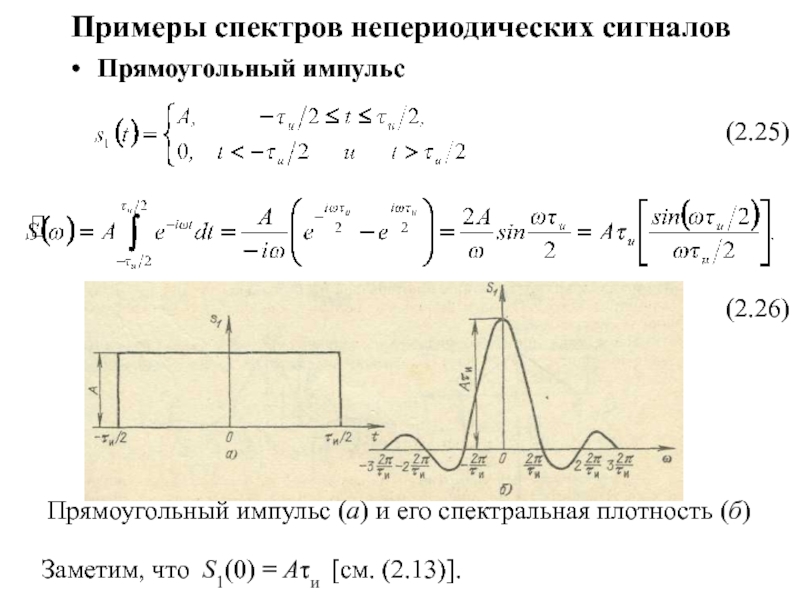
Слайд 2Three Stages of Memory: Atkinson-Schiffrin Model
Memory: active system that receives,
stores, organizes, alters, and recovers information
Atkinson-Schiffrin three-stage model
Sensory memory
Short-term memory
(STM)
Long-term memory (LTM)
Слайд 3Atkinson-Schiffrin Model: Key Processes
Encoding: converting information into a useable
form
Storage: holding this information in memory for later use
Retrieval: taking
memories out of storage
Слайд 4Atkinson-Schiffrin Model: Sensory Memory
Sensory memory: stores an exact copy of
incoming information for a few seconds or less (either what
is seen or heard); the first stage of memory
We are normally unaware of sensory memory
Selective attention to sensory memory transfers information to short-term memory
Слайд 5Types of Sensory Memory
Iconic memory: a visual sensory image stored
for about half a second
Echoic memory: after a sound is
heard, a brief continuation of the activity in the auditory system for about two seconds
Слайд 6Atkinson-Schiffrin Model: STM
Short-term memory (STM): stores small amounts of information
for a dozen seconds or so
We are consciously aware of
short-term memories
Encoding in STM is usually phonetic, by sound
Very sensitive to interruption or interference
Working memory: part of STM; like a mental “scratchpad”
Слайд 7Atkinson-Schiffrin Model: LTM
Long-term memory (LTM): storing meaningful information relatively permanently
Encoding in LTM is usually based on meaning
Слайд 8Capacity of Short-Term Memory
Storage capacity of STM limited to “magic
number” seven (plus or minus two) information bits at once
Information
bit: meaningful single piece of information, like a number or letter
Digit span: test of attention and short-term memory; string of numbers is recalled forward or backward
Слайд 9Chunking in Short-Term Memory
Recoding: reorganizing or modifying information to
assist storage in memory
Information chunks: bits of information that are
grouped into larger units
Слайд 10Rehearsal in Short-Term Memory
Maintenance rehearsal: repeating information silently to prolong
its presence in STM; storage is brief without maintenance rehearsal
Rote
rehearsal (rote learning): the use of repetition to transfer information to LTM; not very effective
Elaborative processing: links new information with existing memories and knowledge in LTM; more effective way to transfer information to LTM
Слайд 11Storage in Long-Term Memory
LTM memories are only rarely permanent
Elaborative processing
can revise memories on basis of reasoning or adding new,
possibly false, information
Pseudo-memories: false memories that a person believes are true or accurate
Source confusion: occurs when the origins of a memory are misremembered
Слайд 12Retrieval from Long-Term Memory
Network model: LTM stored as a network
of linked ideas
Redintegration: memories that are reconstructed or expanded by
starting with one memory and then following network of links to related memories
Cognitive Interview: use of various cues and strategies to improve eyewitness memory
Слайд 13Types of Long-Term Memories
Procedural (skilled) memory: LTM for conditioned responses
and learned skills
Declarative (fact) memory: LTM for factual information
Semantic memory:
part of declarative memory for impersonal facts and everyday knowledge
Episodic: part of declarative memory for personal experiences linked with specific times and places
Слайд 14Measuring Memory
Tip-of-the-tongue (TOT) state: feeling that a memory is available
but not quite retrievable
Feeling of knowing: feeling that allows people
to predict beforehand whether they will be able to remember something
Слайд 15Measuring Memory: Recall
Recall: direct retrieval of facts or information
Hardest to
recall items in the middle of an ordered list; known
as the serial position effect
Easier to remember first and last items in a list
Слайд 16Measuring Memory: Recognition
Recognition: previously learned material is correctly identified
Usually superior
to recall
Distractors: false items included with a correct item
Wrong choices
on multiple-choice tests
False positive: false sense of recognition
Слайд 17Measuring Memory: Relearning
Relearning: learning again something that was previously learned
Used
to measure memory of prior learning
Savings score: amount of time
saved when relearning information
Слайд 18Implicit and Explicit Memories
Explicit memory: past experiences that are consciously
brought to mind
Implicit memory: a memory not known to exist;
memory that is unconsciously retrieved
Priming: when cues are used to activate hidden memories
Слайд 19Forgetting in Long-Term Memory
Curve of forgetting: graph that shows the
amount of memory information remembered after varying lengths of time
Nonsense
syllables: meaningless three-letter words (fej, quf) that test learning and forgetting
Слайд 20Encoding Failure in Long-Term Memory
Encoding failure: when a memory was
never fully formed in the first place
Other people may all
“look alike” due to encoding failure
Слайд 21Storage Failure in Long-Term Memory
Memory traces: physical changes in nerve
cells or brain activity that occur when memories are stored
Memory
decay: when memory traces become weaker; fading or weakening of memories
Disuse: theory that memory traces weaken when memories are not periodically used or retrieved
Слайд 22Retrieval Failure in Long-Term Memory
Availability: a memory is available when
it is stored in LTM
Accessibility: a memory is accessible in
LTM when it can be successfully retrieved
Information in LTM can be available but NOT accessible
Memory cue: any stimulus associated with a memory; usually enhances retrieval of a memory
A person may “forget” (be inaccessible) if cues are missing at retrieval time
Слайд 23State-Dependent Learning
State-dependent learning: when memory retrieval is influenced by bodily
state at time of learning; if your body state is
the same at the time of learning AND the time of retrieval, retrieval will be improved
Слайд 24Interference
Tendency for new memories to impair retrieval of older
memories, and the reverse
Retroactive interference: tendency for new memories to
interfere with retrieval of old memories
Proactive interference: prior learning inhibits (interferes with) recall of later learning
Слайд 25Transfer of Training
Positive transfer: mastery of one task aids learning
or performing another
Negative transfer: mastery of one task conflicts with
learning or performing another
Слайд 26Repression and Suppression
Repression: unconsciously pushing painful, embarrassing, or threatening memories
out of awareness/consciousness
Motivated forgetting
Suppression: consciously putting something painful or threatening
out of mind or trying to keep it from entering awareness
Слайд 27Memory Formation and the Brain
Consolidation: forming a long-term memory in
the brain
Retrograde amnesia: forgetting events that occurred before an injury
or trauma
Anterograde amnesia: forgetting events that follow an injury or trauma
Electroconvulsive shock (ECS): mild electrical shock passed through the brain can prevent consolidation of any memory being formed at the time
Слайд 28Memory Formation and the Hippocampus
Hippocampus: brain structure associated with emotion
and transfer of information passing from short-term memory into long-term
memory
If damaged, person can no longer “create” long-term memories and thus will always live in the present
Memories prior to damage will remain intact
Слайд 29Memory Formation and the Limbic System
Flashbulb memory: memory created during
times of personal tragedy, accident, or other emotionally significant events
Includes
both positive and negative experiences; great confidence is placed in them even though they may be inaccurate
Due to involvement of limbic system
Слайд 30Photographic and Eidetic Imagery
Photographic memories: persistent mental images (mental pictures)
Eidetic
imagery: occurs when a person (usually a child) has visual
images clear enough to be scanned or retained for at least 30 seconds
Usually projected onto a “plain” surface, like a blank piece of paper
Usually disappears during adolescence and is rare by adulthood
Слайд 31Ways to Improve Memory: Encoding Strategies
Elaborative processing: look for connections
to existing knowledge
Selection: select only the most important concepts to
memorize
Organization: organize difficult items into chunks; a type of recoding
Слайд 32Ways to Improve Memory: Encoding Strategies (cont’d)
Whole learning (vs. part
learning): study the largest meaningful amount of information you can
at one time
Progressive-part method: for very long or complex material, break a learning task into a series of shorter sections
Serial position: since most errors occur while remembering the middle of the list, spend more study time there
Слайд 33Ways to Improve Memory: Encoding Strategies (cont’d)
Cues: stimuli that aid
retrieval are most effective if they were present during encoding;
engage in more elaborative encoding to increase the number of available retrieval cues
Overlearning: continue studying beyond bare mastery
Spaced practice: alternate short study sessions with brief rest periods; better than massed practice, studying for long periods without rest periods
Слайд 34Ways to Improve Memory: Retrieval Strategies
Retrieval practice: practice retrieval (e.g.,
through recitation) for feedback
Knowledge of results: lets you check progress
Recitation:
summarizing aloud while learning
Review: review your learning before retrieval
Use a strategy to aid recall: carry out planned searches of memory
Extend how long you remember: lengthen the amount of time between retrieval practice
Слайд 35Ways to Improve Memory: Sleep and Hunger
Lack of sleep decreases
retention; sleep aids consolidation
Hunger decreases retention
Слайд 36Mnemonics: Memory “Trick”
Any kind of memory system or aid
Uses
mental pictures
Makes things meaningful
Makes information familiar
Forms bizarre, unusual, or exaggerated
mental associations
Слайд 37Keyword Method
Aid to memory; using a familiar word or image
to link two items
Слайд 38Using Mnemonics to Remember Things in Order
Form a chain or
story: remember lists in order, forming an exaggerated association connecting
item one to two, and so on
Take a mental walk: mentally walk along a familiar path, placing objects or ideas along the path
Use a system