Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
CONSTRUCTION AND OPTIMIZATION OF ALGORITHMS Computational complexity theory
Содержание
- 1. CONSTRUCTION AND OPTIMIZATION OF ALGORITHMS Computational complexity theory
- 2. Literature Thomas H. Cormen Charles E.
- 3. Time complexity Тhe time complexity
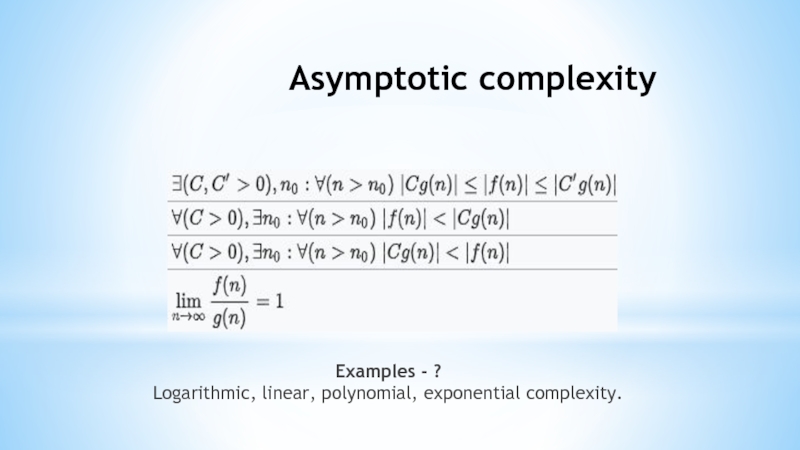
- 4. Asymptotic complexity Examples - ? Logarithmic, linear, polynomial, exponential complexity.
- 5. Other measures of complexity Other measures
- 6. Other measures of complexity If
- 7. Other measures of complexity If
- 8. Other measures of complexity
- 9. Calculate the complexity of the algorithm
- 10. Calculate the complexity of the algorithm
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. Слайд 13
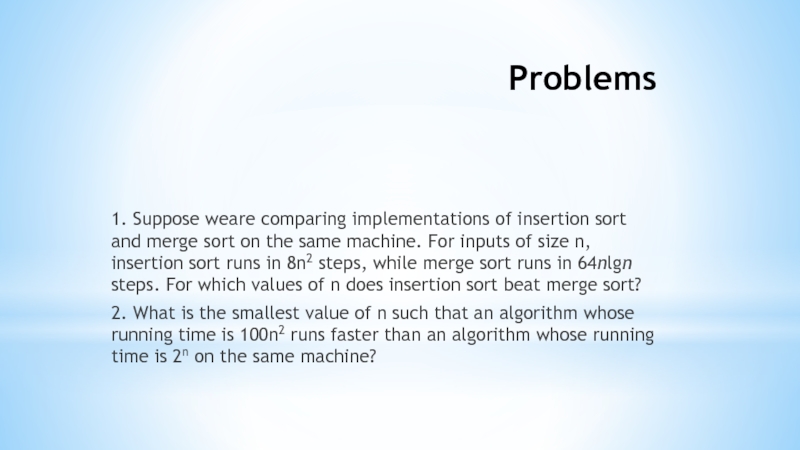
- 14. Problems 1. Suppose weare comparing implementations
- 15. Problems 3. For each function f(n)
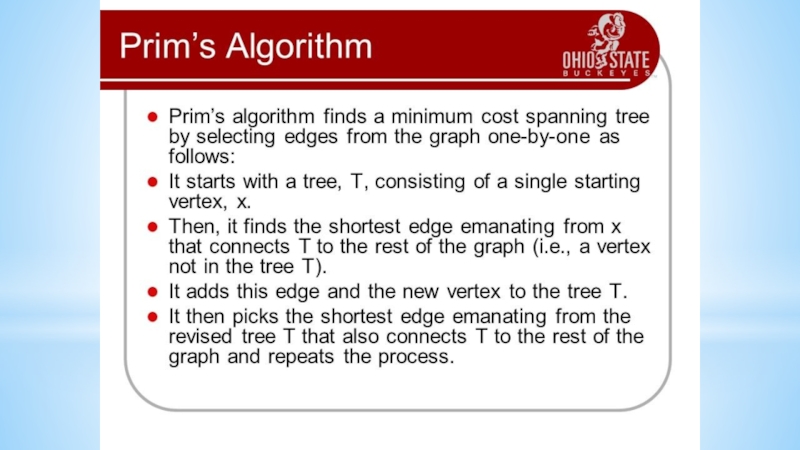
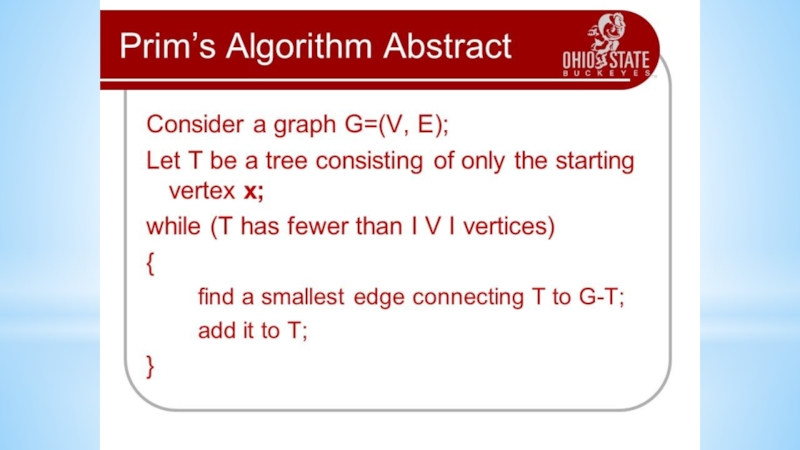
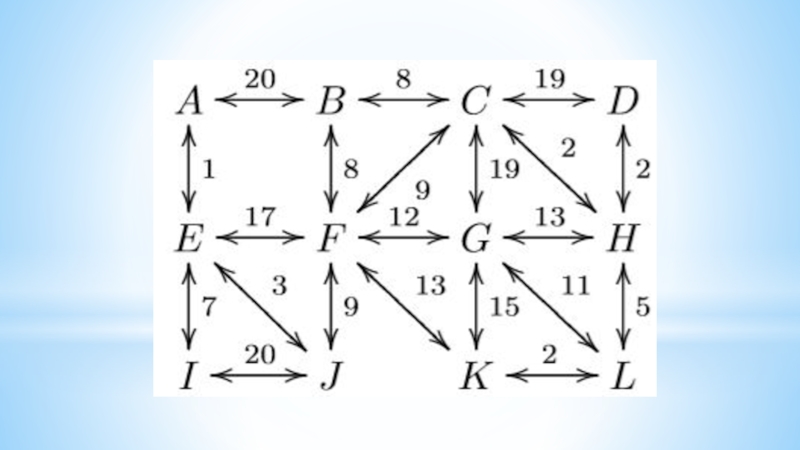
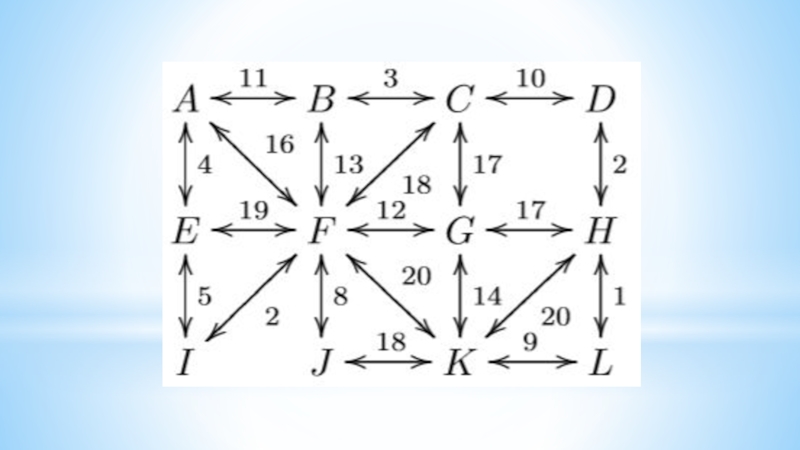
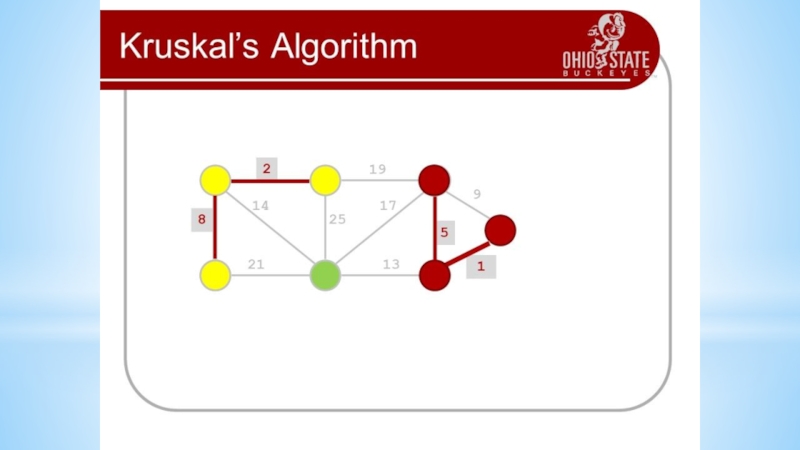
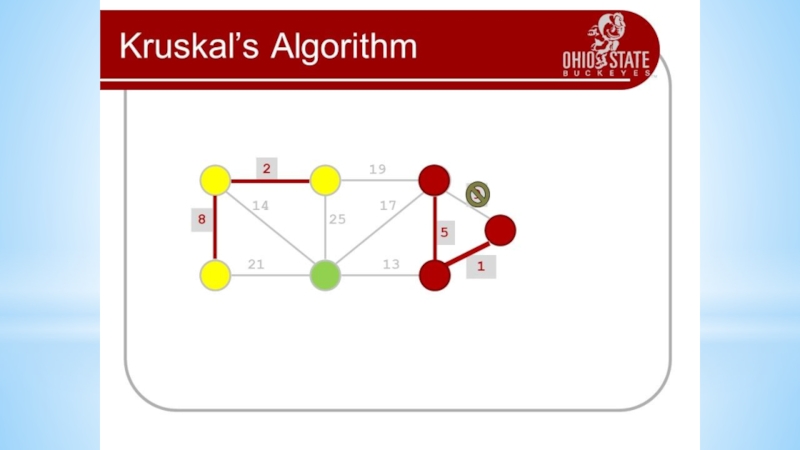
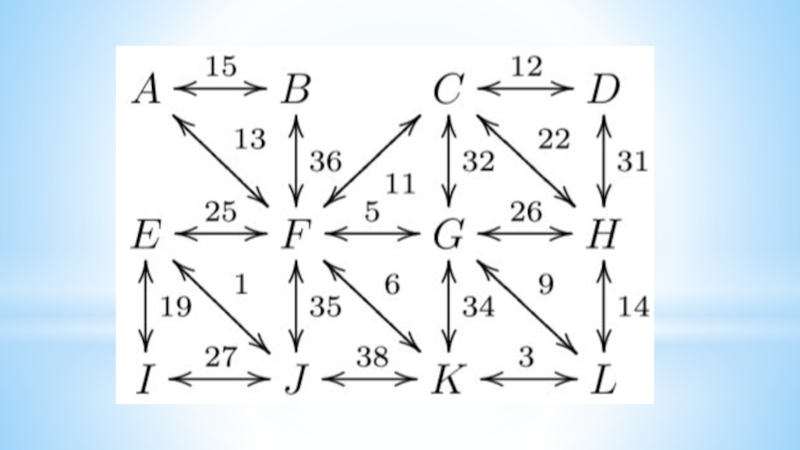
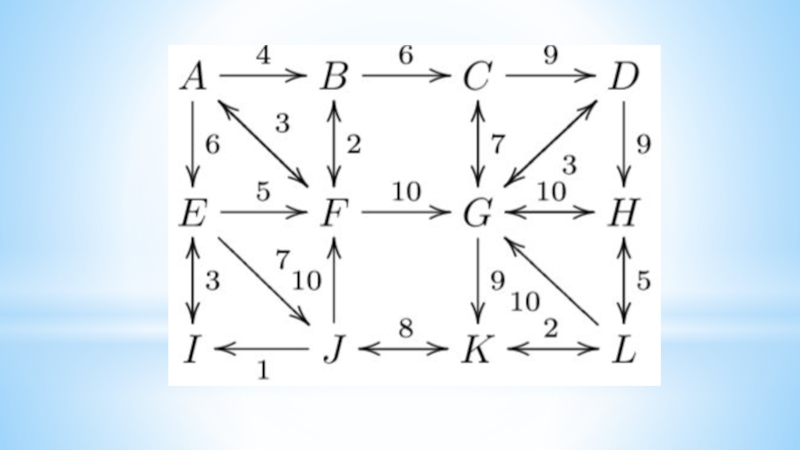
- 16. Algorithms on graphsFirst examples1. Connect six points
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Слайд 22
- 23. Слайд 23
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. Слайд 25
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. Слайд 27
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. Слайд 31
- 32. Скачать презентанцию
Literature Thomas H. Cormen Charles E. Leiserson Ronald L. Rivest Clifford Stein. Introduction to Algorithms.N. Wirth. Algorithms and Data Structures.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1CONSTRUCTION AND OPTIMIZATION OF ALGORITHMS
Computational complexity theory
Computational complexity theory focuses on
Слайд 2Literature
Thomas H. Cormen Charles E. Leiserson Ronald L. Rivest Clifford
Stein. Introduction to Algorithms.
N. Wirth. Algorithms and Data Structures.
Слайд 3Time complexity
Тhe time complexity of the algorithm in the
worst, best or average case. In some particular cases, we
shall be interested in the average-case running time of an algorithm; we shall see the technique of probabilistic analysis applied to various algorithms.1. The larger of the two natural numbers is 34. What should be the smaller number for the Euclidean algorithm to have as many steps as possible?
2. The larger of the two natural numbers is 55. What should be the smaller number for the Euclidean algorithm to have as many steps as possible?
Слайд 5Other measures of complexity
Other measures of complexity are also used,
such as
the amount of communication (used in communication complexity),
the number of gates in a circuit (used in circuit complexity) and
the number of processors (used in parallel computing).
One of the roles of computational complexity theory is to determine the practical limits on what computers can and cannot do.
Слайд 6Other measures of complexity
If the created program is used only
a few times, then the cost of writing and debugging
the program will dominate the total cost of the program, that is, the actual execution time will not have a significant impact on the total cost. In this case, you should prefer the algorithm that is the easiest to realize.Слайд 7Other measures of complexity
If the program will only work with
“small” input data, the degree of growth in the execution
time will be less important than the constant present in the asymptotic runtime formula. At the same time, the notion of “smallness” of the input data depends on the exact execution time of competing algorithms. There are algorithms, such as the algorithm of integer multiplication, which are asymptotically the most efficient, but which are never used in practice even for large tasks, since their proportionality constants far exceed those of other, simpler and less “efficient” algorithms.Слайд 8Other measures of complexity
Sometimes there are incorrect algorithms that either
get looped or sometimes give the wrong result. But they
still apply, because in most cases they lead to the desired result. For example, Kramer’s rule or resolution method.Слайд 14Problems
1. Suppose weare comparing implementations of insertion sort and merge
sort on the same machine. For inputs of size n,
insertion sort runs in 8n2 steps, while merge sort runs in 64nlgn steps. For which values of n does insertion sort beat merge sort?2. What is the smallest value of n such that an algorithm whose running time is 100n2 runs faster than an algorithm whose running time is 2n on the same machine?
Слайд 15Problems
3. For each function f(n) and time t in the
following table, determine the largest size n of a problem
that can be solved in time t, assuming that the algorithm to solve the problem takes f(n) microseconds.Слайд 16Algorithms on graphs
First examples
1. Connect six points with non-intersecting segments
so that 3 points leave each point.
2. Connect 14 points
with non-intersecting segments so that 4 points leave each point.3. Draw a closed six-pattern broken line that intersects each of its links once.
4. The volleyball net has a size of 10 by 50 cells. What is the greatest number of ropes can be cut so that the grid does not fall apart into pieces?