Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
D. Ricardo’s theory of “comparative advantages ”
Содержание
- 1. D. Ricardo’s theory of “comparative advantages ”
- 2. Introduction1. Historical background2. Principles of the theory
- 3. “Principles of Political Economy and Taxation” (1817)Mercantilism
- 4. Even if a country had a considerable
- 5. Basic assumptions:Only two nations and two commodities;Free
- 6. Input (labor) requirements per unit of outputAbsolute advantage in both productsPrinciple of Comparative Advantage
- 7. Countries should specialize in producing those goods
- 8. Explanation of the theory: example Input (labor)
- 9. Output per 100 units of input (labor)Explanation
- 10. Production Possibility FrontierSource: Paul R. Krugman, M.
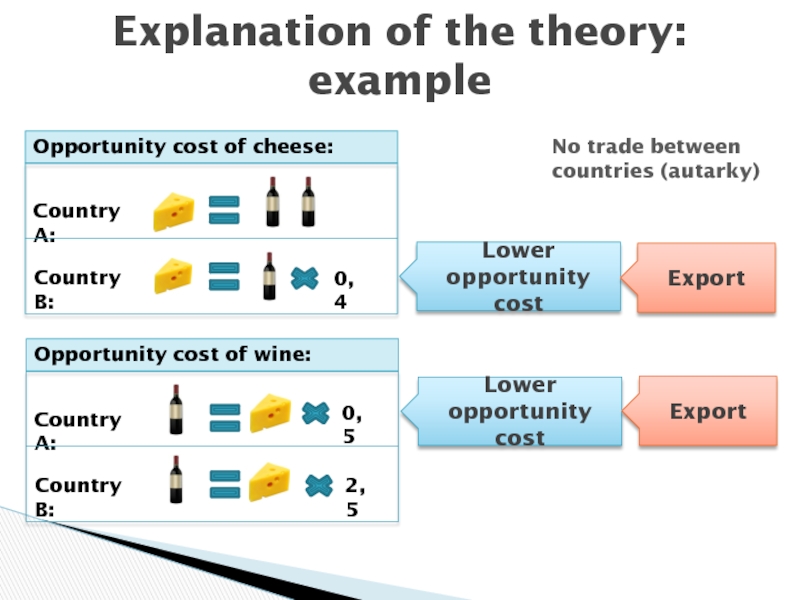
- 11. Explanation of the theory: example 2,5Lower opportunity costExportLower opportunity costExportNo trade between countries (autarky)
- 12. When countries specialize in producing the goods
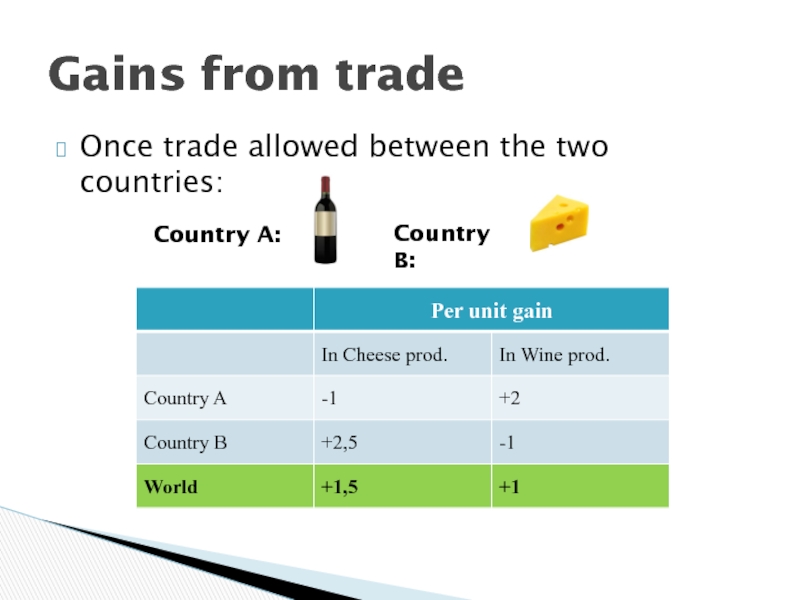
- 13. Once trade allowed between the two countries:Gains from tradeCountry A:Country B:
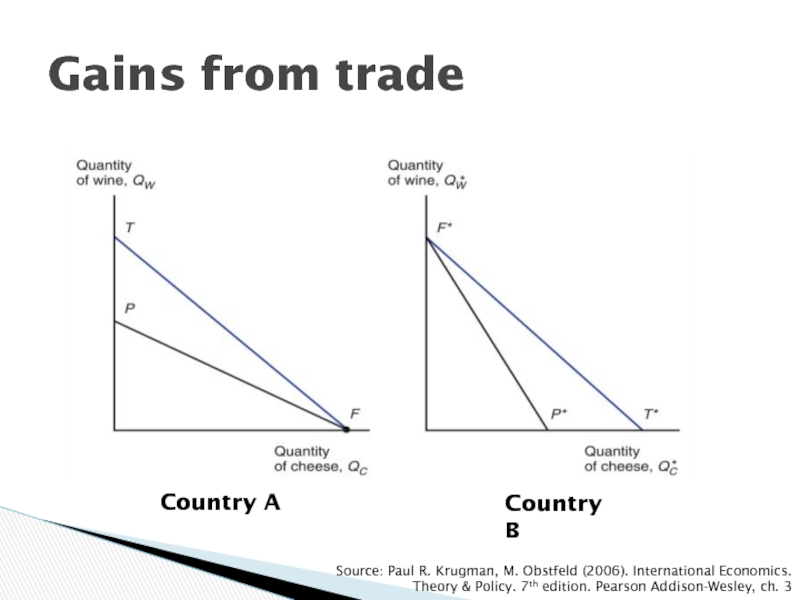
- 14. Gains from tradeCountry ACountry BSource: Paul R.
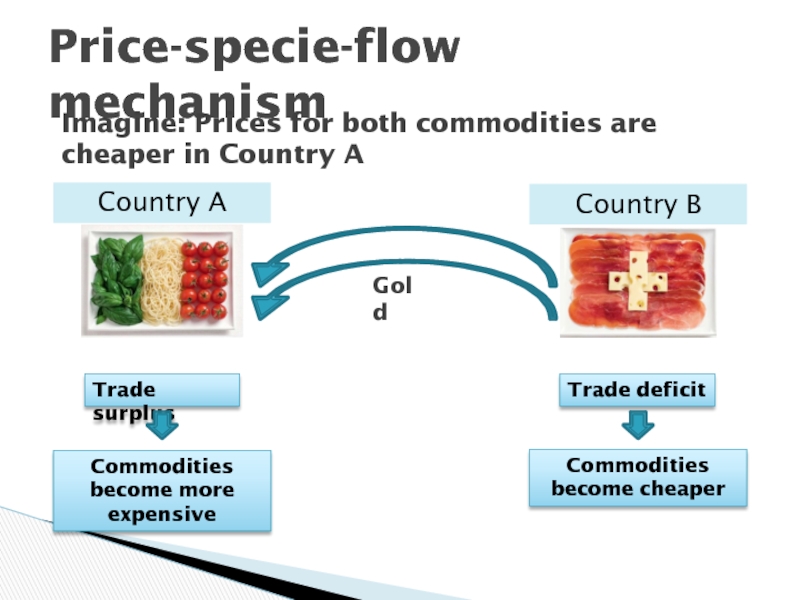
- 15. Price-specie-flow mechanismCountry ACountry BImagine: Prices for both
- 16. Price-specie-flow mechanismCountry ACountry BThe prices of both
- 17. Each nations seeks to maximise its own
- 18. Thank you for your time!
- 19. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Introduction
1. Historical background
2. Principles of the theory of comparative advantage:
3.
Explanation of the theory
Слайд 3“Principles of Political Economy and Taxation” (1817)
Mercantilism (e.g. The Corn Laws in 1815)
Adam
Smith (The Wealth of Nations in 1776)
Historical background
Слайд 4Even if a country had a considerable absolute advantage in
the production of both goods, Ricardo would argue that specialization
and trade are still mutually beneficial.Principle of Comparative Advantage
WHY?
Слайд 5Basic assumptions:
Only two nations and two commodities;
Free trade;
Labor theory of
value;
Absence of transportation costs;
Labor is perfectly mobile within a country
but it is perfectly immobile within countries;Constant cost of production;
Full employment of labor;
Technology remains unchanged.
Principle of Comparative Advantage
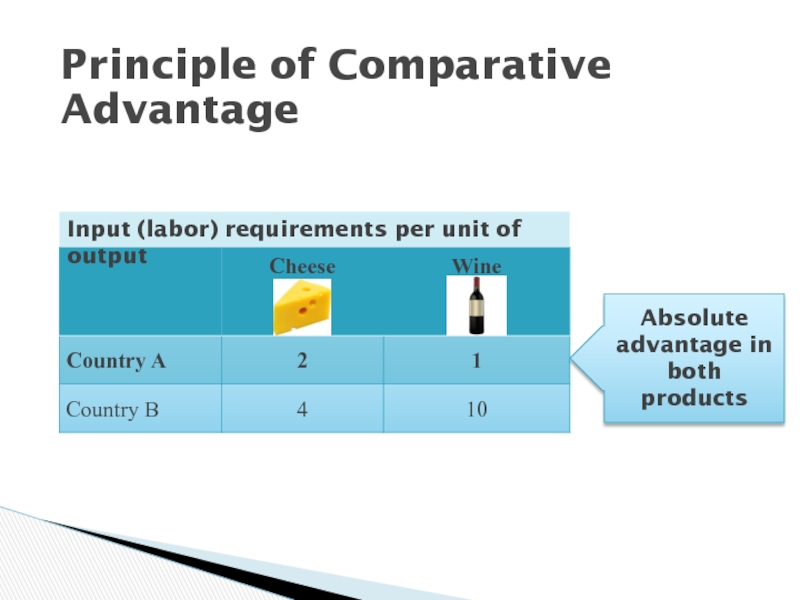
Слайд 6Input (labor) requirements per unit of output
Absolute advantage in both
products
Principle of Comparative Advantage
Слайд 7Countries should specialize in producing those goods in which they
have the lowest opportunity costs or greatest comparative advantage
Countries with
higher opportunity costs of production should import from a lower opportunity cost country.Principle of Comparative Advantage
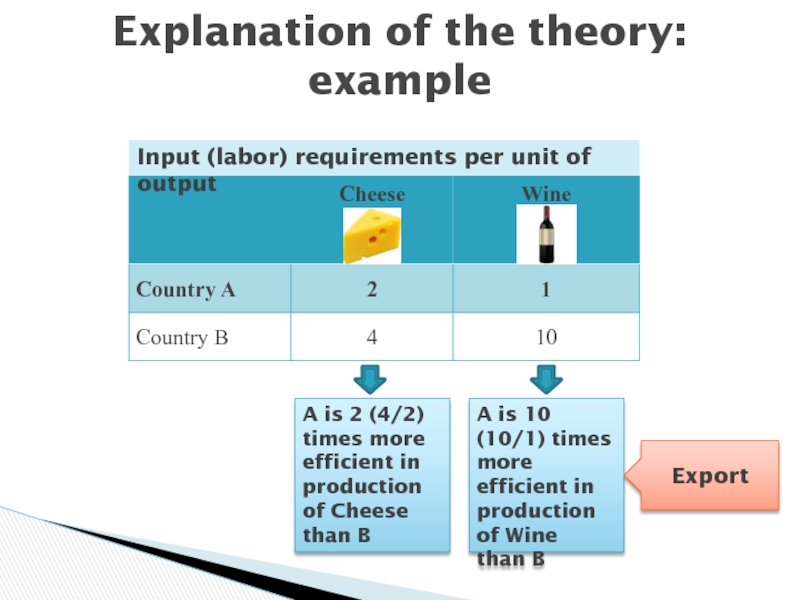
Слайд 8Explanation of the theory: example
Input (labor) requirements per unit of
output
A is 2 (4/2) times more efficient in production of
Cheesethan B
A is 10 (10/1) times more efficient in production of Wine
than B
Export
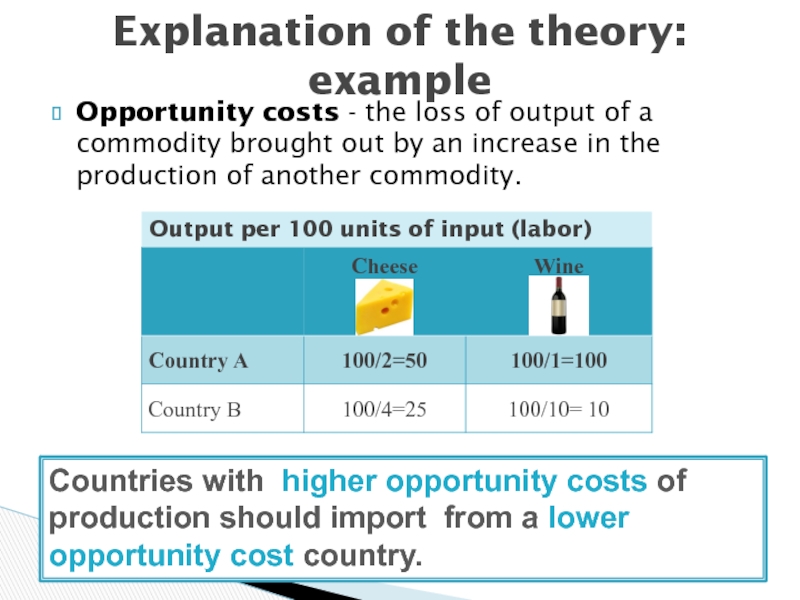
Слайд 9Output per 100 units of input (labor)
Explanation of the theory:
example
Opportunity costs - the loss of output of a commodity
brought out by an increase in the production of another commodity. Countries with higher opportunity costs of production should import from a lower opportunity cost country.
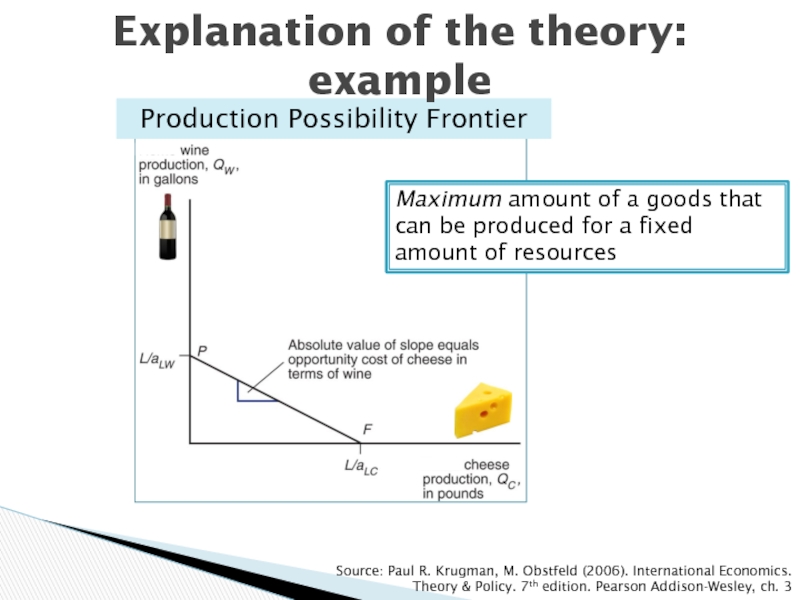
Слайд 10Production Possibility Frontier
Source: Paul R. Krugman, M. Obstfeld (2006). International
Economics. Theory & Policy. 7th edition. Pearson Addison-Wesley, ch. 3
Explanation
of the theory: example
Maximum amount of a goods that can be produced for a fixed amount of resources
Слайд 11Explanation of the theory: example
2,5
Lower opportunity cost
Export
Lower opportunity cost
Export
No trade
between countries (autarky)
Слайд 12When countries specialize in producing the goods in which they
have a comparative advantage, they maximize their combined output and
allocate their resources more efficientlyGains from trade
Trade makes it possible to trespassing the national production possibility frontier
Слайд 14Gains from trade
Country A
Country B
Source: Paul R. Krugman, M. Obstfeld
(2006). International Economics. Theory & Policy. 7th edition. Pearson Addison-Wesley,
ch. 3Слайд 15Price-specie-flow mechanism
Country A
Country B
Imagine: Prices for both commodities are cheaper
in Country A
Gold
Trade surplus
Trade deficit
Commodities become more expensive
Commodities become cheaper
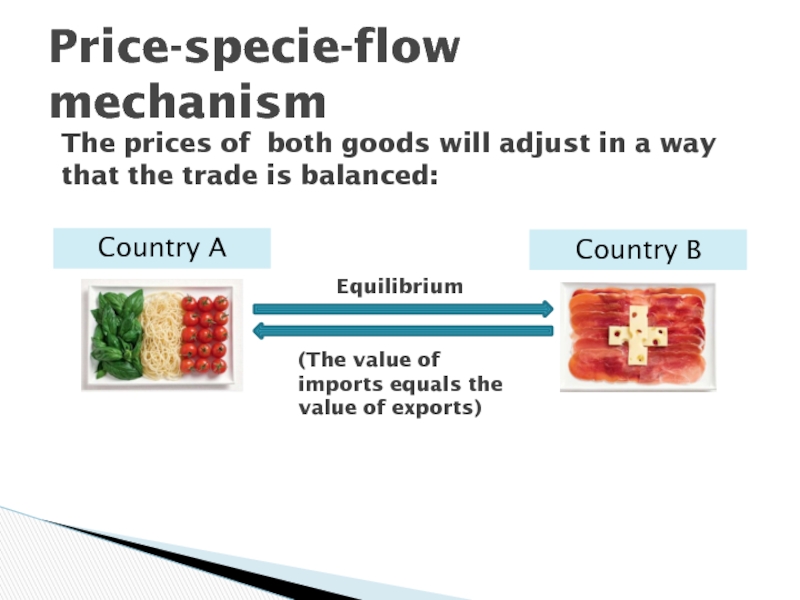
Слайд 16Price-specie-flow mechanism
Country A
Country B
The prices of both goods will adjust
in a way that the trade is balanced:
(The value of
imports equals the value of exports)Equilibrium