Слайд 1Drugs affecting
adrenergic synapses
Adrenomimetics
lecture of associate professor of pharmacology
Goldobina Galina
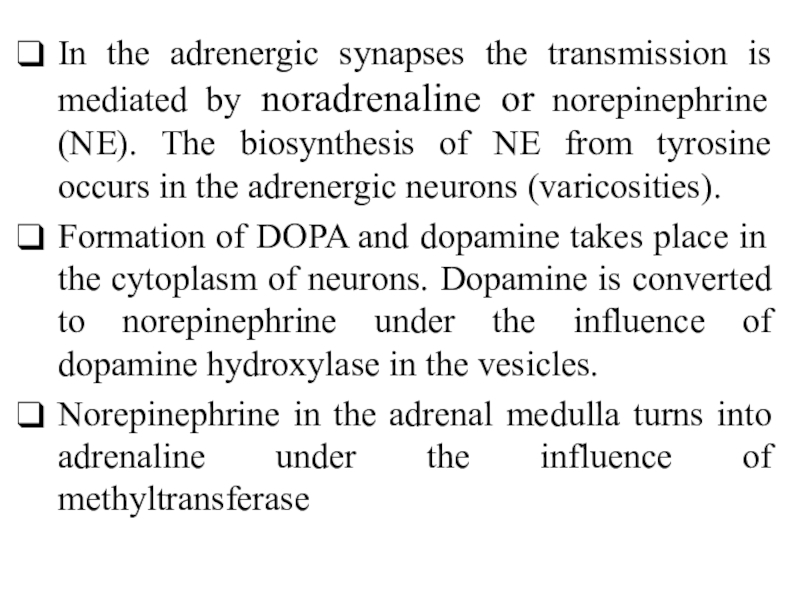
Слайд 3In the adrenergic synapses the transmission is mediated by noradrenaline
or norepinephrine (NE). The biosynthesis of NE from tyrosine occurs
in the adrenergic neurons (varicosities).
Formation of DOPA and dopamine takes place in the cytoplasm of neurons. Dopamine is converted to norepinephrine under the influence of dopamine hydroxylase in the vesicles.
Norepinephrine in the adrenal medulla turns into adrenaline under the influence of methyltransferase
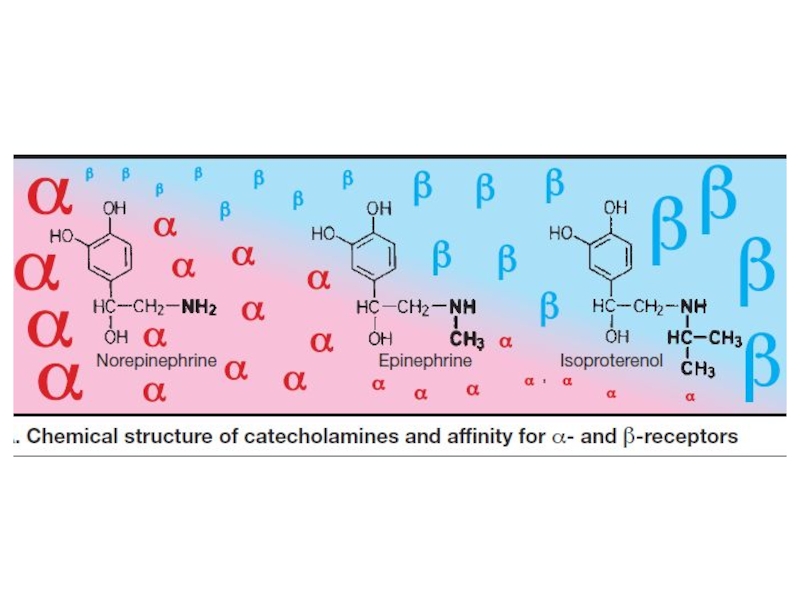
Слайд 4Noradrenaline (NE), dopamine and adrenaline are called catecholamines.
In presynaptic
endings noradrenaline is in a free state (mobile pool) and
in vesicles.
Inactivation of NE via monoamine oxidase (MAO) may regulate prejunctional levels of transmitter in the mobile pool.
Nerve impulses induce the release of NE into the synaptic gap. And NE interacts with its receptors.
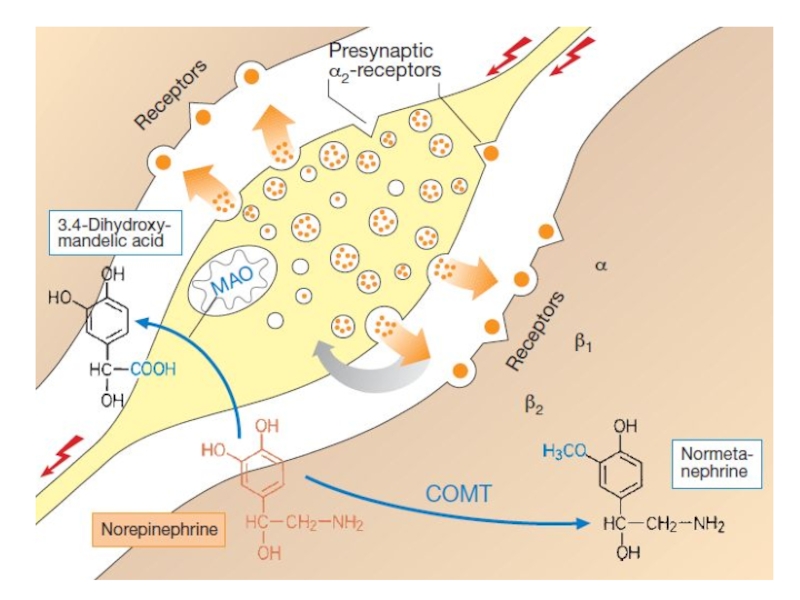
Слайд 6The action of NE on receptors is short-term. It is
mainly caused by the swift uptake (70-80%) by the terminals
of the anrenergic fibres. Small amounts of NE undergo extraneuronal uptake by the effector cells (smooth muscles).
Catabolism of NE is controlled by MAO and catechol O-methyltransferase.
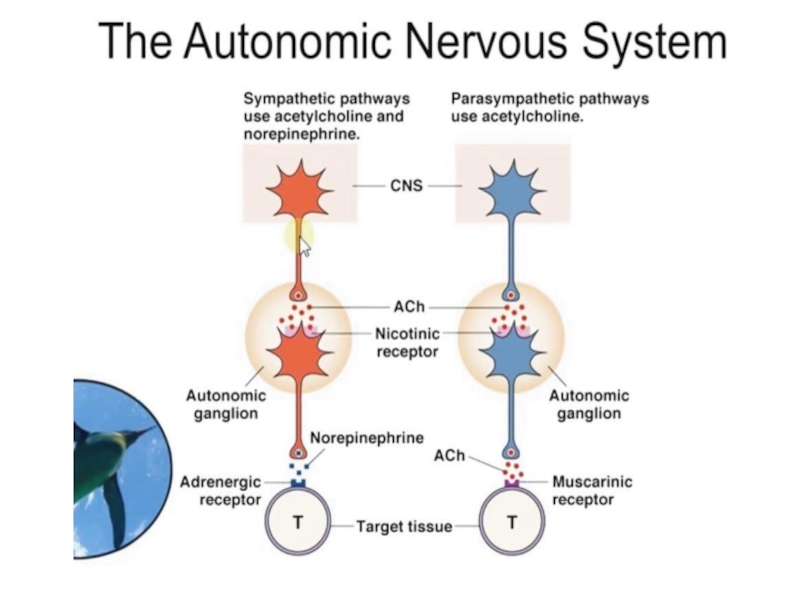
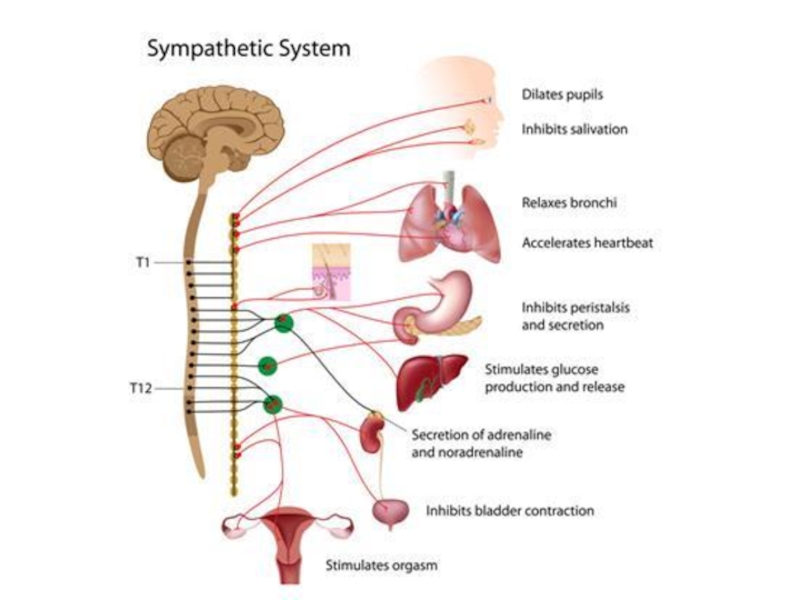
Adrenoreceptors are divided into α- and β-subtypes.
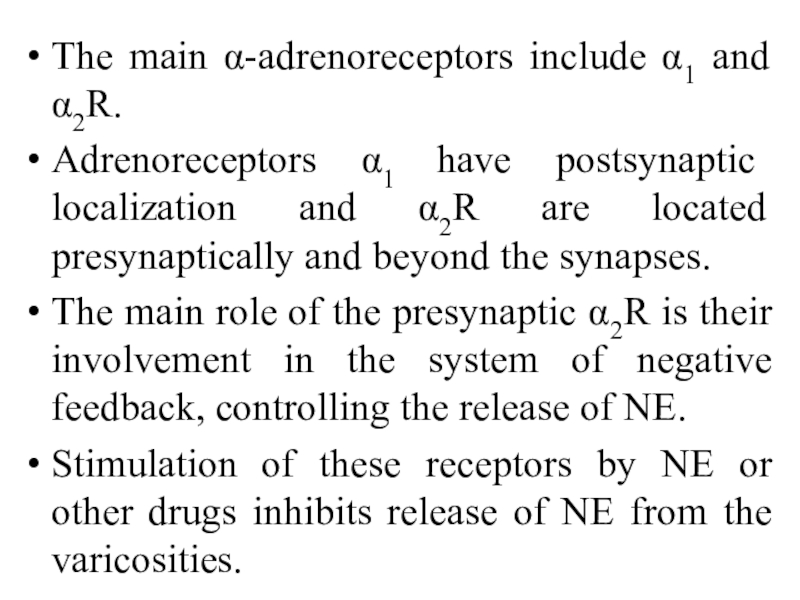
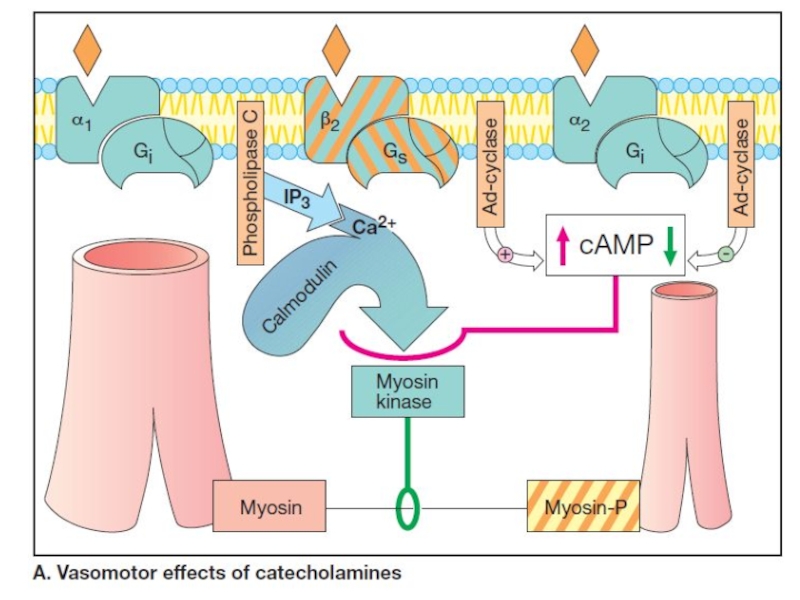
Слайд 7The main α-adrenoreceptors include α1 and α2R.
Adrenoreceptors α1 have postsynaptic
localization and α2R are located presynaptically and beyond the synapses.
The main role of the presynaptic α2R is their involvement in the system of negative feedback, controlling the release of NE.
Stimulation of these receptors by NE or other drugs inhibits release of NE from the varicosities.
Слайд 8Among β-R there are also post-, pre-, and extrasynaptic receptors.
Presynaptic β2-R perform positive reverse feedback, stimulating NE release. So,
it can be confirmed that β-agonists facilitate the release of the NE and β-antagonists inhibit it.
Слайд 10The main effects associated with the stimulation of post-and extrasynaptic
adrenoreceptors
α1 - adrenoreceptors:
Constriction of vessels of the skin, kidneys, intestines;
Contraction
of the radial muscle of iris (mydriasis);
Contraction of myometrium;
Contraction of sphincters of the gastrointestinal tract;
Contraction in the capsule of the spleen;
Decrease of motility and tone of the intestine.
Слайд 11α2 –adrenoceptor (extrasynaptic):
Vasoconstriction;
Increased platelet aggregation;
Decrease in insulin secretion.
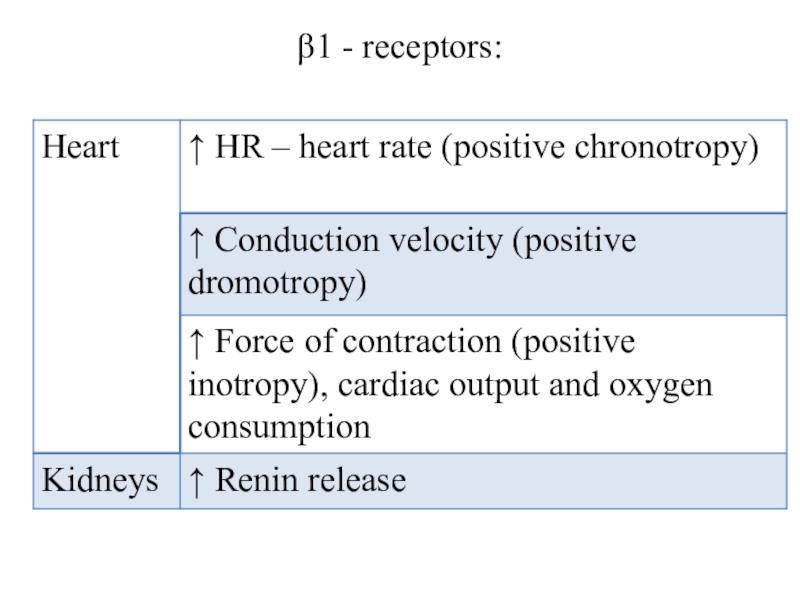
Слайд 13β2 - receptors:
Dilation of vessels of the skeletal muscles, liver,
coronary;
Decrease in muscle tone of the bronchi;
Decrease in intestinal motility
and tone;
Decrease in the tone of myometrium;
Activation of glycogenolysis and lipolysis;
Increase in insulin secretion.
Слайд 15Classification
Drugs of presynaptic action, affecting release and storage of NE
or sympathomimetics or adrenomimetics of indirect action: Ephedrine
Слайд 16α and β adrenomimetics: Epinephrine, Norepinephrine;
α1: Phenylephrine;
α2: Naphazoline,
Xylometazoline, Oxymetazoline;
β1, 2: Isoprenaline;
β1: Dobutamine;
Β2: Salbutamol, Salmeterol, Fenoterol,
Berodual (ipratropium bromide
+fenoterol).
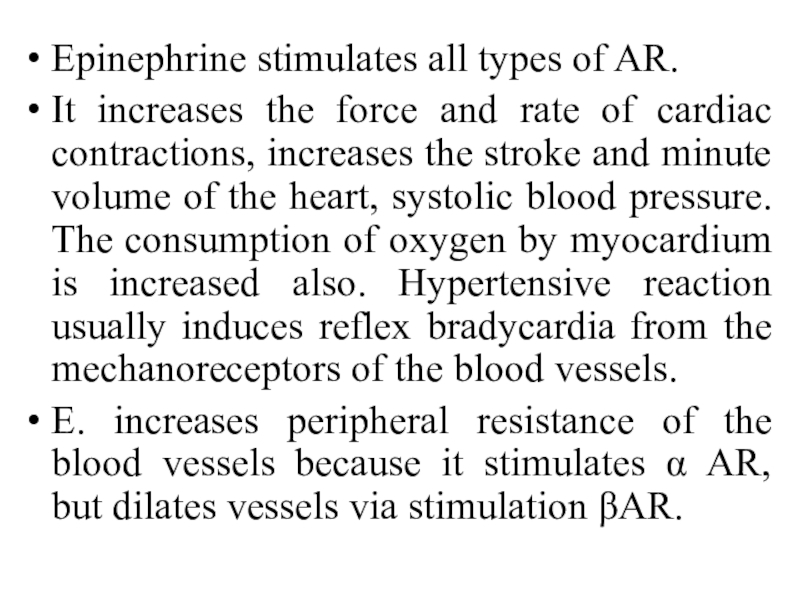
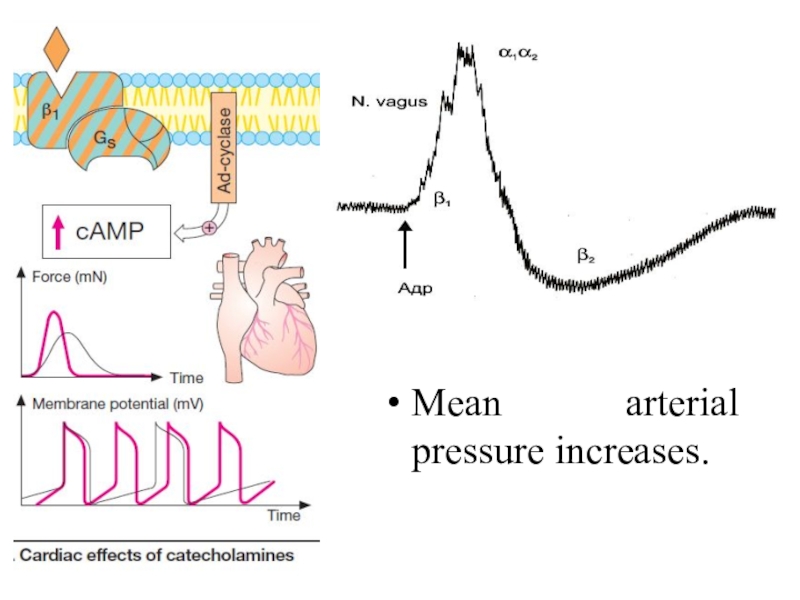
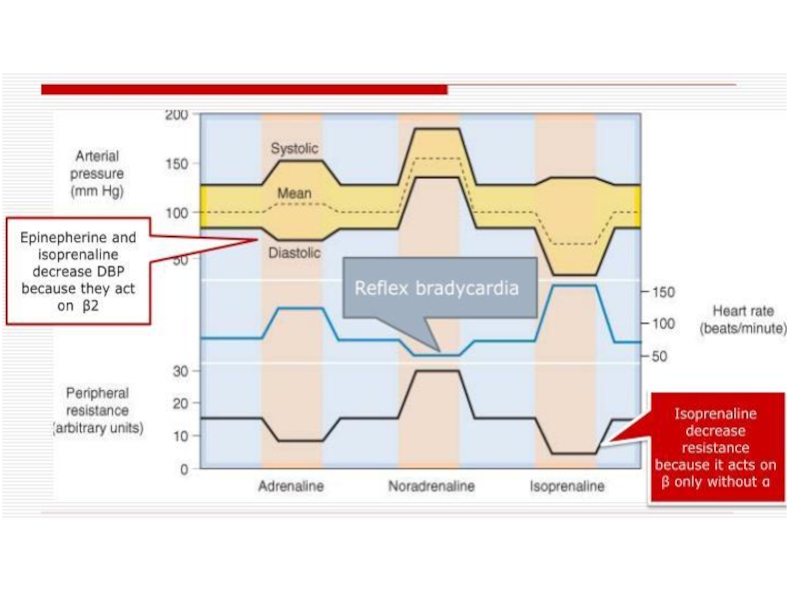
Слайд 17Epinephrine stimulates all types of AR.
It increases the force
and rate of cardiac contractions, increases the stroke and minute
volume of the heart, systolic blood pressure. The consumption of oxygen by myocardium is increased also. Hypertensive reaction usually induces reflex bradycardia from the mechanoreceptors of the blood vessels.
E. increases peripheral resistance of the blood vessels because it stimulates α AR, but dilates vessels via stimulation βAR.
Слайд 18Mean arterial pressure increases.
Слайд 19E. relaxes smooth muscles of bronchi, eliminates bronchospasm. E. reduces
the secretion of the bronchial glands, reduces the release of
inflammatory mediators (histamine) from mast cells.
E. reduces the tone and motility of gastrointestinal tract, but increases the tone of sphincters.
E. induces the contraction of the splenic capsule.
E. increases neuromuscular transmission.
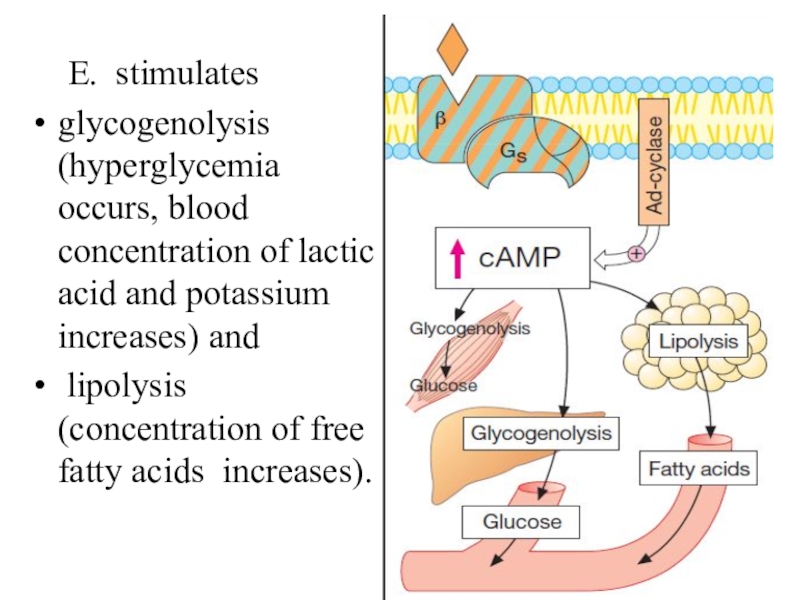
Слайд 20 E. stimulates
glycogenolysis (hyperglycemia occurs, blood concentration of lactic acid
and potassium increases) and
lipolysis (concentration of free fatty acids
increases).
Слайд 21Local effects:
E. dilates the pupils (mydriasis) due to the contraction
of the radial muscles of the iris and decreases intraocular
pressure (production of the intraocular fluid is decreased).
Epinephrine causes spasm of blood vessels of the skin and mucous membranes, reduces exudation and inflammation.
Слайд 22Duration of action: intravenously - 5-10 min., subcutaneous injections -
up to 30 minutes.
Indications for use:
to prolong the effect
and reduce the toxicity of local anesthetics;
anaphylactic shock, allergic laryngeal edema;
relief of bronchospasm;
insulin overdose, hypoglycemia;
cardiac arrest, acute heart failure, hypotension.
Слайд 23 Side effects: headache, fear, anxiety, tremor, vomiting, tachycardia, extrasystoles.
Слайд 24Norepinephrine stimulates predominantly α-adrenergic receptors and to a small extent
β-AR.
It causes severe vasospasm and increases blood pressure (5-10
times stronger than epinephrine). Norepinephrine increases force of heart contractions, stroke volume of the heart, causes a reflex bradycardia (activation of the vagus nerve).
Norepinephrine is administered intravenously with vascular collapse during surgery, intoxication, injuries.
Слайд 26Norepinephrine can not be administered subcutaneously due to the possibility
of necrosis.
It is contraindicated in hemorrhagic and cardiogenic shock
because it causes spasm of arterioles and increases the load on the heart.
Side effects: arrhythmias, headache, breathing disorders.
Слайд 27Phenylephrine stimulates α1-AR but acts weaker than norepinephrine.
It increases arterial
pressure and causes reflex bradycardia. But it does not affect
the heart.
It is more stable (duration of action after intravenous administration – 20 min; after subcutaneous – 40-50 min). It is effective after oral administration.
Слайд 28Indications for the use:
relief and prevention of shock and
collapse,
to potentiate the action and reduce the toxicity of
local anesthetics,
open-angle glaucoma, conjunctivitis, rhinitis,
hemorrhoids (in suppositories).
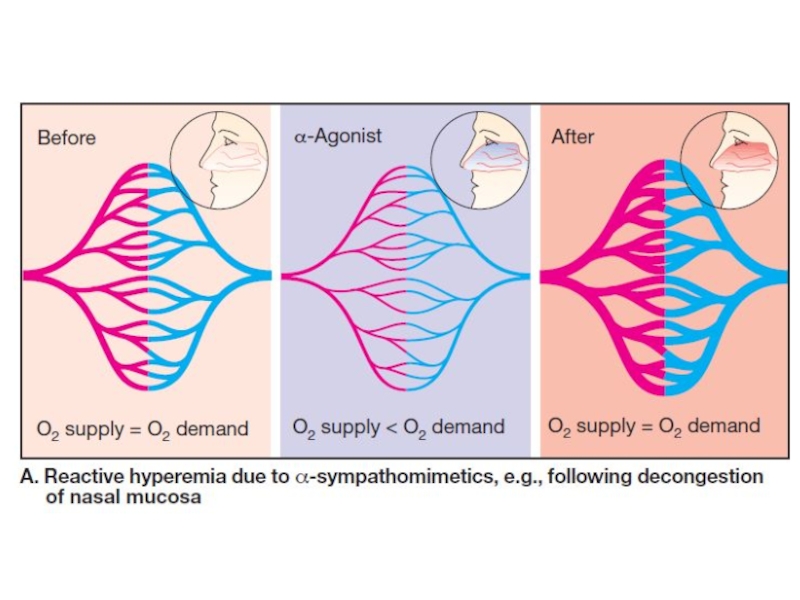
Слайд 29Naphazoline, Oxymetazoline and Xylometazoline constrict the vessels of the nasal
mucosa, reduce inflammatory response, exudation.
They are used in rhinitis.
Side effects: irritant effect, atrophy of the nasal mucosa, tolerance.
Naphazoline has an inhibitory effect on the CNS.
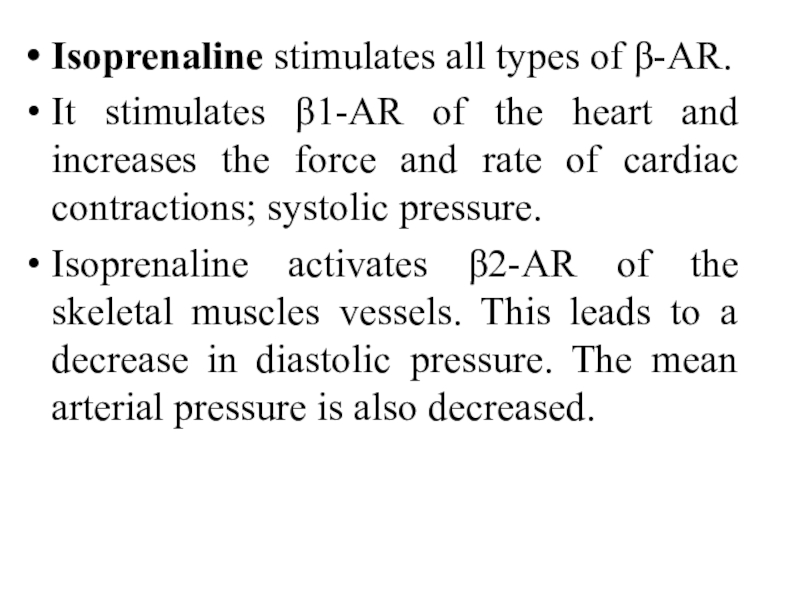
Слайд 31Isoprenaline stimulates all types of β-AR.
It stimulates β1-AR of
the heart and increases the force and rate of cardiac
contractions; systolic pressure.
Isoprenaline activates β2-AR of the skeletal muscles vessels. This leads to a decrease in diastolic pressure. The mean arterial pressure is also decreased.
Слайд 33The drug facilitates atrioventricular conduction and increases heart automatism.
Слайд 34I. decreases the tone of bronchi, muscles of gastrointestinal tract;
causes hyperglycaemia.
Indications for use: bronchial spasm, atrioventricular block.
Routes of
administration: sublingual, inhalation, intravenous, SC.
Adverse affects: tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, headache, tremor.
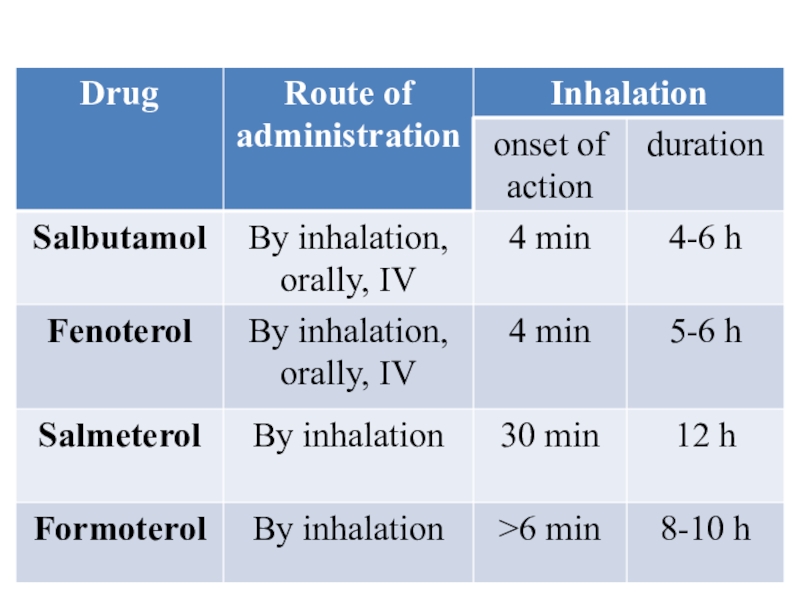
Слайд 35Salbutamol, fenoterol, salmeterol stimulate B2-AR. They expand the bronchi and
are used for the prevention and relief of bronchospasm.
They cause
relaxation of the uterus, prevent premature labor. They are used in threatened preterm labor.
They cause hyperglycemia, vasodilation, low blood pressure.
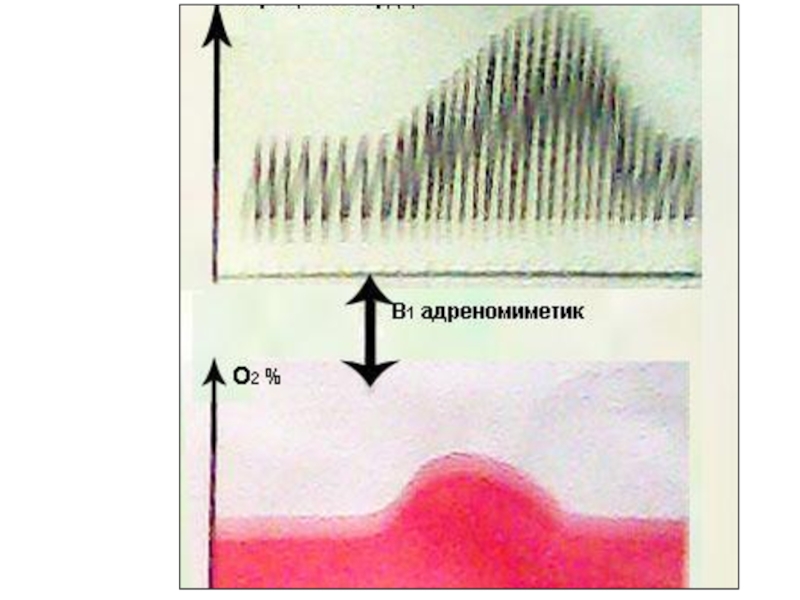
Слайд 37Dobutamine stimulates β1-AR.
It moderately increases heart rate, stroke and
minute volume of the heart.
It improves atrioventricular conduction, increases myocardial
oxygen consumption.
It is used intravenously drip in acute heart failure.
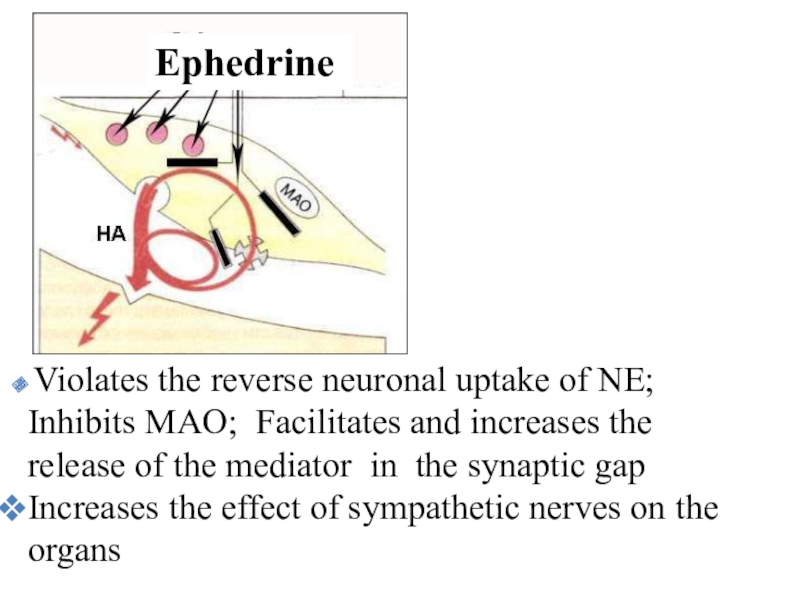
Слайд 39 Violates the reverse neuronal uptake of NE; Inhibits MAO;
Facilitates and increases the release of the mediator in the
synaptic gap
Increases the effect of sympathetic nerves on the organs
Ephedrine
Слайд 40Effects: It stimulates heart function, increases blood pressure, causes a
broncholytic effect, inhibits intestinal peristalsis, dilates pupils.
It acts longer
and weaker than epinephrine.
It is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and penetrates through the BBB, resistant to MAO action.
Indication for the use: spasm of bronchi, to increase arterial pressure, atrioventricular block, rhinitis, narcolepsy.
Слайд 41Side effects:
tachyphylaxis with frequent use (reduction in norepinephrine storage
in the varicosities),
tachycardia, increased blood pressure, hyperglycemia,
mental dependence
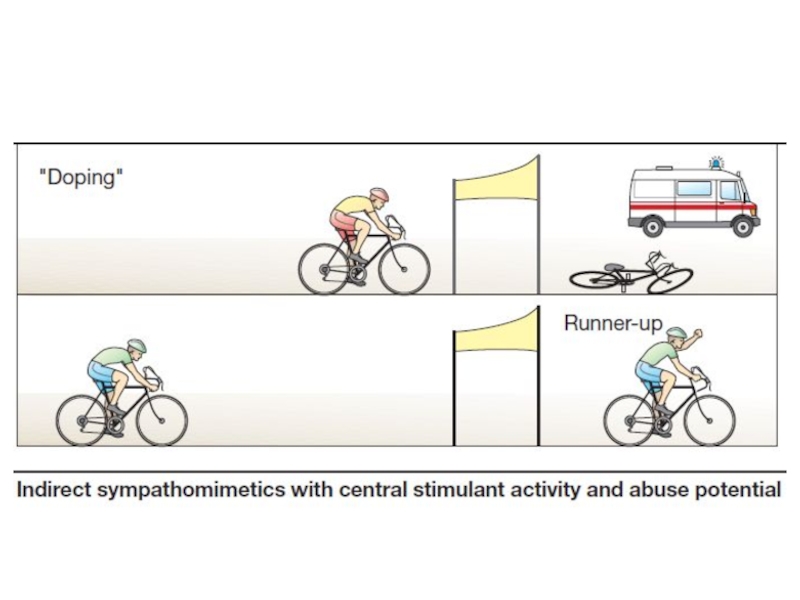
(causes euphoria), excitation, insomnia, tremor, doping effect.
Слайд 43Literature
1. Tripathi K.D. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology. Eighth Edition. -2019.-
Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers. The Health Sciences Publisher. -New Delhi.
London. Panama
2. D.A.Kharkevich. Pharmacology. Textbook for medical students. Translation of 12th edition of Russion textbook “Pharmacology” (2017). – М., ГЭОТАР-Медиа, 2017.
3. Review of pharmacology. Gobind Rai Garg, Sparsh Gupta. 13th edition. - 2019.- Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers. The Health Sciences Publisher. -New Delhi. London. Panama
4. Whalen Karen. Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Pharmacology. Sixth Edition. - Wolters Kluwer. - 2015.-Philadelphia
5. Color Atlas of Pharmacology. 2nd edition, revised and expanded. Heinz Lüllmann.- 2000 Thieme
6. Pharmacology Examination & Board Review. Tenth Edition. Trevor Anthony J., Katzung Bertram G., Kruidering-Hall Marieke, Susan B. Masters. - a LANGE medical book. - 2013.-New York
7. Medical Pharmacology at a Glance. Eighth Edition. Neal Michael J. – 2016. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
8. USMLE Step 1. Lecture Notes. Pharmacology. Lionel P.Raymon and others.- Kaplan Medical.Inc. -2009