Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
ECG - MI
Содержание
- 1. ECG - MI
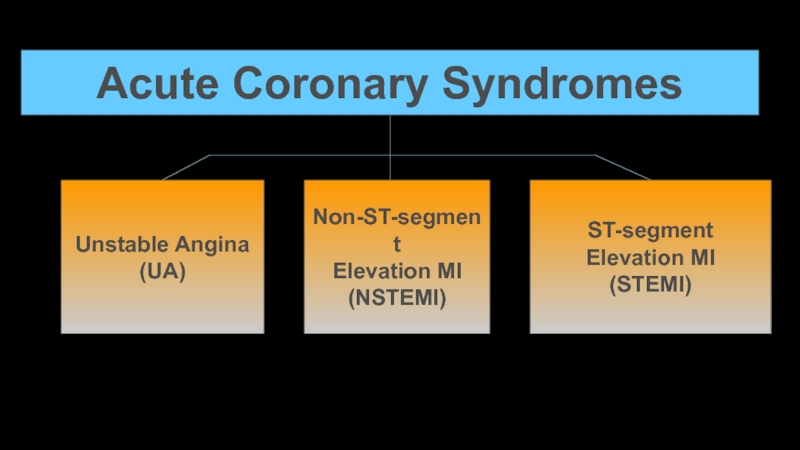
- 2. Acute Coronary SyndromesUnstable Angina(UA)Non-ST-segmentElevation MI(NSTEMI)ST-segmentElevation MI(STEMI)
- 3. Acute Coronary Syndromes Excessive demand or inadequate
- 4. Coronary Artery OcclusionPatient’s clinical presentation and outcome
- 5. Acute Coronary Syndromes
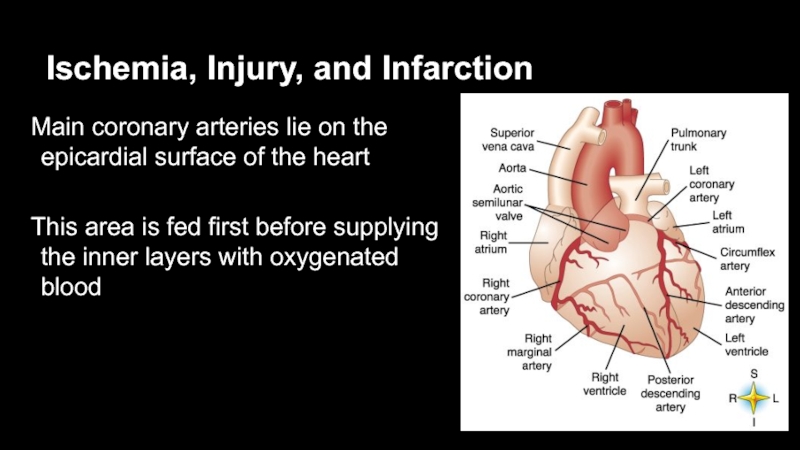
- 6. Ischemia, Injury, and InfarctionMain coronary arteries lie
- 7. Ischemia, Injury, and InfarctionMyocardial ischemiaImbalance between the
- 8. Ischemia, Injury, and InfarctionMyocardial ischemia delays repolarizationECG
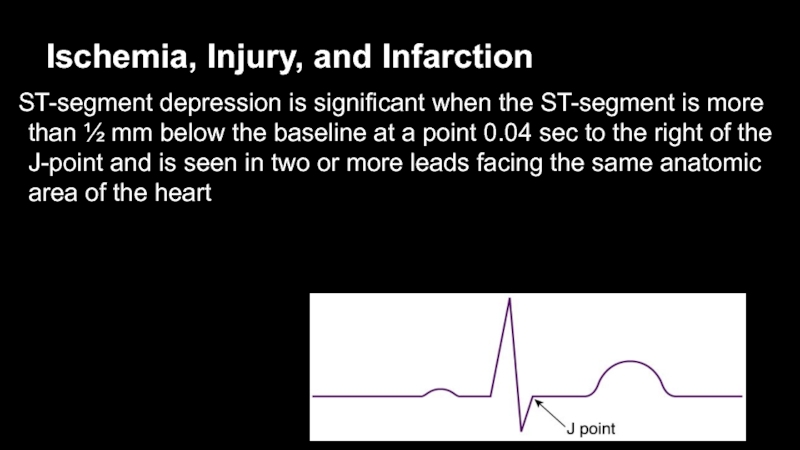
- 9. Ischemia, Injury, and InfarctionST-segment depression is significant
- 10. Ischemia, Injury, and InfarctionLocate J-pointCompare ST-segment deviation to isoelectric line
- 11. Ischemia, Injury, and InfarctionInjured cells will die
- 12. Ischemia, Injury, and InfarctionInjured cells will show ST-segment elevation in leads facing the affected area
- 13. Ischemia, Injury, and InfarctionSuspect ventricular aneurysm if
- 14. Ischemia, Injury, and InfarctionInfarction occurs when blood
- 15. Myocardial Infarction—DiagnosisTypical rise and gradual fall (troponin)
- 16. Infarction—ECG ChangesNon-ST-segment elevation MI (NSTEMI)ST-segment depression in
- 17. Infarction—ECG ChangesMost patients with ST-segment elevation MI
- 18. Infarction—Indicative ECG Changes
- 19. Infarction—ECG ChangesST-segment elevation“Smiley” face (upward concavity) is
- 20. R-Wave ProgressionChest leads in a normal heartAs
- 21. R-Wave ProgressionV3 and V4 normally record an equiphasic (equally positive and negative) RS complex Transitional zone
- 22. Poor R-Wave ProgressionA phrase used to describe R waves that decrease in size from V1-V4
- 23. Layout of the 12-Lead ECG
- 24. Indicative ECG ChangesIndicative changes are significant when
- 25. Indicative ECG Changes
- 26. Indicative ECG Changes Which leads of a standard
- 27. Which Leads Show ST-Segment Elevation?Are they anatomically contiguous leads?
- 28. ST-Segment Elevation is Present in II, III, aVFThey are anatomically contiguous; inferior MILateralLateralLateralLateralInferiorInferiorInferiorAnteriorAnteriorSeptumSeptum
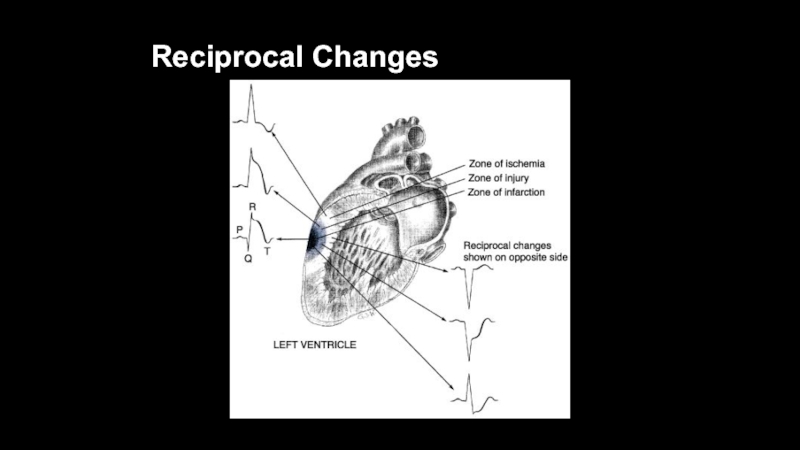
- 29. Reciprocal Changes
- 30. Localization of Infarction
- 31. Predicting the Site of Coronary Artery
- 32. Assessing the Extent of InfarctionEvaluate how many
- 33. Specific Types of MIs
- 34. Anterior Wall MI (AWMI)Leads V3 and V4
- 35. Anterior Wall MI (AWMI)
- 36. Evolution of Anteroseptal MIIndicative changes in leads
- 37. Inferior Wall MI (IWMI)
- 38. Inferior Wall MI (IWMI)
- 39. Inferior Wall MI (IWMI)
- 40. Inferior Wall MI (IWMI)
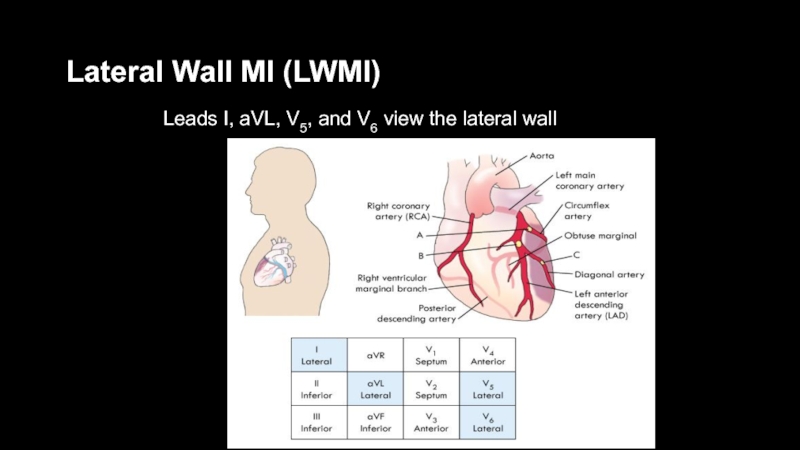
- 41. Lateral Wall MI (LWMI)Leads I, aVL, V5, and V6 view the lateral wall
- 42. Lateral Wall MI (LWMI)
- 43. Lateral Wall MI (LWMI)
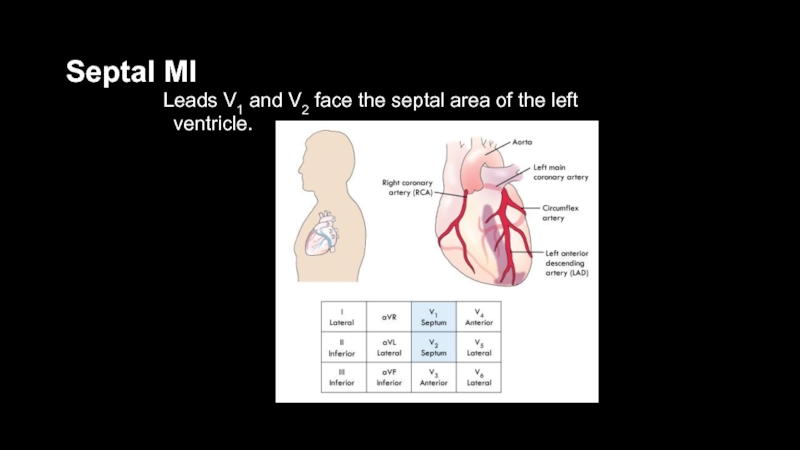
- 44. Septal MILeads V1 and V2 face the septal area of the left ventricle.
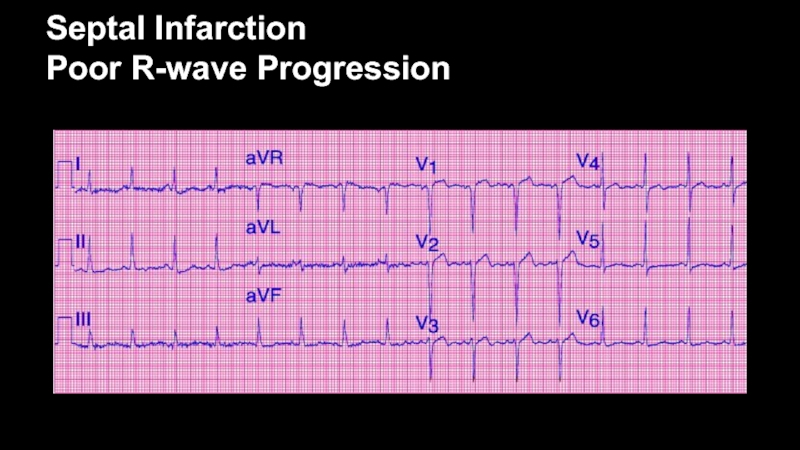
- 45. Septal Infarction Poor R-wave Progression
- 46. Posterior MI
- 47. Posterior MI
- 48. Posterior Chest Lead Placement
- 49. Posterior InfarctionEvolutionary changes in inferior and posterior
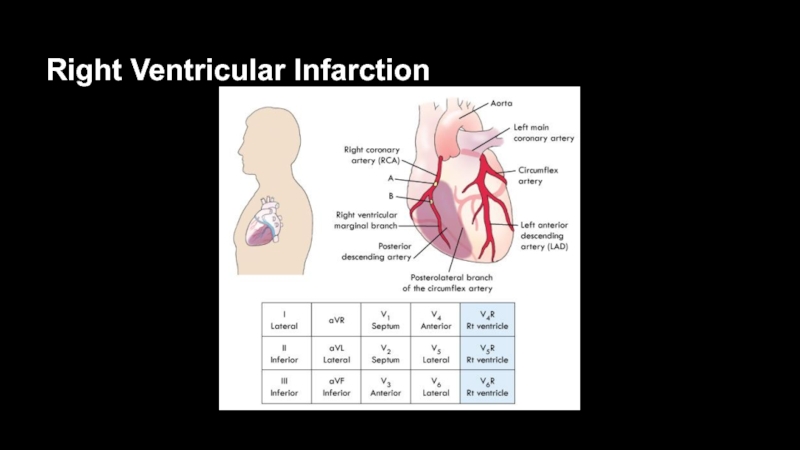
- 50. Right Ventricular Infarction
- 51. Right Chest Leads Right chest leads used
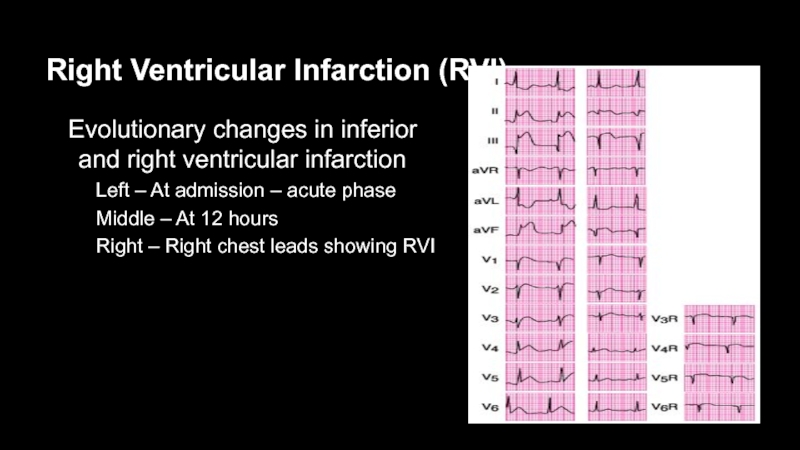
- 52. Right Ventricular Infarction (RVI)Evolutionary changes in inferior
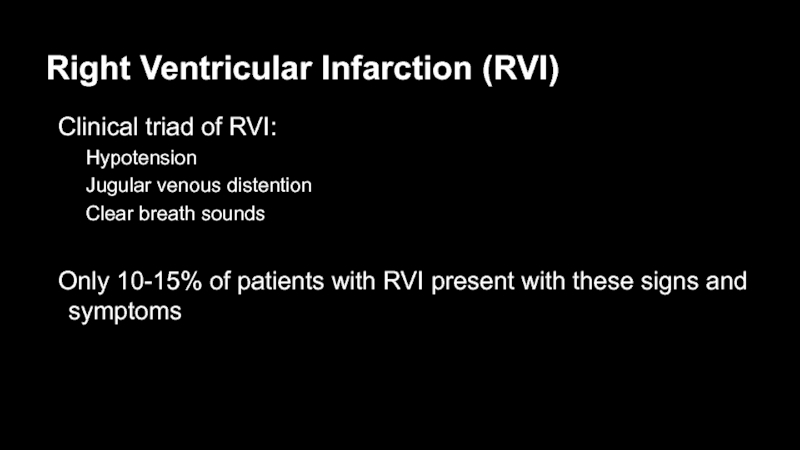
- 53. Right Ventricular Infarction (RVI)Clinical triad of RVI:
- 54. Скачать презентанцию
Acute Coronary SyndromesUnstable Angina(UA)Non-ST-segmentElevation MI(NSTEMI)ST-segmentElevation MI(STEMI)
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Acute Coronary Syndromes
Unstable Angina
(UA)
Non-ST-segment
Elevation MI
(NSTEMI)
ST-segment
Elevation MI
(STEMI)
Слайд 3Acute Coronary Syndromes
Excessive demand or inadequate supply of oxygen
and nutrients to the heart muscle
Слайд 4Coronary Artery Occlusion
Patient’s clinical presentation and outcome depend on factors
including:
Amount of myocardium supplied by affected artery
Severity and duration of
myocardial ischemiaElectrical instability of the ischemic myocardium
Degree and duration of coronary obstruction
Presence (and extent) or absence of collateral coronary circulation
Слайд 6Ischemia, Injury, and Infarction
Main coronary arteries lie on the epicardial
surface of the heart
This area is fed first before supplying
the inner layers with oxygenated bloodСлайд 7Ischemia, Injury, and Infarction
Myocardial ischemia
Imbalance between the metabolic needs of
the myocardium (demand) and the flow of oxygenated blood to
it (supply)Angina: The pain resulting from an imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand
1. Characteristic Quality and Duration: Retrosternal: Jaw, Left Arm, Neck
2. Provoked by Exertion or Emotional Stress
3. Relieved by Rest or Nitroglycerin
Слайд 8Ischemia, Injury, and Infarction
Myocardial ischemia delays repolarization
ECG changes include temporary
changes in the ST-segment and T wave
When looking for evidence
of infarction, most of the information is obtained from analyzing a single, representative complex in each lead.Слайд 9Ischemia, Injury, and Infarction
ST-segment depression is significant when the ST-segment
is more than ½ mm below the baseline at a
point 0.04 sec to the right of the J-point and is seen in two or more leads facing the same anatomic area of the heartСлайд 10Ischemia, Injury, and Infarction
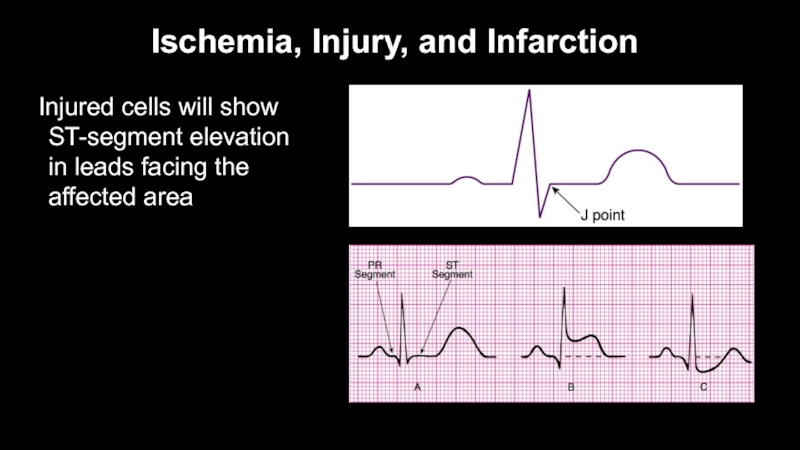
Locate J-point
Compare ST-segment deviation to isoelectric line
Слайд 11Ischemia, Injury, and Infarction
Injured cells will die unless blood flow
is quickly restored
Myocardial injury is viewed on the ECG as
ST-segment elevation in the leads facing the affected areaСлайд 12Ischemia, Injury, and Infarction
Injured cells will show ST-segment elevation in
leads facing the affected area
Слайд 13Ischemia, Injury, and Infarction
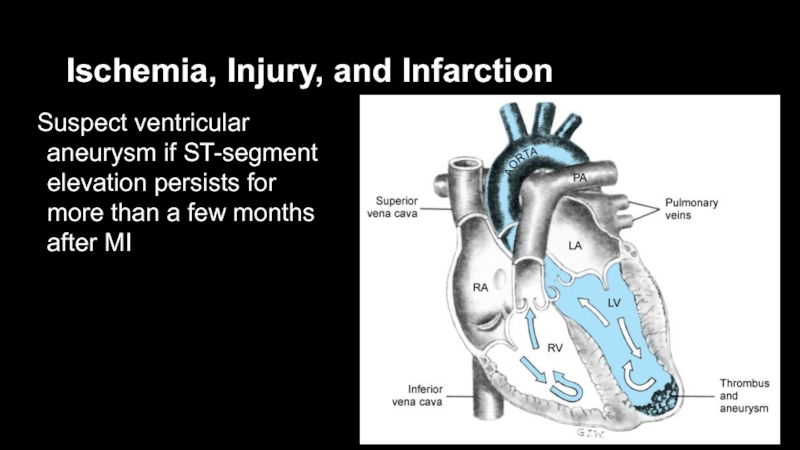
Suspect ventricular aneurysm if ST-segment elevation persists
for more than a few months after MI
Слайд 14Ischemia, Injury, and Infarction
Infarction occurs when blood flow to the
heart muscle stops or is suddenly decreased long enough to
cause cell deathInfarcted cells:
Cannot respond to an electrical stimulus
Do not provide any mechanical function
Слайд 15Myocardial Infarction—Diagnosis
Typical rise and gradual fall (troponin) or more rapid
rise and fall (CK-MB) of biochemical markers of myocardial necrosis
with at least one of the following:Ischemic symptoms
Development of pathologic Q waves on ECG
ECG changes (ST-segment elevation or depression)
Or coronary artery intervention
Pathologic findings of an acute MI
Слайд 16Infarction—ECG Changes
Non-ST-segment elevation MI (NSTEMI)
ST-segment depression in leads facing the
affected area
MI diagnosed if ECG changes are accompanied by elevations
of serum cardiac markersСлайд 17Infarction—ECG Changes
Most patients with ST-segment elevation MI will develop Q-wave
MI
Abnormal (pathologic) Q wave
>0.04 sec in duration and >1/3 the
amplitude of the following R wave in that leadIndicates dead myocardial tissue, loss of electrical activity
Слайд 19Infarction—ECG Changes
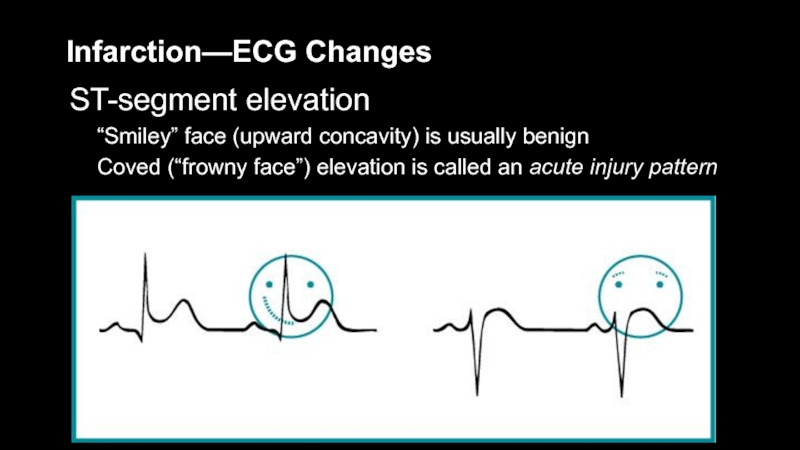
ST-segment elevation
“Smiley” face (upward concavity) is usually benign
Coved (“frowny
face”) elevation is called an acute injury pattern
Слайд 20R-Wave Progression
Chest leads in a normal heart
As the electrode is
moved from right to left:
R wave becomes taller
S wave becomes
smallerСлайд 21R-Wave Progression
V3 and V4 normally record an equiphasic (equally positive
and negative) RS complex
Transitional zone
Слайд 24Indicative ECG Changes
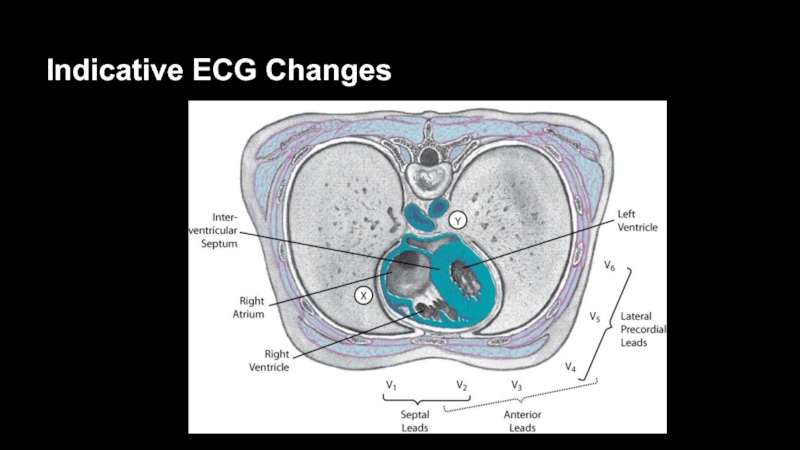
Indicative changes are significant when they are seen
in two anatomically contiguous leads
Two leads are contiguous if:
They look
at the same area of the heartOr they are numerically consecutive chest leads
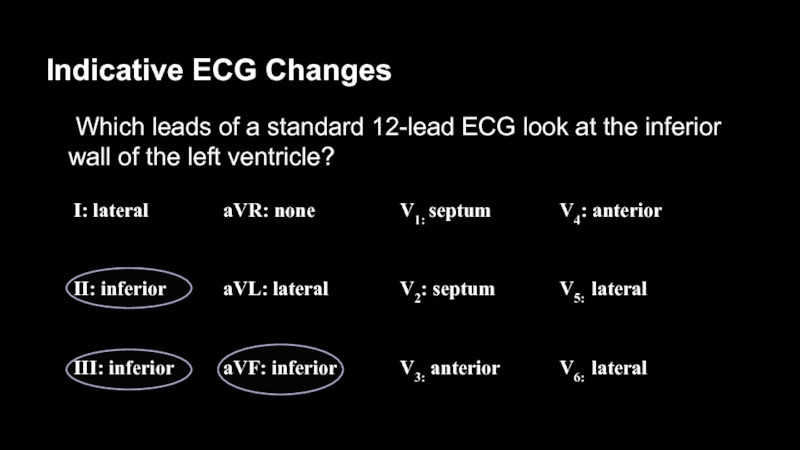
Слайд 26Indicative ECG Changes
Which leads of a standard 12-lead ECG look
at the inferior wall of the left ventricle?
Слайд 28ST-Segment Elevation is
Present in II, III, aVF
They are anatomically contiguous;
inferior MI
Lateral
Lateral
Lateral
Lateral
Inferior
Inferior
Inferior
Anterior
Anterior
Septum
Septum
Слайд 31Predicting the Site of
Coronary Artery Occlusion
Leads II, III, and
aVF = inferior wall
Supplied by RCA in most of
the populationLeads viewing areas supplied by the left coronary artery:
I, aVL, V5, V6 – lateral wall
V1-V2 – septum
V3-V4 – anterior wall
Слайд 32Assessing the Extent of Infarction
Evaluate how many leads are showing
indicative changes
Changes in only a few leads suggests a smaller
infarctionIn general, the more proximal the occlusion:
The larger the infarction
The greater the number of leads showing indicative changes
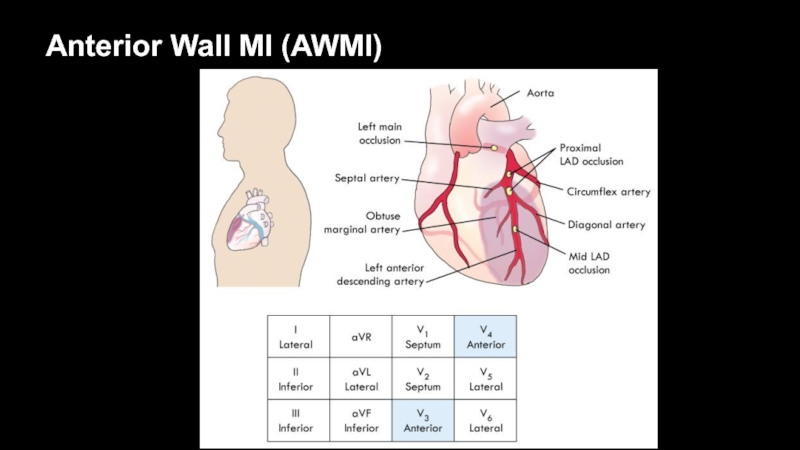
Слайд 34Anterior Wall MI (AWMI)
Leads V3 and V4 face anterior wall
of left ventricle
Left main coronary artery supplies:
Left anterior descending
artery (LAD) Circumflex artery
Left main coronary artery occlusion
“Widow maker”
Often leads to cardiogenic shock and death without prompt reperfusion
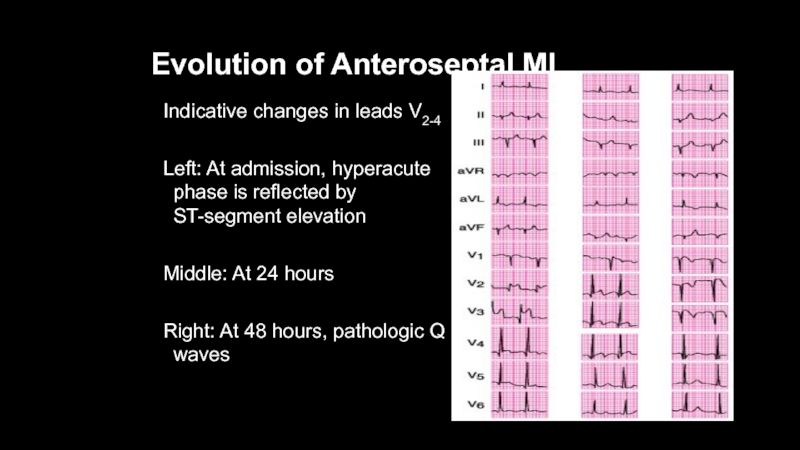
Слайд 36Evolution of Anteroseptal MI
Indicative changes in leads V2-4
Left: At admission,
hyperacute phase is reflected by ST-segment elevation
Middle: At 24 hours
Right:
At 48 hours, pathologic Q waves Слайд 49Posterior Infarction
Evolutionary changes in inferior and posterior MI
Left: Acute inferior
and apical injury
Right: At 24 hours: Note tall R wave
in lead V1 not present in A, suggesting posterior MIBottom: (V7-9) Posterior infarction confirmed
Слайд 51Right Chest Leads
Right chest leads used to view right
ventricle
If time does not permit obtaining all of the
right chest leads, V4R is lead of choiceСлайд 52Right Ventricular Infarction (RVI)
Evolutionary changes in inferior and right ventricular
infarction
Left – At admission – acute phase
Middle – At
12 hoursRight – Right chest leads showing RVI