Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
English Grammar I
Содержание
- 1. English Grammar I
- 2. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsModal auxiliary verbs
- 3. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsTable 8.1: Modals
- 4. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsCan: Can is
- 5. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs3) to express
- 6. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs* Can is
- 7. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsCould: Could is
- 8. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbsto express future
- 9. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsShall: shall is
- 10. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsWill: Will is
- 11. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsWould: Would is
- 12. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs3) to express
- 13. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsShould: Should is
- 14. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs2) to express
- 15. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs4) Should with
- 16. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsMust &Have to:
- 17. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs You must not
- 18. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsMay: May is
- 19. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs3) to express wish or hope. May you a long life!
- 20. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsMight: Might is
- 21. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs2) might with
- 22. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs8.1 Difference between
- 23. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs2) The modals
- 24. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs3) The modals
- 25. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs* Use may
- 26. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs4) The modals
- 27. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs* had better
- 28. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs5) The modals
- 29. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs I would rather
- 30. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs8.1-2 Exercise: Use
- 31. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsA: _______ I
- 32. Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs_________ you answer
- 33. Скачать презентанцию
Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary VerbsModal auxiliary verbs are used with a main verb to show, mood and ideas such as ability, possibility and permission. The main Modal auxiliary verbs are listed
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 4Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Can: Can is used
1) to express
ability:
Ryan can speak French but he cannot speak German.
Superman
can do things that ordinary people can’t. 2) to express request:
Can you help Sue?
Can I offer you something to drink?
Слайд 5Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
3) to express permission:
Can I use
your cell phone?
You can’t go out with Victor.
4)
to express possible: If the weather is perfect tomorrow, we can go on a picnic.
I can be ready by five.
I will be ready five.
Слайд 6Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
* Can is used to express
a statement that is less uncertain than will.
5) be
able to: be able to is used to describe an ability that a person will have in the future. My baby will be able to walk in a few months.
I am busy but I will be able to talk to you in ten minutes.
Слайд 7Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Could: Could is used
to express abilities
in the past:
Jason could do 50 push-ups in five minutes
when he was young.Jason could talk when he was four.
to express permission:
Could you lend me two grants?
Слайд 8Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
to express future possibility: it expresses
more uncertainty than may
I could get an A or
B in grammar. It depends on the final exam. could with present perfect tense is used to express something in the past may be real.
You could have been killed in that accident.
I could have won that game.
Слайд 9Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Shall: shall is used to express
the simple future for the first person.
Shall we meet
at the bus stop?I shall never forget your help.
Слайд 10Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Will: Will is used
present to future
tense:
Sean will leave tomorrow. She will be back in a
few days.If it rains, the soccer game will be put off.
express willing,
If you won’t go and help him, I will.
I will wash the dishes if you cook.
Слайд 11Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Would: Would is used
1) as
the past tense of will:
She said she would buy dinner
on her way home.I believed it would rain so I brought my raincoat.
2) to express polite request:
Would you please take off your coat?
Would you mind turning the radio off?
Слайд 12Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
3) to express actions take place
in the past:
I would fish and swim in the river
when I lived in the countryside.I used to go swimming in the river when I lived in the countryside.
4) to express desire
I would like to have one day off.
I’d love to stay for a few more days.
Слайд 13Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Should: Should is used
1) to give
advice and opinions
You are driving too fast; you should slow
down a little bit.You have gained a lot of weight. You should go on a diet.
Слайд 14Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
2) to express expectations:
Are you ready?
The taxi should be here soon.
Twenty dollars is enough. It
shouldn’t cost more than that.3) to suggest a less strong possibility
If you should pass the bakery, can you buy some bread?
Слайд 15Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
4) Should with present perfect tense
means something in the past should not be done.
The baby
is crying. You shouldn’t have talked so loudly.Mom is angry. You shouldn’t have come back so late.
Слайд 16Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Must &Have to: must/have to are
used to
1) express something is necessary and essential
You must
pay by cash. You have to drive on the right in France.
2) Students have to wear uniform.
must not is used to express something is not permitted or allowed.
You mustn’t smoke, eat and drink in the museum.
Слайд 17Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
You must not drink and drive.
3) not have to is used to express something that
is not to be done necessarily.We don’t have to get up early on Saturday.
She doesn’t have to live in the hotel. She can live with us.
Слайд 18Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
May: May is used to
1)
express possibility in the present or in the future.
It may
rain. Elizabeth may know his telephone number.
2) for permission:
May I come in?
You may come if you want.
Слайд 20Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
Might: Might is used
1) to
express possibility in the present or in the future.
Ashley might
be in the library. I am not sure.George might come as well.
He may come.
He might come. (the chance that he comes is less likely than may)
Слайд 21Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
2) might with present perfect tense
means speculation about the past.
Edward is late. He might have
missed his bus or he might have overslept. Слайд 22Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
8.1 Difference between the modal verbs.
1)
The modals used to express future possibility are: may, might,
could and can. Could and might express more uncertainty than may.I may take a vacation in Bali Island.
You could be right. I am not sure.
There are only few jobs available, so she might not find one.
Слайд 23Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
2) The modals used to express
request are: can, could, will and would. However, could and
would are more polite.Could you give me a raise? Yes, I can.
Can you close the window? Sure I can.
* Be sure to use “can” and “will” for an affirmative short answer even if the question starts with would and could.
Слайд 24Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
3) The modals used to express
permission are: can, could and may. May is used in
formal situation.Where may I park my car? You can park right in front of the store.
Could I borrow your MP3? Yes, you may.
You may not park in the handicapped parking space.
Слайд 25Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
* Use may and can in
short answers.
could cannot be used to give and refuse
permission. Слайд 26Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
4) The modals used to give
advice are: could, might, should, must, have to, had better,
and ought to.You could meet me tonight or tomorrow morning.
You had better tell us the truth.
Your son ought to see a doctor.
You should not wear sandals and shorts to work.
Слайд 27Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
* had better is stronger than
should, ought to,
could and might are used when there are
more than one choice.Слайд 28Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
5) The modals used to express
preference are: prefer, would prefer, would rather and would like.
I
would prefer to have Japanese food for dinner.I would prefer to spend the night at home rather than drive out.
I would rather go by bus.
Слайд 29Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
I would rather go out than
stay home tonight.
I would like to have some tea.
Слайд 30Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
8.1-2 Exercise: Use an appropriate modal
verb to compete each sentence
Owen _______( not) do his homework
because tomorrow is Saturday.Drivers ________ stop at a stop sign.
________ you make a copy for me?
We _______ leave now or we will be late.
Слайд 31Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
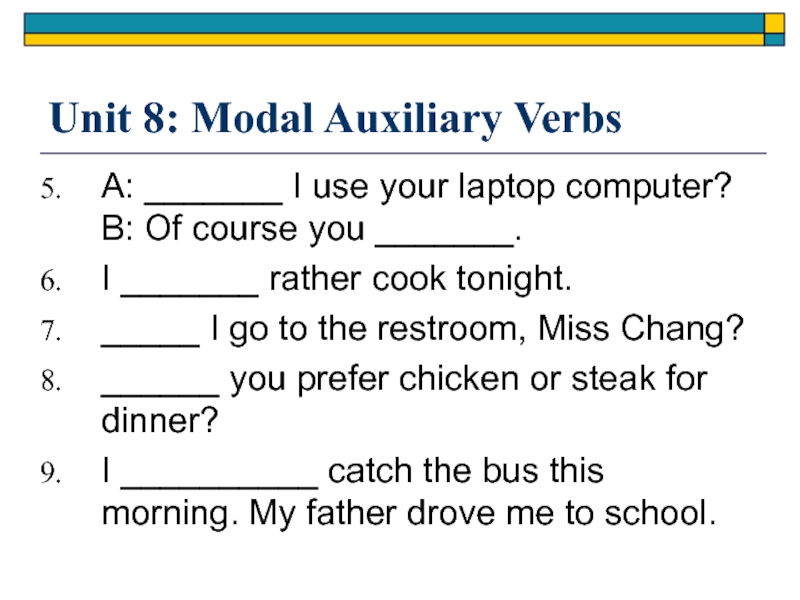
A: _______ I use your laptop
computer? B: Of course you _______.
I _______ rather cook tonight.
_____
I go to the restroom, Miss Chang?______ you prefer chicken or steak for dinner?
I __________ catch the bus this morning. My father drove me to school.
Слайд 32Unit 8: Modal Auxiliary Verbs
_________ you answer the phone?
When I
was young, I ________ speak better English than now.
You look
pale. You ______ go to a doctor.You have been driving for ten hours. You _________ be exhausted.
We __________ rent a car. My father will lend us his.