Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
European Integration History: Phases, Results and Achievements. Political
Содержание
- 1. European Integration History: Phases, Results and Achievements. Political
- 2. 3. European Integration Challengers, Achievements and Debates about its Future
- 3. Division of Policy Authority Challenge The EU
- 4. Division of Policy Authority Challenge Subsidiarity -
- 5. TEU Article 53. Under the principle of
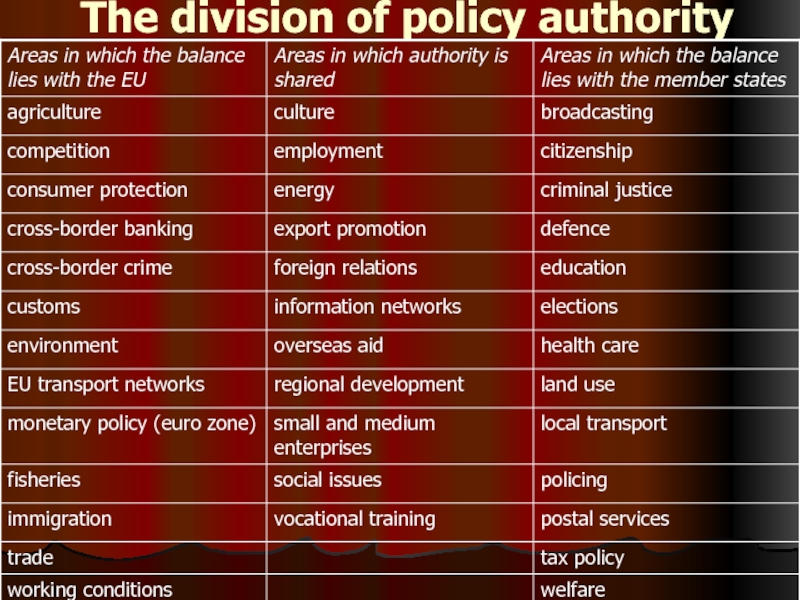
- 6. The division of policy authority
- 7. Europeanization is usually defined as the process
- 8. The EU Policy Process Challenge Features of the policy process:compromise and bargainingpolitical gamesmulti-speed integrationformal versus informalincrementalismspillover
- 9. How EU laws are madeCitizens, interest groups,
- 10. European Citizenship Challenge communicationidentityinvolvement
- 11. Social Challenge migrationsocial standards
- 12. Economic Challenge The recent economic crisis has
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. 2011 EU budget: €141.9 billion =
- 15. Слайд 15
- 16. Enlargement Challenge Article 61. The Union
- 17. Article 49Any European State which respects the
- 18. The Copenhagen Criteriastable institutions that guarantee democracy,
- 19. The Madrid CriterionA candidate country must also
- 20. Development Prospects “Europe 2020” is the EU's
- 21. Слайд 21
- 22. Скачать презентанцию
3. European Integration Challengers, Achievements and Debates about its Future
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1European Integration History: Phases, Results and Achievements. Political Challenges of the EU
Слайд 3Division of Policy Authority Challenge
The EU Policy Process Challenge
European Citizenship Challenge
Social Challenge
Economic Challenge
Enlargement Challenge
Crises and
Reforms Dialectics Challenge Development Prospects
Слайд 4Division of Policy Authority Challenge
Subsidiarity - the principle that
decisions should be taken at the lowest level possible for
effective action.It was first raised in the European context in 1975 when the European Commission argued that the Community should be given responsibility only for those matters that the member states were no longer capable of dealing with efficiently.
Слайд 5TEU Article 5
3. Under the principle of subsidiarity, in areas
which do not fall within its exclusive competence, the Union
shall act only if and in so far as the objectives of the proposed action cannot be sufficiently achieved by the Member States, either at central level or at regional and local level, but can rather, by reason of the scale or effects of the proposed action, be better achieved at Union level.The institutions of the Union shall apply the principle of subsidiarity as laid down in the Protocol on the application of the principles of subsidiarity and proportionality. National Parliaments ensure compliance with the principle of subsidiarity in accordance with the procedure set out in that Protocol.
4. Under the principle of proportionality, the content and form of Union action shall not exceed what is necessary to achieve the objectives of the Treaties.
The institutions of the Union shall apply the principle of proportionality as laid down in the Protocol on the application of the principles of subsidiarity and proportionality.
Слайд 7Europeanization is usually defined as the process by which laws
and policies in the member states have been brought into
alignment with EU law and policy.Слайд 8The EU Policy Process Challenge
Features of the policy process:
compromise
and bargaining
political games
multi-speed integration
formal versus informal
incrementalism
spillover
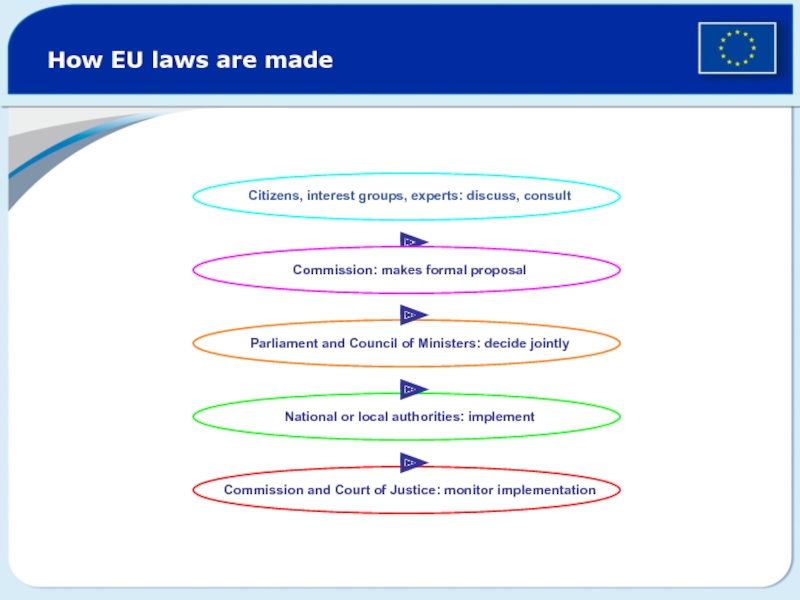
Слайд 9How EU laws are made
Citizens, interest groups, experts: discuss, consult
Commission:
makes formal proposal
Parliament and Council of Ministers: decide jointly
Commission and Court of Justice: monitor implementation
National or local authorities: implement
Слайд 12Economic Challenge
The recent economic crisis has no precedent in
European generation. The steady gains in economic growth and job
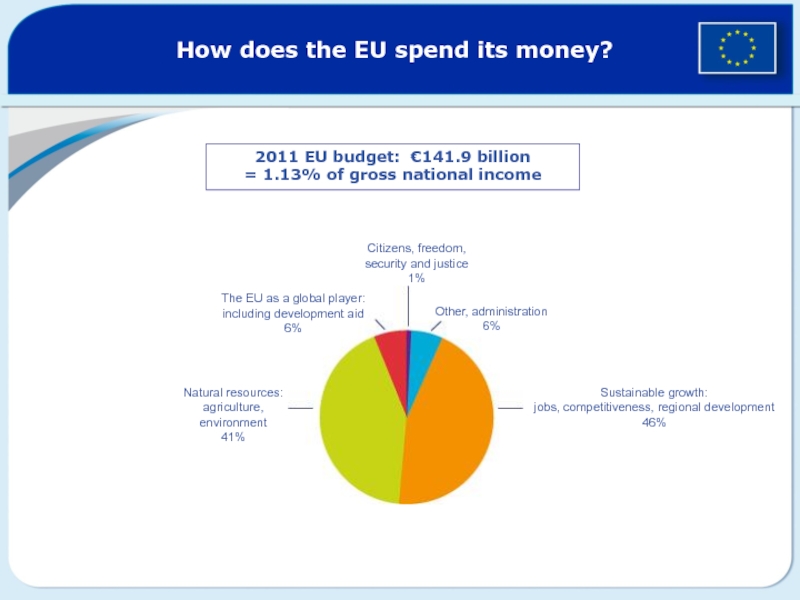
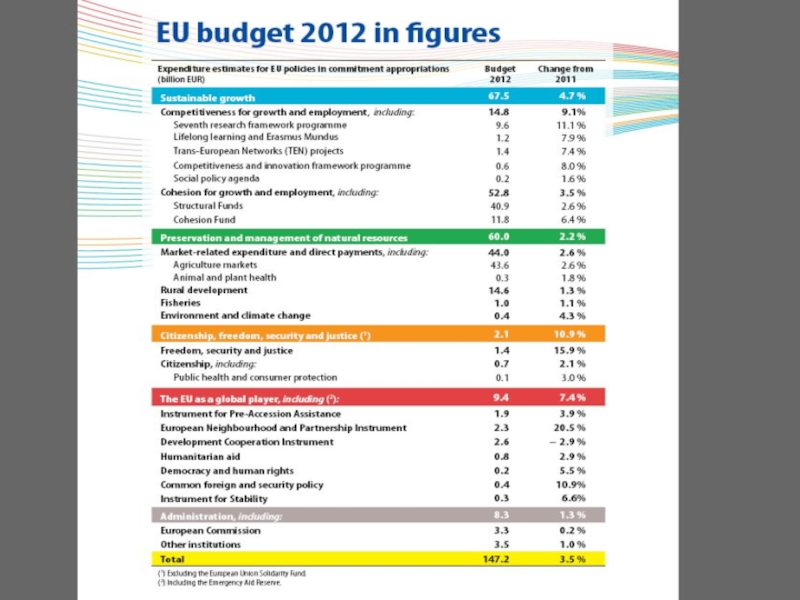
creation witnessed over the last decade have been wiped out – the EU GDP fell by 4% in 2009, industrial production dropped back to the levels of the 1990s and 23 million people - or 10% of active population - are now unemployed. The crisis has been a huge shock for millions of citizens and it has exposed some fundamental weaknesses of the EU economy.Слайд 142011 EU budget: €141.9 billion = 1.13% of gross national
income
Citizens, freedom,
security and justice
1%
Other, administration
6%
Sustainable growth:
jobs, competitiveness, regional development
46%
The EU
as a global player:including development aid
6%
Natural resources:
agriculture,
environment
41%
How does the EU spend its money?
Слайд 16Enlargement Challenge
Article 6
1. The Union is founded on
the principles of liberty, democracy, respect for human rights and
fundamental freedoms, and the rule of law, principles which are common to the Member States.2. The Union shall respect fundamental rights, as guaranteed by the European Convention for the Protection of Human Rights and Fundamental Freedoms signed in Rome on 4 November 1950 and as they result from the constitutional traditions common to the Member States, as general principles of Community law.
3. The Union shall respect the national identities of its Member States.
4. The Union shall provide itself with the means necessary to attain its objectives and carry through its policies.
Слайд 17Article 49
Any European State which respects the principles set out
in Article 6(1) may apply to become a member of
the Union. It shall address its application to the Council, which shall act unanimously after consulting the Commission and after receiving the assent of the European Parliament, which shall act by an absolute majority of its component members.The conditions of admission and the adjustments to the Treaties on which the Union is founded, which such admission entails, shall be the subject of an agreement between the Member States and the applicant State. This agreement shall be submitted for ratification by all the contracting States in accordance with their respective constitutional requirements.
Слайд 18The Copenhagen Criteria
stable institutions that guarantee democracy, the rule of
law, human rights and respect for and protection of minorities;
a functioning market economy, as well as the ability to cope with the pressure of competition and the market forces at work inside the Union;
the ability to assume the obligations of membership, in particular adherence to the objectives of political, economic and monetary union.
Слайд 19The Madrid Criterion
A candidate country must also be able to
put the EU rules and procedures into effect. Accession also
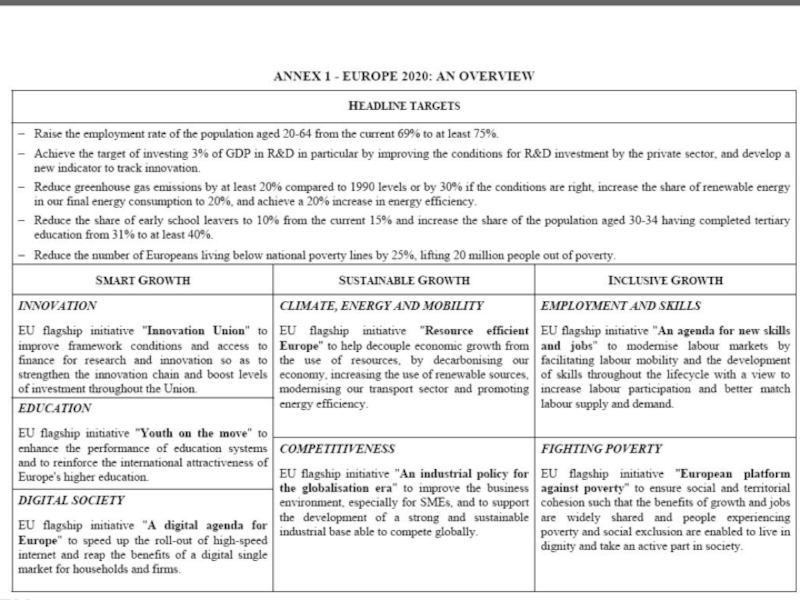
requires the candidate country to have created the conditions for its integration by adapting its administrative structures. While it is important for EU legislation to be transposed into national legislation, it is even more important for the legislation to be implemented and enforced effectively through the appropriate administrative and judicial structures. This is a prerequisite of the mutual trust needed for EU membership.Слайд 20Development Prospects
“Europe 2020” is the EU's growth strategy for
the coming decade.
Europe 2020 puts forward three mutually reinforcing priorities:
Smart
growth: developing an economy based on knowledge and innovation.Sustainable growth: promoting a more resource efficient, greener and more competitive economy.
Inclusive growth: fostering a high-employment economy delivering social and territorial cohesion.