Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
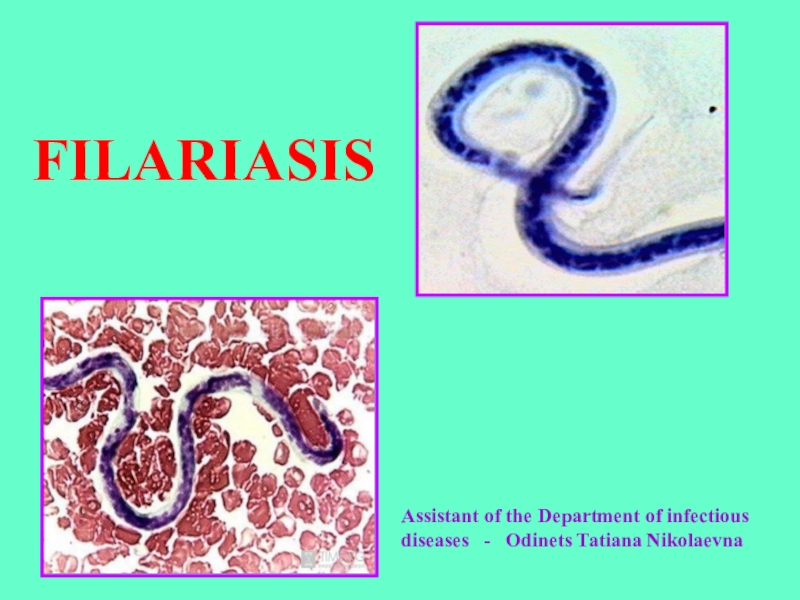
FILARIASIS Assistant of the Department of infectious diseases - Odinets Tatiana
Содержание
- 1. FILARIASIS Assistant of the Department of infectious diseases - Odinets Tatiana
- 2. Filariasis - is tropical transmissible biohelminthiasis
- 3. Lymphatic filariasis - Wuchereriasis and Brugiasis common
- 4. Onchocercosis - is distributed in 34 countries,
- 5. Loa-loa disease (loaosis) - is found only in the forest zone of West and Central Africa;
- 6. General properties of filariasis: 1. They are
- 7. 6. The cycle of
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. 11. There are three groups of filariasis
- 10. Wuchereriasis and Brugiasis (Filariasis Bancrofti, F. Malayi)
- 11. Vectors of W.- mosquitoes of the Culex
- 12. PATHOGENESIS: 1. Sensitization of human organism by
- 13. Early stage (migration) - 2-7 years -
- 14. Слайд 14
- 15. rupture of lymph nodes in the
- 16. Obstruction stage (develops in 10-15 years): -
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Swelling spreads - the foot, ankle, thighextremity
- 19. IMMUNITY - low reactivity antigens of filaria
- 20. ONCHOCERCOSIS River blindness - Helminthiasis, characterised
- 21. Vectors - gnats Simulium that lives near
- 22. Слайд 22
- 23. CLINIC. Incubation period - is
- 24. Dermatitis: In the first – expressed
- 25. - pseudoadanitis – skin bags with subcutaneous
- 26. Formation of onchocercoma - dense, mobile, painless
- 27. affection of lymphatic system - lymphadenitis (groin
- 28. Affection of eyescorneal-conjunctivitis syndrome: - pruritus,
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. EPIDEMIOLOGY Source of invasion -
- 31. PATHOGENESIS – the same to other filariasisCLINIC
- 32. O.volvulus без чехликаBrugia malayi с чехликомLOA LOA
- 33. Слайд 33
- 34. 3. Detection of microfilaria
- 35. Слайд 35
- 36. Слайд 36
- 37. Be not like others!
- 38. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2
Filariasis - is tropical transmissible biohelminthiasis caused by nematodes
(roundworms) that inhabit the lymphatic and subcutaneous tissues.
Eight main
species infect humans: Wuchereria bancrofti and Brugia malayi cause lymphatic filariasis
Onchocerca volvulus causes onchocercosis (river blindness).
The other five species are
Loa loa, Mansonella perstans,
M. streptocerca, M. ozzardi,
Brugia timori. (The last species
also causes lymphatic filariasis.)
Слайд 3
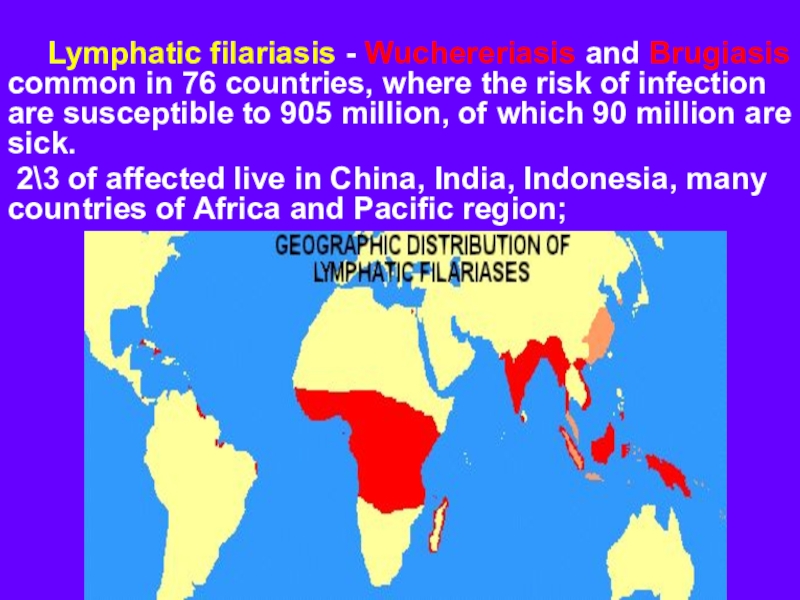
Lymphatic filariasis - Wuchereriasis and Brugiasis common in 76 countries,
where the risk of infection are susceptible to 905 million,
of which 90 million are sick.2\3 of affected live in China, India, Indonesia, many countries of Africa and Pacific region;
Слайд 4
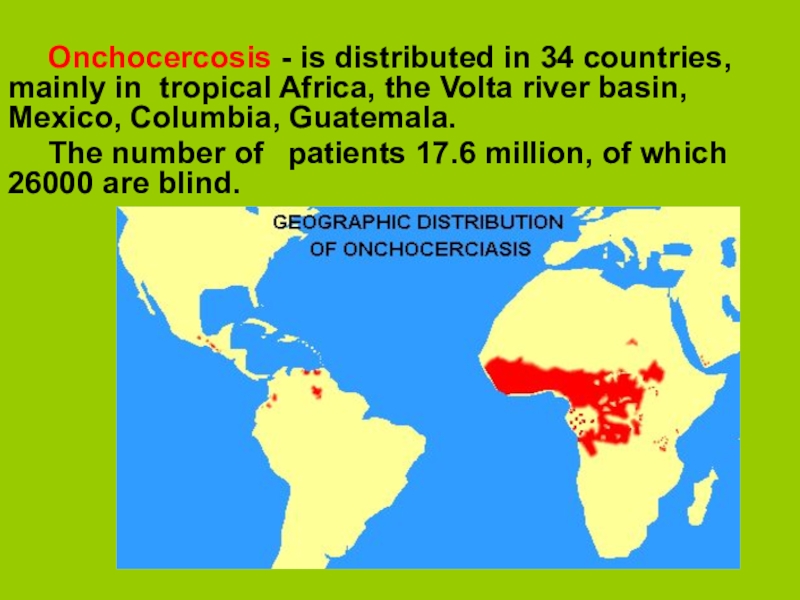
Onchocercosis - is distributed in 34 countries, mainly in
tropical Africa, the Volta river basin, Mexico, Columbia, Guatemala.
The number
of patients 17.6 million, of which 26000 are blind.Слайд 6
General properties of filariasis:
1. They are – all biohelminths ,
developing with the change
of owners. 2. The final host – is human, intermediate hosts of – arthropods
(mosquitoes, midges, mokrets).
3. All filarias divide on male and female.
4. The adults (macrofilaria)dwell in various human tissues
where they can live for several years (subcutaneous tissue –
onchocercosis, loaosis, streptocercosis, lymph vessels –
wuchereriasis and brugiasis connective tissue etc).
5. Females produce a larvae (microfilaria) which penetrate into
blood stream or superficial skin layers (onchocercosis),
they do not grow and change morphologically. 6. Length of adult males up to 50 mm, females - up to 100 mm,
microfilaria - 0,3 mm.
Слайд 7
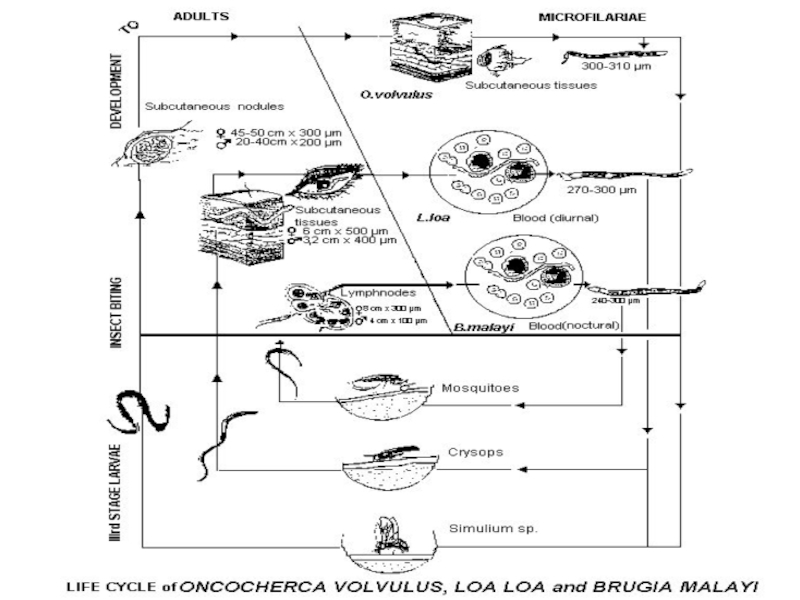
6. The cycle of development the same
for all filarias:
human infection is
only transmissible.Infective larvae are transmitted by infected biting arthropods during a blood meal. The larvae migrate to the appropriate site of the host's body, where they develop into microfilariae-producing adults.
7. Vectors swallow larvae at blood-suction and become infected in 2-3 weeks.
8. All filariasis have proloned incubation period - 2-18 months, when helminths reach sexual maturity.
9. Disease develops slowly.
10. Duration of the disease more than 10 years (the period of life of macrofilaria), microfilaria lives about 70 days.
Слайд 9
11. There are three groups of filariasis depending on the
concentration of larvae in the peripheral blood: - periodical –peak of
the highest concentration of larvae in peripheral blood is observed in a day or at night, in other times filarias are absent , - subperiodical - larvae is constantly present in the peripheral blood, but the highest concentration may be seen only in the same time of the day. - non-recurrent – microfilarias are allways present in the blood in constant concentration.Frequency coincides with the period of maximal activity of the vector.
Слайд 10
Wuchereriasis and Brugiasis
(Filariasis Bancrofti, F. Malayi)
- helminthiasis affecting
the lymphatic system.
ETIOLOGY: causative agent of
wuchereriasis – Wuchereria bancrofti
(Wucherer and Bancroft - scientists, who have described the helminth),
brugiasis - Brugia malayi (Brug – scientist) Macrofilarias parasites in the lymph nodes and vessels,
microfilarias - in the blood. EPIDEMIOLOGY: source of infection
in W.(anthroponosis) – man,
in B. (zoonosis) – human, cats, dogs, monkeys.
Слайд 11
Vectors
of W.- mosquitoes of the Culex (in city), Anopheles,
Aedes (in village);
of B. - Aedes mosquito, Anopheles (in
city), Mansoni (in the wild nature).
Periodical forms of W. and B. – have night peak of filaria concentration.Subperiodical - with daily peak in W. and night peak – in B. (natural-focal zoonosis, source - animals, a vector – Mansoni mosquito).
Слайд 12
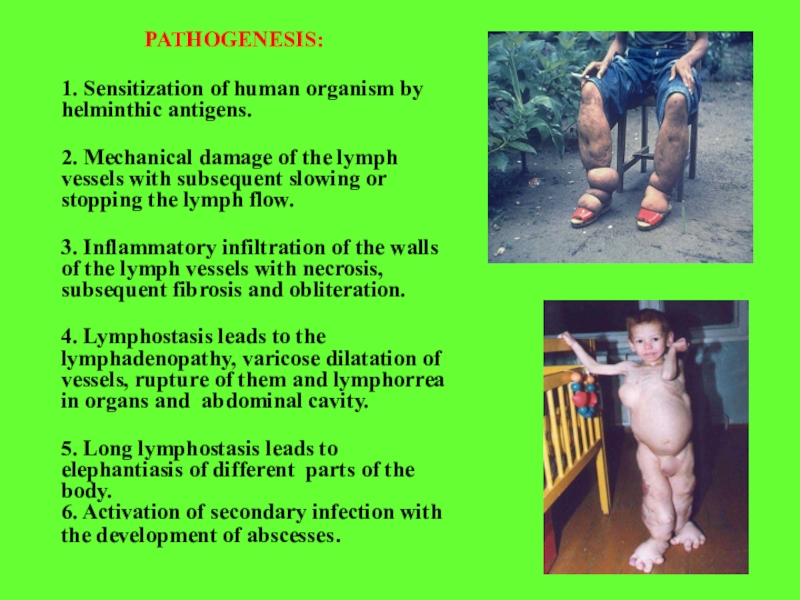
PATHOGENESIS:
1. Sensitization of human organism by helminthic antigens.
2. Mechanical damage
of the lymph vessels with subsequent slowing or stopping the
lymph flow.3. Inflammatory infiltration of the walls of the lymph vessels with necrosis, subsequent fibrosis and obliteration.
4. Lymphostasis leads to the lymphadenopathy, varicose dilatation of vessels, rupture of them and lymphorrea in organs and abdominal cavity.
5. Long lymphostasis leads to elephantiasis of different parts of the body. 6. Activation of secondary infection with the development of abscesses.
Слайд 13
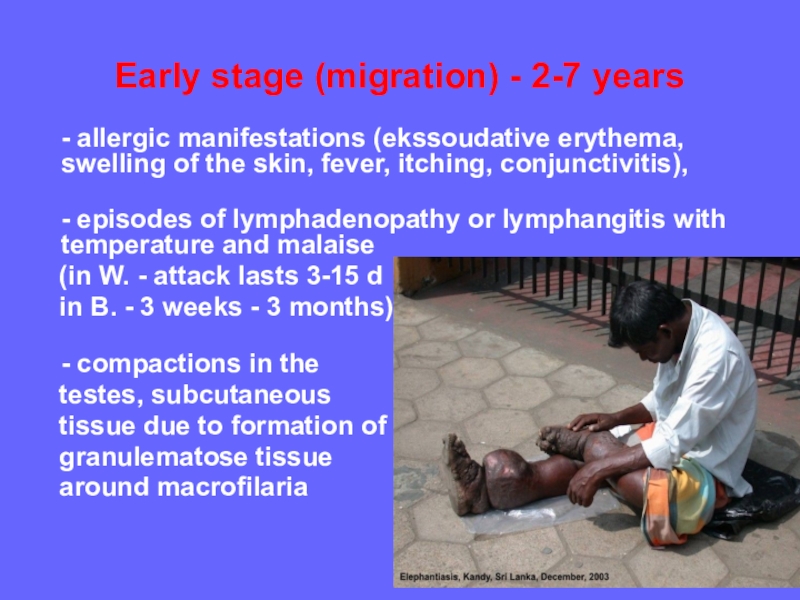
Early stage (migration) - 2-7 years
- allergic manifestations (ekssoudative erythema,
swelling of the skin, fever, itching, conjunctivitis),
- episodes of lymphadenopathy
or lymphangitis with temperature and malaise(in W. - attack lasts 3-15 d
in B. - 3 weeks - 3 months)
- compactions in the
testes, subcutaneous
tissue due to formation of
granulematose tissue
around macrofilaria
Слайд 14
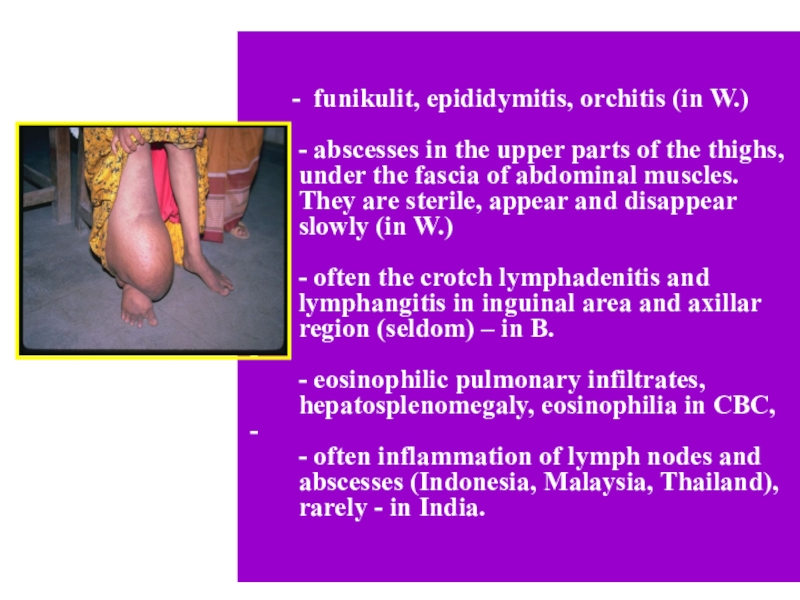
- funikulit,
epididymitis, orchitis (in W.)
- abscesses in the upper parts of
the thighs, under the fascia of abdominal muscles. They are sterile, appear and disappear slowly (in W.)- often the crotch lymphadenitis and lymphangitis in inguinal area and axillar region (seldom) – in B.
- eosinophilic pulmonary infiltrates, hepatosplenomegaly, eosinophilia in CBC,
- often inflammation of lymph nodes and abscesses (Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand), rarely - in India.
Слайд 15
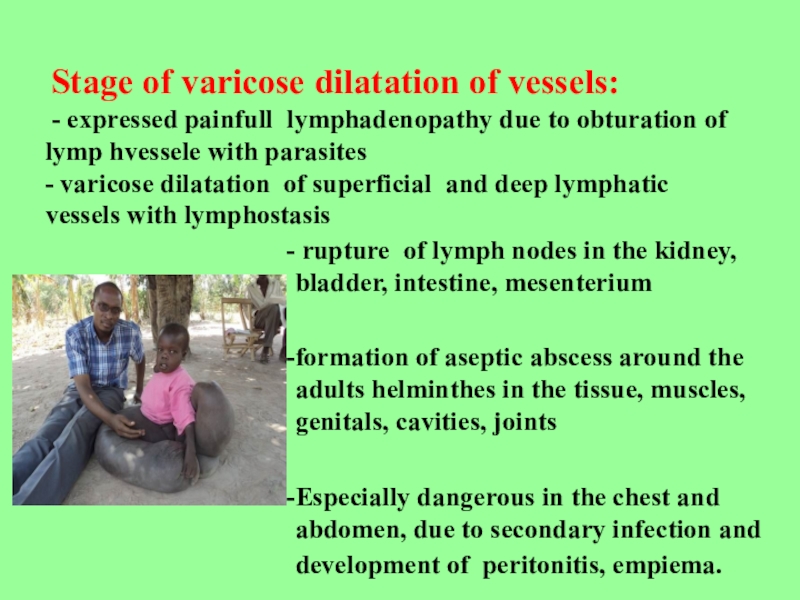
rupture of lymph nodes in the kidney, bladder, intestine,
mesenterium
formation of aseptic abscess around the adults helminthes in the
tissue, muscles, genitals, cavities, jointsEspecially dangerous in the chest and abdomen, due to secondary infection and development of peritonitis, empiema.
Stage of varicose dilatation of vessels:
- expressed painfull lymphadenopathy due to obturation of lymp hvessele with parasites
- varicose dilatation of superficial and deep lymphatic vessels with lymphostasis
Слайд 16
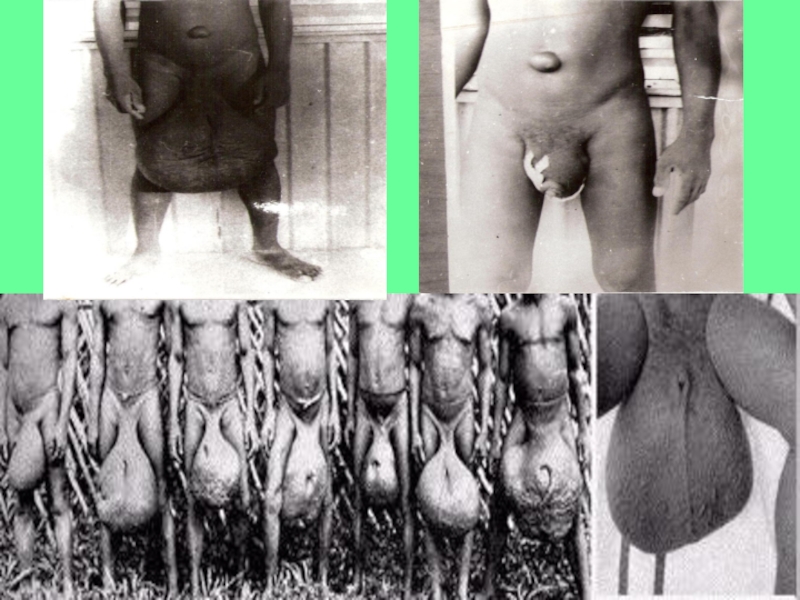
Obstruction stage
(develops in 10-15 years):
- hydrocele - is the
most common
manifestation of Wuchereriasis
in Africa, Egypt, Indonesia, Northern
India, it should be preceded by funikulit or orchitis, may be bleeding and abscess,
not typical,
- elephantiasis fever – develops due to activation of secondary microflora. It is more aggressive with the rapid course.Слайд 18
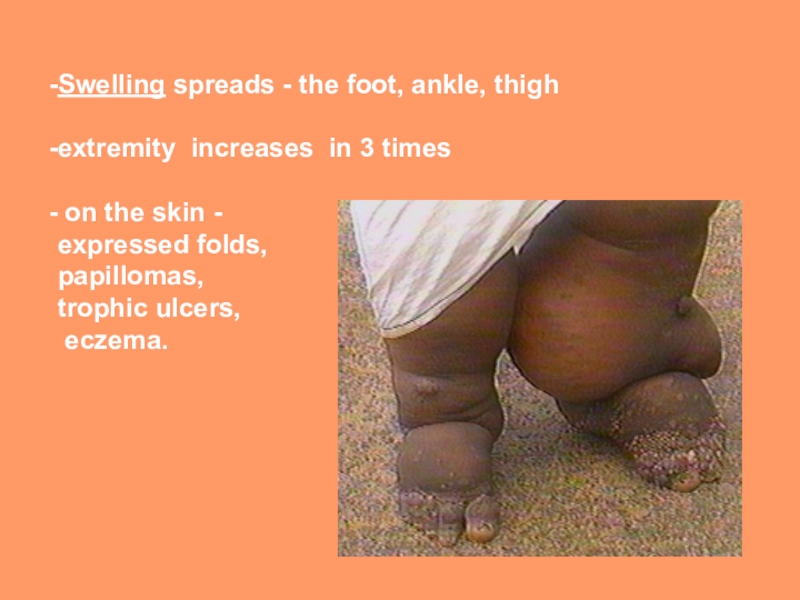
Swelling spreads - the foot, ankle, thigh
extremity increases in 3
times
on the skin -
expressed folds,
papillomas,
trophic ulcers,
eczema.Слайд 19
IMMUNITY
- low reactivity antigens of filaria
- development of immunosuppression
(serum-factors,
T-lymphocytes, monocytes),
- high ratio of suppressors to helper T-cells,
-titles of
IgE are high, but signs of allergic reactivity are not observed.
Антиген
Слайд 20
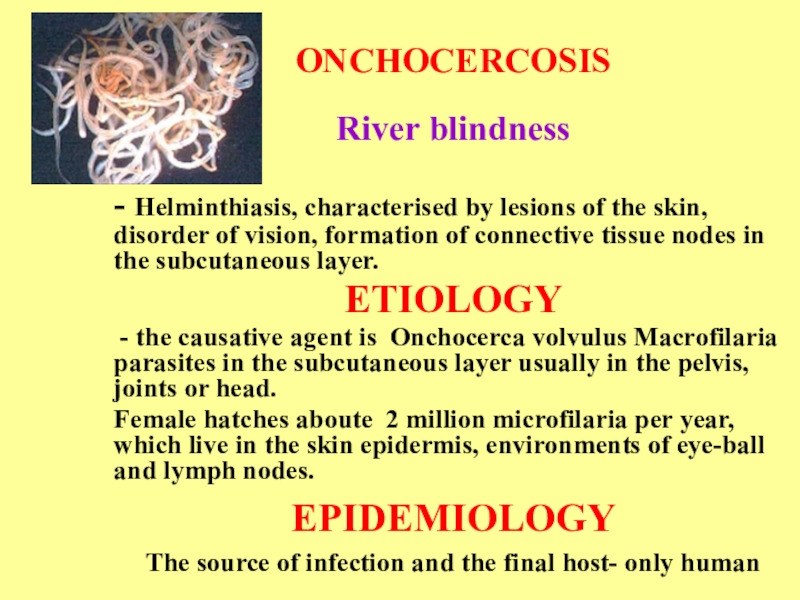
ONCHOCERCOSIS
River blindness
- Helminthiasis, characterised by lesions of the skin, disorder
of vision, formation of connective tissue nodes in the subcutaneous
layer.ETIOLOGY
- the causative agent is Onchocerca volvulus Macrofilaria parasites in the subcutaneous layer usually in the pelvis, joints or head.
Female hatches aboute 2 million microfilaria per year, which live in the skin epidermis, environments of eye-ball and lymph nodes.
EPIDEMIOLOGY
The source of infection and the final host- only human
Слайд 21Vectors - gnats Simulium that lives near rapid rivers.
In
Africa there are two strain - Savannah zone (more virulent,
affects often the organ of vision that leads to blindness) and forest zone.In South America affect the vision organ is rarely
Слайд 22
PATHOGENESIS 1. Mechanical effluence of adult parasites, around which
onchocercoma is formed (connective tissue node) 2. Toxic-allergic effects of mature parasites and it’s larvae (especially dead worm)3. Penetration of the larvae in the eyeball is manifested as iritis or iridocyclitis («anterior uveitis») and/or chorioiditis or chorioretinitis («posterior uveitis»), as keratitis, conjunctivitis with subsequent development of gradual sclerosis of the eyes, optic nerve atrophy and blindness
4. Parasitizing microfilaria causes dermatitis with lymph swelling of the skin of genitals, lower extremities, and elephantiasis
5. In the final stages depigmentation, atrophy, ulceration is developed
Слайд 23
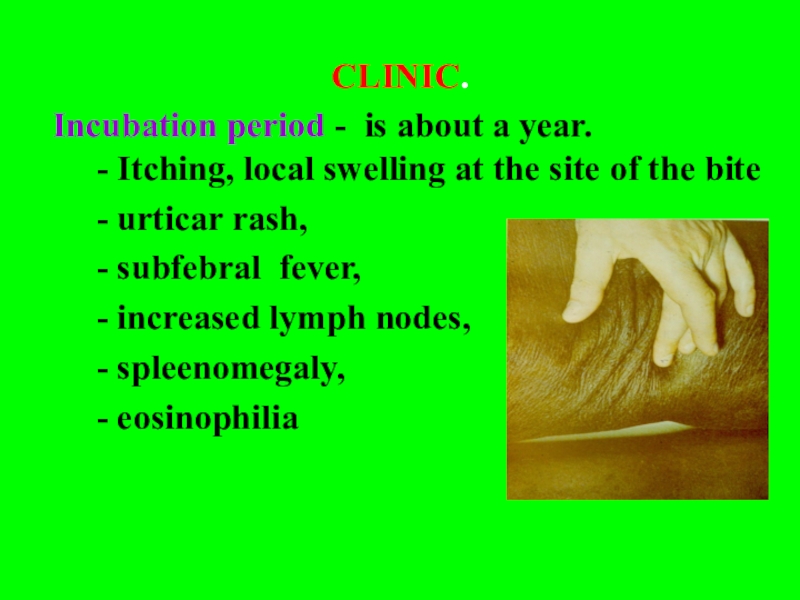
CLINIC.
Incubation period - is about a
year. - Itching, local swelling at the site of
the bite- urticar rash,
- subfebral fever,
- increased lymph nodes,
- spleenomegaly,
- eosinophilia
Слайд 24
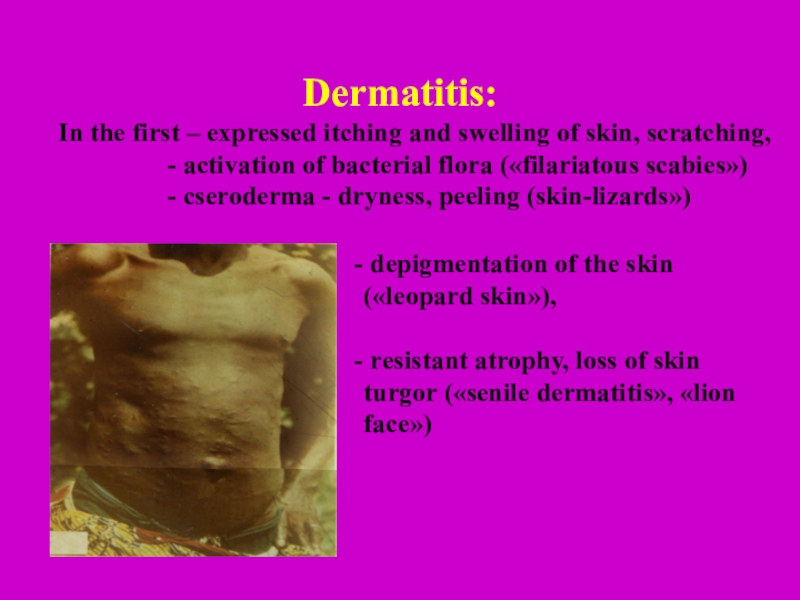
Dermatitis:
In the first – expressed itching and swelling of
skin, scratching,
- activation of bacterial flora («filariatous scabies»)- cseroderma - dryness, peeling (skin-lizards»)
depigmentation of the skin («leopard skin»),
resistant atrophy, loss of skin turgor («senile dermatitis», «lion face»)
Слайд 25
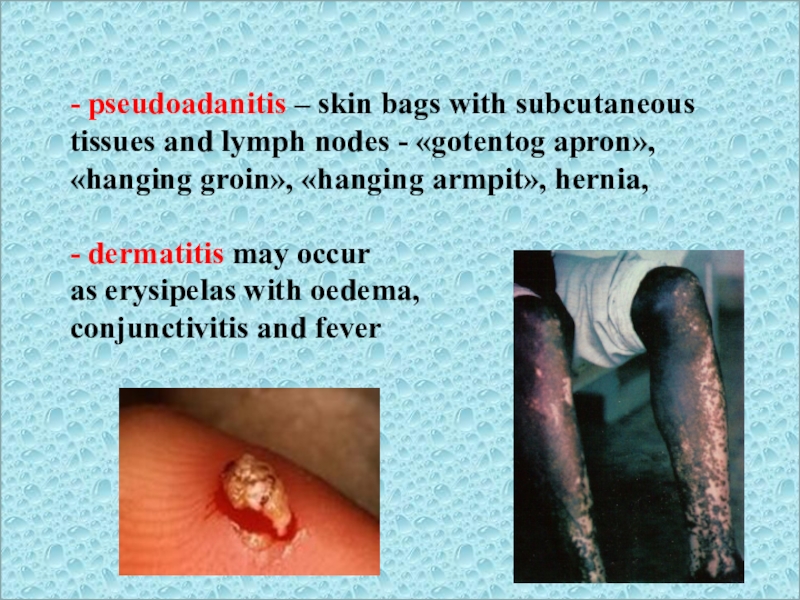
- pseudoadanitis – skin bags with subcutaneous tissues and lymph
nodes - «gotentog apron», «hanging groin», «hanging armpit», hernia,
- dermatitis
may occur as erysipelas with oedema,
conjunctivitis and fever
Слайд 26
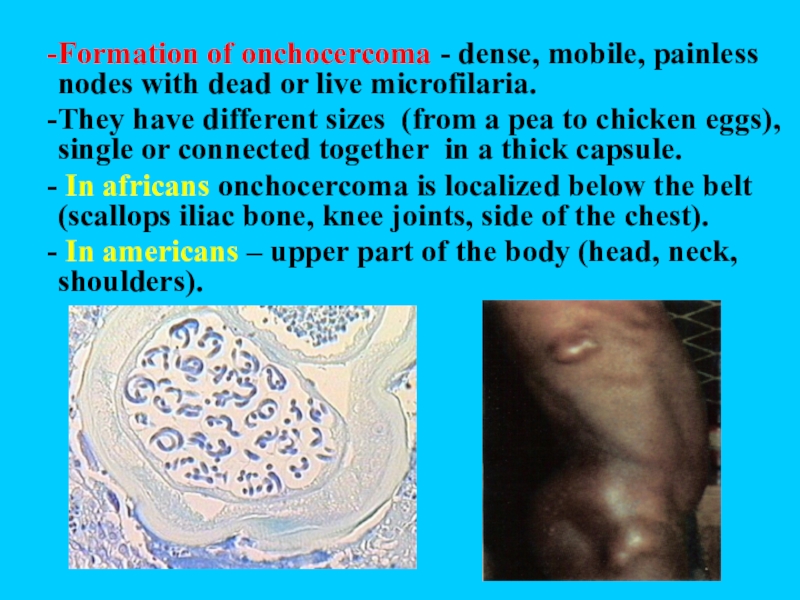
Formation of onchocercoma - dense, mobile, painless nodes with dead
or live microfilaria.
They have different sizes (from a pea to
chicken eggs), single or connected together in a thick capsule.In africans onchocercoma is localized below the belt (scallops iliac bone, knee joints, side of the chest).
In americans – upper part of the body (head, neck, shoulders).
Слайд 27affection of lymphatic system - lymphadenitis (groin and armpit), lymph
oedema,orchitis, hydrocele, elephantiasis of the lower limbs and genitals -
microfilaria is detected in urine, sputum, vaginal discharge, lymphatic and blood circulation system, saliva, cerebrospinal fluid, liver, kidneys, lungs, spleenOnchocercosis is a systemic disease
Слайд 28
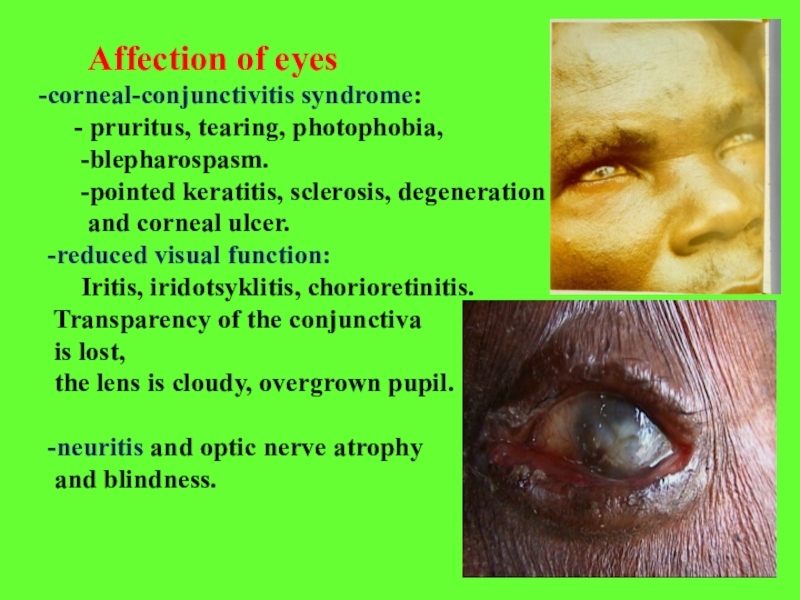
Affection of eyes
corneal-conjunctivitis syndrome:
- pruritus, tearing, photophobia,
-blepharospasm.
-pointed keratitis, sclerosis, degeneration
and corneal ulcer.-reduced visual function:
Iritis, iridotsyklitis, chorioretinitis.
Transparency of the conjunctiva
is lost,
the lens is cloudy, overgrown pupil.
-neuritis and optic nerve atrophy
and blindness.
Слайд 29
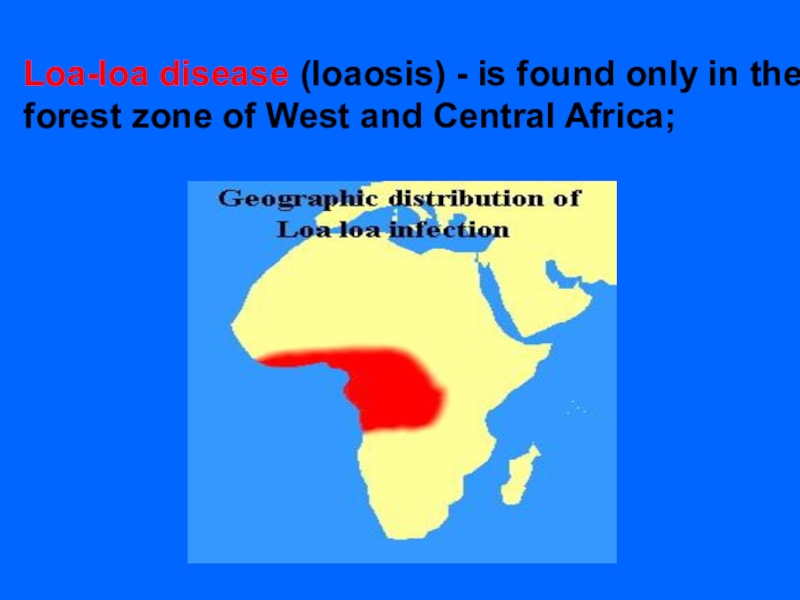
LOAOSIS
(Calabar swelling disease)Helminthiasis, characterised by the swelling of soft tissues, affection of eyes and genital organs.
ETIOLOGY
Pathogen - Loa loa, adult worm parasites under the conjunctiva of the eye and pericardium, microfilaria – in the blood in afternoon.
Слайд 30
EPIDEMIOLOGY
Source of invasion - man (sometimes monkeys)
Vectors - horse-flies of the
genus Chrysops that lives
in small water reservoirs.
Adult flies live in trees and
attack in the afternoon,
prefer people with dark skin.
Слайд 31PATHOGENESIS – the same to other filariasis
CLINIC
Incubation period -
4 months, more than a year. 1. Skin itching, rash, neuropathic
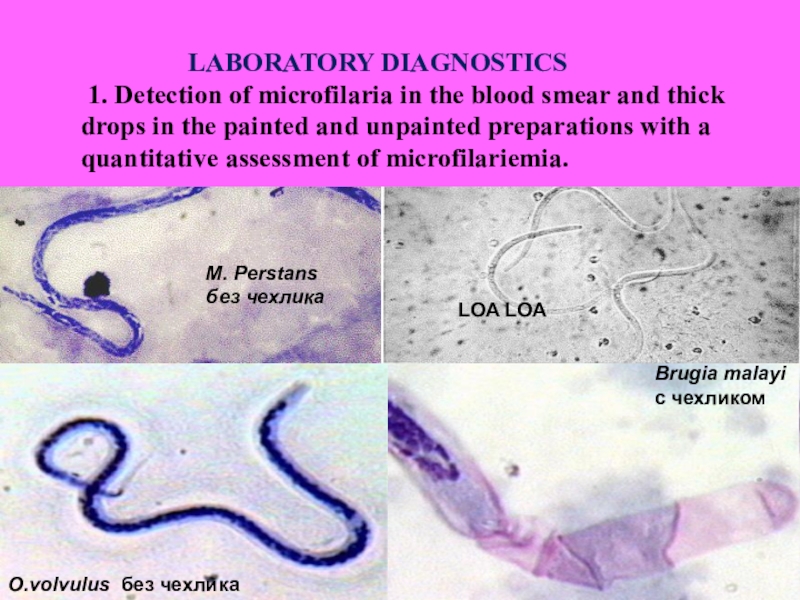
pain, subfibrale fever, hypereosinophilia. 2. Calabarien swelling on limited areas of the body (often on the extremities), disappears slowly, painless, skin is pale, hot, fossa is not remain. 3. Swelling, hyperemia of the conjunctiva, pain, lacrimation. Helminth is visible by eyes. 4. Symptoms are correspond to the place of helminth migration (dysuria, meningoencephalitis, neuritis, nephrotic syndrome, hydrocele). 5. Abscesses around the dead worms. 6. Sometimes parasites visible under the skin and come out through the skin.Слайд 32O.volvulus без чехлика
Brugia malayi
с чехликом
LOA LOA
M. Perstans
без
чехлика
LABORATORY
DIAGNOSTICS
1. Detection of microfilaria in the blood smear and thick drops in the painted and unpainted preparations with a quantitative assessment of microfilariemia.
Слайд 33
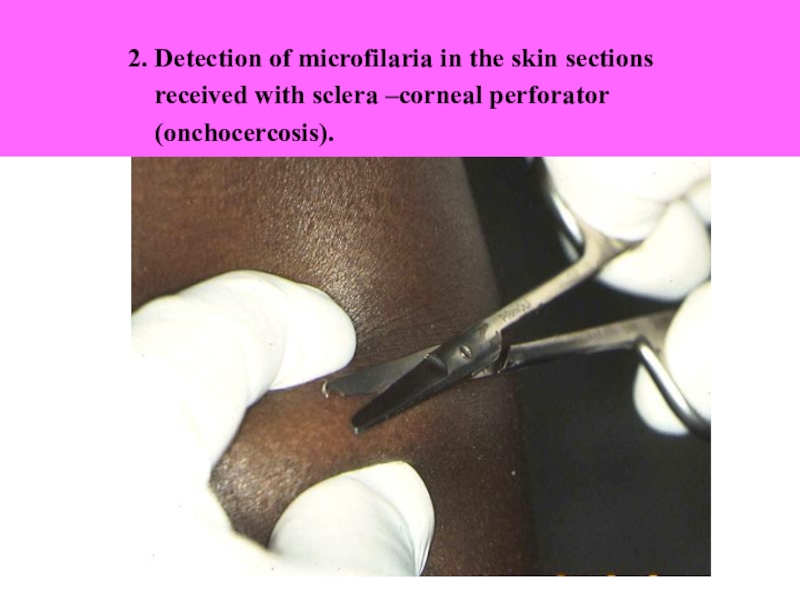
2. Detection of microfilaria in the
skin sectionsreceived with sclera –corneal perforator
(onchocercosis).
Слайд 34
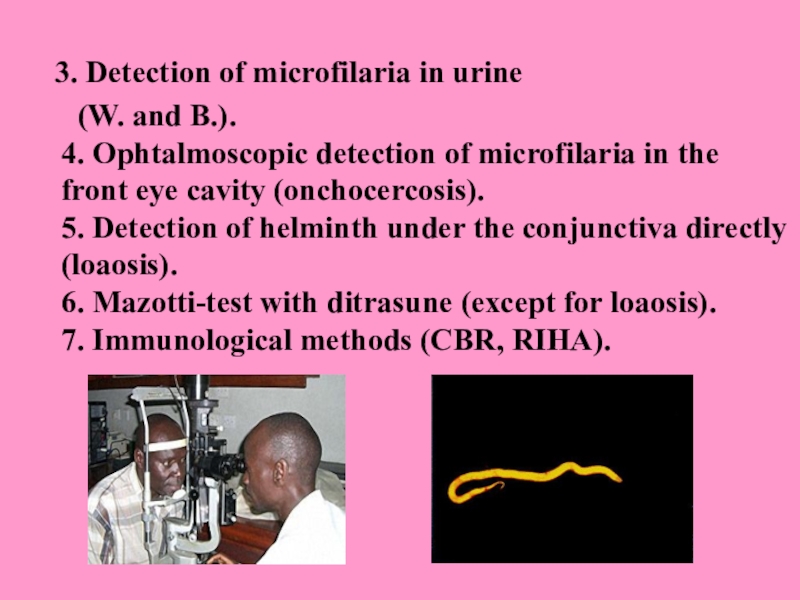
3. Detection of microfilaria in urine
(W. and B.). 4. Ophtalmoscopic detection of microfilaria
in the front eye cavity (onchocercosis). 5. Detection of helminth under the conjunctiva directly (loaosis). 6. Маzоtti-test with ditrasune (except for loaosis). 7. Immunological methods (CBR, RIHA).Слайд 35
TREATMENT Dietylcarbamasepine
- is effective in acute and chronic stage, in latent filariasis6 mg /kg /day (after meal) - 12 days (from 3 to 6 mg / kg / day). In loaosis - on the first day - 1\2 of doses, gradually increasing to 0.1 (3-4 times) - 2-3 weeks. Onchocercosis: Dietylcarbamasepine (initial dose reduced) -12 days Antripol (suramin)- 10% - 5ml - 1st day 10% - 10 ml - 2nd day 10% - 10 ml -1 times in 7 days -
5-7 weeks Ivermectine (mektisane) 150 mg\kg 1 time in 6 months.
Слайд 36
PREVENTION 1. Straggle with the intermediate hosts
2. Improvement of the source of the invasion: therapy of sick people
3. Sanitary-hygienic measures on improvement of settlements (water, sewerage, shower and other).
4. Individual prevention - protective clothing at risk groups.
5. Health education of the population (not pollute the water with feces, not to swim and others).
6. Sanitary supervision over natural reservoirs