development, biochemical or physiological properties, or behaviour.
Patients with an
identified phenotype of obstructive lung disease may share a cluster of clinical, functional and/or inflammatory features, without any implication of a common underlying mechanism
Examples: allergic asthma, aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease, severe eosinophilic asthma
Endotype: A subtype of disease, defined functionally and pathologically by a distinct molecular mechanism or by distinct treatment responses (Anderson, Lancet 2008)
Among patients with obstructive lung disease, there are likely to be several specific endotypes associated with divergent underlying molecular causes, and with distinct treatment responses. These endotypes may or may not align with clinical or inflammatory phenotypes identified from studies limited to asthma or to COPD
Examples: emphysema due to alpha1-antitrypsin deficiency
Biomarker: A defined characteristic measured as an indicator of normal biologic processes, pathogenic processes or response to an intervention
Potential examples: FeNO, blood eosinophils – but these may not meet quality criteria for biomarkers
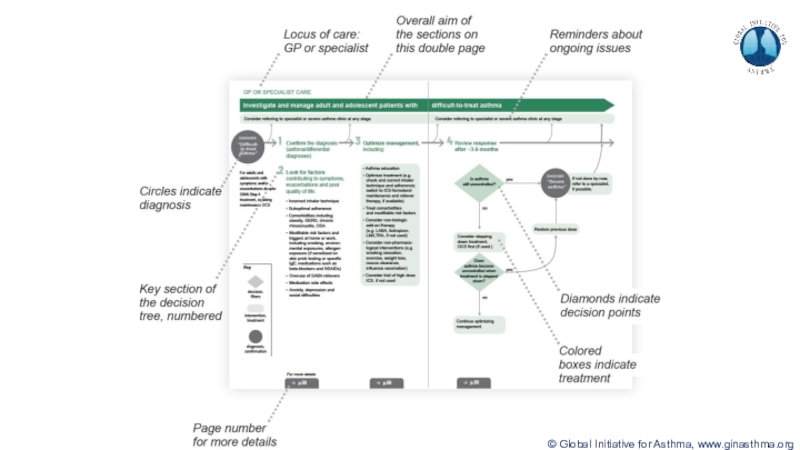
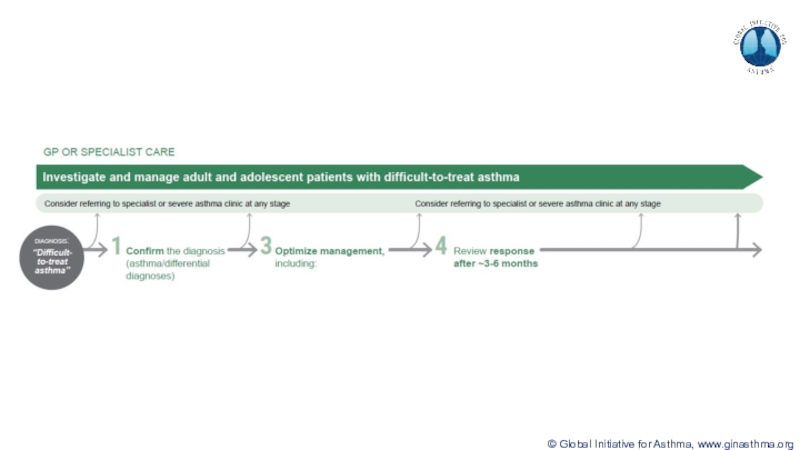
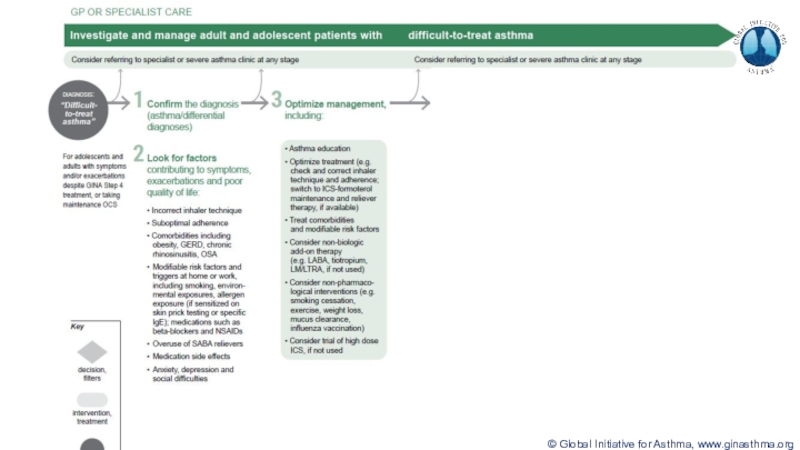
Terminology
Anderson, Lancet 2008; Reddel, ERJ Open Res 2019
© Global Initiative for Asthma, www.ginasthma.org

![GINA Pocket Guide Difficult to treat and severe asthma in adults and adolescents [PLEASE ADD YOUR DECLARATION OF INTEREST HERE]The work of GINA is [PLEASE ADD YOUR DECLARATION OF INTEREST HERE]The work of GINA is supported only by the sale and](/img/tmb/7/604702/cbedafb021b9eac98492f448cd1c37b7-800x.jpg)