Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Lecture 6 Ecology
Содержание
- 1. Lecture 6 Ecology
- 2. EcologyEcology is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among
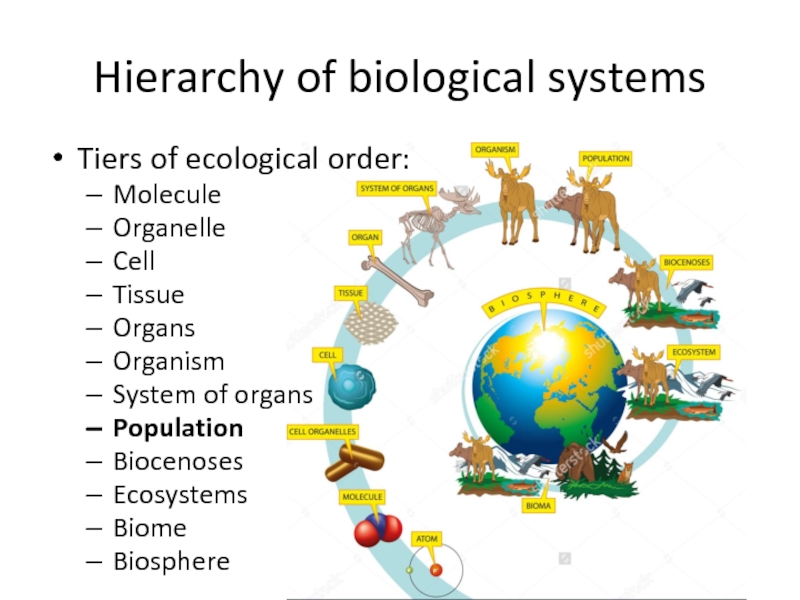
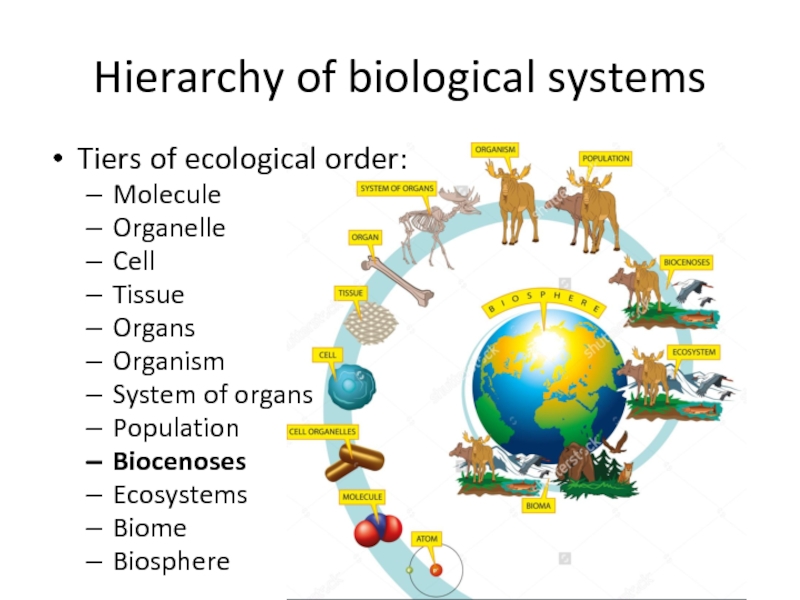
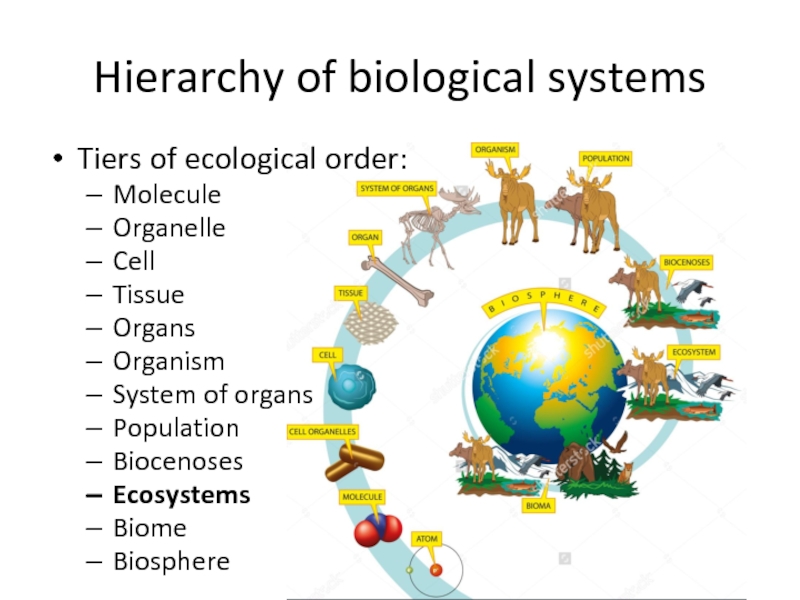
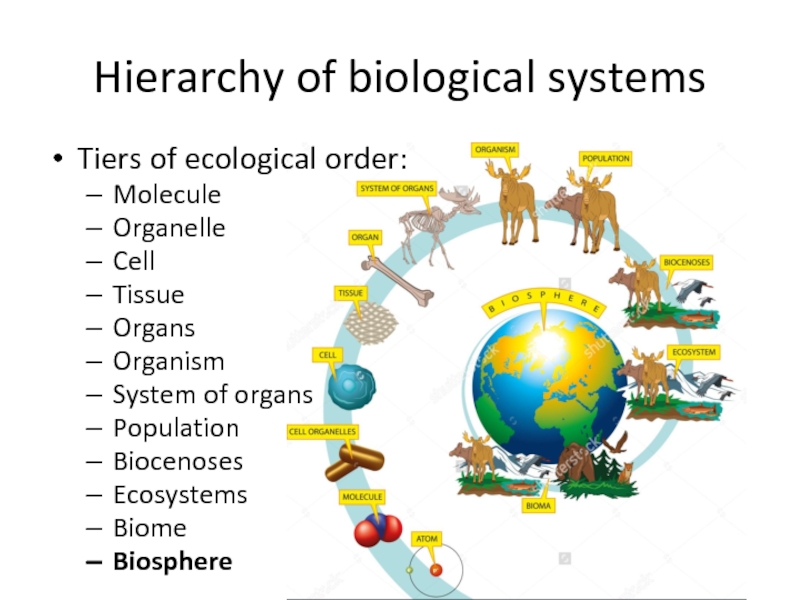
- 3. Hierarchy of biological systemsTiers of ecological order:MoleculeOrganelleCellTissueOrgansOrganismSystem of organsPopulationBiocenosesEcosystemsBiomeBiosphere
- 4. PopulationPopulation is a summation of all the organisms of the
- 5. Population growthLimiting factors of population growth:foodtemperaturematesspaceLimiting factors:density-dependentdensity-independent
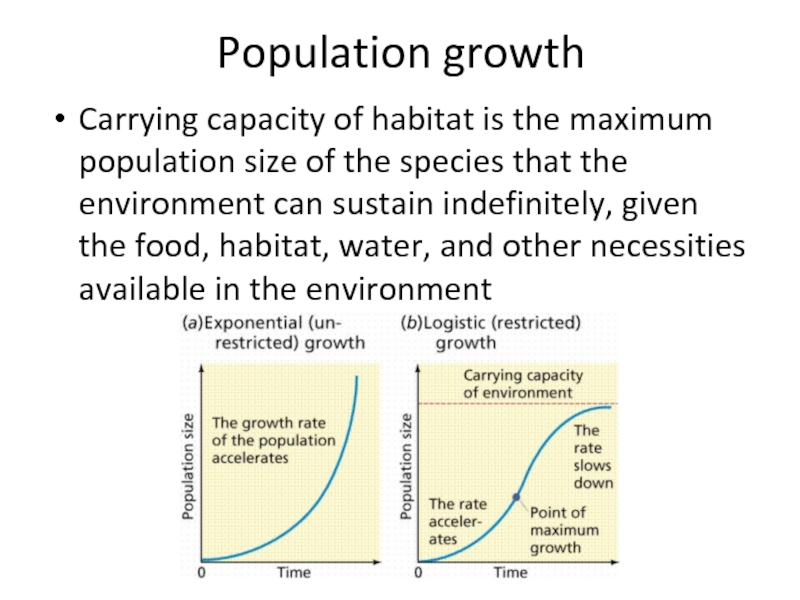
- 6. Population growthCarrying capacity of habitat is the
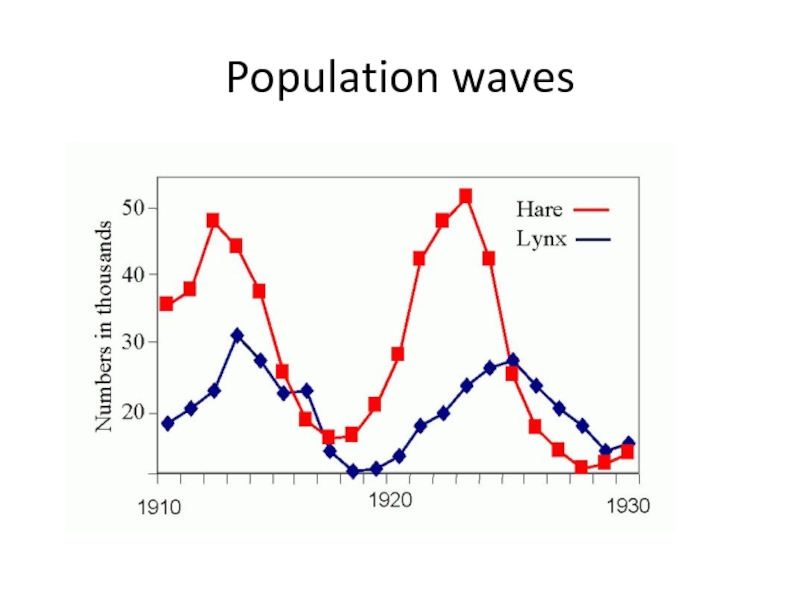
- 7. Population waves
- 8. Hierarchy of biological systemsTiers of ecological order:MoleculeOrganelleCellTissueOrgansOrganismSystem of organsPopulationBiocenosesEcosystemsBiomeBiosphere
- 9. CommunityCommunity (biocenosis) is an assemblage or association of populations of two
- 10. Interspecific interactionsPredation – the predator species benefits
- 11. 12435
- 12. Community ecologyCommunity ecology studies how the interactions
- 13. Hierarchy of biological systemsTiers of ecological order:MoleculeOrganelleCellTissueOrgansOrganismSystem of organsPopulationBiocenosesEcosystemsBiomeBiosphere
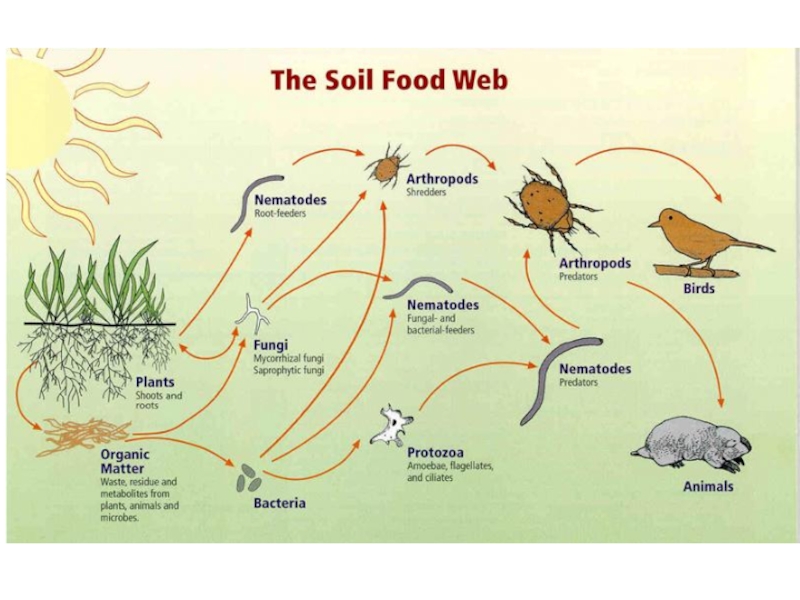
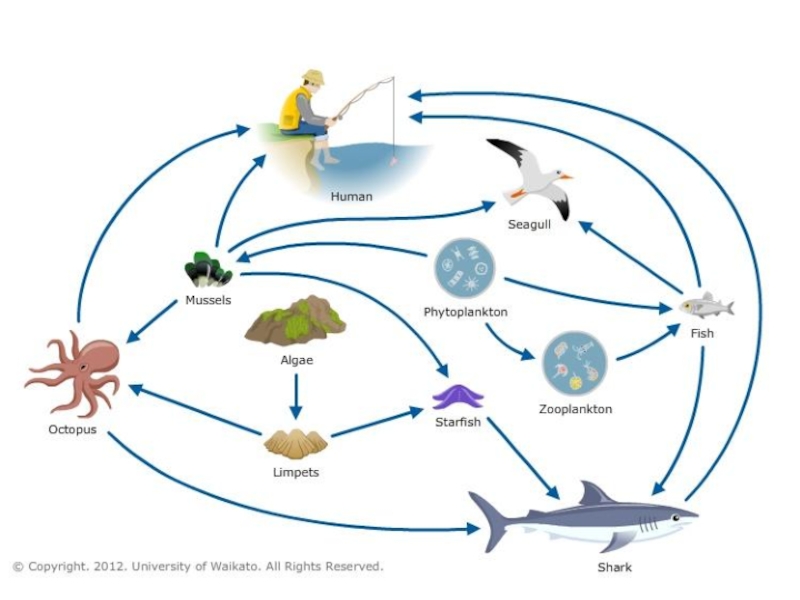
- 14. EcosystemAn ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with
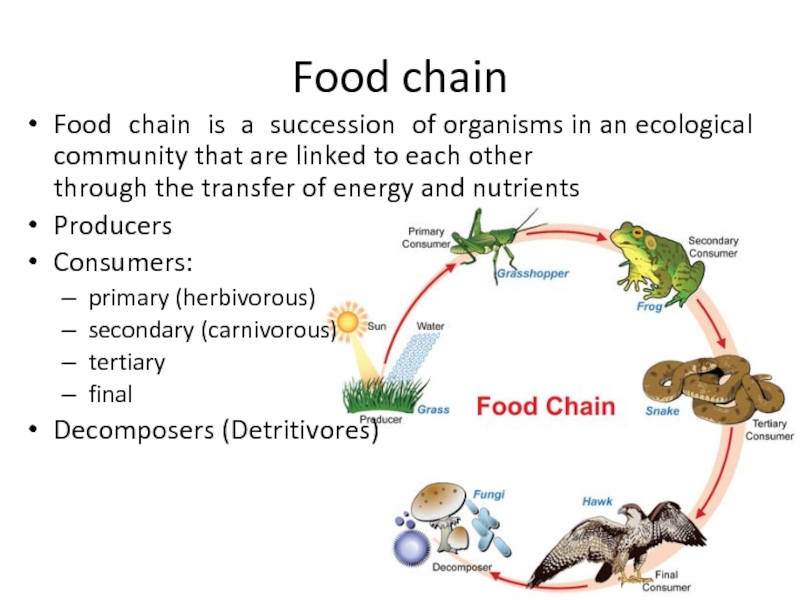
- 15. Food chainFood chain is a succession of organisms in an ecological community that are linked to each other through the transfer of energy and nutrientsProducersConsumers:primary (herbivorous)secondary (carnivorous)tertiaryfinalDecomposers (Detritivores)
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Слайд 18
- 19. Ecological pyramidBiomass is the mass of living
- 20. Ecological pyramidEcological pyramid is a graphical representation
- 21. Hierarchy of biological systemsTiers of ecological order:MoleculeOrganelleCellTissueOrgansOrganismSystem of organsPopulationBiocenosesEcosystemsBiomeBiosphere
- 22. BiomeA biome is a formation of plants and animals that have common characteristics
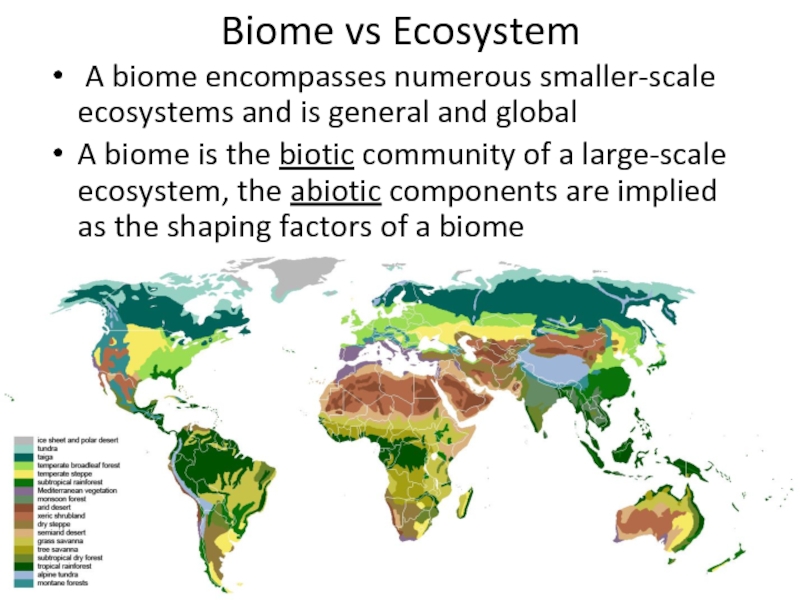
- 23. Biome vs Ecosystem A biome encompasses numerous smaller-scale
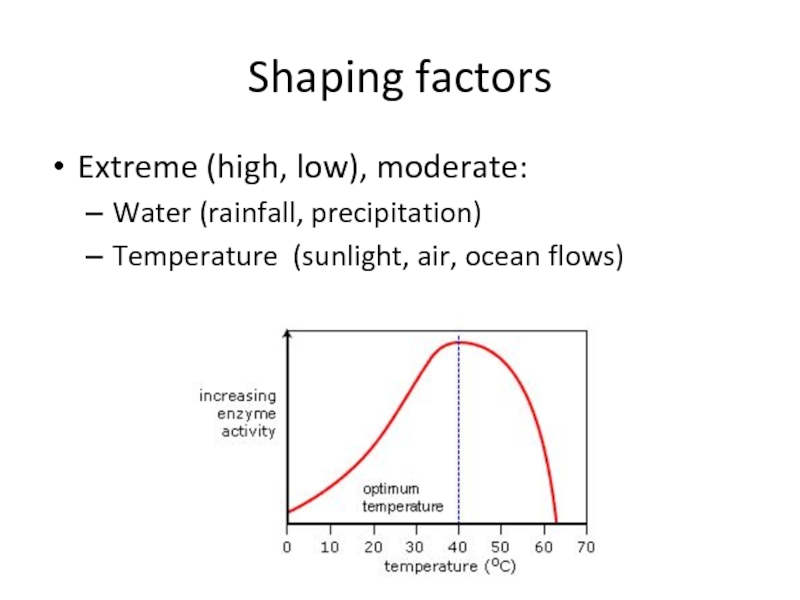
- 24. Shaping factorsExtreme (high, low), moderate:Water (rainfall, precipitation)Temperature (sunlight, air, ocean flows)
- 25. 123456TemperatureWater -------------------Biodiversity
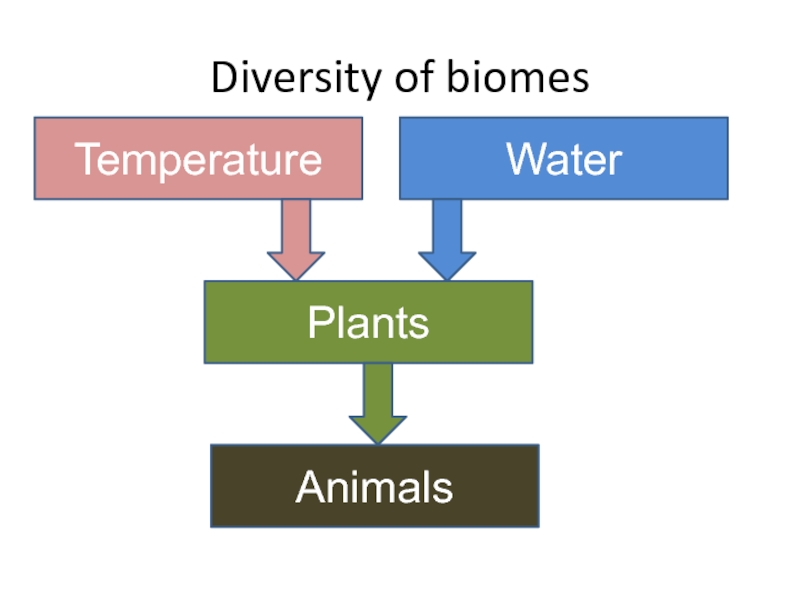
- 26. Diversity of biomesTemperatureWaterPlantsAnimals
- 27. Hierarchy of biological systemsTiers of ecological order:MoleculeOrganelleCellTissueOrgansOrganismSystem of organsPopulationBiocenosesEcosystemsBiomeBiosphere
- 28. BiosphereThe biosphere is the global sum of all ecosystemsThe living
- 29. Ecological problems
- 30. Vocabulary 6hierarchytiersfecunditybiocenosis (pl. biocenoses)predatorpreyhostparasiteto benefitat the expenseto harmenvironmentencompassshaping factortundrataigarainforeststeppedesertprairiesavannaconiferous forestshabitatbiotic and abiotic factorsrainfallprecipitationmoderate/extreme temperaturesproducersconsumersdecomposers detritivoreherbivorous animal
- 31. Скачать презентанцию
EcologyEcology is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their environmentPut individual organisms together, they can interact with each other and their environments to create something larger than the sum of
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Ecology
Ecology is the scientific analysis and study of interactions among organisms and their
environment
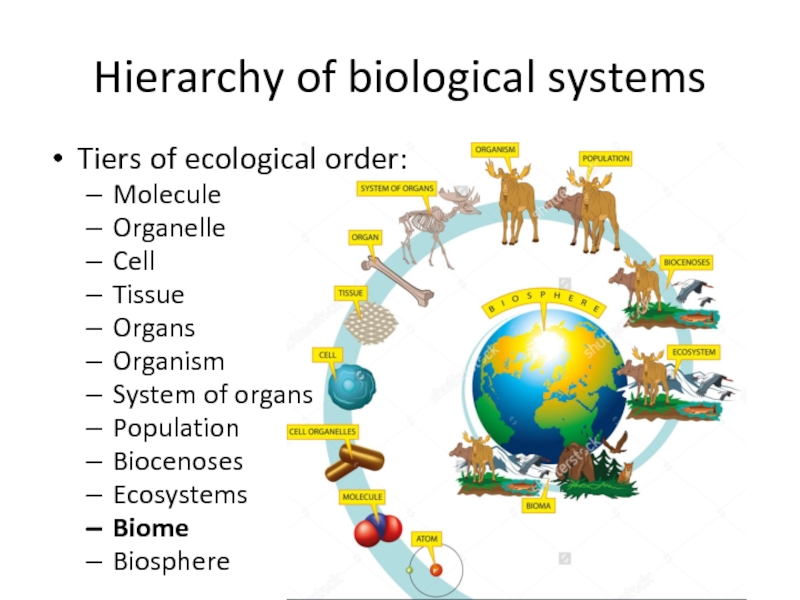
and their environments to create something larger than the sum of this partsСлайд 3Hierarchy of biological systems
Tiers of ecological order:
Molecule
Organelle
Cell
Tissue
Organs
Organism
System of organs
Population
Biocenoses
Ecosystems
Biome
Biosphere
Слайд 4Population
Population is a summation of all the organisms of the same group or species,
which live in a particular geographical area, and have the capability
of interbreedingDensity of population:
born and immigration (+)
death and emigration (-)
dispersion
fecundity
Слайд 5Population growth
Limiting factors of population growth:
food
temperature
mates
space
Limiting factors:
density-dependent
density-independent
Слайд 6Population growth
Carrying capacity of habitat is the maximum population size
of the species that the environment can sustain indefinitely, given
the food, habitat, water, and other necessities available in the environmentСлайд 8Hierarchy of biological systems
Tiers of ecological order:
Molecule
Organelle
Cell
Tissue
Organs
Organism
System of organs
Population
Biocenoses
Ecosystems
Biome
Biosphere
Слайд 9Community
Community (biocenosis) is an assemblage or association of populations of two or more different
species occupying the same geographical area and in a particular
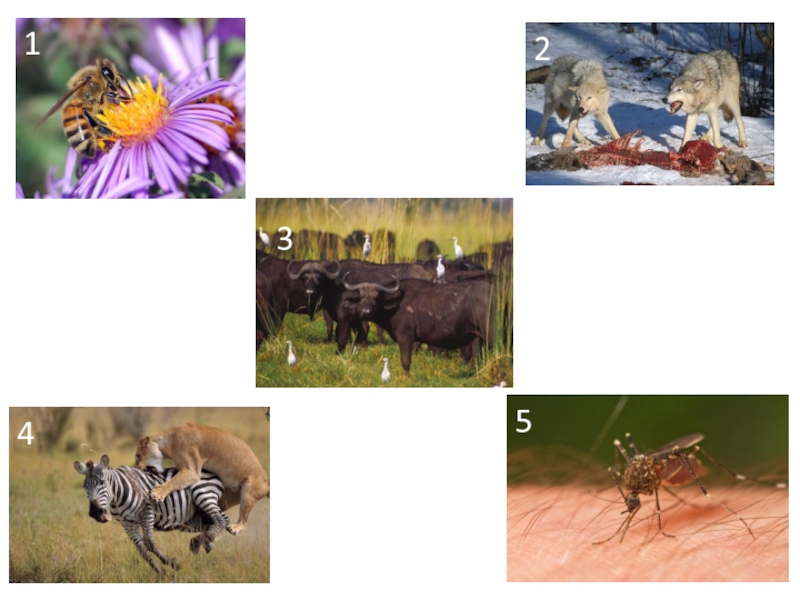
time.Слайд 10Interspecific interactions
Predation – the predator species benefits while the prey
species is harmed (+/-)
Competition – species can compete with each other for
finite resources Mutualism – interaction in which both species benefit (+/+)
Parasitism – one species, the parasite, benefits at the expense of the other, the host (+/-)
Commensalism – one organism benefits while the other organism is neither benefited nor harmed (+/0)
Amensalism – a product of one organism has a negative effect on another organism (+/-)
Слайд 12Community ecology
Community ecology studies how the interactions between community members
and their environment affect how much of each species there
are within a communityСлайд 13Hierarchy of biological systems
Tiers of ecological order:
Molecule
Organelle
Cell
Tissue
Organs
Organism
System of organs
Population
Biocenoses
Ecosystems
Biome
Biosphere
Слайд 14Ecosystem
An ecosystem is a community of living organisms in conjunction with the nonliving components of their
environment (things like air, water and mineral soil), interacting as
a systemEcosystem ecology explores how energy and materials flow through an ecosystem, and how the physical environment impacts the living organisms
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism. Habitat provides area (living or non-living)
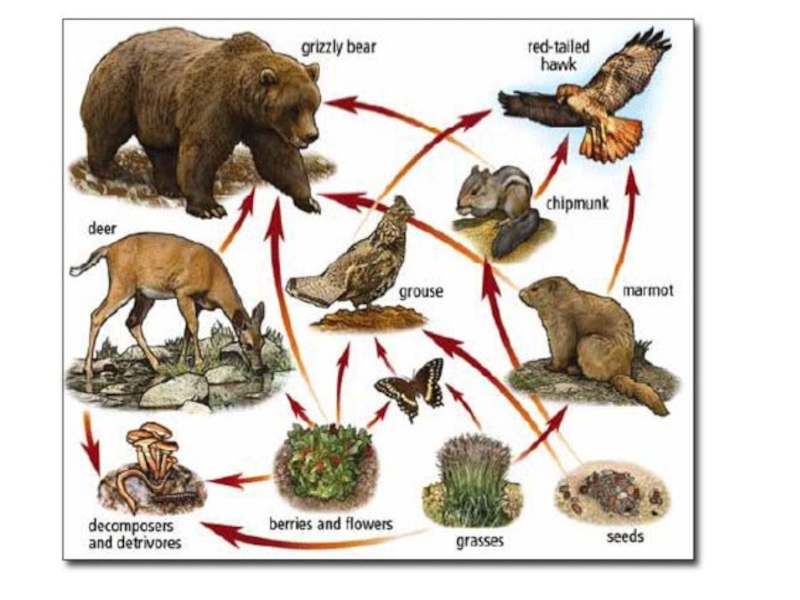
Слайд 15Food chain
Food chain is a succession of organisms in an ecological community that are linked to each other through the transfer of energy and nutrients
Producers
Consumers:
primary (herbivorous)
secondary
(carnivorous)
tertiary
final
Decomposers (Detritivores)
Слайд 19Ecological pyramid
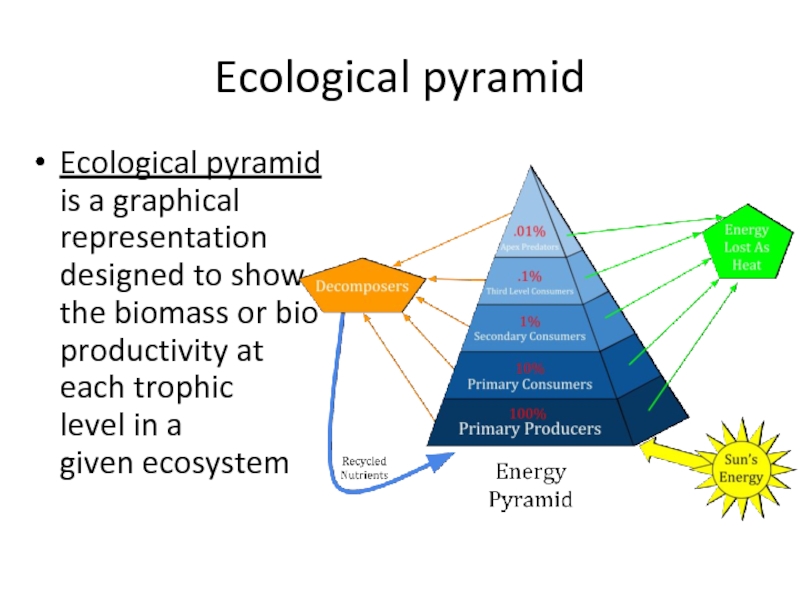
Biomass is the mass of living biological organisms in
a given area or ecosystem at a given time
Ecosystem productivity is the
rate of generation of biomass in an ecosystemEcosystem efficiency describes the efficiency with which energy is transferred from one trophic level to the next
Слайд 20Ecological pyramid
Ecological pyramid is a graphical representation designed to show
the biomass or bio productivity at each trophic level in a given ecosystem
Слайд 21Hierarchy of biological systems
Tiers of ecological order:
Molecule
Organelle
Cell
Tissue
Organs
Organism
System of organs
Population
Biocenoses
Ecosystems
Biome
Biosphere
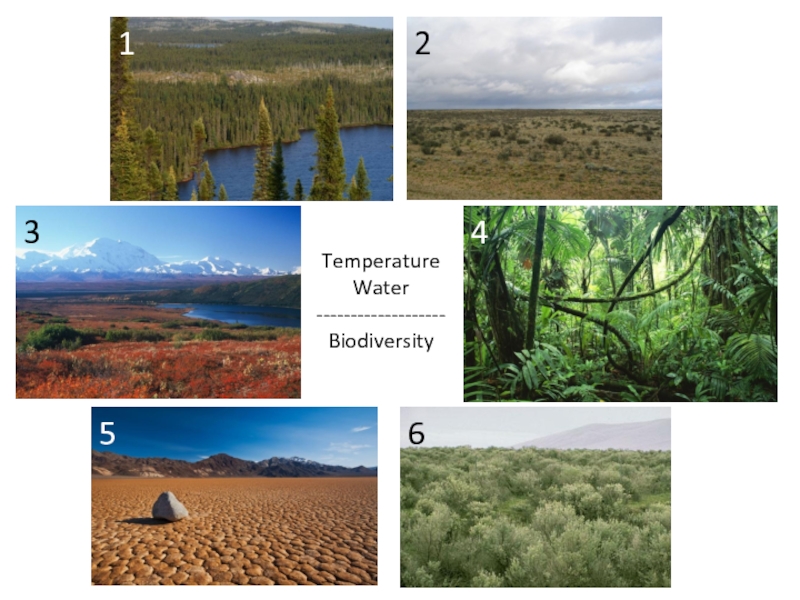
Слайд 22Biome
A biome is a formation of plants and animals that have common characteristics due to similar
climates and can be found over a range of continents
Usually
a biome is named after its predominant vegetation association:grassland
rainforests
tundra
…