Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Lecture on Pediatric Surgery for 5-th year students of medical faculty Theme: “
Содержание
- 1. Lecture on Pediatric Surgery for 5-th year students of medical faculty Theme: “
- 2. Plan of the lecture: 1.
- 3. BackgroundTrauma - the most common cause of
- 4. Trauma
- 5. Polytrauma Always accompanied by hypovolemic shock.When
- 6. Traumatic diseasePathogenesis : hypovolemic shock, blood loss,
- 7. Traumatic shock - a powerful reaction of
- 8. Pathogenesis of shock Developing acute vascular
- 9. Clinic of shockIn erectile stage of shock
- 10. Clinic of shock Breathing is frequent
- 11. Principles of shock treatment :Most important are
- 12. Principles of shock treatment : 5.
- 13. Principles of shock treatment : 6.
- 14. As additional trauma aggravates during shock should
- 15. Injury of the thoracic cavity
- 16. Injury of the thoracic cavity
- 17. Concussion of chestOccurs more frequently in case
- 18. Contusion of the chestOccurs when a strong
- 19. Pneumothorax- accumulation in the pleural cavity of
- 20. Left-sided valvular pneumothorax
- 21. Treatment of pneumothoraxWhen closed - pleural puncture
- 22. Hemothorax -accumulation of blood in the pleural
- 23. Clinic of Hemothoraxrapid weak pulse, tachypnea, decreased
- 24. Left-sided hemothorax
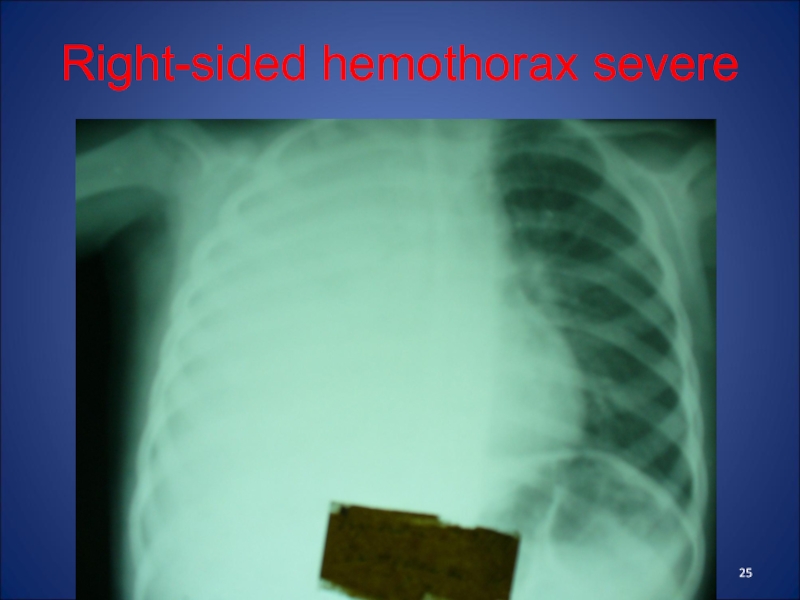
- 25. Right-sided hemothorax severe
- 26. Pneumohemothoraxaccumulation of blood and air in the
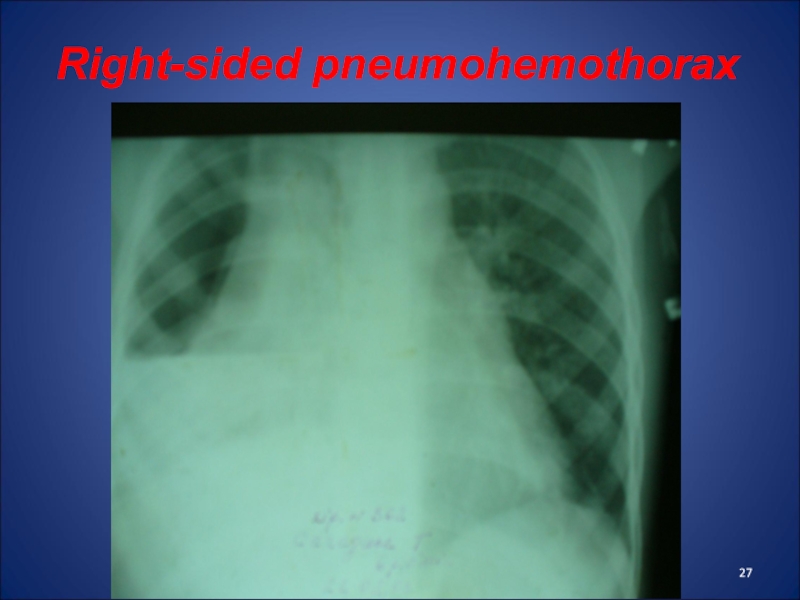
- 27. Right-sided pneumohemothorax
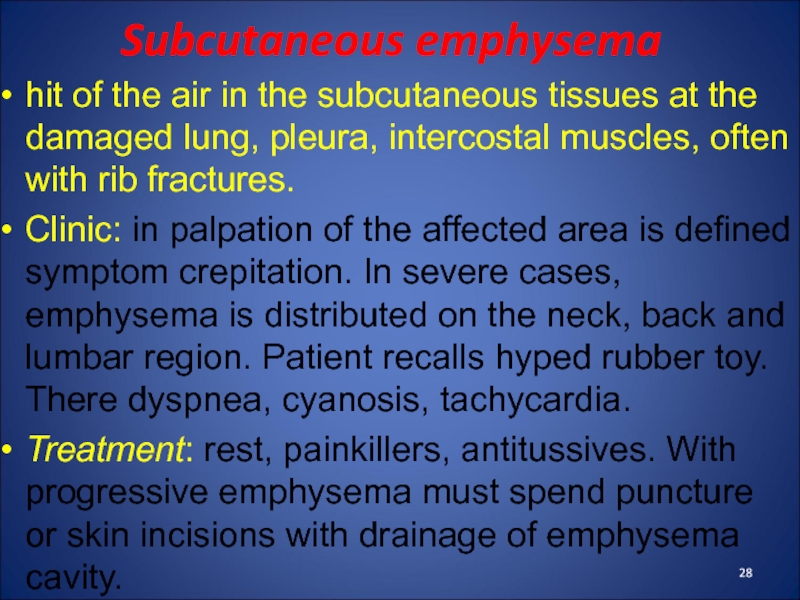
- 28. Subcutaneous emphysema hit of the air in
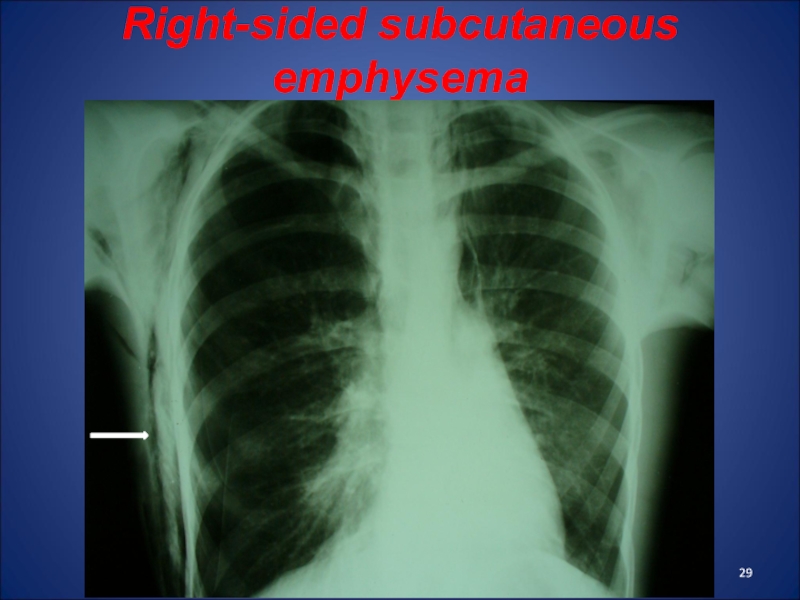
- 29. Right-sided subcutaneous emphysema
- 30. Mediastinal emphysema occurs when rupture of the
- 31. In the diagnosis of great importance belongs
- 32. Compression of the chestoccurs in compression between
- 33. Rib fractures Occurs when a direct blow,
- 34. Слайд 34
- 35. Damage of the esophaguscaused by injuries in
- 36. Acute suppurative destructive pneumonia (ASDP) –
- 37. Classification of ASDP in children
- 38. ІІІ. Clinical and radiographic forms
- 39. Complications of ASDP: sepsis, pericarditis, mediastinal emphysema,
- 40. Clinic of ASDPOn the background of SARS
- 41. Physical dataDepends on the form of the
- 42. Clinic of lung abscessesThe clinic depends on
- 43. Diagnosis of ASDPGeneral analysis of blood: high
- 44. Bullous form of ASDP
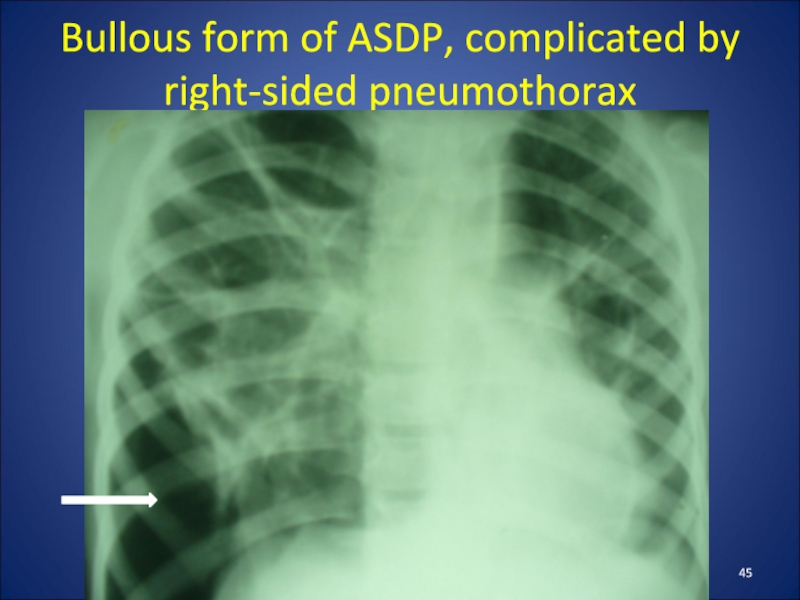
- 45. Bullous form of ASDP, complicated by right-sided pneumothorax
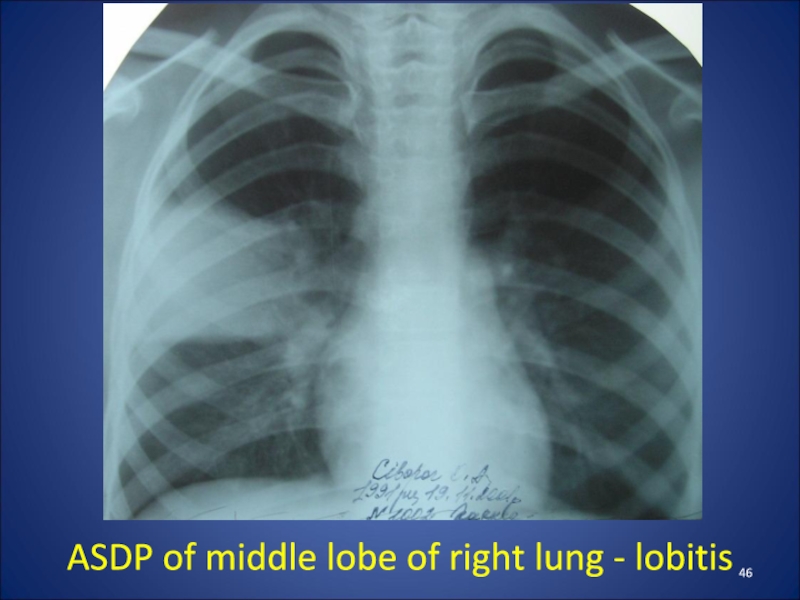
- 46. ASDP of middle lobe of right lung - lobitis
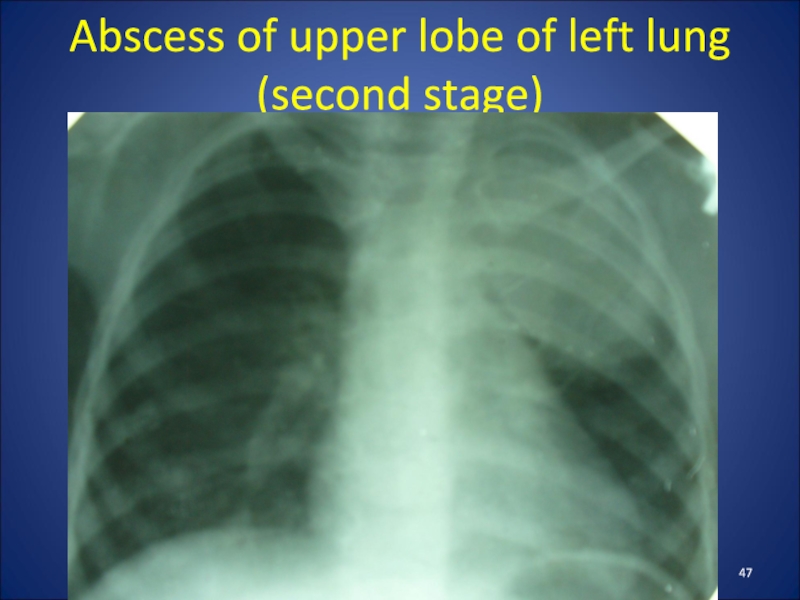
- 47. Abscess of upper lobe of left lung (second stage)
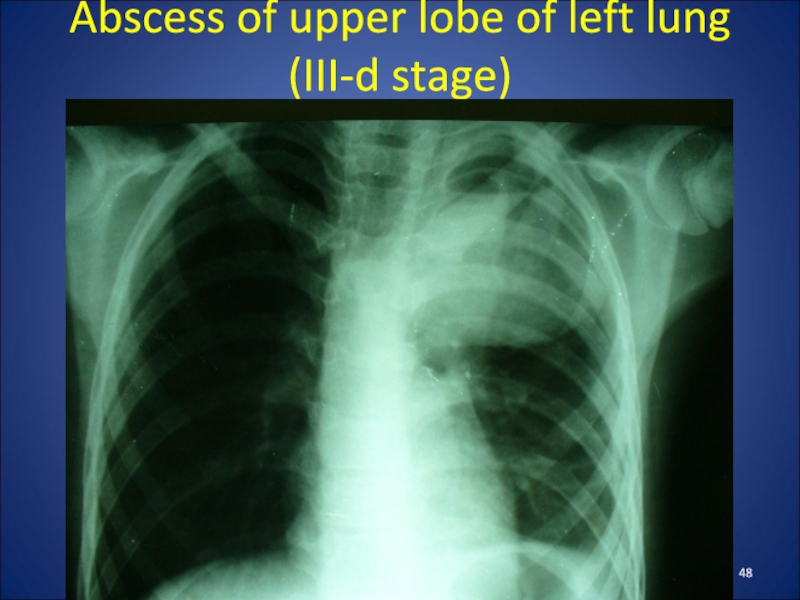
- 48. Abscess of upper lobe of left lung (III-d stage)
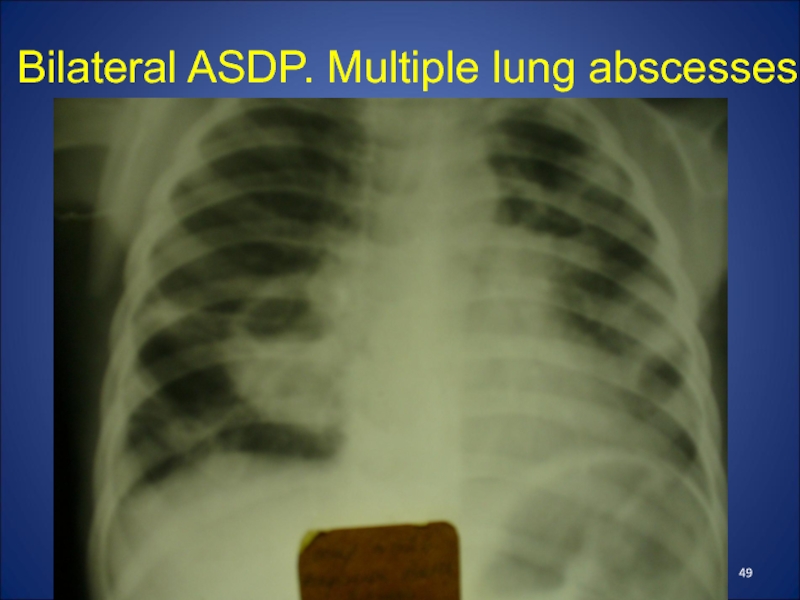
- 49. Bilateral ASDP. Multiple lung abscesses
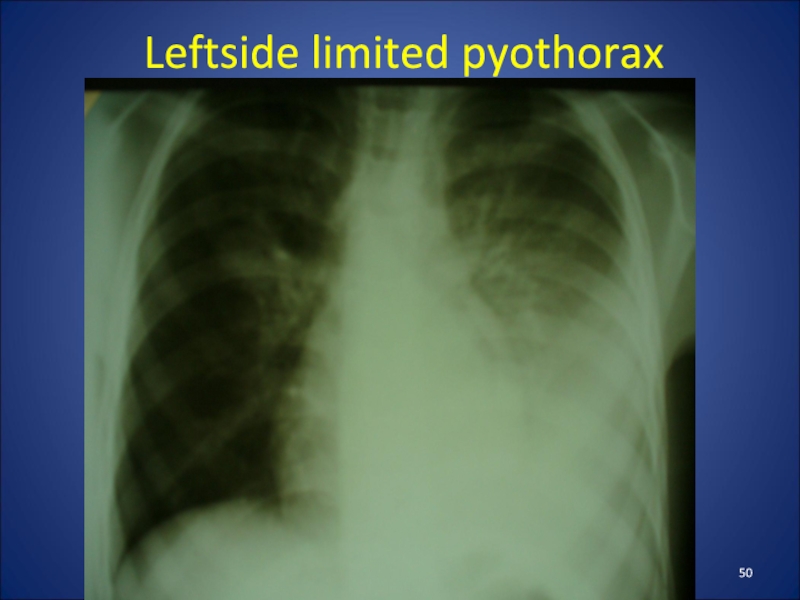
- 50. Leftside limited pyothorax
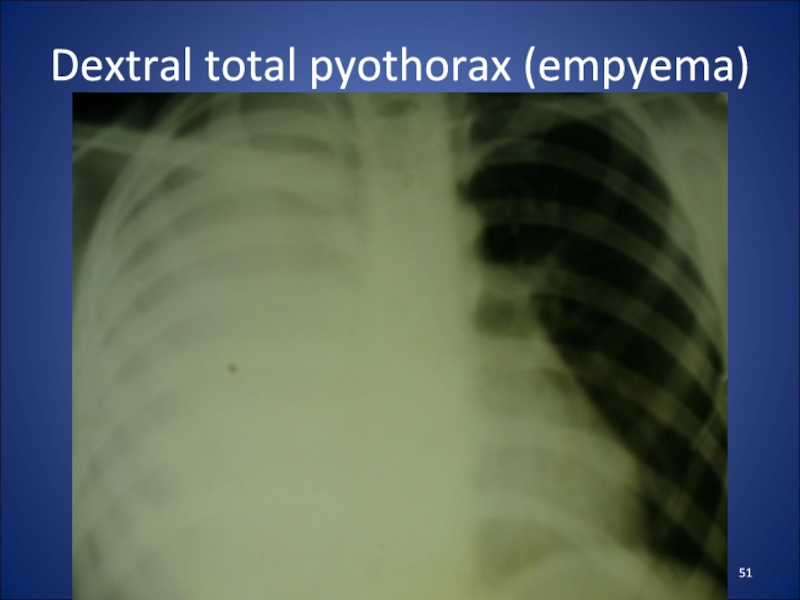
- 51. Dextral total pyothorax (empyema)
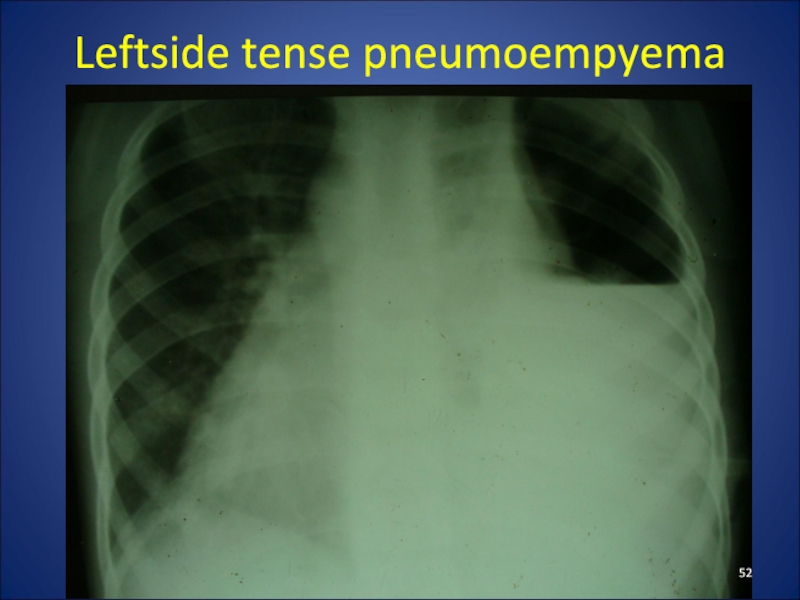
- 52. Leftside tense pneumoempyema
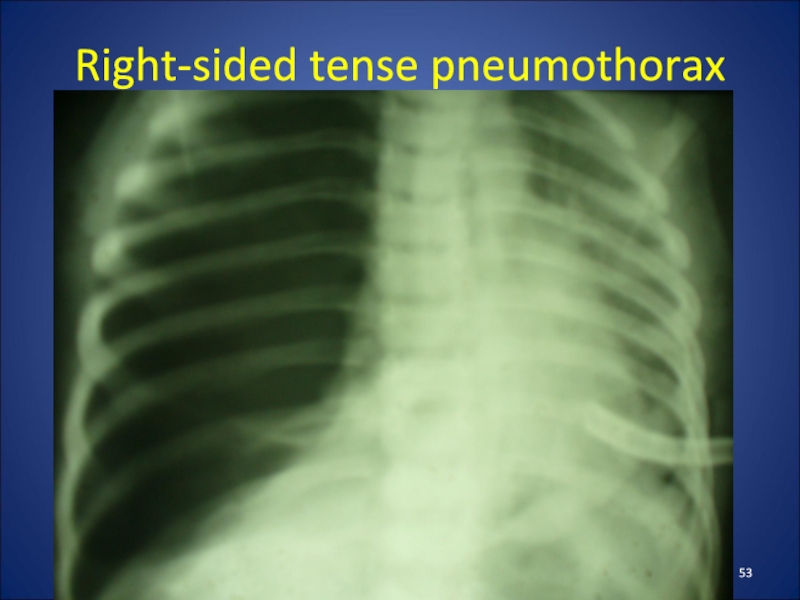
- 53. Right-sided tense pneumothorax
- 54. Treatment consists of 3 directions
- 55. 2. Effect on pathological focusIt consists in
- 56. Widely used physiotherapy: UHF, electrophoresis
- 57. Thank you!
- 58. Скачать презентанцию
Plan of the lecture: 1. Polytrauma in children. 2. Traumatic shock. 3. Injuries of the chest. 4. Purulent diseases of lungs and pleura.
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Plan of the lecture:
1. Polytrauma in children.
2. Traumatic
shock. 3. Injuries of the chest. 4. Purulent diseases of lungs and
pleura.Слайд 3Background
Trauma - the most common cause of death of children
in developed countries.
The problem of treatment of patients with
polytrauma remains valid, due to the rapid urbanization of society and, consequently, the increasing number of disasters. In developed countries, injuries rank second in the structure of infant mortality.
Damage of the chest in children is 3-4% of all injuries.
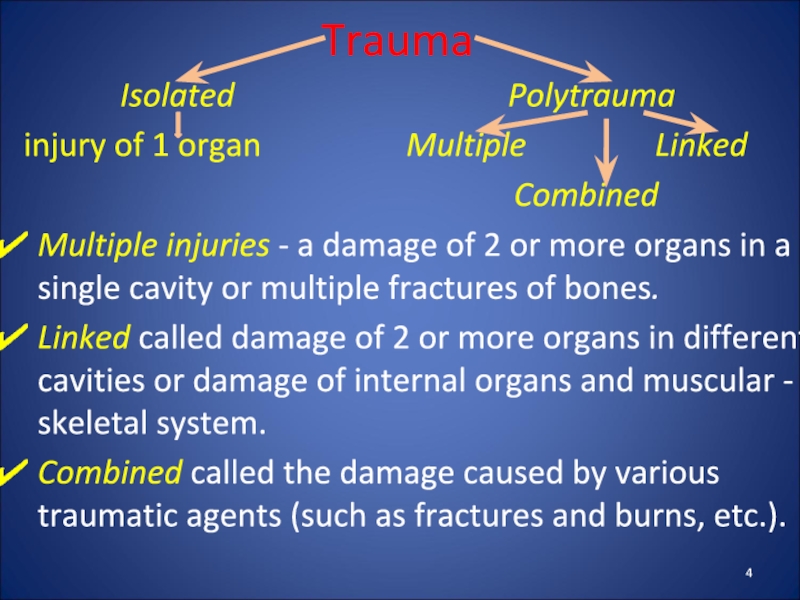
Слайд 4Trauma
Isolated
Polytrauma
injury of 1 organ Multiple Linked
Combined
Multiple injuries - a damage of 2 or more organs in a single cavity or multiple fractures of bones.
Linked called damage of 2 or more organs in different cavities or damage of internal organs and muscular - skeletal system.
Combined called the damage caused by various traumatic agents (such as fractures and burns, etc.).
Слайд 5Polytrauma
Always accompanied by hypovolemic shock.
When polytrauma occurs syndrome relative
burden - the severity of the victim exceeds the arithmetic
sum of multiple injuries.Always evolving traumatic disease.
In 95% of children with polytrauma are observed fractures, 60% - multiple fractures, 25% of fractures involving brain trauma, 9% - combined with injuries of the abdomen.
Слайд 6Traumatic disease
Pathogenesis : hypovolemic shock, blood loss, disruption of damaged
organs, catabolism, tissue necrosis, reduced immunity. As a result of
these changes comes a redistribution of blood flow, increased erythropoiesis, entering the bloodstream ekstravassel fluid, anabolism, tissue regeneration.Characterized by acute onset, no latency, hypoxia.
In the course of traumatic disease distinguish 3 periods: 1 - shock, 2 - detailed clinical picture, 3 - during rehabilitation.
Слайд 7Traumatic shock - a powerful reaction of organism in response
to injury
Pathogenesis of shock (nervous - reflex theory)
Shock is regarded as neuro - degenerative process. Powerful afferent impulses entering the central nervous system, causing intermittent systemic violations in the form of excitement - erectile stage of shock. Soon excitement is replaced by brake - torpid phase of shock, which is characterized by depression of all vital functions. Слайд 8Pathogenesis of shock
Developing acute vascular failure, respiratory failure,
metabolic, endocrine disorders. This depresses the central nervous system. Among
the major circulatory disorders - the fall of arterial and venous pressure, decreased blood volume, reflex spasm of small vessels. As a result of circulatory and respiratory disorders develops hypoxia, which affects all organs and tissues, particularly the CNS. The prognosis of shock depends not only on the severity of the damage, as the duration and severity of hypoxia.Слайд 9Clinic of shock
In erectile stage of shock patient in mind,
there is a motor and language stimulation. Face and visible
mucous membranes are hyperemic, breathing is frequent, normal pulse, blood pressure is lowered. Pronounced reaction to pain. This stage is short (sometimes several minutes).In torpid stage of shock are observed inhibition of the patient, mental depression, dramatically reduced response to pain. In patient there is pale skin, sharp facial features. Body temperature is reduced, the skin is cold, covered with sticky sweat.
Слайд 10Clinic of shock
Breathing is frequent , superficial. Pulse
is of poor volume and tension, frequent. Blood pressure (maximal,
minimal and pulse) is reduced. Patients worried thirst, sometimes - vomiting. Often there is oligouria, anuria.Depending on the severity of victims providing 4 degrees severity of shock: 1 - Lightweight, 2 - Moderate, 3 – Heavy, 4 – Terminal.
Слайд 11Principles of shock treatment :
Most important are early pain relief,
proper transportation and immobilization.
1. Warming of patients.
2. Providing
of Trendelenburg position (lying at an angle with a lowered head end).3. Introduction of painkillers (Promedol, Omnopon). Contraindicated only for head trauma, critical incidence of blood pressure and violation of external breathing.
4. Novocaine blockade on Vishnevsky.
Слайд 12Principles of shock treatment :
5. Intravenous and intraarterial
transfusion of blood products: Plasma, Albumin, red cell mass, Ringer
solution, Physiologic solution, 5% Glucose, Refortan, Stabisol, Perftoran et al. With shock 4 at first is performed an arterial transfusion, then move on to venous. With shock 3 is performed venous transfusion, then move to a drip. The usage of red blood cell mass depends on the degree of blood loss.Слайд 13Principles of shock treatment :
6. Prescribing of cardiovascular
drugs (Strofantin, Corglikon with 5% Glucose). In severe shock is
shown Ephedrine, Noradrenalin, Mezaton and Glucocorticoids.7. To combat hypoxia is hold oxygen therapy, injections of Cititon or Lobeline. When breathing disorders are expressed spend tracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation.
8. Together with antishock measures to patients, if indicated, injected antibiotics, tetanus serum toxoid.
Слайд 14As additional trauma aggravates during shock should refrain from surgery
to tide the patient with shock.
Exceptions to
this rule are situations in which operations are conducted for vital indications:• Bleeding that lasts
• Asphyxia
• Anaerobic infection
• Open pneumothorax.
In these patients surgery is performed immediately, along with anti-shock measures.
Слайд 15Injury of the thoracic cavity
Classification:
1. Slaughter of the soft tissues of the chest.
2. Closed chest trauma:
A) without damage of internal organs
B) with injury of the chest cavity organs
C) thoracoabdominal injury
3. Open chest trauma:
A) without damage to internal organs
B) with injury of the chest cavity organs
C) thoracoabdominal injury
Слайд 16Injury of the thoracic cavity
Classification:
Trauma
can be one - and bilateral. By severity of damage distinguish mild, moderate and severe injury.
Among the closed chest trauma is released concussion, contusion, compression of the chest, pneumothorax, hemothorax, pneumohemothorax, subcutaneous and mediastinal emphysema.
Слайд 17Concussion of chest
Occurs more frequently in case of a fall
on the breast. Clinic reminds traumatic shock: pale skin, covered
with cold sweat, pulse is frequent, of low volume and tension, shallow frequent breathing. Sometimes there comes a loss of consciousness, vomiting. In severe cases, death can occur due to dysfunction of the vagus nerve.Treatment of mild concussion-bedrest for 2-3 days and warming. In severe concussion besides prescribed analgesics, cardiac drugs (Cordiamin, Camphor), oxygen therapy, bilateral vagosympatyc novocaine blockade is conducted.
Слайд 18Contusion of the chest
Occurs when a strong kick or fall
on a solid object and is accompanied by pain and
swelling at the site of injury. Prevalence increases with palpation or deep breaths. Strong contusion often is accompanied by damage to the chest, fractures of the ribs.Слайд 19Pneumothorax
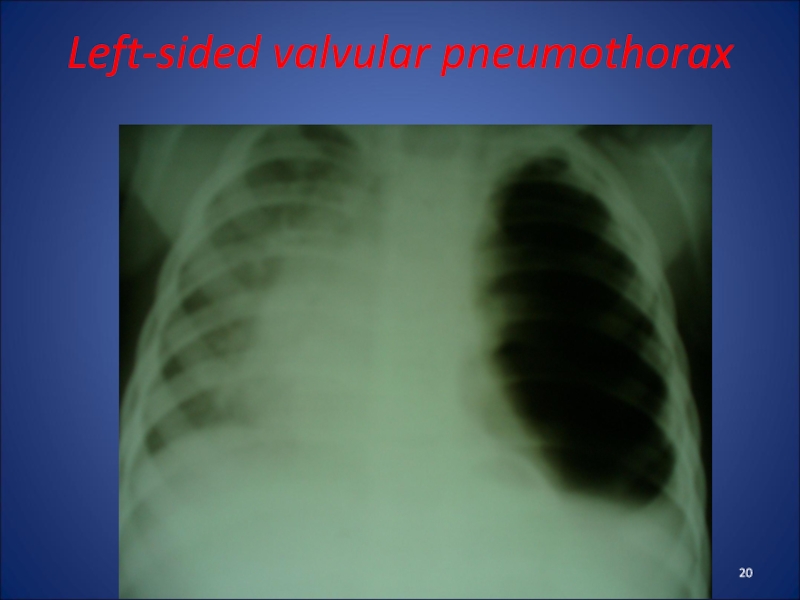
- accumulation in the pleural cavity of air that comes
from the damaged lung or bronchus. This compresses the lung.
There are closed, opened and valvular pneumothorax. The most difficult is the valvular pneumothorax, which expresses intrapleural tension.Clinic: dyspnea, cyanosis, affected half of the chest is not involved in breathing. Percussion - tympanitis, auscultation - weakened breathing on the affected side. There tachycardia may be impaired consciousness.
Radiologically - enlightenment on the affected side, offset shadow of heart to healthy side.
Слайд 21Treatment of pneumothorax
When closed - pleural puncture
In the open
- thoracotomy surgery and suturing the damaged lung or bronchus
In valvular pneumothorax first task - to translate it into the open and to reduce the pleural pressure. A puncture or thoracotomy (between 2 and 3 ribs to medial clavicular line).
If the air continues to enter the pleural cavity, after the withdrawal of the shock patient is operated.
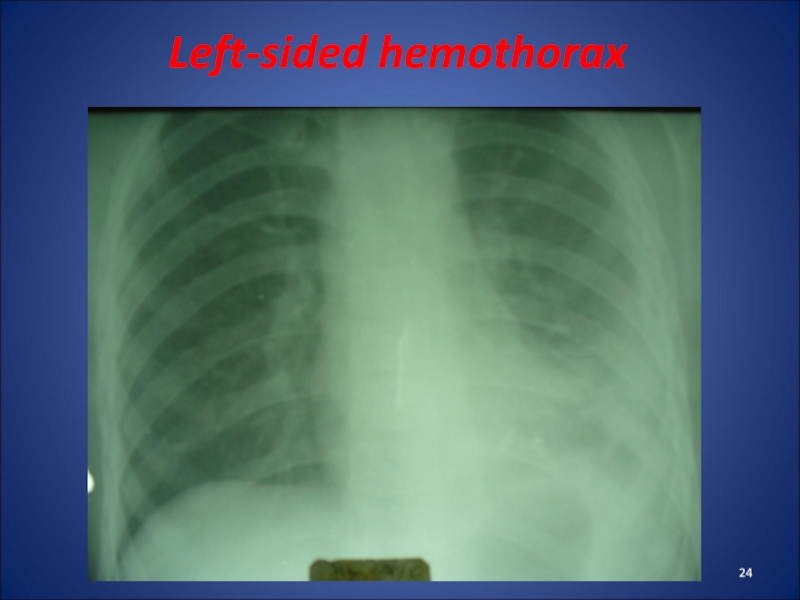
Слайд 22Hemothorax -
accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity, which comes
from the damaged vessels of lungs or chest wall. At
first blood clots and then diluted by fibrinolysis. Bleeding stops when equalized pressure in the pleural cavity and in bleeding vessel (original tamponade).Classification: Hemothorax may be lightweight (to 500 mL), medium (500-1000 ml) and massive (more than 1000 ml).
Слайд 23Clinic of Hemothorax
rapid weak pulse, tachypnea, decreased AP, pale skin.
In patients there are pain in the affected side of
the chest, cough.Percussion - dull sound, auscultation - missing or weakened breathing. After 3-6 days the body temperature rises.
Radiologically – eclipse, shift shadowof heart in a healthy side.
Treatment: pleural puncture (not earlier than 3-4 days). Earlier puncture can help to restore bleeding. Also, spend haemostatic and infusion therapy.
Слайд 26Pneumohemothorax
accumulation of blood and air in the pleural cavity, coming
from damaged lungs, vessels and bronchus
Clinic: rapid weak pulse, tachypnea,
decreased AP, pale skin, pain in the affected side of the chest, cough, shortness of breath.Percussion - dull sound in the lower departments and tympanitis - in the upper, auscultation - missing or weakened breathing.
Treatment of pneumohemotorax: imposition of drainage on Bulau in 6-7 intercostal space, haemostatics, infusion and antibiotic therapy.
Слайд 28Subcutaneous emphysema
hit of the air in the subcutaneous tissues
at the damaged lung, pleura, intercostal muscles, often with rib
fractures.Clinic: in palpation of the affected area is defined symptom crepitation. In severe cases, emphysema is distributed on the neck, back and lumbar region. Patient recalls hyped rubber toy. There dyspnea, cyanosis, tachycardia.
Treatment: rest, painkillers, antitussives. With progressive emphysema must spend puncture or skin incisions with drainage of emphysema cavity.
Слайд 30Mediastinal emphysema
occurs when rupture of the trachea or bronchus
and air fills in parabronhial intervals to mediastinal tissues.
Clinic
- acute, progressive course. In the patient are observed thickening of the neck and face, swelling of the neck veins, difficult breathing and swallowing, chest pain, bouts of coughing. Provisions in bed forced, semisitting.
The voice becomes hoarse, increases dyspnea and cyanosis of mucous membranes and skin. Signs of hemodynamic disorders as a result of a kind "extracardiac tamponade“ is appeared.
Слайд 31In the diagnosis of great importance belongs X-ray examination -
in this case determined pneumomediastinum.
TreatmentEmergency surgery - suprajugular mediastinotomia. The operation is performed under local anesthesia. Anesthesia is contraindicated because enhances intrabronhial pressure and increased tension in the mediastinum.
When failure - suturing the defect of the trachea or bronchus. A endotracheal intubation.
Слайд 32Compression of the chest
occurs in compression between two solid objects.
It is the outflow of blood from the lungs and
congestion in the superior cava vein.Clinical features: the head, neck and upper part of the chest, mucous membranes appear multiple hemorrhages. Often there is swelling of the neck and face, cyanosis of the upper body, reflex narrowing of the glottis.
Treatment: conservative - rest, painkillers, heart and restorative drugs.
Слайд 33Rib fractures
Occurs when a direct blow, fall or squeezing
chest. Observed in 67% of children with injuries of chest.
Can be single and multiple rib fractures.
Dangerous is a double fracture of several ribs (while there flotation rib flap).
Fractures of the ribs with displacement lead to damage of the pleura, lungs, blood vessels, accompanied by pneumohemotorax and subcutaneous emphysema.
Слайд 34
Clinic
Sharp pain that increases with
deep inspiration, palpation, cough. The affected half of the chest behind the act of breathing, you can see swelling, hemorrhage, in the soft tissue palpation - crackling.
In diagnosing a main role X-ray examination.
Treatment:
novocaine blockade, plaster immobilization or using of brace.
Слайд 35Damage of the esophagus
caused by injuries in children are rare.
Frequently observed yatrogenic damage or foreign bodies. This occurs in
patients with complaints of pain while swallowing or dysphagia. Later it may be subcutaneous emphysema of neck, the symptoms of shock, mediastinitis.Diagnosis of the esophagus damages helps X-ray study of the esophagus with contrast and FES.
Treatment: antibiotic therapy, surgery - drainage of the mediastinum. With significant injuries - suturing the esophagus, esophageal drainage and blending gastrostomy.
Слайд 36Acute suppurative destructive pneumonia (ASDP) – severe pneumonia, which is
accompanied by a purulent disintegration of lung parenchyma and possible
involvement in the process of the pleural cavity. ASDP is 1-15% of the total number of pneumonia. However, the pattern of mortality of purulent-septic pathologists up to 50%.Слайд 37Classification of ASDP in children
І. Etiology.
Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Pseudomonas, mixed.
ІІ. Type of injury.
1. Primary (aerogenic way of infection):
A) true primary (complication of bacterial pneumonia)
B) conditionally primary (in cystic fibrosis of pancreas, respiratory - viral infection, congenital malformations of the lungs).
2. Secondary (through hematogenous infection).
Слайд 38 ІІІ. Clinical and radiographic forms
Pulmonary forms:
A) Lung
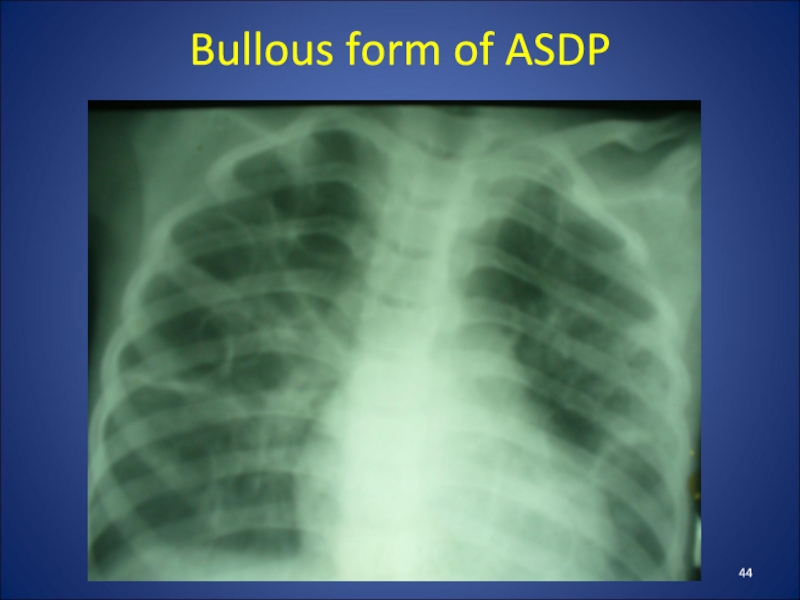
abscesses (11%)B) Bullous form of destruction (7-9%)
Pulmonary and pleural forms:
A) Pyothorax (limited, covered, total) (25%)
B) Pneumothorax (limited, intense, not intense)
C) Pneumoempyema (limited, intense, not intense) (40%)
Слайд 39Complications of ASDP: sepsis, pericarditis, mediastinal emphysema, pulmonary hemorrhage.
More often
affected right lung, due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics
of the right main bronchus.In 85% of cases BDL is a direct complication of viral and bacterial pneumonia or SARS.
Almost always the disease develops on the background of the humble immunity.
Слайд 40Clinic of ASDP
On the background of SARS or pneumonia in
children deteriorating state, growing dyspnea and hyperthermia, there is pain
in the affected side of the chest, hoarse cough, cyanosis of nasolabial triangle. Severe intoxication symptoms: pale skin, lethargy, weakness, tachycardia, muffled heart sounds, flatulence.Breathing becomes frequent and superficial, sometimes - noisy. In breathing involved supporting muscles. Provisions in bed - orthopnea. Compensatory curvature of the spine (scoliosis), the affected part of the chest behind or do not participate in the act of breathing.
Слайд 41Physical data
Depends on the form of the disease.
When abscesses and
pyothorax determined blunting or dullness during percussion over the affected
lung.When pneumothorax - the box sound. The syndrome of intrapleural pressure - displacement of cardiac dullness to healthy side.
When pneumoempyema - in the upper tympanitis at the bottom - stupidity.
Auscultation in most cases determined weakened breathing.
Слайд 42Clinic of lung abscesses
The clinic depends on their stage of
development.
When formed an abscess in a child hectic body temperature,
maximum manifestations of intoxication. Radiological findings at this stage can be seen round shadow with perifocal infiltration.
After breaking an abscess in the bronchus patient's condition improved somewhat, there is a cough with purulent sputum discharge .
The X-ray shows round shadow with horizontal fluid level and the air above it.
Слайд 43Diagnosis of ASDP
General analysis of blood: high leukocytosis with a
shift leukocyte formula, anemia, toxic granulation neutrophils.
Biochemical studies: dysproteinemia, hypoproteinemia,
increasing concentrations of CRP.Microbiological research pus and phlegm.
Immunological studies.
The crucial method in the diagnosis of BDL is x-ray in an upright position in a straight line and lateral projections.
Слайд 54Treatment consists of 3 directions
1. Effect on pathogen
- antibiotics.
First, designate a combination of antibiotics,
which cover the entire range of possible pathogens. Pathogens are often staphylococcus, opportunistic gram-negative bacteria or their combination. Upon receipt of the results of crop change antibiotics according to the sensitivity of microflora. The preferred route of administration - intravenous, besides administering them intrapleural. Most use cephalosporins, carbapenems, aminoglycosides, glycopeptides. Слайд 552. Effect on pathological focus
It consists in adequate sanation of
focus and elimination of syndrome intrapleural pressure.
In this case
the following surgical procedures: pleural puncture, thoracostomy with active or passive aspiration, drainage of abscess by Monaldi, video sanitation of pleural cavity, thoracotomy, decortication lungs. When lung abscess, which drained into the bronchial tubes, spend sanation bronchoscopy.
In broncho-pleural fistulas sometimes use occlusion of the bronchi.
Слайд 56 Widely used physiotherapy: UHF, electrophoresis of antibiotics and
antiseptics, inhalations.
3. Impact on Macro-organism -
correction of homeostasis. Spend immunotherapy, detoxification infusion therapy, administered vitamins B, C, E, protease inhibitors, antioxidants, oxygen therapy, if necessary - mechanical ventilation, symptomatic treatment.