Слайд 1
LEPTOSPIROSIS ( L. )
-canicola fever, harvest (mud) fever, the
7-the days fever
The acute zoonotic disease is characterized by an intoxication and myalgia ( in a septic stage ) with sub-sequent damage of kidneys, liver, nervous and vascular systems and possible development of a hemorrhagic syndrome and icterus (in an immunological stage)
- 1886 - А. Weil described 4 cases of leptospirosis from
group of icteric diseases for the first time
- 1888 – W.P. Vasiliev described 17 cases of leptospirosis
- 1915 - А. Inado and со-authors revealed of the infectious
agent of the disease also described its morphology
Слайд 2
ETIOLOGY:
The infectious agent – leptospira ( F. Spirochaetacea
K. Leptospira) also is subdivided on pathogenic
for the man ( L.icterrogans ) and saprophytic ( L. Biflexa )
Nowadays is revealed more 200 serotypes, united in 23 serogroups
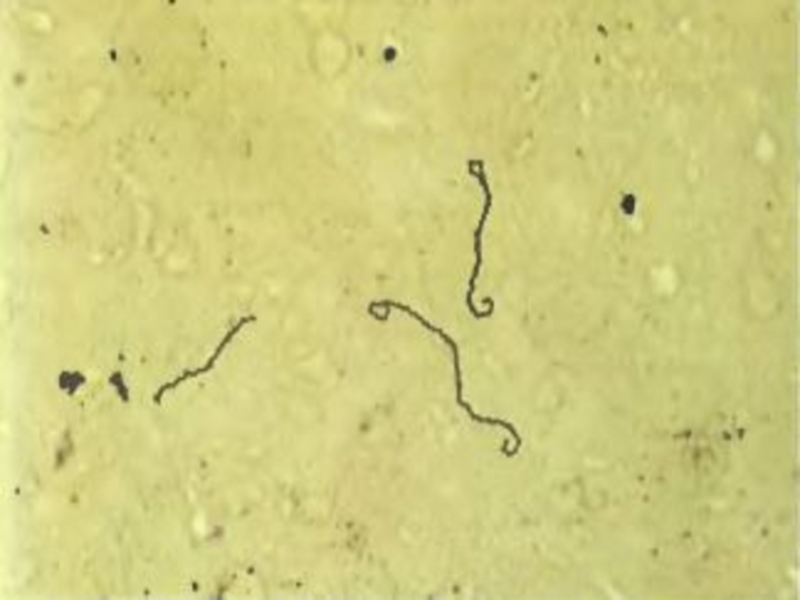
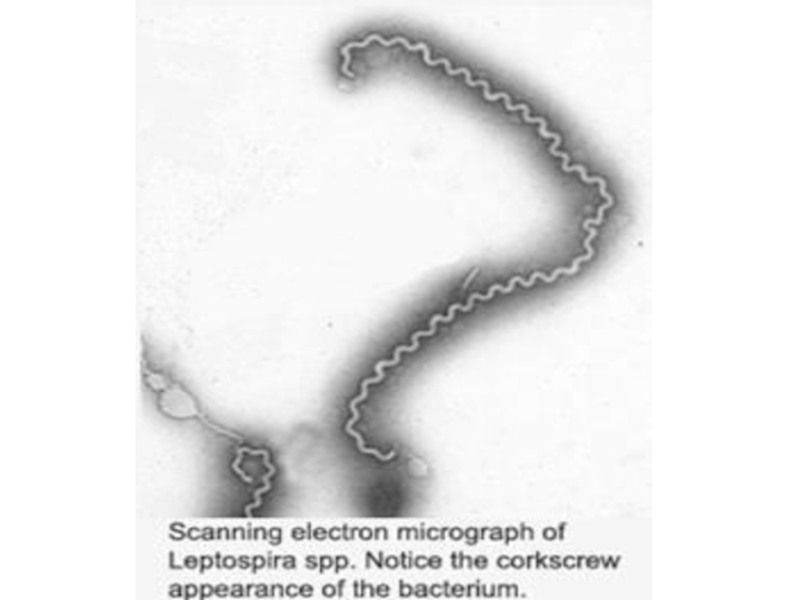
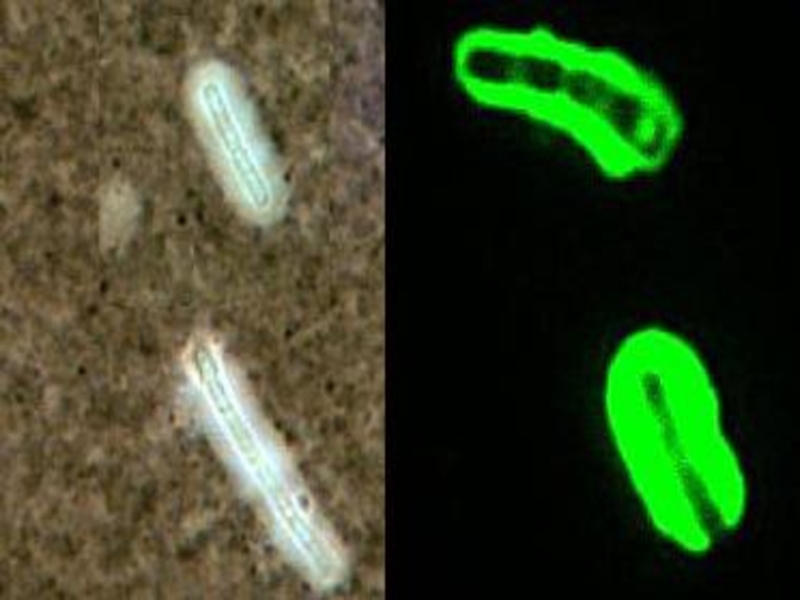
L. are thin ( 0.1 – 0.2 microns of width. ) spirally arched cells 3 - 30 microns of length with a plenty of the bends (more than 20) with the twirled ends having flagellae, are mobiling.
Gram negative, but are staining on Giemsa have pink colour, and at are staining silver have black-brown colour.
Слайд 5
Optimal conditions of the
growth on the medium with addition 5 - 10 %
serum of the rabbit: temperature + 28- 30 d.C and рН 7.0 – 7.4 ( from 5-10 of days to 3-4 weeks.)
Survive at low temperature about 8 months, in fresh water from 1 to 30 days, in wet ground about 200 days, but in dry ground only 2- 3 hours (hydrophilic)
L. fast inactivated by desiccation, low рН, disinfectants, at pasteurizing and boiling.
At destruction L. is secreted endotoxin with pyrogenic, skin-necrotic, lethal properties
The main pathogenic factor - adhesiveness concerning epithelial cells and erythrocytes with use plasmocoagu-lase, fibrinolysinum, hemolysin, V- antigene.
Слайд 6
L. have 2 antigenes: - genuspecific (deep)
- and typespecific (surface).
During illness will be derivated agglutinins, precipitins and complement - fixing of the antibodies
EPIDEMIOLOGY:
- wide-spread everywhere except for the northen districts
and deserts of the earth
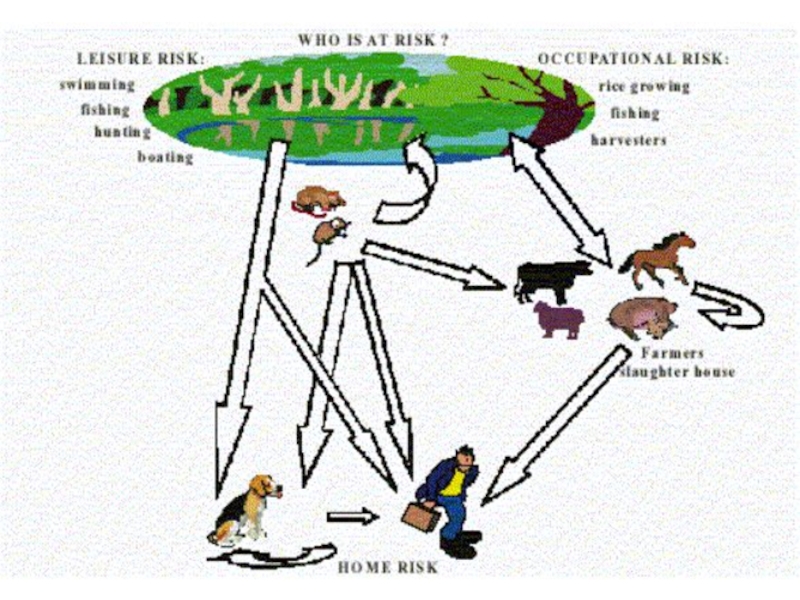
The main source - wild small rodents ( mice, hedgehogs,
rats ect.) and home animals ( cattele, pigs, dogs, rats)
Modes of transmission:
- nutritional ( nutrition, water, bathing )
- contact through a broken skin and mucous
Слайд 8DWELLING-PLACE OF wild small rodents mice, rats hedgehogs ect.)
Слайд 10
Seasonal rise - summur- autumn ( superactivity rodents, frequent
contacts of the people to FRESH water)
Sporadic case rate
- the year round
Susceptibility - general, but more often the teenagers and
adult men are sick
Immunity after illness - proof, but homologous, therefore repeated diseases are possible!!!
The most important pathogenes anicteric of the forms of
leptospirisis:
- L. Hebdomadis - Japanese the 7-th days fever
- L. grippotyphosa - water fever
- L. australis - Australian the 7-the days fever
- L. canicola - canicolosis
- L. autumnalis - autumn fever
- L. pomona - illness swine-herd
Слайд 11
The main pathogene of an icteric leptospirosis
-
L. icterohaemorragie ( but the icteric form maybe at
any severe leptospirosis!!!)
PATHOGENY:
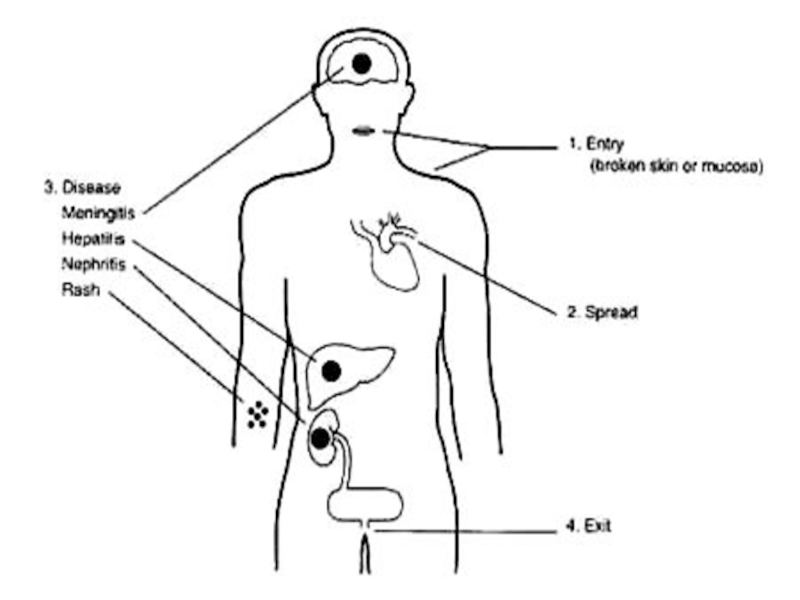
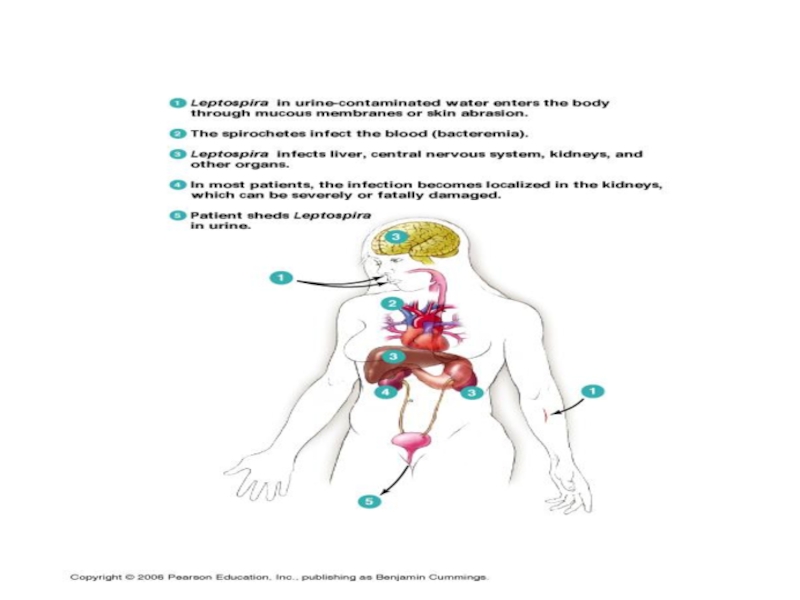
1. Implantation through a injure skin and mucous, colonize and intensive reproduction in a place of implantation with the subsequent advance leptospiras on lymphatic vessels without a lymphangitis, but with a lymphadenitis (increase of lymph nodes), which, however delay their advance can not
2. Infiltration in blood flow with a dissimination in a liver, kidneys, the paranephroses, lungs,spleen, in a CNS Clinical this stage does not appear! But they are detected in CSF by a method PCR)
Слайд 12
3. Reproduction in these bodies and secondary bacteriemia, which results
in appearance of a SEPTIC phase of illness, at which
toxic the syndrome is prevail. Duration of this phase is 2 - 7 days, then the bacteriemia terminates and the state of the patient on short time is improved (but maybe and not vary)
4. Then the IMMUNOLOGICAL phase of illness stipulated by appearance of antibodies in a blood and signs of a damage of the following bodies starts:
- liver - mesenchymal hepatitis without or with an icterus
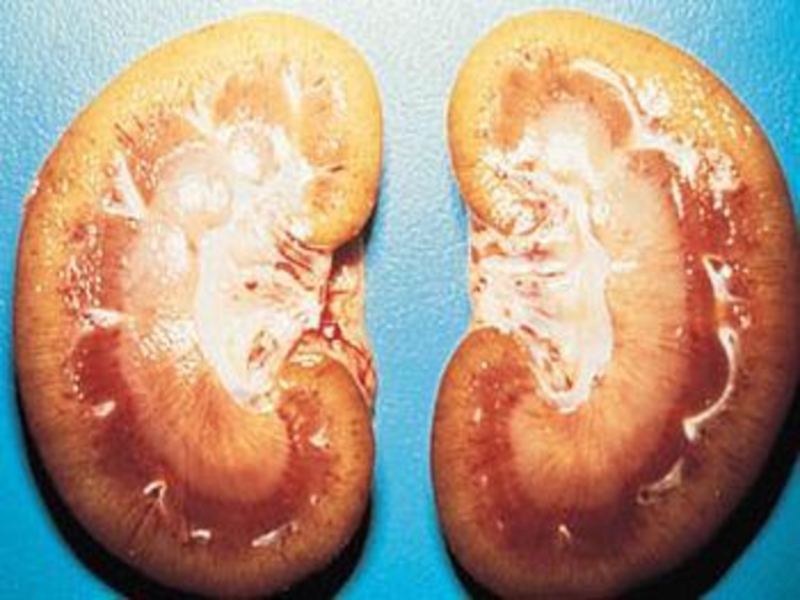
- kidneys - acute nephrosonephritis
- СVS - hemorrhagic syndrome, DIC
- CNS - meningitis or meningoencephalitis
The patients free yourself from leptospira about 2 till 6-th week. With urine maybe allocated about 40 days!!
Слайд 14
Transmission L. from man to man is not registered !
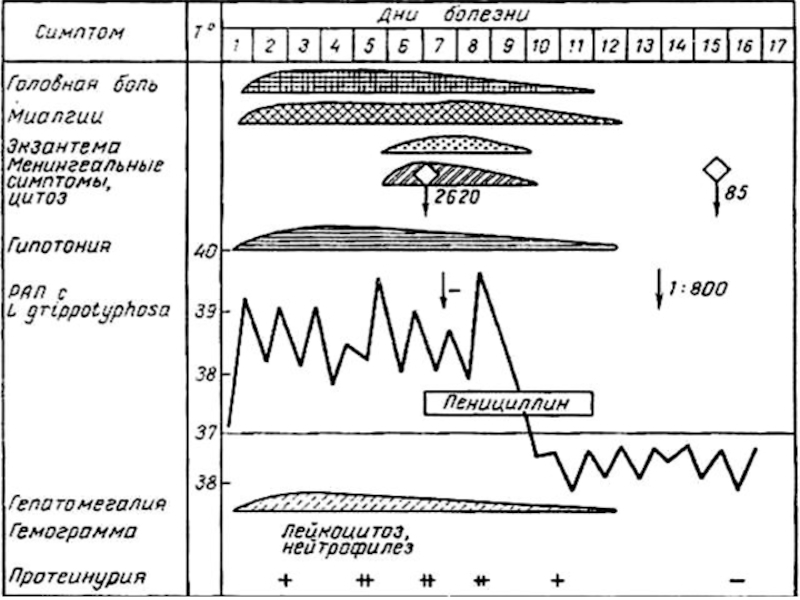
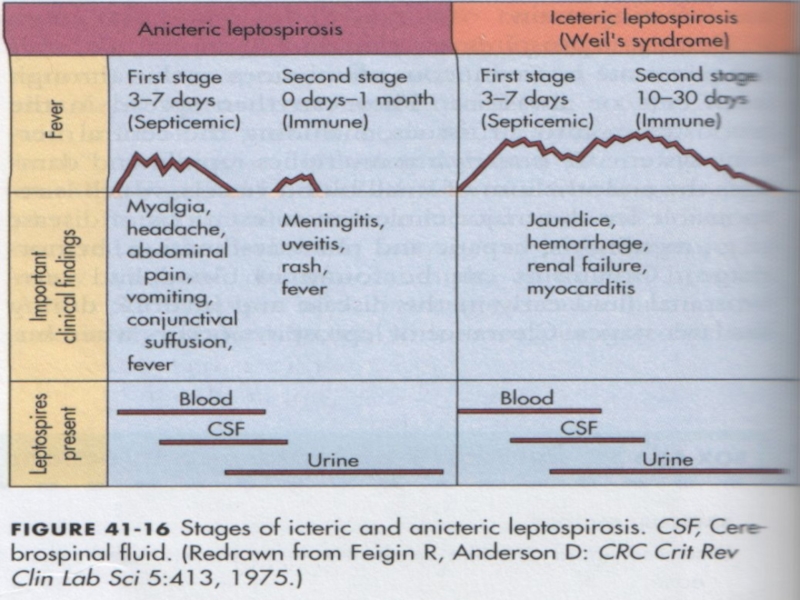
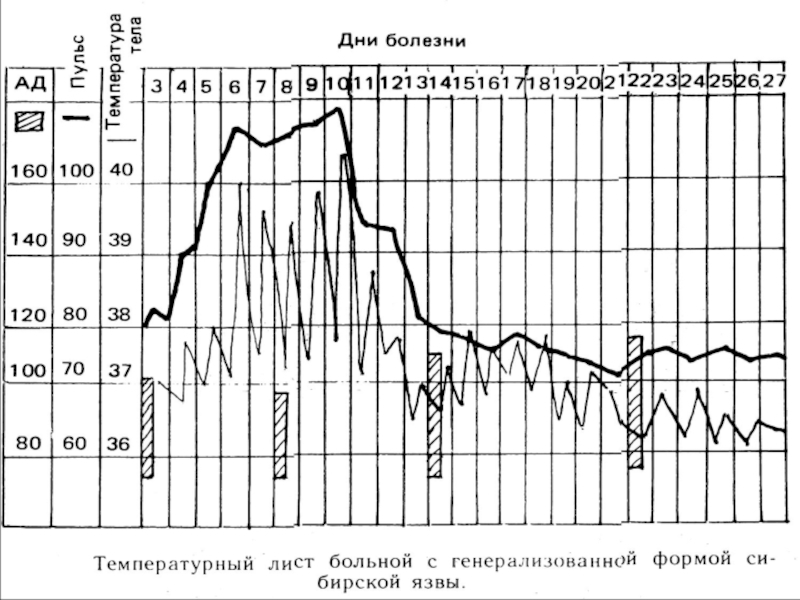
CLINIC: ( incubation interval 5 - 12 days )
Septic
stage: ( 5 - 7 days )
- acute beginning: chill, rise of temperature up to 39 - 40 d.C
- myalgia ( of muscles legs, neck, back, abdomen)
- strong headache
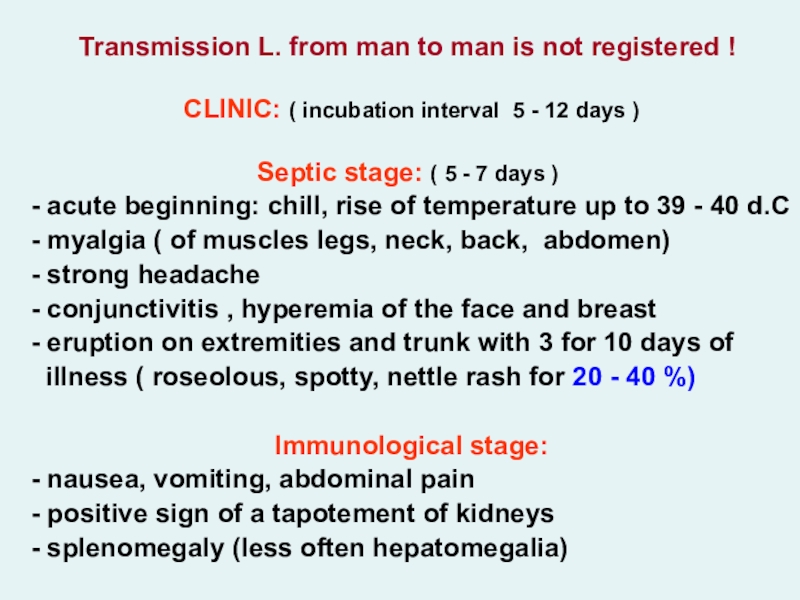
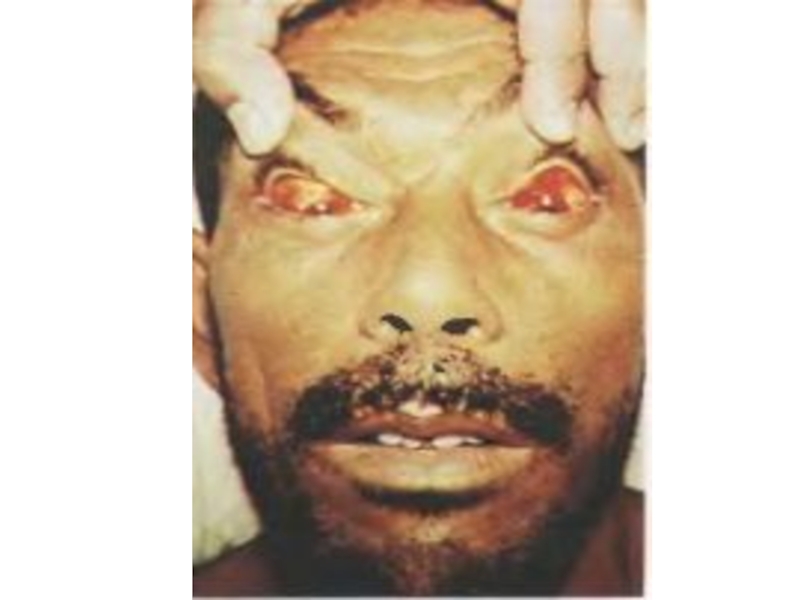
- conjunctivitis , hyperemia of the face and breast
- eruption on extremities and trunk with 3 for 10 days of
illness ( roseolous, spotty, nettle rash for 20 - 40 %)
Immunological stage:
- nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain
- positive sign of a tapotement of kidneys
- splenomegaly (less often hepatomegalia)
Слайд 21
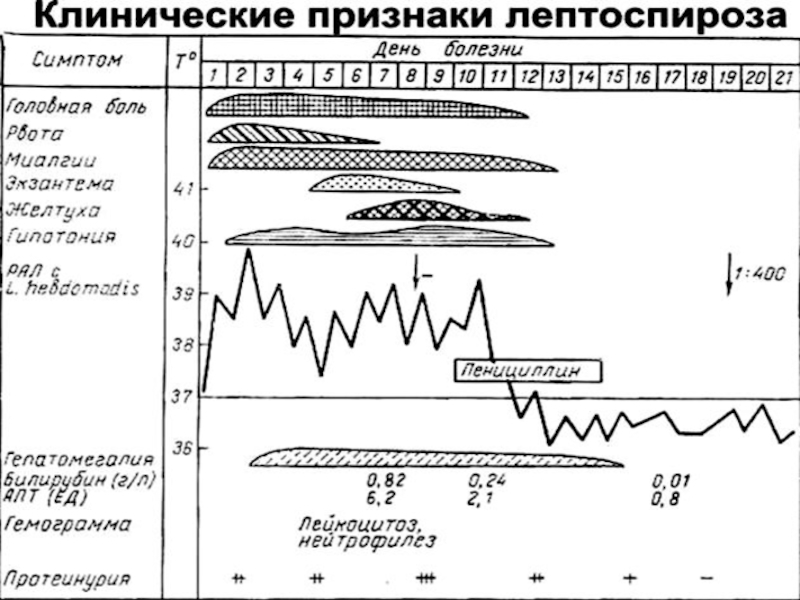
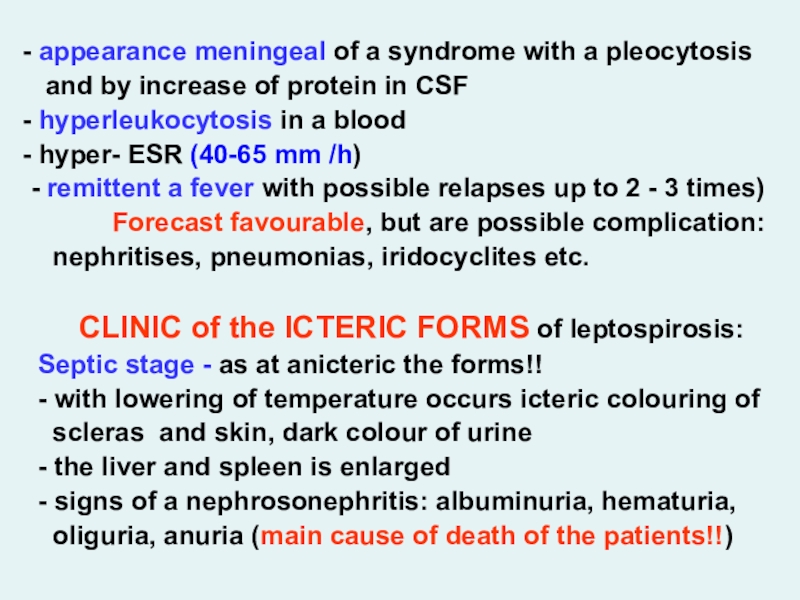
appearance meningeal of a syndrome with a pleocytosis
and by increase of protein in CSF
hyperleukocytosis in a
blood
hyper- ESR (40-65 mm /h)
- remittent a fever with possible relapses up to 2 - 3 times)
Forecast favourable, but are possible complication:
nephritises, pneumonias, iridocyclites etc.
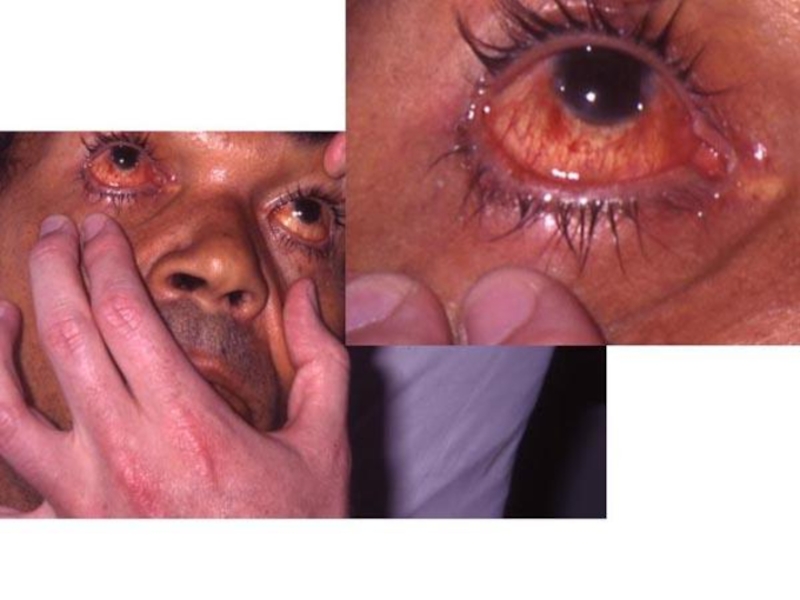
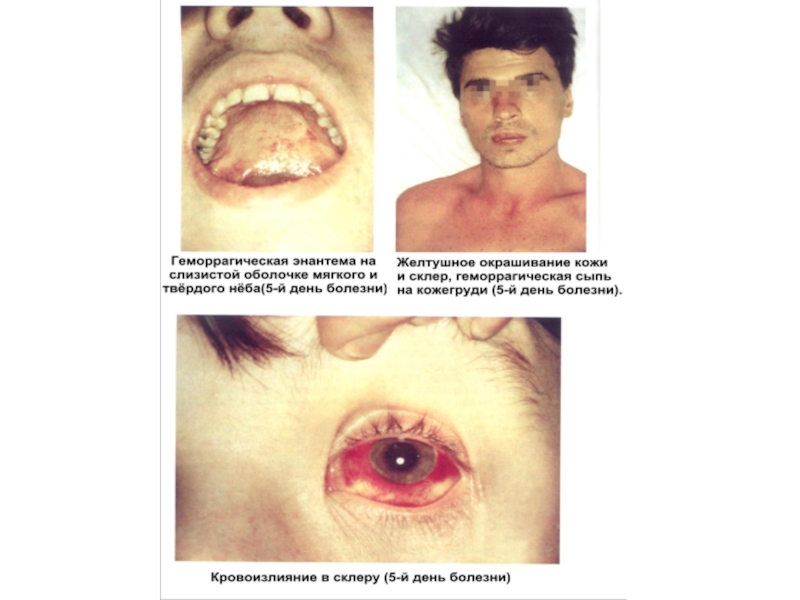
CLINIC of the ICTERIC FORMS of leptospirosis:
Septic stage - as at anicteric the forms!!
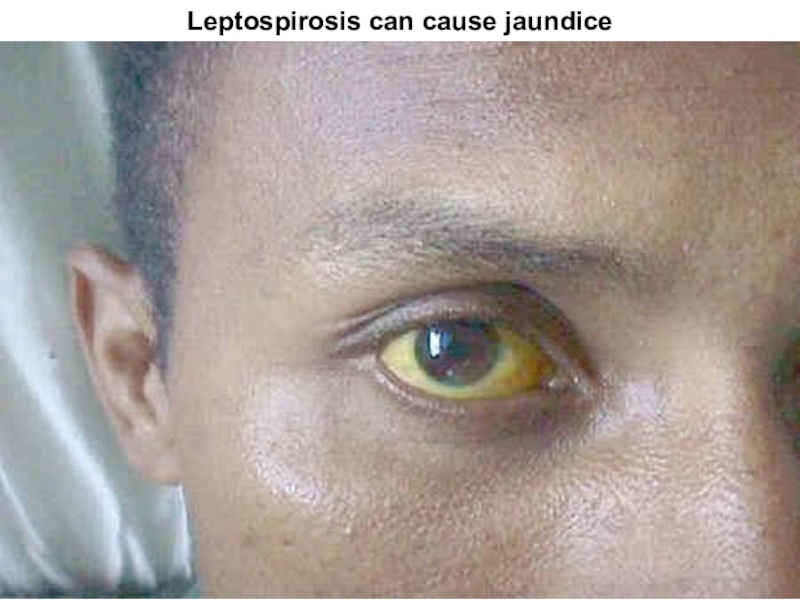
- with lowering of temperature occurs icteric colouring of
scleras and skin, dark colour of urine
- the liver and spleen is enlarged
- signs of a nephrosonephritis: albuminuria, hematuria,
oliguria, anuria (main cause of death of the patients!!)
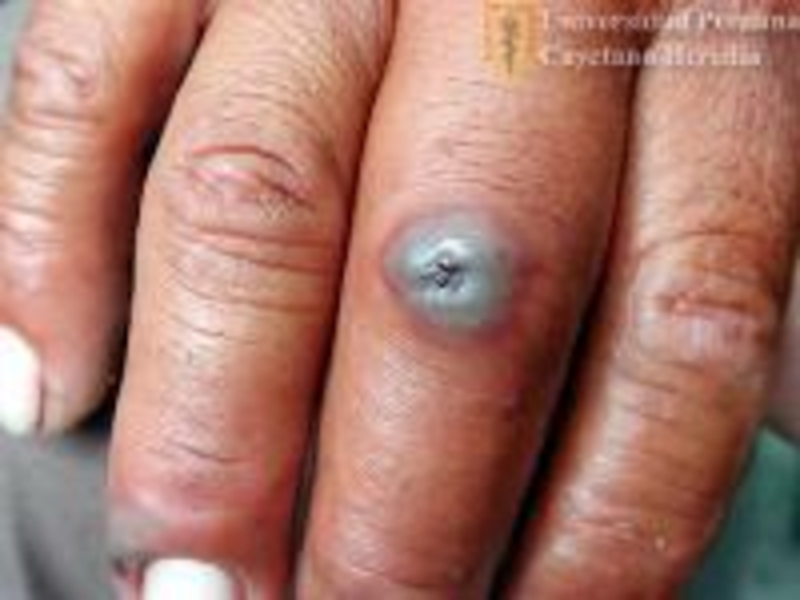
Слайд 24Leptospirosis can cause jaundice
Слайд 27
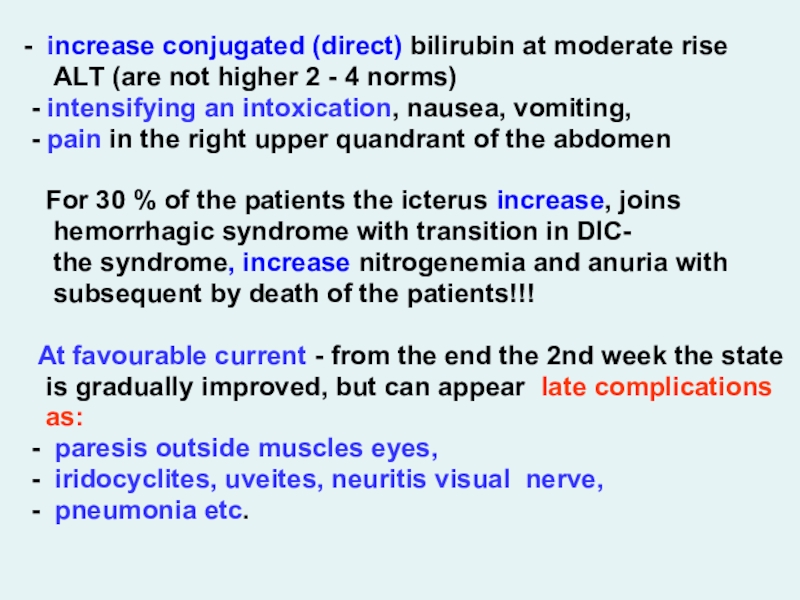
- increase conjugated (direct) bilirubin at moderate rise
АLТ (are not higher 2 - 4 norms)
- intensifying an intoxication, nausea, vomiting,
- pain in the right upper quandrant of the abdomen
For 30 % of the patients the icterus increase, joins
hemorrhagic syndrome with transition in DIC-
the syndrome, increase nitrogenemia and anuria with
subsequent by death of the patients!!!
At favourable current - from the end the 2nd week the state
is gradually improved, but can appear late complications
as:
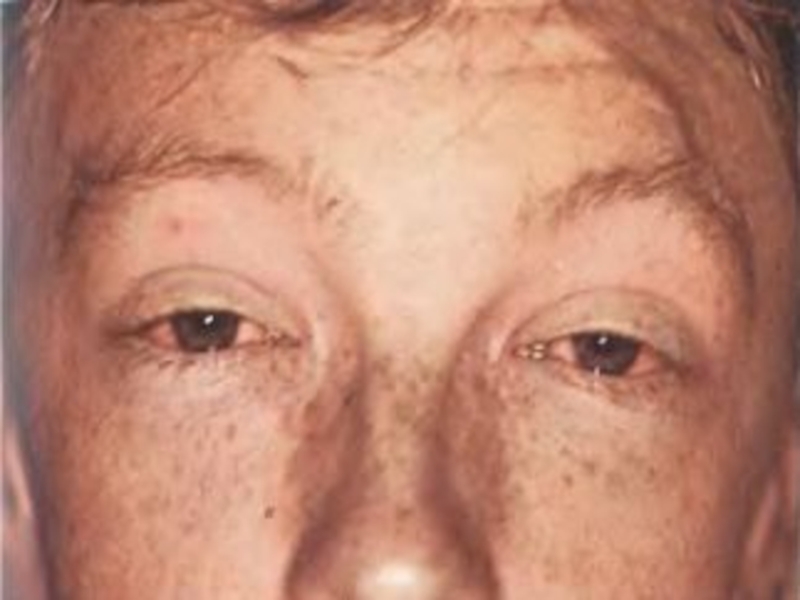
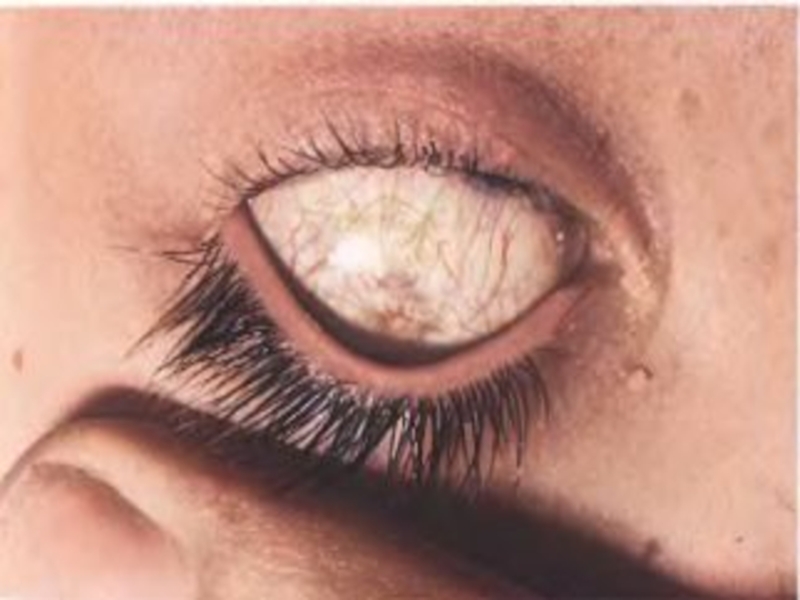
- paresis outside muscles eyes,
- iridocyclites, uveites, neuritis visual nerve,
- pneumonia etc.
Слайд 28
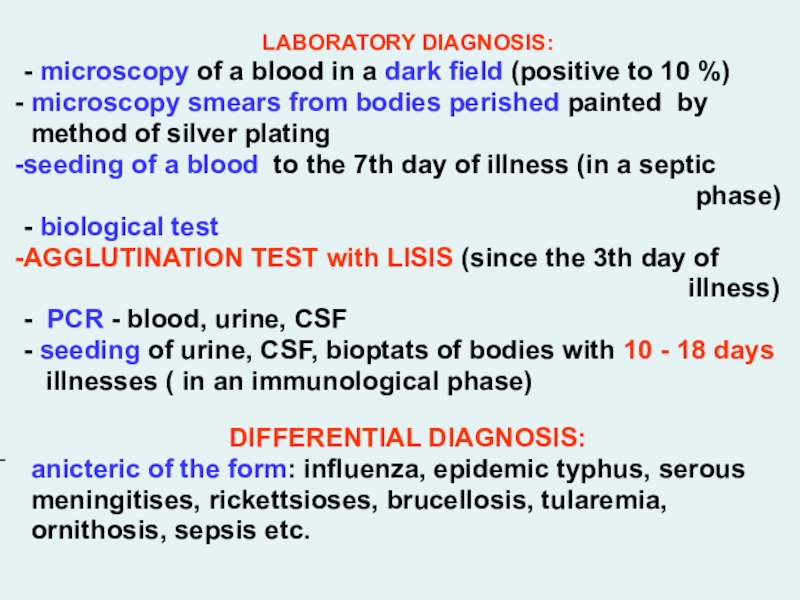
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS:
- microscopy of a blood in a dark field
(positive to 10 %)
microscopy smears from bodies perished painted
by
method of silver plating
seeding of a blood to the 7th day of illness (in a septic
phase)
- biological test
AGGLUTINATION TEST with LISIS (since the 3th day of
illness)
- PCR - blood, urine, СSF
- seeding of urine, CSF, bioptats of bodies with 10 - 18 days
illnesses ( in an immunological phase)
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
anicteric of the form: influenza, epidemic typhus, serous
meningitises, rickettsioses, brucellosis, tularemia,
ornithosis, sepsis etc.
Слайд 29
- the icteric form: virus hepatitises, yellow fever, malaria,
visceral leishmaniasis, yersiniosis, pseudotuberculosis, hemorrhagic fevers etc.
TREATMENT:
1. Antiinfectious therapy:
-
penicillin in a dose 8000 - 33000 IU/kg q4h IM,IV
- tetracyclin 10mg/kg q6h PO
- doxycyclin 2 mg/kg q12h PO
(About 2 - 5 days of normal temperature!!)
2. Antiferment therapy
3. Antifibrinolytic therapy
4. Correction of a hemorrhagic syndrome (coagulopathy or
thrombocytopenic)
Слайд 30
- at acute renal unsufficiency – diuretics (at once
osmotic, at
anuria - saluretics, but if level
of a urea of a blood more
than 50 - 67 mmol/l at once haemodialysis!!!.
- treatment hepatic of unsufficiency
- treatment of a meningoencephalitis
- symptomatic therapy
The immunoglobulin will not be utillized now!
PROPHYLAXIS:
Veterinary measures - revealing, sanitation or liquidation of the sick animals or carriers, protection reservoirs from pollution by fecal mass and urine of the animals
Medical - sanitary enlightenment and vaccination under the indications only in groups of hazard
The acute infectious zoonotic disease described by development for
the man of a serous-hemorrhagic and necrotic inflammation of skin and mucous (99 %) with a possible generalization of the process (1 %)
Included in group of the especially hazard infections
The mankind knows for a long time under the name "the «persian" or "sacred" fire
- 1780г - С.С. Андриевский, studying large flashout of this disease in Siberia, has assigned to its the name "«malignant anthrax" and in experience of an autoinfection has proved identity А. of the man and animal
- 1849г - Pellender has detected of the A. in a blood the
sick animal
- 1857г – F. Brauell has detected it in a blood of the man
- 1876г – R. Koch - has allocated pure growth А.
Слайд 32
ETIOLOGY:
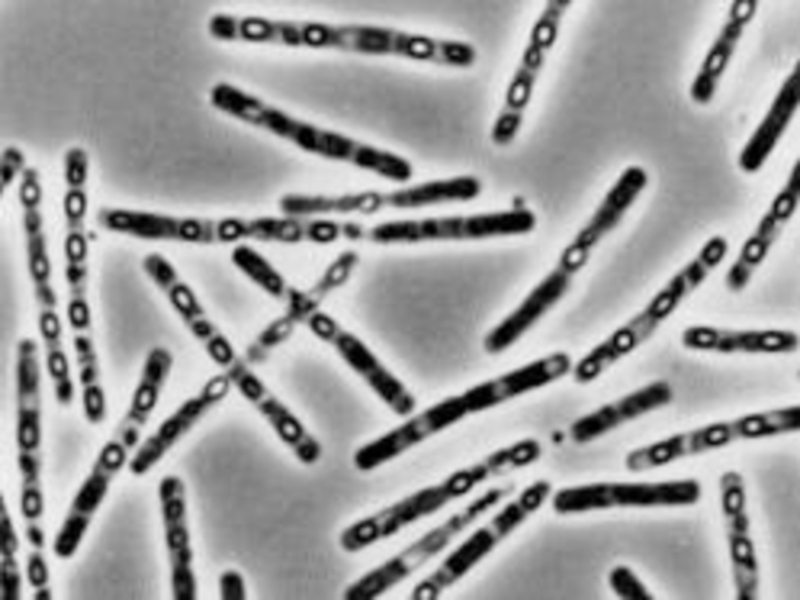
Bacillus anthracis - large rod with equal
edges 3-8 microns of length and 1-1.5 microns of width.
In smears it is found out single, by pairs or chains Gram (+)
The vegetative forms А. maintain boiling no more than 1 minutes,disinfectants are inactivated in some minutes, in corpses survive from 2 to 7 days.
The spores in ground are saved by years, but at boiling perish through 10 - 15 minutes. Dry fever and disinfectants them inactivate only in some hours.
The vegetative forms produce EXOTOXIN, consisting from a lethal toxin, hydropic factor and protective of an antigene
Thermolabile encapsulated protein antigene - has antiphagocytic activity
Слайд 36
Thermostable somatic polysaccharide the antigene is
durably saved in corpses (is discovered by response of a
thermoprecipitation on Аscolli )
EPIDEMIOLOGY:
a main source - sick animals, for which the disease proceeds in the septic form and all their bodies and the secretions contain of agents all period of illness!!
The herbivorous animals (cattle, goats, sheep, camels, horses, the deers etc.) sick often.
Less often sick pigs, dogs, cats, wild predatory animals for which А. can proceed in the localized form with a defeat of a mucous oral cavity and lymphadenitis, but the dermal forms for animal DO NOT DEVELOP!
Animals more often sick since June to September, infecting:
- contact way (through a grass, hay, water)
- through milk (at a feeding of descendants)
Слайд 37
- eating corpses perished animals (predators)
- through stings of insects
(gadflies, horseflies, flies)
Auxiliary source - GROUND, in which
the A. agent support a population by changing of periods vegetation and sporulation
The people are infecting:
1.By contact way (main way of infection)
- maintenance the sick animals - 50 %
- at processing animal skins and fur - 27 %
- at contact with infected by meat - 21 %
- at processing a wool - 6 %
2. Through stings of insects - ?
3. Nutritional way (crude force-meat, milk) - 3- 4 %
4. Aerogenic way (USA)
Слайд 38
Cases of man-to man transmission
is not registered !
More often
are sick cattle-breeder.
The case rate both home and professional registers
PATHOGENY:
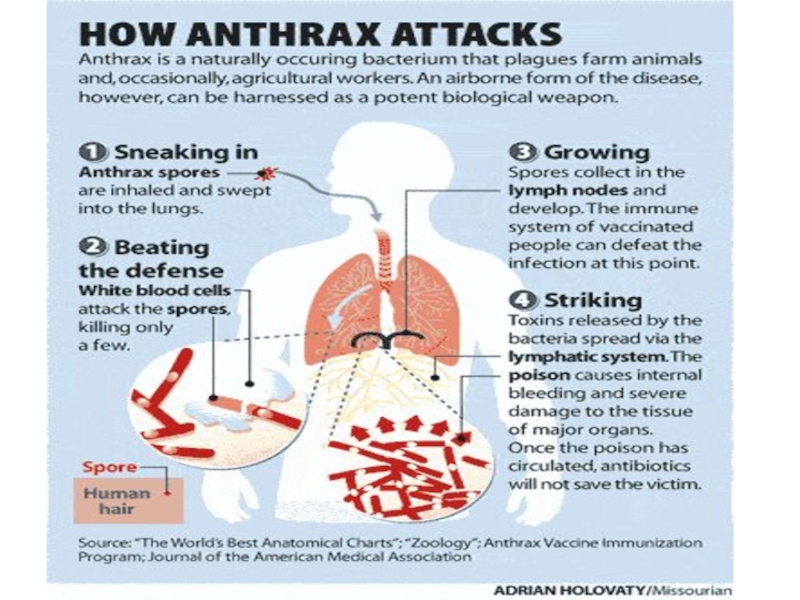
Implantation of the A. agent in skin (through microtrauma) with by appearance through 2 - 14 days in penetrating beds of a derma center of a hemorrhagic-necrotic inflammation with by the expressed edema around of its
A lymph drainage from an anthrax not disturbed, that results in appearance of a lymphangitis and regional lymphadenitis with a serous- hemorrhagic inflammation
From lymphatic nodi the A. is capable to penetrate into a blood with appearance of a bacteriemia or development of the septic form of disease (secondary or primary)
Слайд 39
3. The primary anthracic pneumonia does not develop!
At
aerogenic way of infection of spores will penetrate in
lymphatic nodi of a mediastinum, and then in a blood,
causing hematosepsis about the subsequent lesion
lungs
4. Of a primary anthracic defeat of an intestine is not observed. Penetrated from an intestine of spore cause a mesadenitis, then hematosepsis, which results in a defeat of an intestine.
5. Edema brain, lungs, cerebral coats, ulcer in an intestine - consequence of a toxemia at an anthracic bacteriemia
6. Main reason of death of the patients - bacteriemia -
toxemia - toxico-infectious shock.
PATHOMORPHOLOGY:
For perished from А. of the patients in bodies the signs of a serous-hemorrhagic inflammation with a destruction and hemorrhagia are found out. The blood darkly red, is not coagulated. Veins are overfulled by a blood
Слайд 40
CLINIC: (incubation interval from 2 about 14 days)
The localized form of disease: in a place
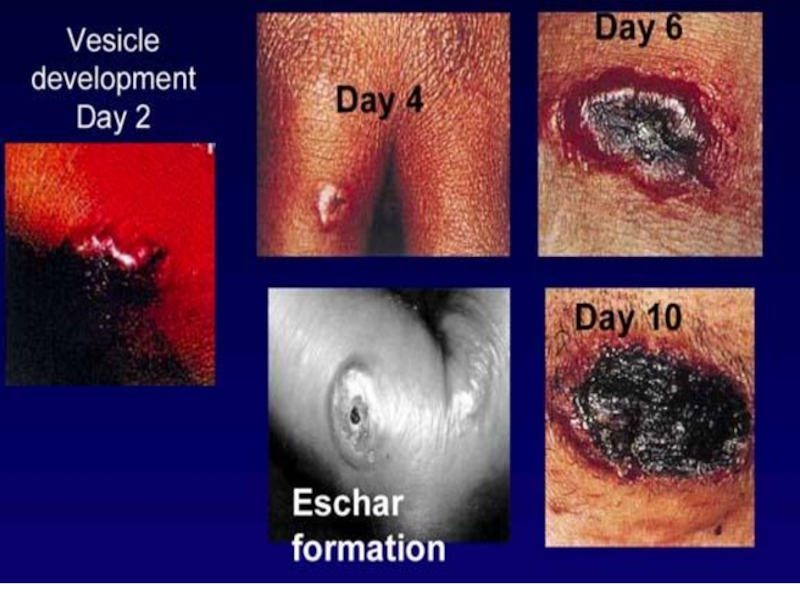
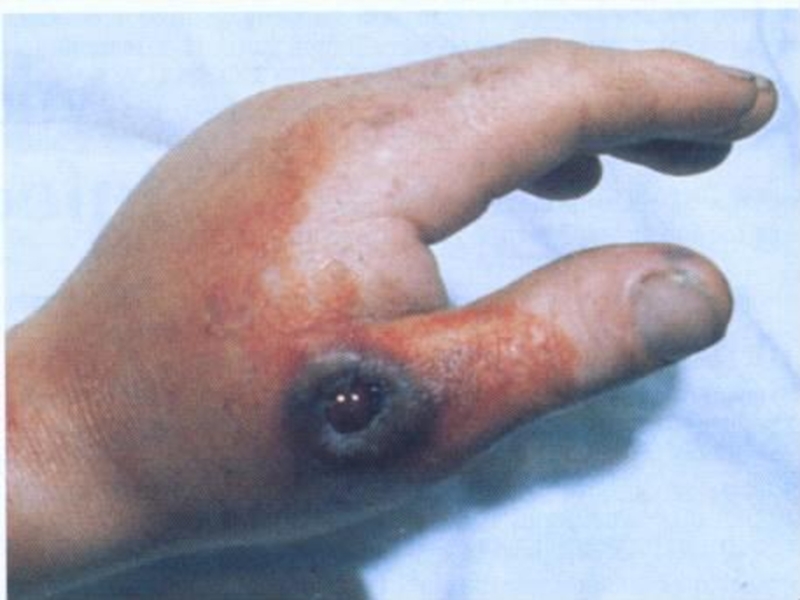
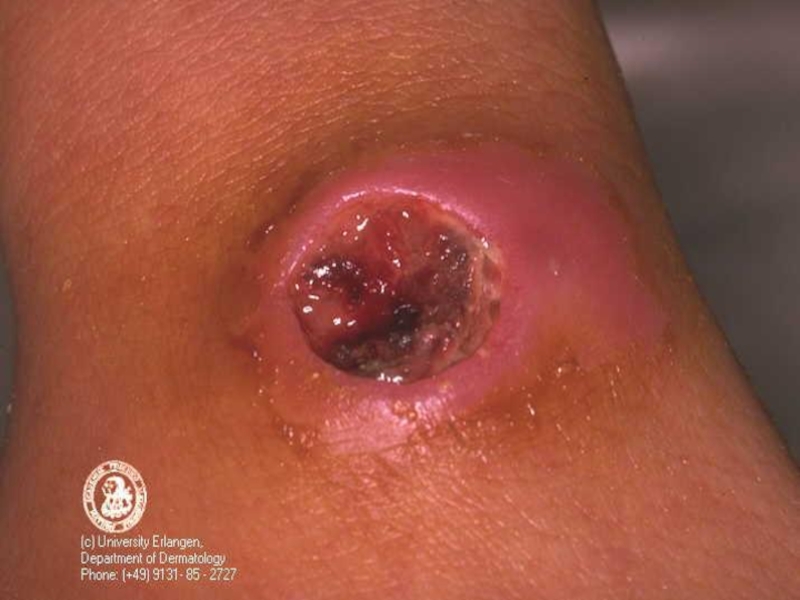
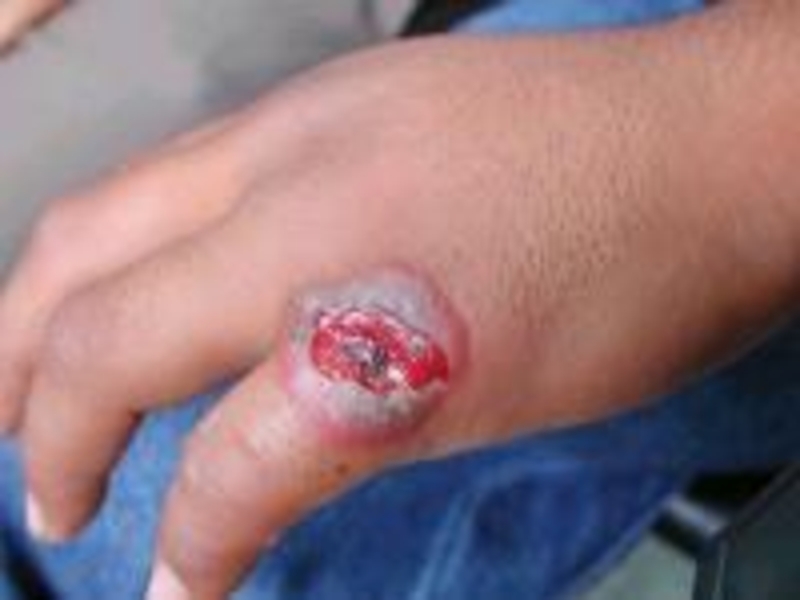
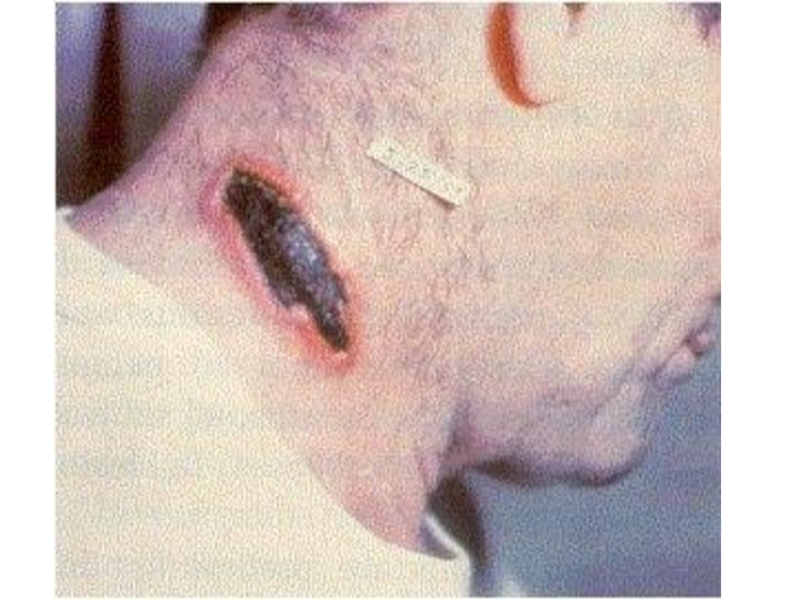
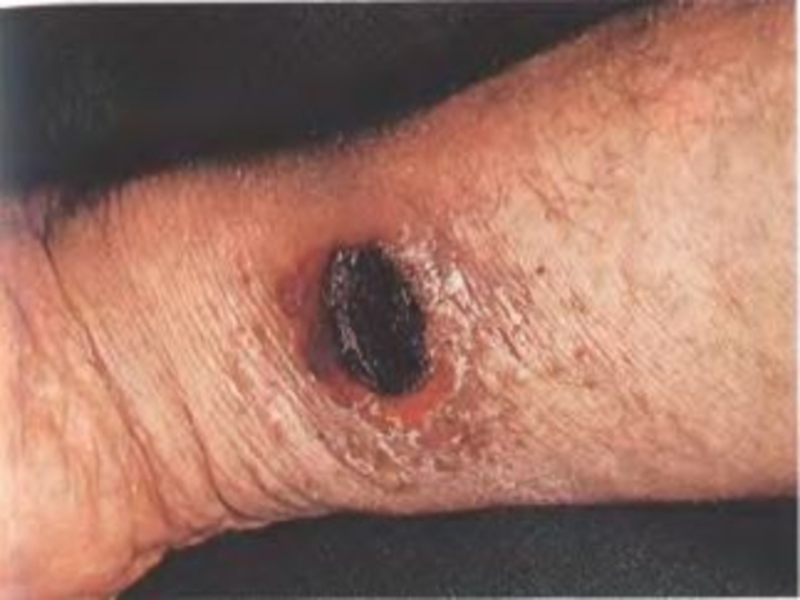
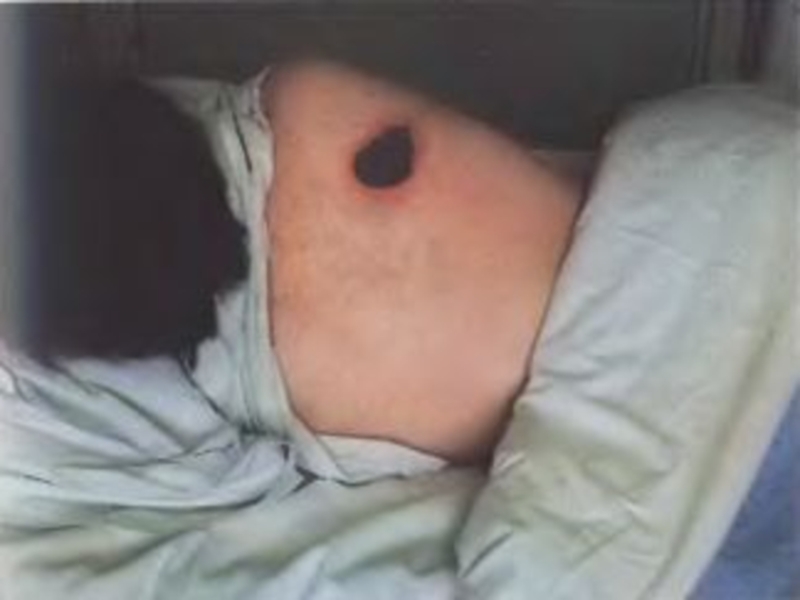
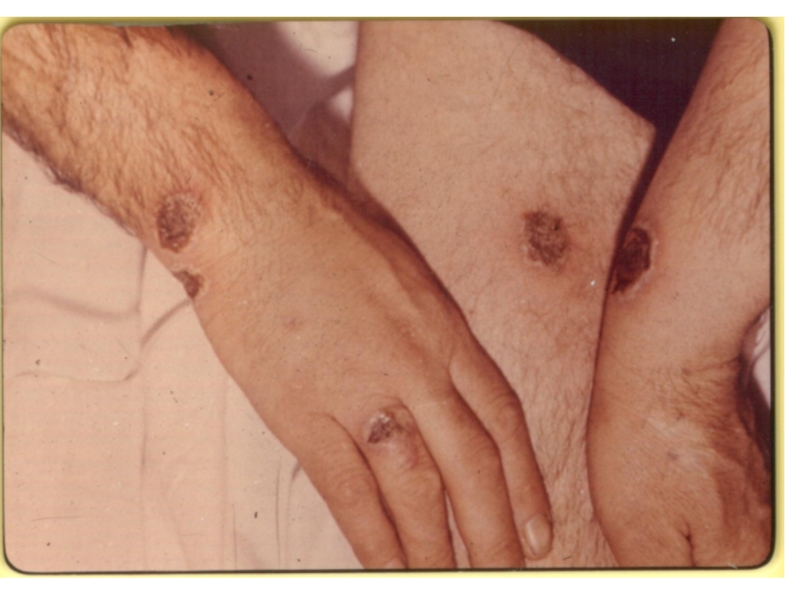
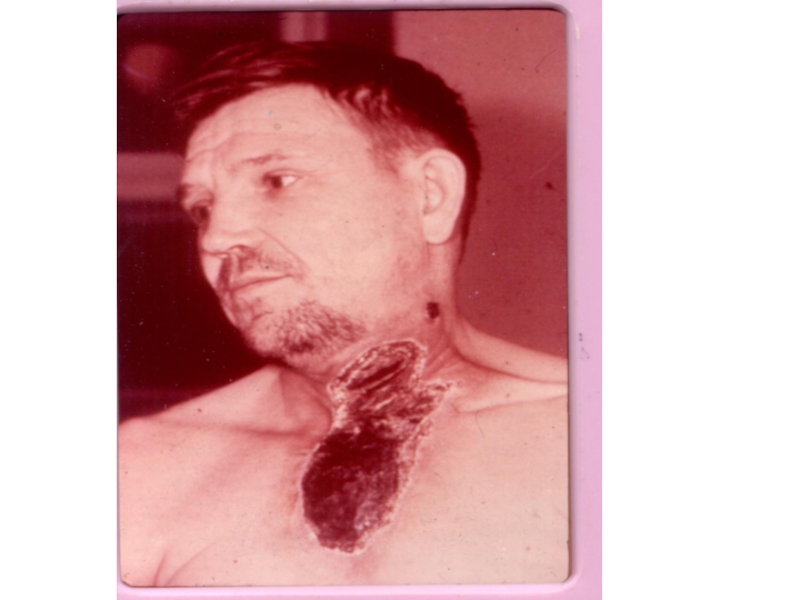
of implantation of the A. there is a stain with an itch, which is fast transmuted into a vesicle (some hours), and then in a small ulcer with a plentiful serous-hemorrhagic secretion. On edges of a ulcer there are new bubbles (crown Шоссье), which after destruction enlarge a size of a ulcer.
The increase of a ulcer occurs about 5-6 days of illness, but in 1-2 days the bottom of a ulcer at centre dries up and is coated with a brown crust, which since 2 week is transmuted into black colour. Bottom of a ulcer painless at intubation. The casting-off of a crust occurs since 3-4 weeks.
After itself leaves seams from inappreciable up to penetrating. More often ulcer single (but can be multiple) are localized on open sites of a body
Слайд 52
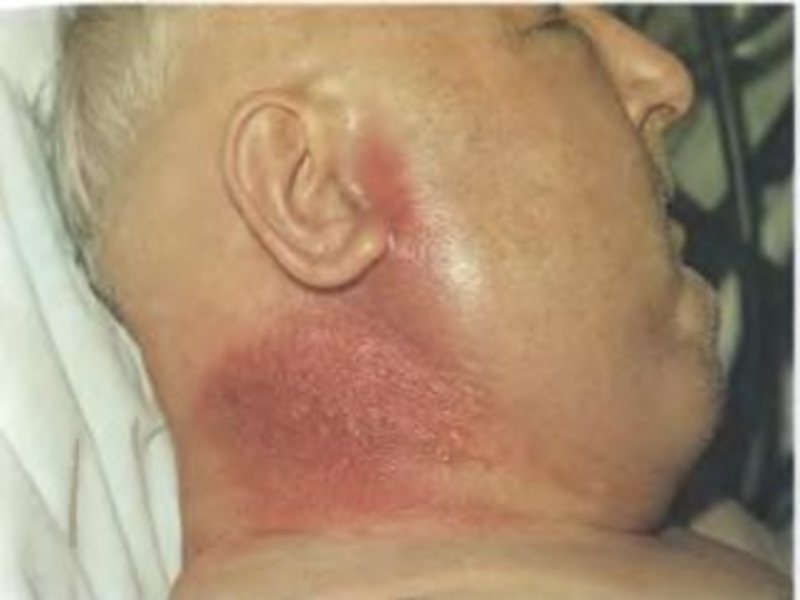
Simultaneously around of a ulcer the edema considerably exceeding
size of a ulcer is shaped. At tapotement of area
of an edema is defined jelly tremblihg (s-m В.К. Стефанского)
Regional the lymphadenitis at А. is always, but lymphatic nodi painless, not suppurate with sluggish regression.
The toxi-infectious syndrome occurs for 2-3 days from a beginning of illness: a malaise, weakness, headache, giddiness, lowering of appetite, fever in limits 37,2 - 39 гр C. Duration of this syndrome 5 - 7 days. Then the fever is critically reduced also state of health is improved.
The infrequent forms А.: edematous, erysipelatous, bullous - on a place of implantation not an anthrax, and edema and surface bubbles is shaped
Слайд 55
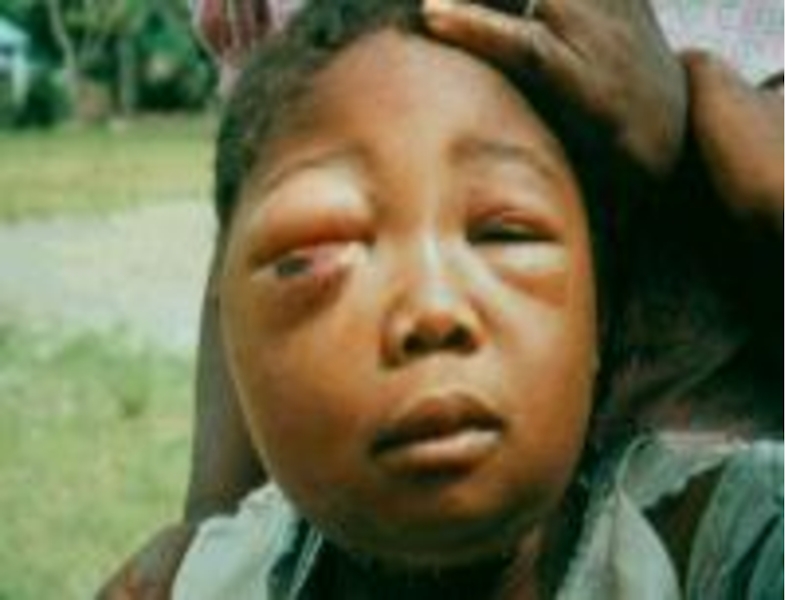
The generalized form А.
- The incubation interval can be
reduced about 1 day
Acute beginning with the expressed toxic
manifestations (fever, headache, weakness, vomiting expressed hypotonia, tachycardia with an arrhythmia, thread pulse, expressed sweating ,ect.)
Early manifestations of a lesion lungs (rhinitis, tearing, at once dry cough, then with serous or serous-hemorrhagic sputum, dyspnea, pain in a chest, common cyanosis. X-ray signs of a bronchoadenitis,, exudate in pleural cavities, pneumonia
There are colicy pains in a stomach, liquid sanguinous a stool less often, which is replaced paresis of an intestine, the peritonitis and necrosis of an intestine is possible
The general analysis of a blood, practically, does not vary!!!
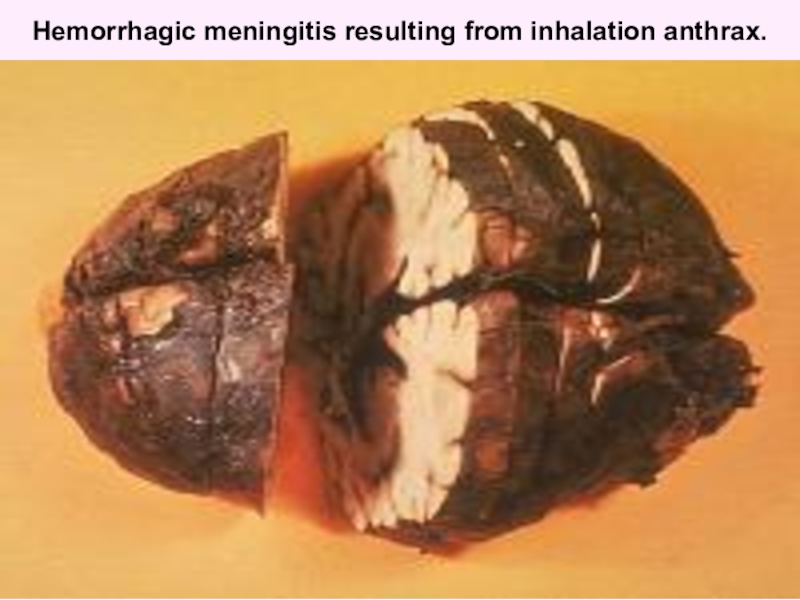
Слайд 56Hemorrhagic meningitis resulting from inhalation anthrax.
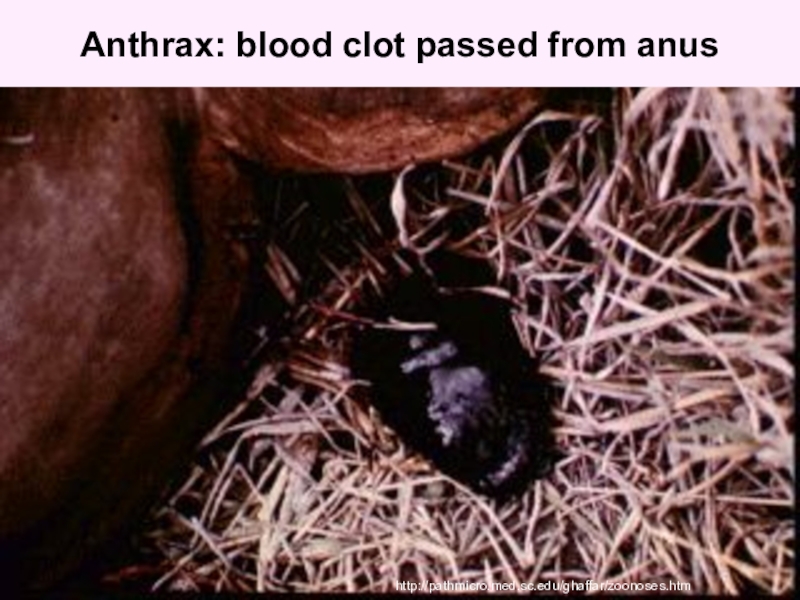
Слайд 57Anthrax: blood clot passed from anus
http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/ghaffar/zoonoses.htm
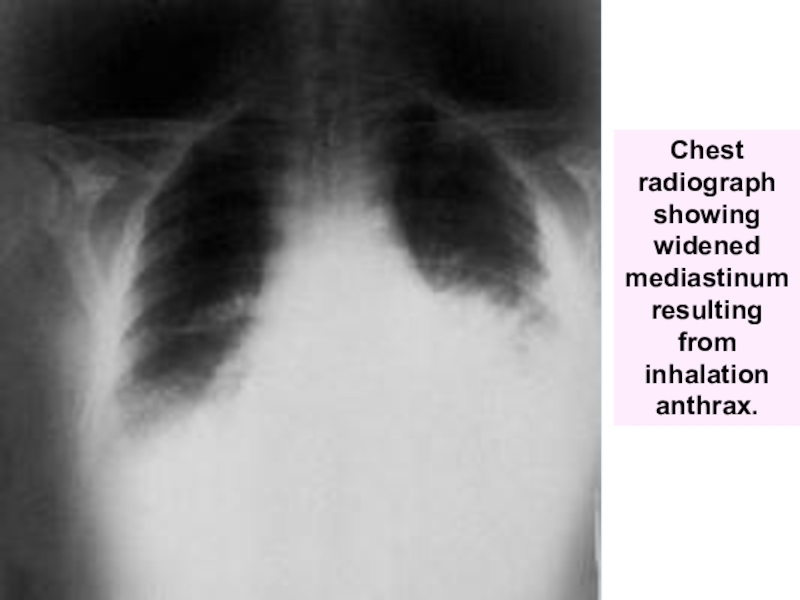
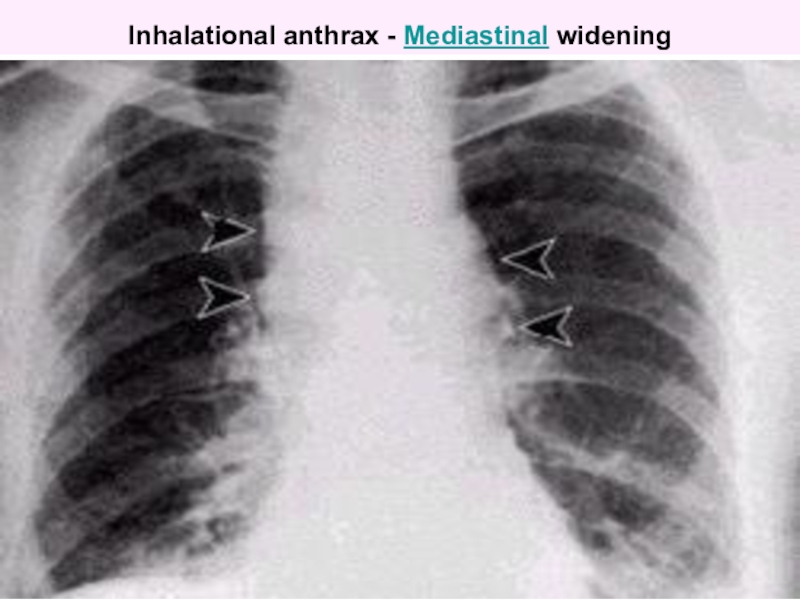
Слайд 58Chest radiograph showing widened mediastinum resulting from inhalation anthrax.
Слайд 59
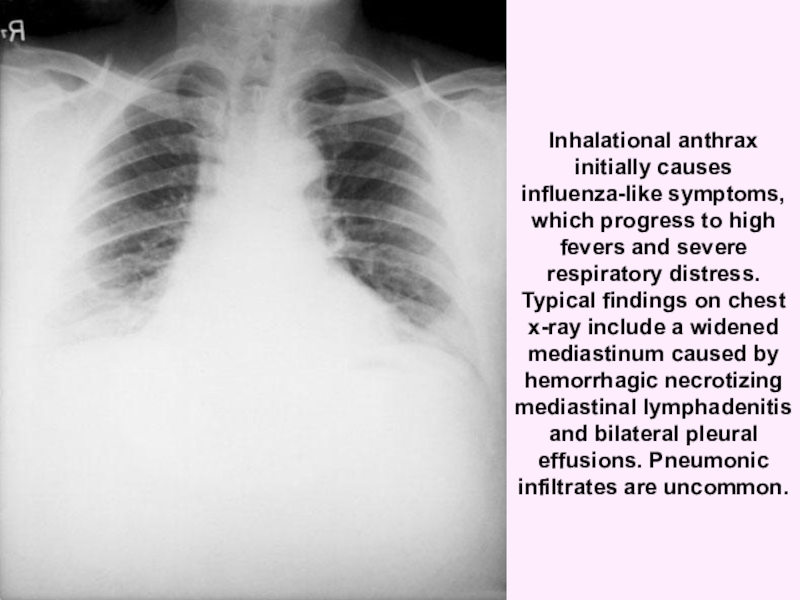
Inhalational anthrax initially causes influenza-like symptoms, which progress to high
fevers and severe respiratory distress. Typical findings on chest x-ray
include a widened mediastinum caused by hemorrhagic necrotizing mediastinal lymphadenitis and bilateral pleural effusions. Pneumonic infiltrates are uncommon.
Слайд 60Inhalational anthrax - Mediastinal widening
Слайд 61
- the patients durably save consciousness in despite of
gravity of a state, except for cases complicated
by a
meningoencephalitis
- the illness by a toxi-infectious shock with the expressed
violations of a hemodynamics, hypoxia, edema and
bloating of a brain is ended
Lethal outcome more often on 3 - 5 days of illness!!
THE DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS:
The dermal form (nonspecific anthrax, plague, tularemia,
erypsipelas, malleus etc.)
The generalized form (severe influenza, pneumonia, plague, fulminant sepsis, hemorrhagic fevers, mesenteric thrombosis
of vessels, peritonitis, hypertoxical forms of a dysentery, septic form of a salmonellosis etc.
Слайд 62
LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS
- contents of pustules, discharge of an ulcer,
blood, urine, sputum, stool, vomitive masses, material autopsy.
1. Microscopy after
colouring on Gram, Rebiger (detection of sheaths) IFT – immun fluor.test (answer in 1-2 hours)
2. Bacteriological research
3. Biological test (at negative bacteriological research)
4. Immunological research (CFT, IAT, ELISA)
5. IC test with antraxin- infiltration more than 3 sm (+)
6. Response of a thermoprecipitation on Ascolli (the corpses of animal or man)
TREATMENT only in an infectious hospital
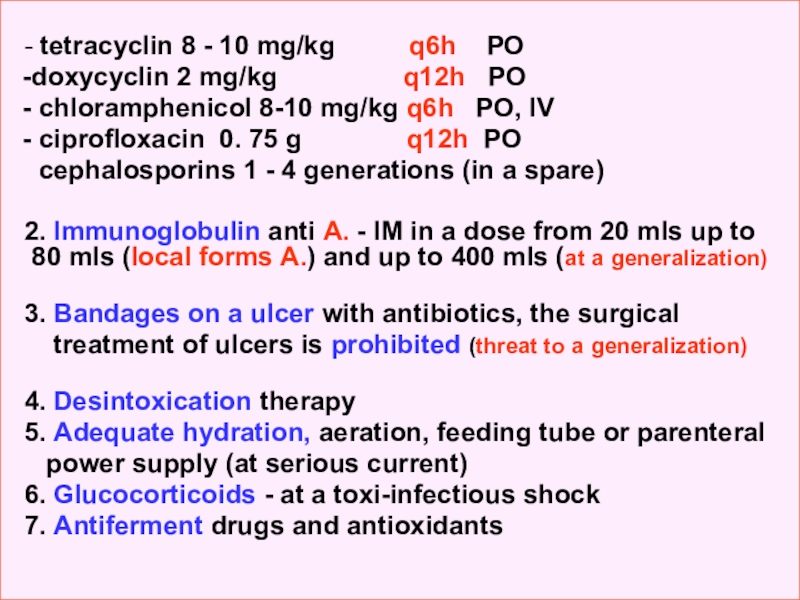
Anti-infectious therapy:
- penicillin G – 10000 – 20000 IU kg q4h IM
- ampicillin 20 – 40 mg/kg q6h IM
Слайд 63
- tetracyclin 8 - 10 mg/kg
q6h РО
doxycyclin 2 mg/kg
q12h РО
chloramphenicol 8-10 mg/kg q6h РО, IV
ciprofloxacin 0. 75 g q12h РО
cephalosporins 1 - 4 generations (in a spare)
2. Immunoglobulin anti А. - IM in a dose from 20 mls up to 80 mls (local forms А.) and up to 400 mls (at a generalization)
3. Bandages on a ulcer with antibiotics, the surgical
treatment of ulcers is prohibited (threat to a generalization)
4. Desintoxication therapy
5. Adequate hydration, aeration, feeding tube or parenteral
power supply (at serious current)
6. Glucocorticoids - at a toxi-infectious shock
7. Antiferment drugs and antioxidants
Слайд 64
PROPHYLAXIS:
Obligatory hospitalization of the patients (EHI)
Overseeing contacts within 14
days
Emergency chemoprophilaxis contacts at confirmation of the diagnosis for the
patient
Immunization of groups of hazard with the human anthrax vaccine
Revealing and hospitalization suspicious on diseasis А. of the persons in the center
Discharge of the patients only after convalescence and obtaining 2 (-) seeding with an interval 5 days
Burning of corpses animals died from А. and correct burial of the people ( dry, raised site of ground with a layer of chloride lime - 10 sm above and under a corpse)
Veterinarianal of a measure (concern only sick and perished animals)