Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Managing Change and Innovation
Содержание
- 1. Managing Change and Innovation
- 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 4. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 5. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 6. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 7. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 8. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall12–Exhibit 12–2 The Change Process
- 9. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 10. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall12–Exhibit 12–3 Three Types of Change
- 11. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 12. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 13. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall12–Exhibit 12–4 Popular OD Techniques
- 14. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 15. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall12–Exhibit 12–5 Reducing Resistance to Change
- 16. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 17. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 18. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 19. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall12–Exhibit 12–7 Symptoms of Stress
- 20. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 21. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 22. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 23. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 24. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 25. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 26. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall12–Exhibit 12–11 Innovation Variables
- 27. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 28. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 29. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 30. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 31. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 32. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Managing
Change and
Innovation
editionСлайд 2Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Learning
Outcomes Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this
chapter.12.1 The Change Process
Explain Lewin’s three-step model of the change process.
Contrast the calm waters and white-water rapids metaphors of change.
12.2 Managing Organizational Change
Define organizational change.
Explain how managers might change structure, technology, and people.
Слайд 3Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Learning
Outcomes
12.3 Managing Resistance to Change
Explain why people resist change and
how resistance might be managed.12.4 Contemporary Issues In Managing Change
• Explain why changing organizational culture is so
difficult and how managers can do it.
• Describe employee stress and how managers can
help employees deal with stress.
• Discuss what it takes to make change happen
successfully.
Слайд 4Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Learning
Outcomes
12.5 Stimulating Innovation
Explain how creativity and innovation differ from one
another.Describe the structural, cultural, and human resource variables that are necessary for innovation.
Слайд 5Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Exhibit
12–1 External and Internal Forces for Change
External
• Changing consumer
needs and wants
• New governmental laws
• Changing technology
• Economic changes
Internal
• New organizational strategy
• Change in composition of workforce
• New equipment
• Changing employee attitudes
Слайд 6Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
What
Is Change?
Characteristics of Change
Is constant yet varies in degree and
directionProduces uncertainty yet is not completely unpredictable
Creates both threats and opportunities
Managing change is an integral part of every manager’s job.
Слайд 7Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
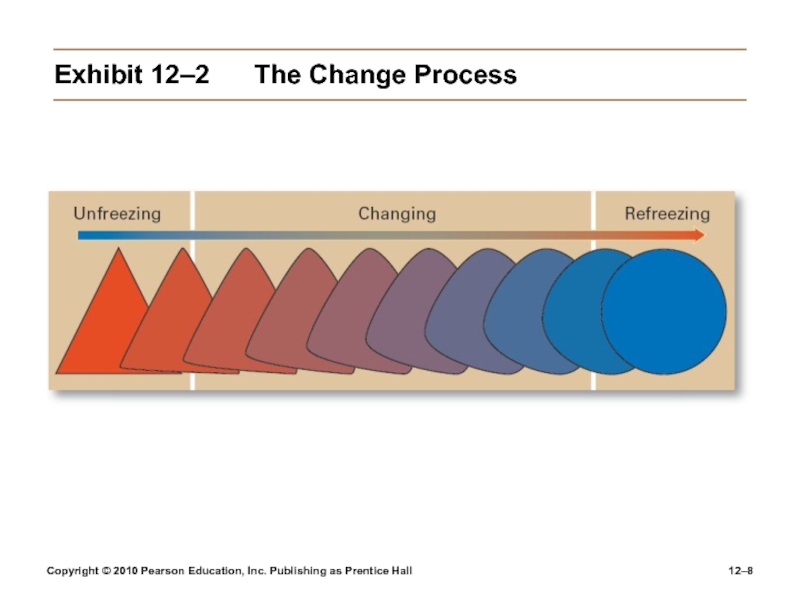
12–
The
Change Process
The Calm Waters Metaphor
Lewin’s description of the change
process as a break in the organization’s equilibrium stateUnfreezing the status quo
Changing to a new state
Refreezing to make the change permanent
White-Water Rapids Metaphor
The lack of environmental stability and predictability requires that managers and organizations continually adapt (manage change actively) to survive.
Слайд 8Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Exhibit
12–2 The Change Process
Слайд 9Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Organizational
Change and Change Agents
Organizational Change
Any alterations in the people, structure,
or technology of an organizationChange Agents
Persons who act as catalysts and assume the responsibility for managing the change process.
Types of Change Agents
Managers: internal entrepreneurs
Nonmanagers: change specialists
Outside consultants: change implementation experts
Слайд 10Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
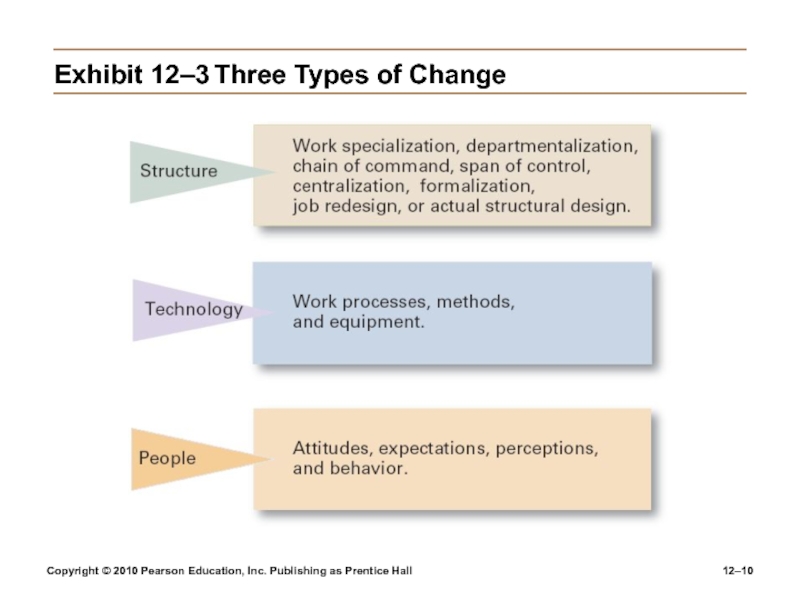
Exhibit
12–3 Three Types of Change
Слайд 11Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Types
of Change
Structure
Changing an organization’s structural components or its structural design
Technology
Adopting
new equipment, tools, or operating methods that displace old skills and require new onesAutomation: replacing certain tasks done by people with machines
Computerization
People
Changing attitudes, expectations, perceptions, and behaviors of the workforce
Слайд 12Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Organizational
Development
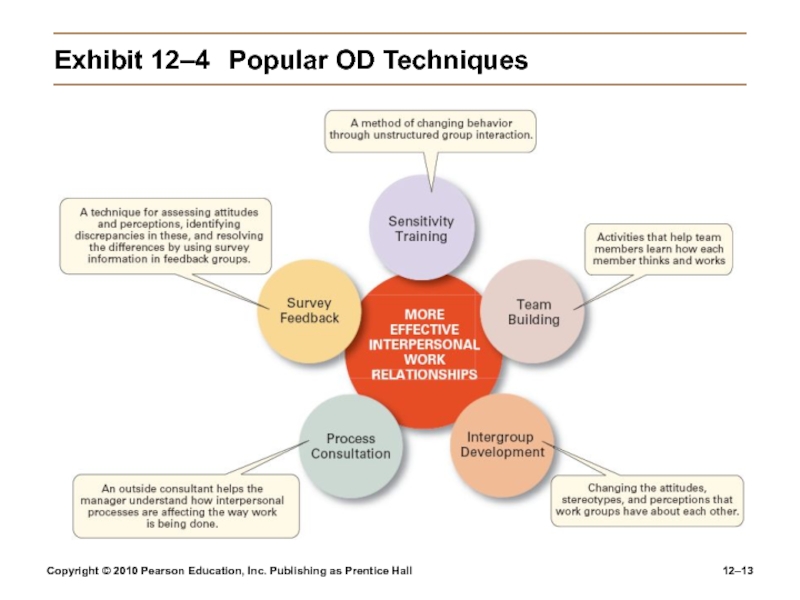
Organizational Development (OD)
Techniques or programs to change people and the
nature and quality of interpersonal work relationships.Global OD
OD techniques that work for U.S. organizations may be inappropriate in other countries and cultures.
Слайд 13Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Exhibit
12–4 Popular OD Techniques
Слайд 14Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Managing
Resistance to Change
Why People Resist Change
The ambiguity and uncertainty that
change introducesThe comfort of old habits
A concern over personal loss of status, money, authority, friendships, and personal convenience
The perception that change is incompatible with the goals and interest of the organization
Слайд 15Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Exhibit
12–5 Reducing Resistance to Change
Слайд 16Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Issues
in Managing Change (cont’d)
Changing Organizational Cultures
Cultures are naturally resistant to
change.Conditions that facilitate cultural change:
The occurrence of a dramatic crisis
Leadership changing hands
A young, flexible, and small organization
A weak organizational culture
Слайд 17Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Exhibit
12–6 Strategies for Managing Cultural Change
Set the tone through management
behavior; top managers, particularly, need to be positive role models.Create new stories, symbols, and rituals to replace those currently in use.
Select, promote, and support employees who adopt the new values.
Redesign socialization processes to align with the new values.
To encourage acceptance of the new values, change the reward system.
Replace unwritten norms with clearly specified expectations.
Shake up current subcultures through job transfers, job rotation, and/or terminations.
Work to get consensus through employee participation and creating a climate with a high level of trust.
Слайд 18Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Issues
in Managing Change (cont’d)
Handling Employee Stress
Stress
The adverse reaction people have
to excessive pressure placed on them from extraordinary demands, constraints, or opportunities. Functional Stress
Stress that has a positive effect on performance.
How Potential Stress Becomes Actual Stress
When there is uncertainty over the outcome.
When the outcome is important.
Слайд 19Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Exhibit
12–7 Symptoms of Stress
Слайд 20Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Issues
in Managing Change (cont’d)
Reducing Stress
Engage in proper employee selection
Use realistic
job interviews for reduce ambiguityImprove organizational communications
Develop a performance planning program
Use job redesign
Provide a counseling program
Offer time planning management assistance
Sponsor wellness programs
Слайд 21Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Issues
in Managing Change (cont’d)
Making Change Happen Successfully
Embrace change—become a change-capable
organization.Create a simple, compelling message explaining why change is necessary.
Communicate constantly and honestly.
Foster as much employee participation as possible—get all employees committed.
Encourage employees to be flexible.
Remove those who resist and cannot be changed.
Слайд 22Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Exhibit
12–8 Characteristics of Change-Capable
Organizations
Link the present
and the future.Make learning a way of life.
Actively support and encourage day-to-day improvements and changes.
Ensure diverse teams.
Encourage mavericks.
Shelter breakthroughs.
Integrate technology.
Build and deepen trust.
Слайд 23Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Stimulating
Innovation
Creativity
The ability to combine ideas in a unique way or
to make an unusual association.Innovation
Turning the outcomes of the creative process into useful products, services, or work methods.
Слайд 24Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Exhibit
12–9 World’s Most Innovative Companies
Source: “The World’s Most Innovative Companies by
Region,” BusinessWeek, BusinessWeekOnline, April 15, 2008, businessweek.comСлайд 25Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
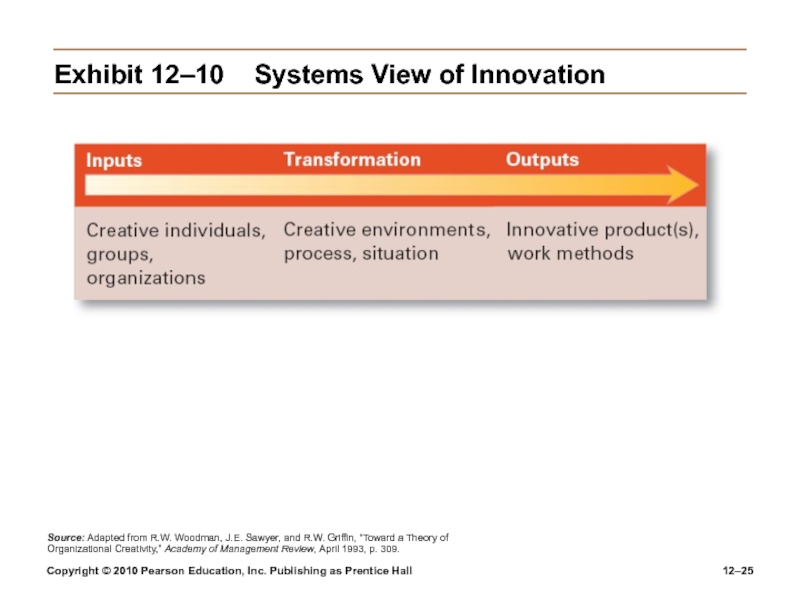
Exhibit
12–10 Systems View of Innovation
Source: Adapted from R.W. Woodman, J.E. Sawyer,
and R.W. Griffin, “Toward a Theory of Organizational Creativity,” Academy of Management Review, April 1993, p. 309.Слайд 26Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
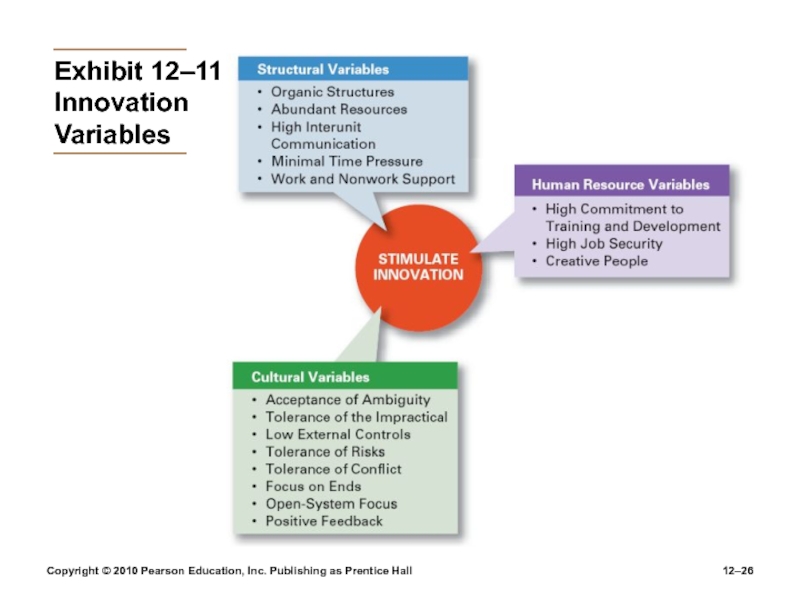
12–
Exhibit
12–11
Innovation Variables
Слайд 27Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Stimulating
Innovation
Structural Variables
Adopt an organic structure
Make available plentiful resources
Engage in frequent
inter-unit communicationMinimize extreme time pressures on creative activities
Provide explicit support for creativity
Слайд 28Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Stimulating
Innovation (cont’d.)
Cultural Variables
Accept ambiguity
Tolerate the impractical
Have low external controls
Tolerate risk
takingTolerate conflict
Focus on ends rather than means
Develop an open-system focus
Provide positive feedback
Слайд 29Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
12–
Stimulating
Innovation (cont’d.)
Human Resource Variables
Actively promote training and development to keep
employees’ skills current.Offer high job security to encourage risk taking.
Encourage individual to be “champions” of change.
Idea Champion
Dynamic self-confident leaders who actively and enthusiastically inspire support for new ideas, build support, overcome resistance, and ensure that innovations are implemented.