Слайд 1Ministry education and Science of Republic of Kazakhstan
Karaganda State University
named after academician Ye.A. Buketov
Biological and geographical faculty
Botany Department
Course – Botany
Specialty - 5В011300 – «Biology»
Lecture № 12
Algae. Bacillariophyta, Phaeophyta, Rhodophyta. Basic parameters of ecology of algae
(1 hour)
Lecturer: candidate of biological science, associated professor
Ishmuratova Margarita Yulaevna
Слайд 2Plan of lecture:
1 Red algae.
2 Diatoms algae .
3 Brown
algae.
Слайд 3Основная литература:
1 Еленевский А.Г., Соловьев М.П., Тихомиров В.Н. Ботаника:
систематика высших, или наземных, растений. 2 изд. - М.: Academіa,
2001. - 429 с.
2 Нестерова С.Г. Лабораторный практикум по систематике растений. - Алматы: Қазақ ун-ті, 2011. - 220 с.
3 Родман А.С. Ботаника. – М.: Колос, 2001. - 328 с.
Дополнительная литература:
1 Абдрахманов О.А. Систематика низших растений. – Караганда: Изд-во КарГУ, 2009. - 188 с.
2 Билич Г.Л., Крыжановский В.А. Биология. Т. 2: Ботаника. - М.: Оникс 21 век, 2002. - 543 с.
3 Абдрахманов О.А. Практические работы по систематике низших растений. Ч. 2. Грибы и водоросли. – Караганда: Изд-во КарГУ, 2001. - 144 с.
4 Абдрахманов О.А. Лабораторный практикум по бактериям и водорослям. Учебное пособие. - Алматы: Казакадем образование, 2000. - 130 с.
Слайд 4Euglenophyta (euglenoids)
The Euglenophyta or euglenoids are 800 species of unicellular,
protozoan-like algae, most of which occur in fresh waters. The
euglenoids lack a true cell wall, and are bounded by a proteinaceous cell covering known as a pellicle. Euglenophytes have one to three flagellae for locomotion, and they store carbohydrate reserves as paramylon. The primary photosynthetic pigments of euglenophytes are chlorophylls a and b, while their accessory pigments are carotenoids and xanthophylls.
Most euglenoids have chloroplasts, and are photosynthetic. Some species, however, are heterotrophic, and feed on organic material suspended in the water. Even the photosynthetic species, however, are capable of surviving for some time if kept in the dark, as long as they are "fed" with suitable organic materials.
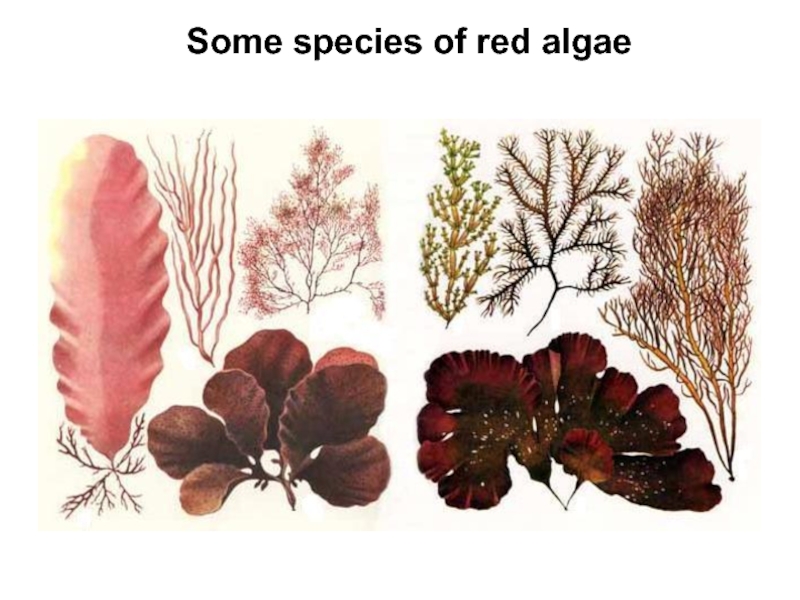
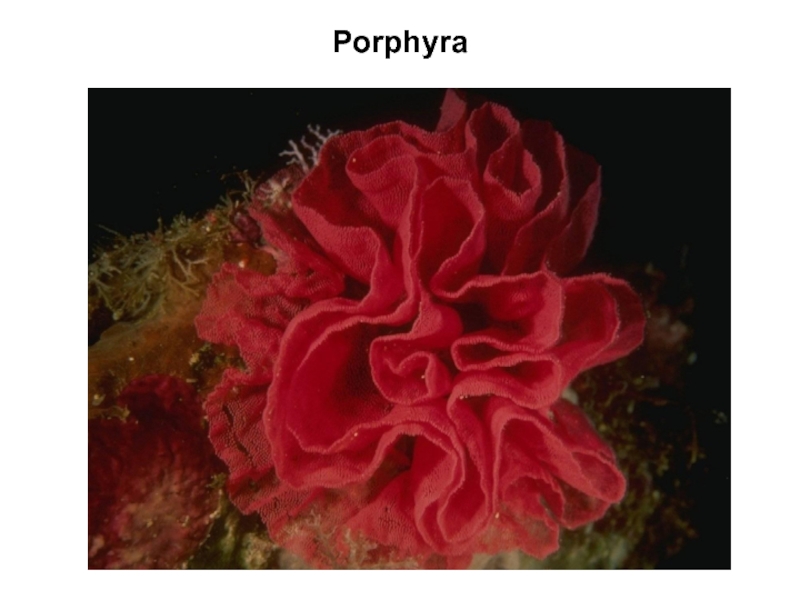
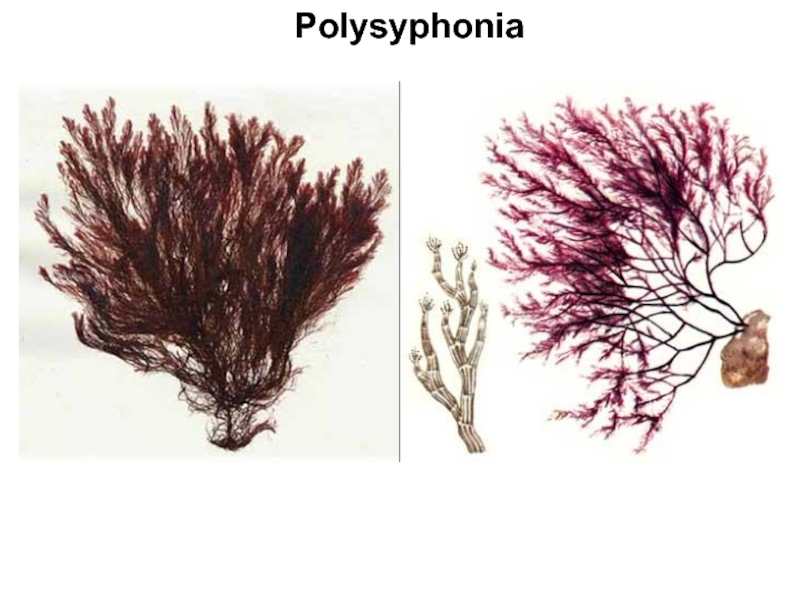
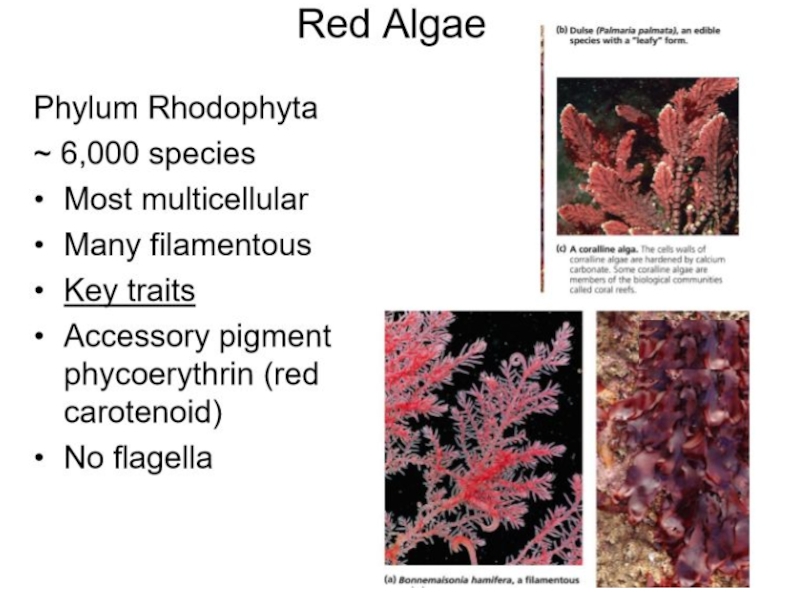
Слайд 9Rhodophyta (red algae)
The Rhodophyta or red algae are 4,000 species
of mostly marine algae, which are most diverse in tropical
waters. Species of red algae range from microscopic to macroscopic in size. The larger species typically grow attached to a hard substrate, or they occur as epiphytes on other algae. The cell walls of red algae are constructed of cellulose and polysaccharides, such as agar and carrageenin. These algae lack flagellae, and they store energy as a specialized polysaccharide known as floridean starch. The photosynthetic pigments of red algae are chlorophylls a and d, and their accessory pigments are carotenoids, xanthophyll, and phycobilins.
Some examples of red algae include filamentous species such as Pleonosporum spp., so-called coralline algae such as Porolithon spp., which become heavily encrusted with calcium carbonate and contribute greatly to the building of tropical reefs, and thalloid species, such as the economically important Irish moss (Chondrus crispus).
Слайд 15The Paeophyta or brown algae number about 1,500 species, almost
all of which occur in marine environments. These seaweeds are
especially abundant in cool waters. Species of brown algae are macroscopic in size, including the giant kelps that can routinely achieve lengths of tens of meters. Brown algae have cell walls constructed of cellulose and polysaccharides known as alginic acids. Some brown algae have relatively complex, differentiated tissues, including a holdfast that secures the organism to its substrate, air bladders to aid with buoyancy, a supporting stalk or stipe, wide blades that provide the major surface for nutrient exchange and photosynthesis, and spore-producing, reproductive tissues. The specialized, reproductive cells of brown algae are shed into the water and are motile, using two flagella to achieve locomotion. The food reserves of these algae are carbohydrate polymers known as laminarin. Their photosynthetic pigments are chlorophylls a and c, while the accessory pigments are carotenoids and xanthophylls, including fucoxanthin, a brown-colored pigment that gives these algae their characteristic dark color.
Some examples of brown algae include the sargassum weed (Sargassum spp.), which dominates the extensive, floating ecosystem in the mid-Atlantic gyre known as the Sargasso Sea. Most brown seaweeds, however, occur on hard-bottom, coastal substrates, especially in cooler waters.

Слайд 19Control questions:
1 Make a characteristics of brown and red
algae.
2 Which life forms are usual for brown algae?
3 Which
life forms are usual for red algae?
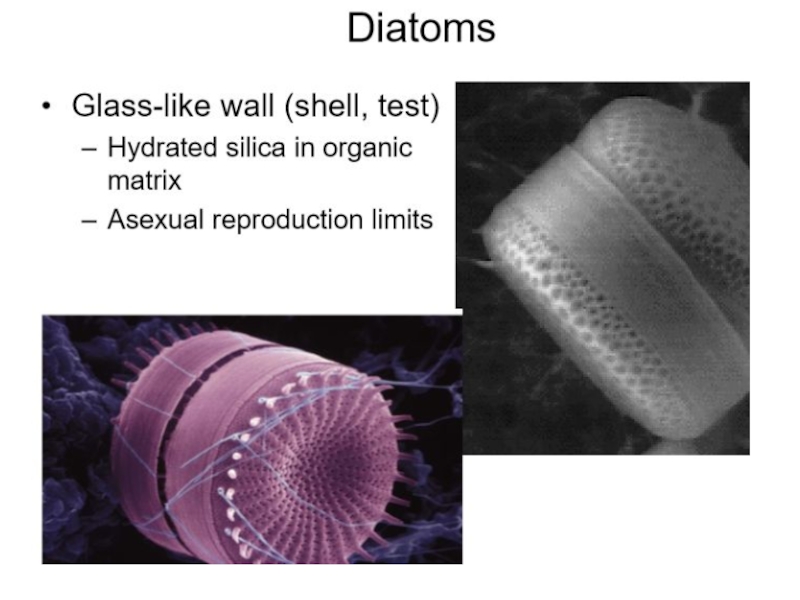
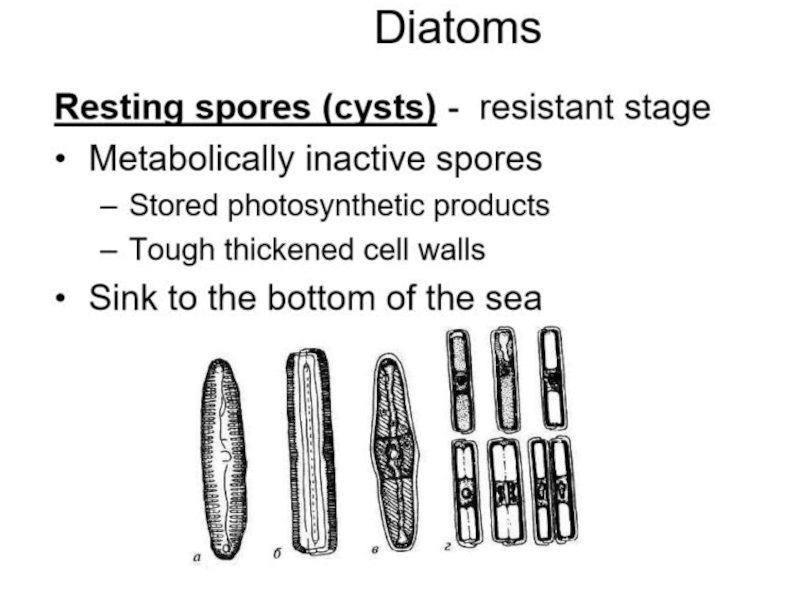
4 Describe the structure of diatoms.
5 Which practical uses do red and brown algae have?
6 Which pigment are usual for red and brown algae?
Слайд 20Test questions:
Basic pigments of brown algae:
А) chlorophyll b
В) chlorophyll d
С)
carotene
Д) chlorophyll а and с
Е) xantophyll
F) Fico erythrin
Individual
of diatom algae:
А) ulotrix
В) diatomae
С) chara
Д) volvox
Е) spirogira