Слайд 1Mrs. Hampton, a 68-year-old retired school teacher, is transferring from
intensive
care to your nursing unit following a cerebrovascular accident.
She entered
the ED 2 days ago with slurred speech and weakness of the right arm and leg. She has a history of primary hypertension, coronary artery disease, and type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Her condition is stabilized.
The intensive care nurse calls you to give a report on Mrs. Hampton.
The nurse notes the admitting diagnosis, vital signs, pain level, and transferring health care provider’s orders.
Слайд 21 Which other information would you like to have about
Mrs. Hampton?
2 The nurse arrives with Mrs. Hampton in a
wheelchair; she is accompanied
by her husband. Which interventions would you select to reduce Mr. and Mrs. Hampton’s anxiety related to the transfer out of the intensive care unit?
3 Mr. Hampton tells you that his wife is going home in a few days because she is doing so well. She will be going home using a walker. He says that he hopes he will be able to take care of her once she is at home. How do you respond to Mr. Hampton?
Which interventions do you need to take before Mrs. Hampton’s
discharge?
Слайд 31 Additional information that would be helpful as you assume
care for
Mrs. Hampton includes:
• Level of consciousness and findings from
neurologic assessment.
• Patient’s medical history, including medications; information
regarding any recent changes in medication or treatment plan.
• Blood glucose level, home insulin schedule and dosages, whether
home insulin was administered before presenting to hospital.
• Results of any testing completed such as computed tomography
(CT) scan of head or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
• Patient’s plans or expectations for discharge (e.g., plans to return
home with assistance of husband).
• Referrals that have been made for physical therapy and speech therapy.
Слайд 42 You introduce yourself to Mr. and Mrs. Hampton, explain
that you
are the nurse who will be caring for Mrs.
Hampton during the day
shift, and accompany them to the assigned room.
Orient them to the room and help put Mrs. Hampton’s belongings away after making sure that all of her personal belongings were brought with her.
Show the Hamptons the call light system and how to get help if needed.
Provide Mr. Hampton with a comfortable chair and support his interactions
with his wife.
Allow Mr. Hampton to participate in Mrs. Hampton’s care to the extent that he is comfortable. Reinforce the reasons for the transfer and answer any questions that the Hamptons have about it.
Allow them the opportunity to express their anxiety about the
move from the intensive care unit.
Слайд 5Recognize that Mr. Hampton’s anxiety is normal and allow him
to
express his concerns related to taking his wife home.
Ask
Mr. Hampton about family or other help that is available.
Have him describe the home and identify which problems may be related to Mrs. Hampton’s mobility and risk for falls.
Discuss with Mr. Hampton changes that can be made in the home to improve safety (e.g., removal of throw rugs, having grab bars installed in the bathroom at the toilet and tub)
Get confirmation that Mrs. Hampton uses her walker
correctly.
Слайд 6Who is responsible for developing a patient’s discharge plan?
1 The
primary nurse
2 The medical social worker
3 The nurse caring for
the patient the longest
4 The patient’s health care team
Слайд 7The discharge planning process is comprehensive and
multidisciplinary, including representatives from
all the services
who provided care.
1 The primary nurse
2 The medical
social worker
3 The nurse caring for the patient the longest
4 The patient’s health care team
Who is responsible for developing a patient’s discharge plan?
Слайд 8Which statement best explains why it is essential to assess
and document the clinical status of a patient immediately before
transfer or at time of discharge?
1 Increased reimbursement to the hospital occurs because of
additional diagnosis codes.
2 Potential changes in a patient’s clinical needs may require
nursing interventions to provide for patient safety during transport.
3 Hospital documentation requirements could prevent transfer
of a patient unless the information is current.
4 The necessary information needs to be reflective of a discharge plan for visiting accrediting agencies.
Слайд 9Which statement best explains why it is essential to assess
and document the clinical status of a patient immediately before
transfer or at time of discharge?
1 Increased reimbursement to the hospital occurs because of
additional diagnosis codes.
2 Potential changes in a patient’s clinical needs may require
nursing interventions to provide for patient safety during transport.
3 Hospital documentation requirements could prevent transfer
of a patient unless the information is current.
4 The necessary information needs to be reflective of a discharge plan for visiting accrediting agencies.
The patient’s current status must be accurate to anticipate the needs that may occur during the transfer or discharge.
Слайд 10You are assigned to Mr. Augsten, a 56-year-old university professor.
He is admitted from the trauma unit following a motorcycle-automobile
accident.
Mr. Augsten has a fractured left humerus and pelvis.
Although he was wearing a helmet, he suffered a concussion. When doing your
admissions assessment you note a cast on his left arm and an intravenous
(IV) line in his right antecubital fossa.
He received IV narcotics in the emergency department and is very sleepy. He awakens only to touch.
Слайд 111 Which admission vital signs can you assign to the
nursing assistive
personnel (NAP)? Which directions do you provide the NAP
regarding
obtaining routine vital signs for this patient?
2 The NAP reports that the blood pressure for Mr. Augsten is 94/60 mm
Hg. You note that the emergency department nurse recorded a
blood pressure of 140/86в mm Hg. Which interventions should you
consider at this time? What might explain the differences in blood
pressure values?
3 The nurse directed the NAP to report a respiratory rate of 16 or less.
The NAP documents a respiratory rate of 12 in the vital sign flow
sheet but does not report the rate to you until you inquire. She states
that Mr. Augsten was speaking with her so it was not important to
bother the nurse. What is your response to the NAP? Explain the
significance of the respiratory rate.
4 You direct the NAP to repeat Mr. Augsten’s blood pressure and
respiratory rate in 30 minutes. In a half hour the NAP reports a blood
pressure in the right arm of 160/100 and a respiratory rate of 20.
She also notes that Mr. Augsten was sleeping quietly. What is your
response?

Слайд 121 The nurse must obtain all admission vital signs.
All
of the routine vital signs can be delegated.
Temperature should
be tympanic or temporal
because patient is sedated and may not be able to hold an oral
thermometer.
Blood pressure can be taken on the right arm or leg.
Слайд 13The NAP reported a change in BP; the priority nursing
intervention is for the nurse to immediately obtain a new
blood pressure reading
and further assess the patient.
Once the nurse determines that the patient is indeed stable, other explanations for the differences can be explored.
Possible explanations for differences are technique, equipment, and patient-related findings.
Technique includes site of blood pressure measurement and whether the nursing assistive personnel (NAP) used the proper method.
The nurse may want to observe the NAP’s technique in blood pressure measurement.
Equipment differences include using a cuff that is too small or an electronic blood pressure machine.
An example of a patient-related finding is that the patient was in pain in the emergency department, thus raising blood pressure. After receiving pain medication the blood pressure decreases.
Слайд 143. The NAP was instructed to report any respiratory rate
less than 16 immediately.
The nurse needs to reinforce that
instruction and determine why this directive was not followed.
The respiratory rate has likely been affected by the pain medication, which can depress the respiratory center of the brain.
Слайд 154 The NAP should be told to obtain the respiratory
rate before waking the patient and taking the blood pressure.
A sleepy patient is unlikely to have a respiratory rate of 20.
The blood pressure was obtained in the right arm, which had a IV present.
The nurse should instruct the NAP to retake the BP and should observe the NAP during this measurement.
Therefore the nurse can identify and correct any problems
with obtaining the BP.
Слайд 16The nurse is assessing the axillary temperature of a confused
patient with a fever.
Which actions by the nurse will
best help provide an accurate measurement? (Select all that apply.)
1 Drying the axilla before placing the thermometer probe
2 Holding the thermometer probe in place
3 Placing the patient in a supine position
4 Checking that the patient has not had anything to eat or drink
recently
Слайд 17The nurse is assessing the axillary temperature of a confused
patient with a fever.
Which actions by the nurse will
best help provide an accurate measurement? (Select all that apply.)
1 Drying the axilla before placing the thermometer probe
2 Holding the thermometer probe in place
3 Placing the patient in a supine position
4 Checking that the patient has not had anything to eat or drink
recently
It is common to find sweat in the axilla of a patient with fever.
Drying the axilla helps the probe make better contact with the skin.
The axillary route would be best because of the patient’s confusion.
As with other sites for measuring body temperature, the probe must be held in the appropriate position for maximum contact.
Слайд 18 After checking the tympanic temperature two consecutive times in
an
82-year-old patient, the nurse finds the reading to be several
degrees
lower than expected. What is the most appropriate nursing
action at this time?
1 Obtain a different thermometer
2 Observe for the presence of cerumen
3 Document the temperature assessed
4 Record the average between the two readings
Слайд 19 After checking the tympanic temperature two consecutive times in
an
82-year-old patient, the nurse finds the reading to be several
degrees
lower than expected. What is the most appropriate nursing
action at this time?
1 Obtain a different thermometer
2 Observe for the presence of cerumen
3 Document the temperature assessed
4 Record the average between the two readings
With aging cerumen (earwax) tends to be drier and can interfere with an accurate tympanic temperature measurement.
The cerumen acts as a barrier; therefore the temperature reading
would not be reliable.
Слайд 20 The nurse is preparing to assess a patient’s blood
pressure.
Which statement by the nurse will help promote an accurate
reading?
1
“Just relax while I put the cuff on your arm.”
2 “This is painless and will take just a minute.”
3 “The cuff can go over your thin silk sleeve.”
4 “Please do not uncross your legs while I do this.”
Слайд 21 The nurse is preparing to assess a patient’s blood
pressure.
Which statement by the nurse will help promote an accurate
reading?
1
“Just relax while I put the cuff on your arm.”
2 “This is painless and will take just a minute.”
3 “The cuff can go over your thin silk sleeve.”
4 “Please do not uncross your legs while I do this.”
Crossing the legs can falsely increase the systolic and diastolic blood pressure. The cuff should be on the bare arm, but uncrossing the legs is more important. The other two statements are true but would not necessarily promote an accurate reading
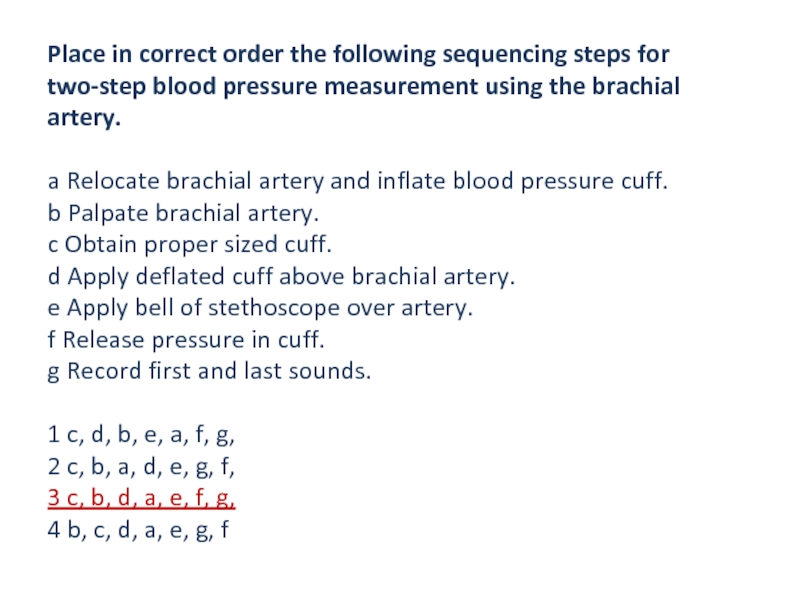
Слайд 22Place in correct order the following sequencing steps for two-step
blood pressure measurement using the brachial artery.
a Relocate brachial artery
and inflate blood pressure cuff.
b Palpate brachial artery.
c Obtain proper sized cuff.
d Apply deflated cuff above brachial artery.
e Apply bell of stethoscope over artery.
f Release pressure in cuff.
g Record first and last sounds.
1 c, d, b, e, a, f, g,
2 c, b, a, d, e, g, f,
3 c, b, d, a, e, f, g,
4 b, c, d, a, e, g, f
Слайд 23Place in correct order the following sequencing steps for two-step
blood pressure measurement using the brachial artery.
a Relocate brachial artery
and inflate blood pressure cuff.
b Palpate brachial artery.
c Obtain proper sized cuff.
d Apply deflated cuff above brachial artery.
e Apply bell of stethoscope over artery.
f Release pressure in cuff.
g Record first and last sounds.
1 c, d, b, e, a, f, g,
2 c, b, a, d, e, g, f,
3 c, b, d, a, e, f, g,
4 b, c, d, a, e, g, f
Слайд 24Electronic blood pressure monitoring cannot be used on certain patients.
Which of these patients can have an electronic blood pressure
monitor?
1 The patient with constant extremity tremors
2 The patient with diabetes mellitus
3 The feverish patient who is shivering
4 The patient with an irregular heart rate
Слайд 25Electronic blood pressure monitoring cannot be used on certain patients.
Which of these patients can have an electronic blood pressure
monitor?
1 The patient with constant extremity tremors
2 The patient with diabetes mellitus
3 The feverish patient who is shivering
4 The patient with an irregular heart rate
Electronic blood pressure measurement devices can be used for the patient with diabetes mellitus.
Patients with constant body movement, irregular heart rates, peripheral vascular disease, and seizures are not candidates for use of the electronic blood
pressure devices.
Слайд 26Mr. Marquis is 87 years old and is admitted to
your medical unit for
pneumonia of 4 days’ duration. His temperature
is 37.2o C (99° F).
The NAP questions why his temperature is so low for a person with
an active infection. Your best response is:
1 His body has compensated for the infection by increasing
heart rate.
2 He probably had an antipyretic in the assisted-living facility
where he lived.
3 He took a cool shower before he was admitted.
4 The baseline temperature of older adults is lower because of
loss of subcutaneous fat.
Слайд 27Mr. Marquis is 87 years old and is admitted to
your medical unit for
pneumonia of 4 days’ duration. His temperature
is 37.2o C (99° F).
The NAP questions why his temperature is so low for a person with
an active infection. Your best response is:
1 His body has compensated for the infection by increasing
heart rate.
2 He probably had an antipyretic in the assisted-living facility
where he lived.
3 He took a cool shower before he was admitted.
4 The baseline temperature of older adults is lower because of
loss of subcutaneous fat.
Older adults are less like to demonstrate a high fever.
Heart rate increases with fever, not infection.
Слайд 28You are checking the vital signs of a 75-year-old patient.
The radial pulse is irregular, and about every fourth beat
is different.
The patient offers no complaints. What is your next action?
1 Report the findings to the health care provider immediately.
2 Obtain a blood pressure.
3 Obtain an apical heart rate.
4 Notify the nurse in charge.
Слайд 29You are checking the vital signs of a 75-year-old patient.
The radial pulse is irregular, and about every fourth beat
is different.
The patient offers no complaints. What is your next action?
1 Report the findings to the health care provider immediately.
2 Obtain a blood pressure.
3 Obtain an apical heart rate.
4 Notify the nurse in charge.
Abnormal radial pulse should be rechecked with apical heart rate assessment.
The radial pulse may be too weak to count.
Слайд 30 Which of the following nursing interventions is/are correct when
determining a pulse deficit? (Select all that apply.)
1 Counting for
30 seconds and multiplying by 2
2 Starting to count after the peripheral first beat is heard
3 Using a peripheral artery and apical pulse
4 Counting simultaneously with another health care provider
Слайд 31 Which of the following nursing interventions is/are correct when
determining a pulse deficit? (Select all that apply.)
1 Counting for
30 seconds and multiplying by 2
2 Starting to count after the peripheral first beat is heard
3 Using a peripheral artery and apical pulse
4 Counting simultaneously with another health care provider
Pulse deficit should be determined with a 60-second
count starting with zero, and any peripheral artery can be used.
Both health care providers must count simultaneously.
Слайд 32Which of the following blood pressures would classify as prehypertension?
(Select all that apply.)
1 118/78
2 126/82
3 130/80
4 132/94
Слайд 33Which of the following blood pressures would classify as prehypertension?
(Select all that apply.)
1 118/78
2 126/82
3 130/80
4 132/94