Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Organizational Culture and Environment
Содержание
- 1. Organizational Culture and Environment
- 2. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 3. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 4. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 5. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 6. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall3–Exhibit 3–1 Parameters of Managerial Discretion
- 7. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 8. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall3–Exhibit 3–2 Dimensions of Organizational Culture
- 9. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 10. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall3–Exhibit 3–3 Contrasting Organizational Cultures
- 11. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 12. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 13. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 14. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 15. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 16. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 17. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 18. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 19. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 20. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 21. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 22. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall3–Exhibit 3–8 Creating a Customer-Responsive Culture
- 23. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 24. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 25. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 26. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall3–Exhibit 3–9 The External Environment
- 27. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 28. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 29. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall3–Exhibit 3–11 Environmental Uncertainty Matrix
- 30. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 31. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 32. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall3–Exhibit 3–12 Organizational Stakeholders
- 33. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 34. Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing
- 35. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Organizational
Culture and Environment
editionСлайд 2Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Learning
Outcomes Follow this Learning Outline as you read and study this
chapter.
3.1 The Manager: Omnipotent Or Symbolic?
Contrast the actions of managers according to the omnipotent and symbolic views.
Identify the two constraints on managerial discretion.
3.2 Organizational Culture
Identify the seven dimensions of organizational culture.
Discuss the impact of a strong culture on organizations and managers.
Explain how a culture is formed and maintained.
Describe how culture affects managers.
Слайд 3Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Learning
Outcomes
3.3 Current Organizational Culture Issues.
Describe the characteristics of an ethical
culture, an innovative culture, and a customer-responsive culture.Explain why workplace spirituality seems to be an important concern.
Describe the characteristics of a spiritual organization.
3.4 The Environment.
List the components of the specific and general environments.
Explain the two dimensions of environmental uncertainty.
Identify the most common organizational stakeholders.
List the four steps in managing external stakeholder relationships.
Слайд 4Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
The
Manager: Omnipotent or Symbolic?
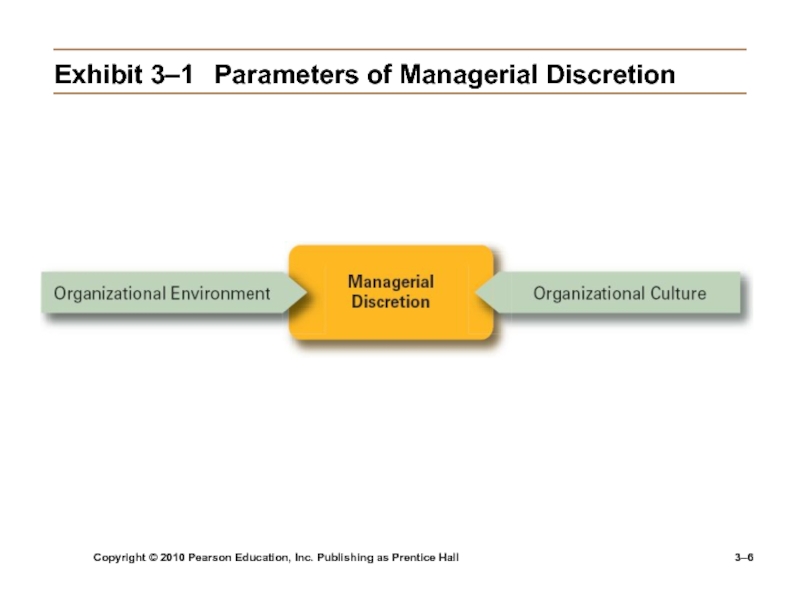
Omnipotent View of Management
Managers are directly responsible
for an organization’s success or failure.The quality of the organization is determined by the quality of its managers.
Managers are held accountable for an organization’s performance, yet it is difficult to attribute good or poor performance directly to their influence on the organization.
Слайд 5Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
The
Manager: Omnipotent or Symbolic?
Symbolic View of Management
Much of an organization’s
success or failure is due to external forces outside of managers’ control.The ability of managers to affect outcomes is influenced and constrained by external factors.
The economy, customers, governmental policies, competitors, industry conditions, technology, and the actions of previous managers
Managers symbolize control and influence through their action.
Слайд 6Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–1 Parameters of Managerial Discretion
Слайд 7Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
The
Organization’s Culture
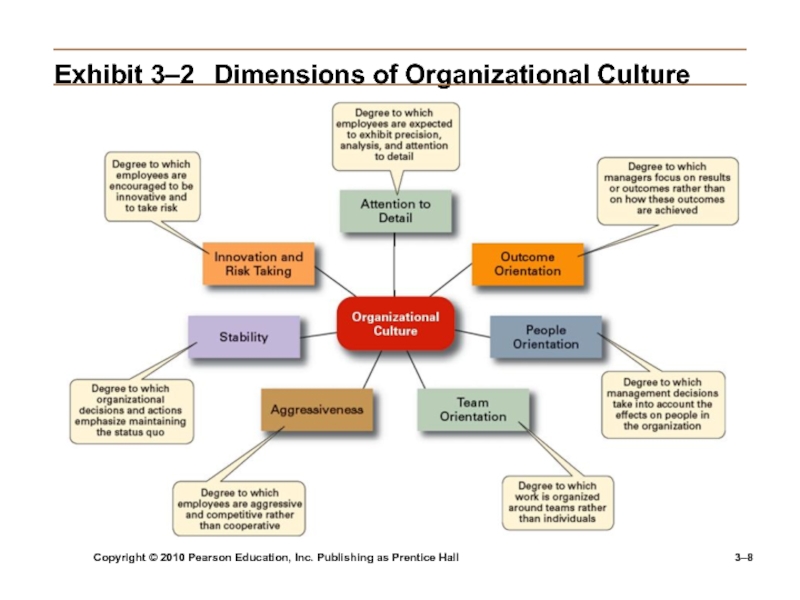
Organizational Culture
A system of shared meanings and common beliefs
held by organizational members that determines, in a large degree, how they act towards each other.“The way we do things around here.”
Values, symbols, rituals, myths, and practices
Implications:
Culture is a perception.
Culture is shared.
Culture is descriptive.
Слайд 8Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–2 Dimensions of Organizational Culture
Слайд 9Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Strong
Versus Weak Cultures
Strong Cultures
Are cultures in which key values are
deeply and widely held.Have a strong influence on organizational members.
Factors Influencing the Strength of Culture
Size of the organization
Age of the organization
Rate of employee turnover
Strength of the original culture
Clarity of cultural values and beliefs
Слайд 10Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
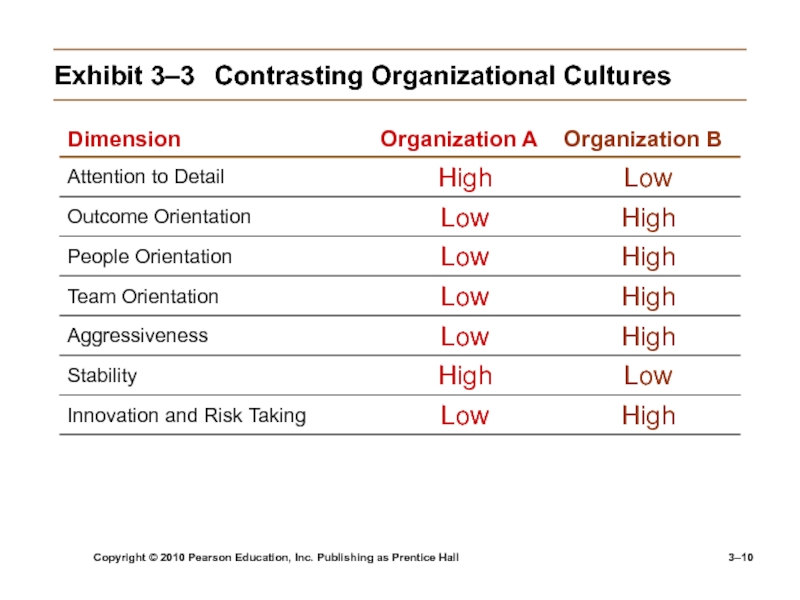
Exhibit
3–3 Contrasting Organizational Cultures
Слайд 11Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Benefits
of a Strong Culture
Creates a stronger employee commitment to the
organization.Aids in the recruitment and socialization of new employees.
Fosters higher organizational performance by instilling and promoting employee initiative.
Слайд 12Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Organizational
Culture
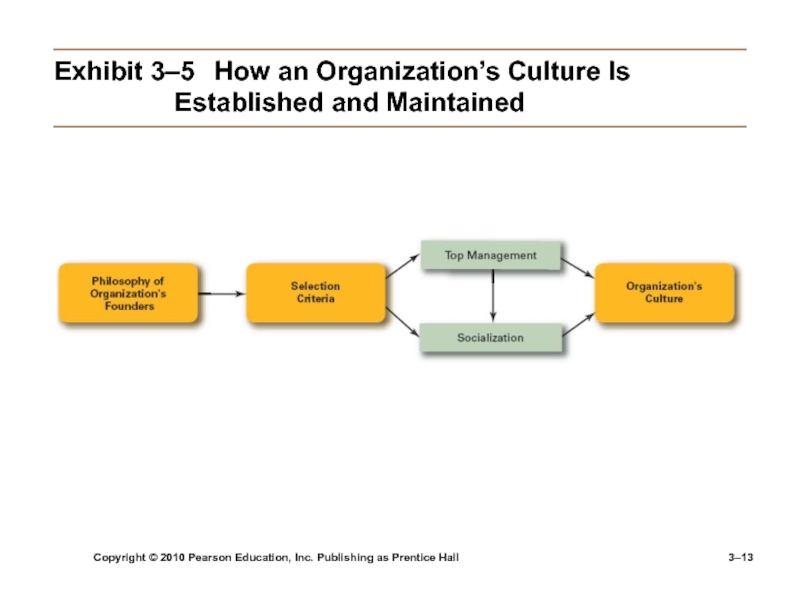
Sources of Organizational Culture
The organization’s founder
Vision and mission
Past practices of
the organizationThe way things have been done
The behavior of top management
Continuation of the Organizational Culture
Recruitment of like-minded employees who “fit”
Socialization of new employees to help them adapt to the culture
Слайд 13Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–5 How an Organization’s Culture Is Established and Maintained
Слайд 14Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–4 Strong Versus Weak Organizational
Cultures
Слайд 15Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
How
Employees Learn Culture
Stories
Narratives of significant events or actions of people
that convey the spirit of the organizationRituals
Repetitive sequences of activities that express and reinforce the values of the organization
Material Symbols
Physical assets distinguishing the organization
Language
Acronyms and jargon of terms, phrases, and word meanings specific to an organization
Слайд 16Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
How
Culture Affects Managers
Cultural Constraints on Managers
Whatever managerial actions the organization
recognizes as proper or improper on its behalfWhatever organizational activities the organization values and encourages
The overall strength or weakness of the organizational culture
Simple rule for getting ahead in an organization:
Find out what the organization rewards and act accordingly.
Слайд 17Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–6 Managerial Decisions Affected by Culture
Planning
The degree of risk that plans
should containWhether plans should be developed by individuals or teams
The degree of environmental scanning in which management will engage
Organizing
How much autonomy should be designed into employees’ jobs
Whether tasks should be done by individuals or in teams
The degree to which department managers interact with each other
Слайд 18Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–6 Managerial Decisions Affected by Culture
(cont’d)
Leading
The degree to which managers are concerned with increasing employee job satisfaction
What leadership styles are appropriate
Whether all disagreements—even constructive ones—should be eliminated
Controlling
Whether to impose external controls or to allow employees to control their own actions
What criteria should be emphasized in employee performance evaluations
What repercussions will occur from exceeding one’s budget
Слайд 19Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Organization
Culture Issues
Creating an Ethical Culture
High in risk tolerance
Low to moderate
aggressivenessFocus on means as well as outcomes
Creating an Innovative Culture
Challenge and involvement
Freedom
Trust and openness
Idea time
Playfulness/humor
Conflict resolution
Debates
Risk-taking
Слайд 20Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–7 Creating a More Ethical Culture
Be a visible role model.
Communicate
ethical expectations.Provide ethics training.
Visibly reward ethical acts and punish unethical ones.
Provide protective mechanisms so employees can discuss ethical dilemmas and report unethical behavior without fear.
Слайд 21Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Organization
Culture Issues (cont’d)
Creating a Customer-Responsive Culture
Hiring the right type of
employees (those with a strong interest in serving customers)Having few rigid rules, procedures, and regulations
Using widespread empowerment of employees
Having good listening skills in relating to customers’ messages
Providing role clarity to employees to reduce ambiguity and conflict and increase job satisfaction
Having conscientious, caring employees willing to take initiative
Слайд 22Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–8 Creating a Customer-Responsive Culture
Слайд 23Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Spirituality
and Organizational Culture
Workplace Spirituality
The recognition that people have an inner
life that nourishes and is nourished by meaningful work that takes place in the context of community.Characteristics of a Spiritual Organization
Strong sense of purpose
Focus on individual development
Trust and openness
Employee empowerment
Toleration of employees’ expression
Слайд 24Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Benefits
of Spirituality
Improved employee productivity
Reduction of employee turnover
Stronger organizational performance
Increased creativity
Increased
employee satisfactionIncreased team performance
Increased organizational performance
Слайд 25Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Defining
the External Environment
External Environment
Those factors and forces outside the organization
that affect the organization’s performance. Components of the External Environment
Specific environment: external forces that have a direct and immediate impact on the organization.
General environment: broad economic, socio-cultural, political/legal, demographic, technological, and global conditions that may affect the organization.
Слайд 26Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–9 The External Environment
Слайд 27Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
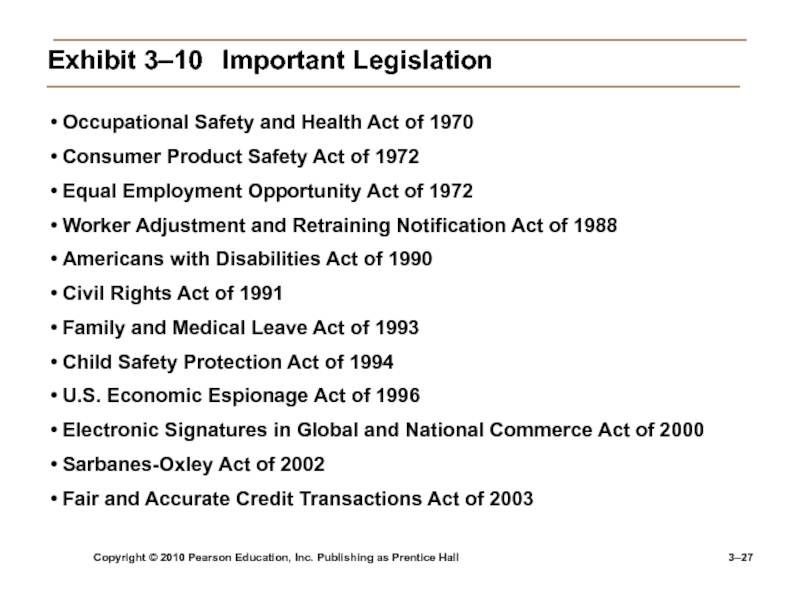
3–
Exhibit
3–10 Important Legislation
Occupational Safety and Health Act of 1970
Consumer
Product Safety Act of 1972Equal Employment Opportunity Act of 1972
Worker Adjustment and Retraining Notification Act of 1988
Americans with Disabilities Act of 1990
Civil Rights Act of 1991
Family and Medical Leave Act of 1993
Child Safety Protection Act of 1994
U.S. Economic Espionage Act of 1996
Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act of 2000
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002
Fair and Accurate Credit Transactions Act of 2003
Слайд 28Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
How
the Environment Affects Managers
Environmental Uncertainty
The extent to which managers have
knowledge of and are able to predict change their organization’s external environment is affected by:Complexity of the environment: the number of components in an organization’s external environment.
Degree of change in environmental components: how dynamic or stable the external environment is.
Слайд 29Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–11 Environmental Uncertainty Matrix
Слайд 30Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Stakeholder
Relationships
Stakeholders
Any constituencies in the organization’s environment that are affected by
the organization’s decisions and actionsWhy Manage Stakeholder Relationships?
It can lead to improved organizational performance.
It’s the “right” thing to do, given the interdependence of the organization and its external stakeholders.
Слайд 31Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Managing
Stakeholder Relationships
Identify the organization’s external stakeholders.
Determine the particular interests and
concerns of the external stakeholders.Decide how critical each external stakeholder is to the organization.
Determine how to manage each individual external stakeholder relationship.
Слайд 32Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Exhibit
3–12 Organizational Stakeholders
Слайд 33Copyright © 2010 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
3–
Terms
to Know
omnipotent view of management
symbolic view of management
organizational culture
strong cultures
socialization
workplace
spiritualityexternal environment
specific environment
general environment
environmental uncertainty
environmental complexity
stakeholders