Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Philosophy of Science: An Introduction
Содержание
- 1. Philosophy of Science: An Introduction
- 2. What is a science?Science (from the Latin
- 3. The earliest roots of science can be
- 4. the formal sciences (e.g., logic, mathematics, and
- 5. The structure of science the goal –
- 6. 2) as a discipline that emerged during
- 7. 1) the general socio-cultural background of a
- 8. The range of the main problems of
- 9. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3The earliest roots of science can be traced to Ancient
Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3500 to 3000 BCE.
Their contributions
to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes.History of science
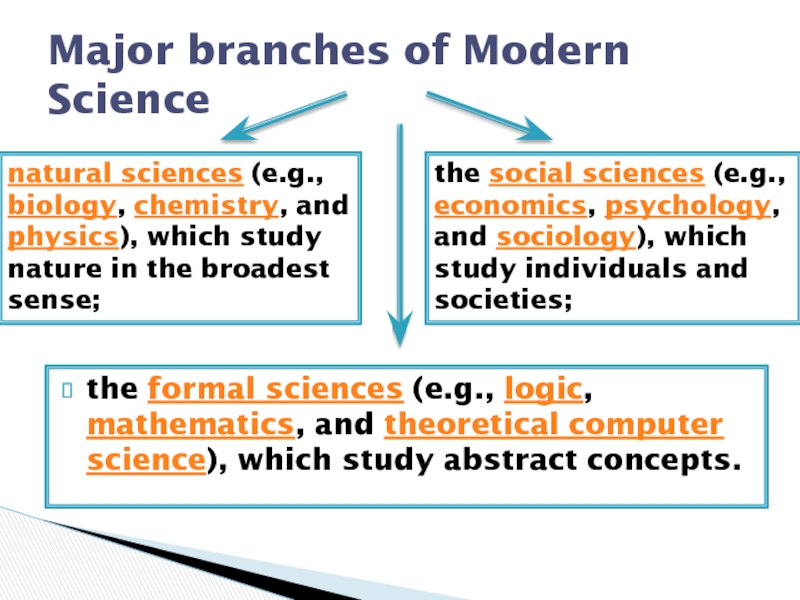
Слайд 4the formal sciences (e.g., logic, mathematics, and theoretical computer science),
which study abstract concepts.
Major branches of Modern Science
natural sciences
(e.g., biology, chemistry, and physics), which study nature in the broadest sense; the social sciences (e.g., economics, psychology, and sociology), which study individuals and societies;
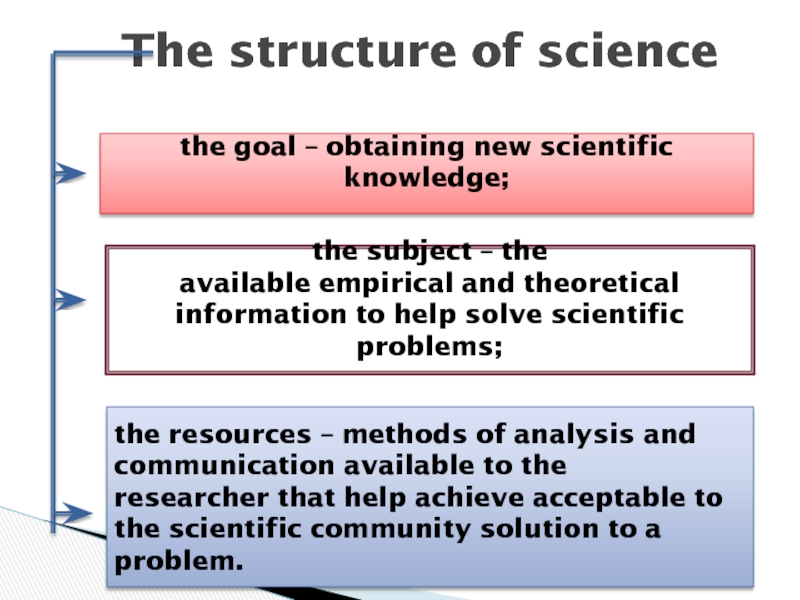
Слайд 5The structure of science
the goal – obtaining new scientific
knowledge;
the subject – the
available empirical and theoretical information to
help solve scientific problems;the resources – methods of analysis and communication available to the
researcher that help achieve acceptable to the scientific community solution to a
problem.
Слайд 62) as a discipline that emerged during the second half
of the XX-th century in response to the need to
understand the socio-cultural function of science in the scientific and technological revolution. Its subjects are the general patterns and trends of the scientific cognition as a special activity for the production of the scientific knowledge taken in its historical development and considered in the changing social and cultural contextAccording to the researcher T. Leshkevich, in creating the image
of the philosophy of science one should distinguish between the two meanings of this term:
1) as a direction of the philosophy presented by a variety of concepts that offer one or another model of the development of the science which originated in the second half of the XIX-th century;
Слайд 71) the general socio-cultural background of a particular historical epoch;
2) gnosiological, epistemological, and methodological studies;
3) theoretical approaches, models
and concepts developed in the framework of the philosophy of science as a branch of the
modern philosophy.
The formation and development of the philosophy of science as a
discipline was influenced by:
Слайд 8The range of the main problems of the philosophy of
science is quite wide:
the scientific criteria and the differences
between the scientific knowledge
and the unscientific one;logic of the scientific research; structure of the scientific knowledge;
mechanisms for generating new knowledge;
scientific rationality; patterns of the history of science; interaction of science and culture;
science base; value of science; ethos of science, etc. All of them are derived from the central problem of the philosophy of science – the problem of growth (development) of the scientific knowledge.
Conclusion