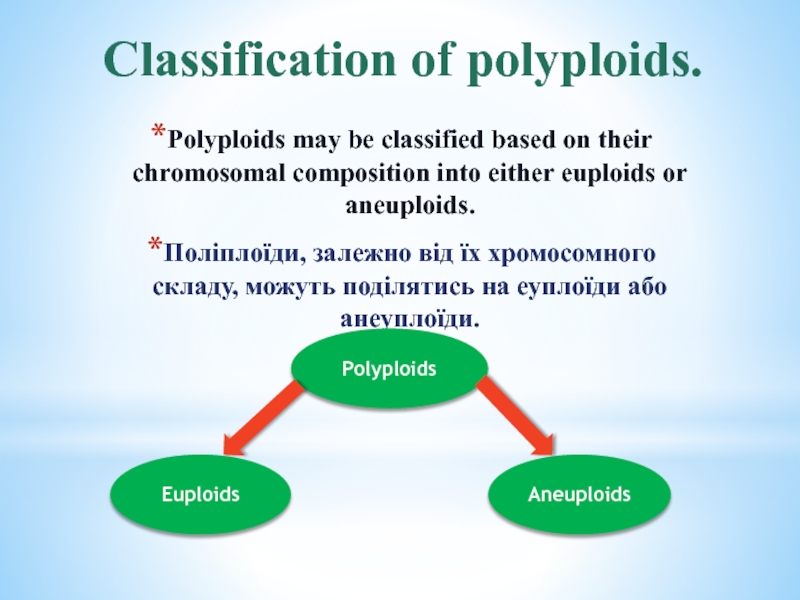
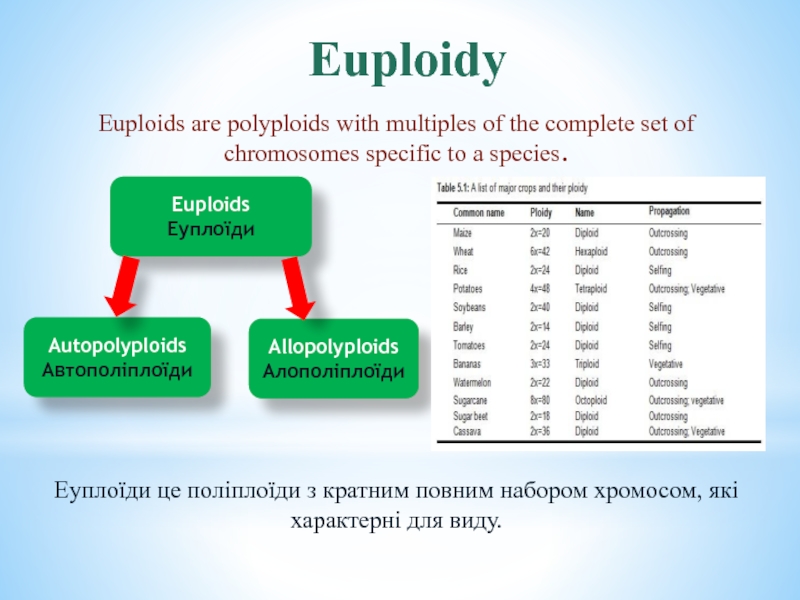
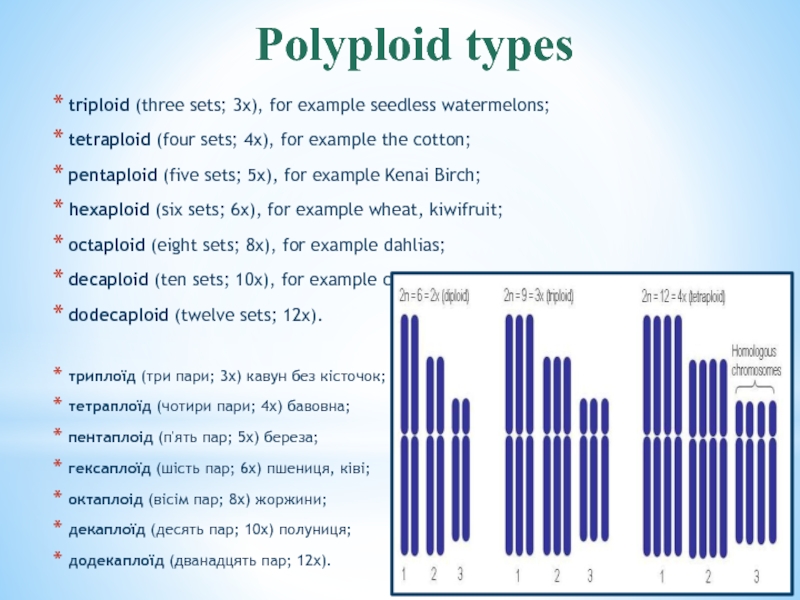
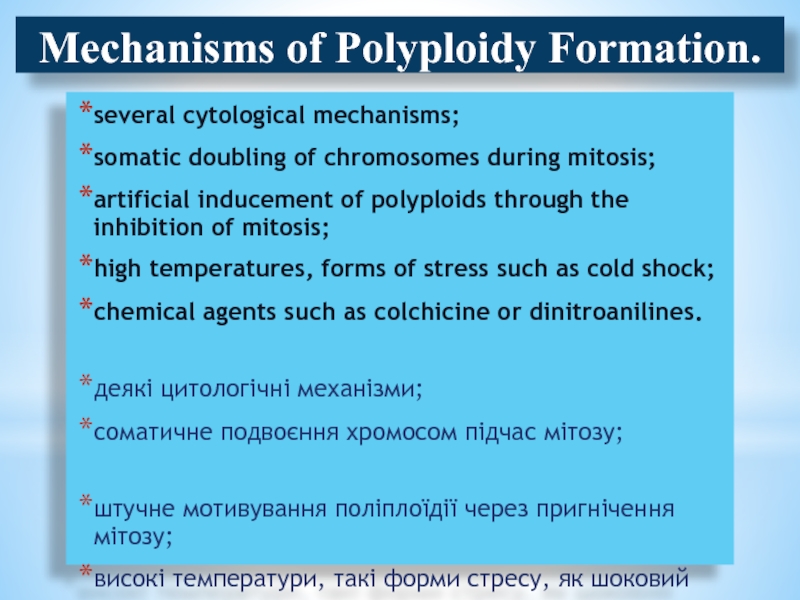
of the diploid number.
Polyploidy is common in nature and provides
a major mechanism for adaptation and speciation.Approximately 50-70% of angiosperms, which include many crop plants, have undergone polyploidy during their evolutionary process.
Поліплоїди це організми з кратними наборами хромосом понад диплоїдне число.
Поліплоїдія поширена в природі і є одним з найважливіших механізмів адаптації та видоутворення.
Приблизно 50-70% покритонасінних, які включають в себе багато культурних рослин, піддавались процесу поліплоїдії під час еволюційного процесу.