Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Psychology and Human Development Lecture 9. Psychosocial Development according
Содержание
- 1. Psychology and Human Development Lecture 9. Psychosocial Development according
- 2. Erickson’s views on social development.Erik Erickson was
- 3. A life-span approach short description.8 stagesEach stage
- 4. Erickson’s stages of psychosocial development.
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. (0-1) Trust vs MistrustIt is a struggle:
- 7. (2-3)Autonomy vs shame and doubt.During this
- 8. (4-5) Initiative vs Guilt (play stage)Developing
- 9. (6-11) Industry vs InferiorityChildren have to learn
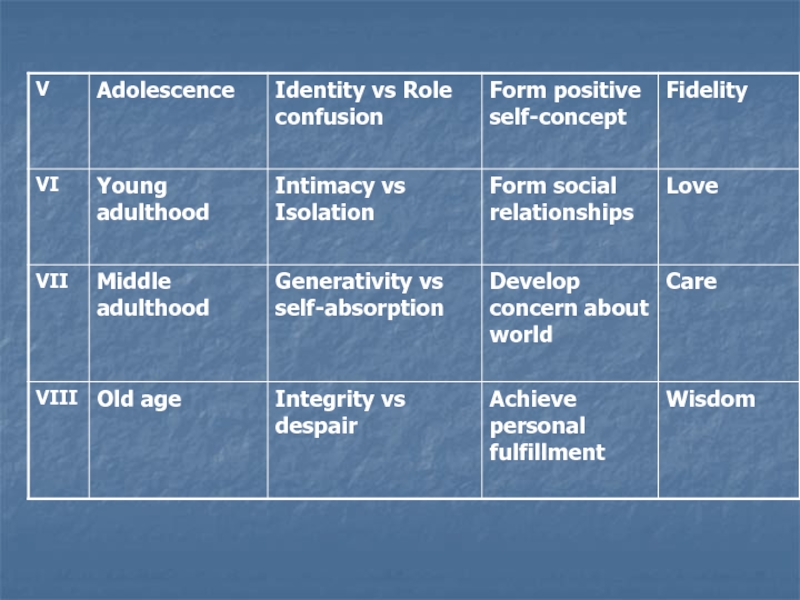
- 10. (11-18) Identity vs role confusionWho am I?They
- 11. (18-35) Intimacy vs IsolationThe challenge of integrating
- 12. (35-60) Generativity vs Self-absorption.The challenge is
- 13. (60- death) Integrity vs Despair. Individuals must
- 14. Evaluation of the Theory.Both Freud and Erickson
- 15. Seminar questions:Give a short description of a
- 16. Скачать презентанцию
Erickson’s views on social development.Erik Erickson was a committed follower of Sigmund Freud but he had his own views on psychoanalytic theory.Main ideas:To form social relationships with other people in life,
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Psychology and Human Development Lecture 9. Psychosocial Development according to Erik
Erickson (1902-1994)
of the theory.Слайд 2Erickson’s views on social development.
Erik Erickson was a committed follower
of Sigmund Freud but he had his own views on
psychoanalytic theory.Main ideas:
To form social relationships with other people in life, a child has to form secure attachment with his mother.
This attachment is very important during the first few years of life
Psychosocial development is seen in 8 stages from birth to death – a life span approach.
Слайд 3A life-span approach short description.
8 stages
Each stage presents a crisis
If
the crisis is successfully met, the person progresses to the
next stageIf the person does not develop the required capacity, there will be problems of varying degrees of severity later on.
Слайд 6(0-1) Trust vs Mistrust
It is a struggle: who to trust
and who not to trust.
Baby has needs – food, warmth,
security.He has to learn who will provide what they need. Learning who to trust allows the infant to develop a sense of security. Children with a strong sense of trust and security develop the confidence to engage with and explore the world.
If infants are loved, they will develop trust for the future. If their life is uncertain, they will develop fear and suspicion of others.
Слайд 7(2-3)Autonomy vs shame
and doubt.
During this stage the child learns
to carry out tasks without the mother’s help and learns
to doubt their abilities (which are new).Encouragement and firm supportive guidance of the parent can help the child develop the skills needed to eat less messily and achieve a strong sense of autonomy (self-confidence for meeting the challenges of growing up). If the parent subjects the child to ridicule and shame, the child develops a strong sense of shame and doubt (suspicious and pessimistic)
Слайд 8(4-5) Initiative vs
Guilt (play stage)
Developing the power to begin
projects on their own.
Children imitate the actions of their parents
in this stage.If parents punish initiatives losing confidence, developing guilt feelings.
Слайд 9(6-11) Industry vs Inferiority
Children have to learn industry, competence, and
persistence at activities which they master.
They learn to be members
of society, who must cooperate with others and channel aggression in acceptable ways (such as in sports). If they do not master the tasks given to them, or severely criticized, they will experience a sense of failure (inferiority)Слайд 10(11-18) Identity vs role confusion
Who am I?
They may imitate other
people, including parents, friends, even teachers.
If these behaviors are conflicting
identity crisis and they must modify their imitations. They must begin to decide what they want to do in life.Слайд 11(18-35) Intimacy vs Isolation
The challenge of integrating one’s whole life
with that of smb else marriage. If a person does
not learn to relate intimately with smb else, he may face isolation and loneliness throughout life.Слайд 12(35-60) Generativity vs
Self-absorption.
The challenge is one of establishing goals,
commitment, and lasting attachments that permit reasonable productivity. The adult
is concerned for his family and with contributing to the world. When the person feels that his own life is the only thing matters self-absorption or stagnation.Слайд 13(60- death) Integrity vs Despair.
Individuals must learn to accept
life as it was lived, with its disappointments as well
as its joys. They need to face death bravely in this final stage.Otherwise, they face despair of believing they are no longer useful and may have indeed missed life altogether.
Слайд 14Evaluation of the Theory.
Both Freud and Erickson believed that we
progress through a series of stages in infancy, which must
be completed for the development of a psychologically healthy personality.The theories explain why we exhibit certain behaviors under stress and consider that the early family experience of a child predicts their future social and psychological outcome.
Слайд 15Seminar questions:
Give a short description of a life-span approach by
E. Erickson.
What does a baby have to learn during the
1 year of life?When and how can a child learn to be autonomous?
What is important to do and not to do during Initiative vs Guilt stage?
Why do children need to learn industry during 5 year period?
What is the developmental psychosocial task for adolescents and how they achieve it?
What will happen to a person who will fail to learn to relate intimately with people?
Describe a middle age crisis.
What should old people learn to reach wisdom?
Why do people exhibit certain behaviors under stress according to Freud and Erikson?