Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
SIW Theme: “Physiology of properties and composition of bile”
Содержание
- 1. SIW Theme: “Physiology of properties and composition of bile”
- 2. PlanIntroductionSignificance of bile in ancient timeSecretion of bileComposition of human bileBile functionsRegulation of bileBiliary excretionPathologyInvestigation of bileConclusionReferences
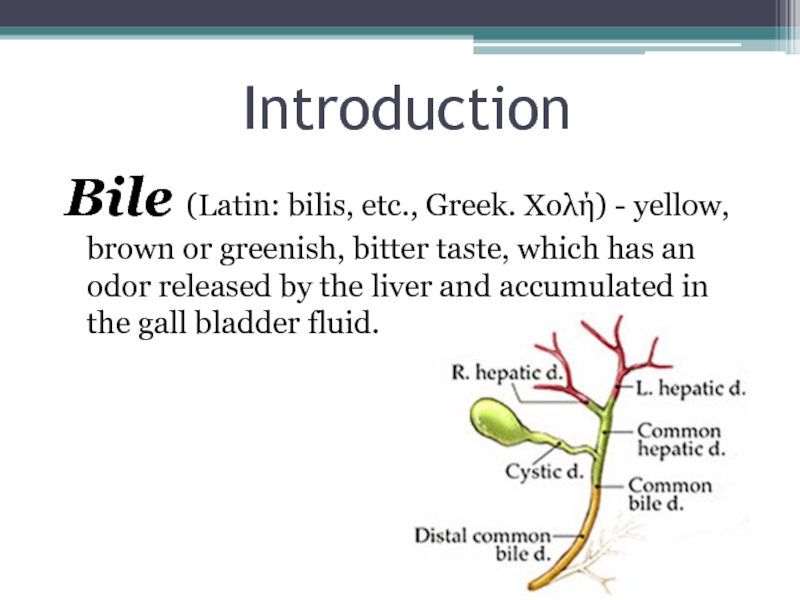
- 3. IntroductionBile (Latin: bilis, etc., Greek. Χολή) - yellow, brown or greenish, bitter taste, which has an odor released by the liver and accumulated in the gall bladder fluid.
- 4. Bile Bile is a composition of the following
- 5. Significance of bile in ancient time In ancient
- 6. Secretion of bileThe main component of bile - bile acids (67%
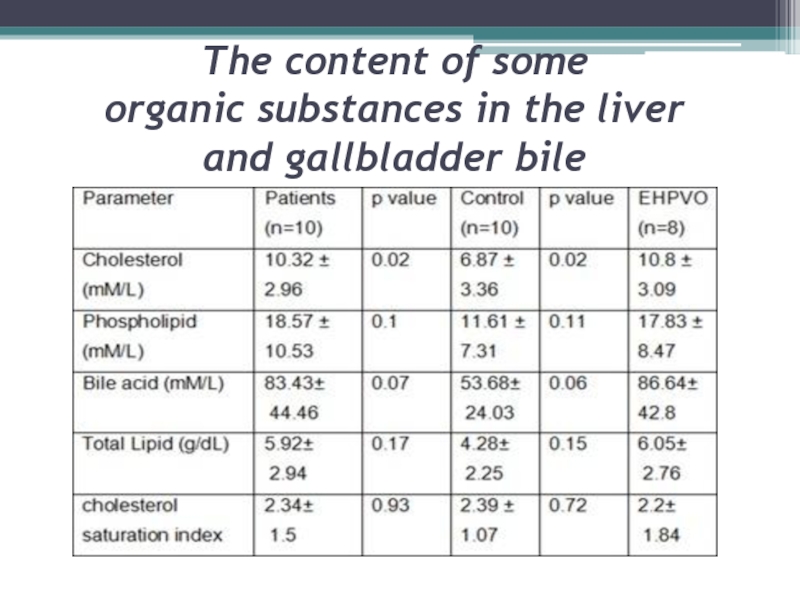
- 7. The content of some organic substances in the liver and gallbladder bile
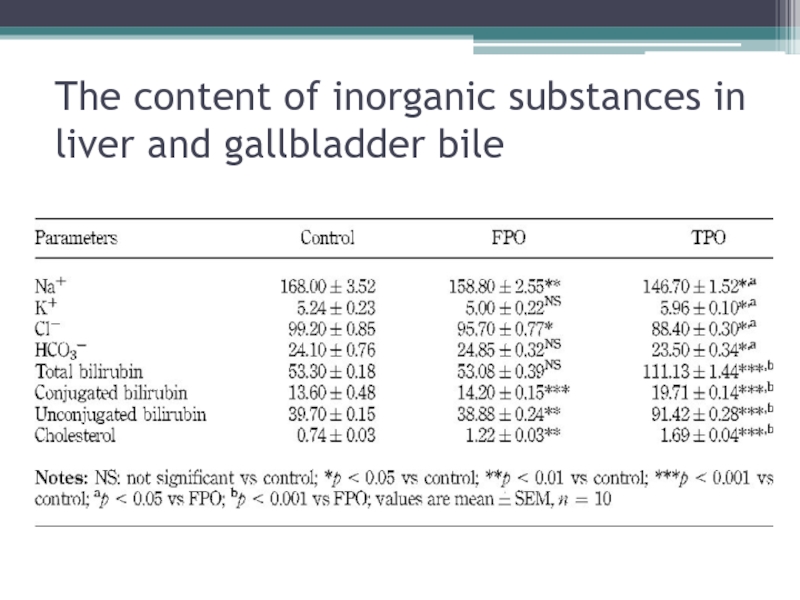
- 8. The content of inorganic substances in liver and gallbladder bile
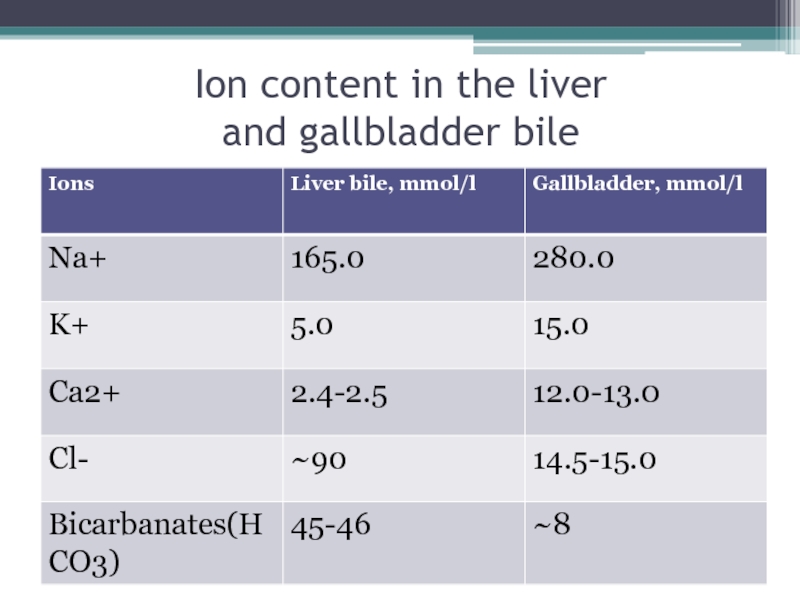
- 9. Ion content in the liver and gallbladder bile
- 10. Secretion of bile22% of bile - phospholipids. In addition, the bile are proteins (immunoglobulins A
- 11. Function of bileBile carries a range of features, most of
- 12. Function of bileBile acids in bile, emulsify fats and participate in micelle formation and
- 13. Regulation of bile Choleresis is continuous, but its intensity changes due
- 14. Bile excretionThe movement of bile in the biliary apparatus due to the
- 15. Bile excretionThe pressure in the biliary secretory apparatus created by the pressure
- 16. For the study of bile used method of fractional duodenal sounding. In carrying
- 17. Normal levels of bileBasal bile (phase I and III, a portion
- 18. What diseases are associated with bileCongenital anomalies of the biliary ductsDamage to the
- 19. ConclusionBile or gall is a bitter-tasting, dark green to yellowish
- 20. Referenceshttp/wikipedia.ruhttp://med4net.ruhttp://medbiol.ruhttp://www.zdorovih.nethttp://www.lib-med.ruhttp://ru.wikipedia.org
- 21. Скачать презентанцию
PlanIntroductionSignificance of bile in ancient timeSecretion of bileComposition of human bileBile functionsRegulation of bileBiliary excretionPathologyInvestigation of bileConclusionReferences
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1
SIW
Theme: “Physiology of properties and composition of bile”
Done by: Iskakbayeva
M., student of 350 group
Слайд 2Plan
Introduction
Significance of bile in ancient time
Secretion of bile
Composition of human
bile
Bile functions
Regulation of bile
Biliary excretion
Pathology
Investigation of bile
Conclusion
References
Слайд 3Introduction
Bile (Latin: bilis, etc., Greek. Χολή) - yellow, brown or greenish, bitter taste, which has an odor released by the
liver and accumulated in the gall bladder fluid.
Слайд 4Bile
Bile is a composition of the following materials: water (85%), bile
salts (10%), mucus and pigments (3%), fats (1%), inorganic salts (0.7%)
and cholesterol (0.3%).Слайд 5Significance of bile in ancient time
In ancient times the bile fluid was considered no less important
than the blood. But if the blood was for the ancient bearer of the soul, the bearer of the
nature of the bile. It was believed that the abundance of light in the body of bile makes the person unstable, gusty. These people were called choleric. But an excess of dark bile supposedly causes depression, gloom, peculiar melancholic. Note: in this and in other word there is the syllable "cold", translated from the Greek “chole ”means bile. It later emerged that the nature of light and dark bile is the same, and neither one nor the other to the nature of man has nothing to do (though still annoying people, called the caustic bile), but has a direct relation to digestion.Слайд 6Secretion of bile
The main component of bile - bile acids (67% - excluding water). Half - primary bile acidscholic and henodezoksiholic.
Secondary: dezoksiholic, lithocholic,and ursodeoxycholic acid alloholic.
Bile acids in
bile is in the form of conjugates (compounds) with glycine and taurine:glikoholic, glikohenodezoksiholic, taurocholic, and other so-called binary acids.
Bile contains a
significant amount of sodium and potassium ions, so that it has an alkaline reaction, and the bile acids and their conjugates are sometimes treated as "bile salts".
Слайд 10Secretion of bile
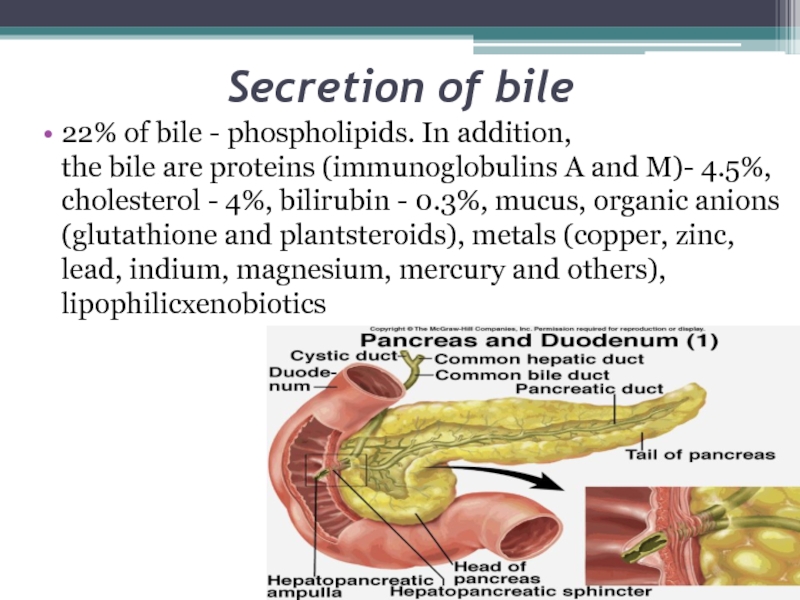
22% of bile - phospholipids. In addition, the bile are proteins (immunoglobulins A and M)- 4.5%, cholesterol -
4%, bilirubin - 0.3%, mucus, organic anions (glutathione and plantsteroids), metals (copper, zinc, lead, indium, magnesium, mercury and others),
lipophilicxenobioticsСлайд 11Function of bile
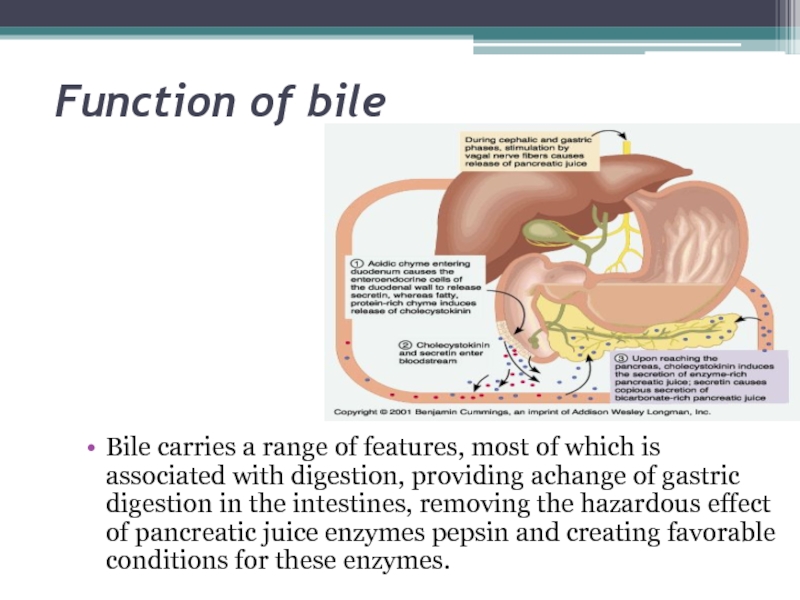
Bile carries a range of features, most of which is associated with digestion,
providing achange of gastric digestion in the intestines, removing the hazardous effect of pancreatic juice enzymes pepsin and creating
favorable conditions for these enzymes.Слайд 12Function of bile
Bile acids in bile, emulsify fats and participate in micelle formation and stimulates motility of the small
intestine, stimulates the production of mucus and gastrointensinalnyhhormones cholecystokinin and secretin, prevent bacterial adhesion and proteinaggregates. Bile is also involved in
the implementation of the excretory function. Cholesterol, bilirubinand other substances can not be filtered by the kidneys and their separation from the body is through the bile. Excreted in the feces 70% located in the bile cholesterol (30%reabsorbed by the intestines), bilirubin, and the above-mentioned metals, steroids, glutathione.Слайд 13Regulation of bile
Choleresis is continuous, but its intensity changes due to regulatory influences. Reinforce the act of
feeding choleresis adopted food. Reflex changes during stimulation of choleresis inner receptors digestive tract and other internal organs and reflex action. Parasympathetic cholinergic nerve
fibers (exposure) increase, and the sympatheticadrenergic - reduce choleresis.Слайд 14Bile excretion
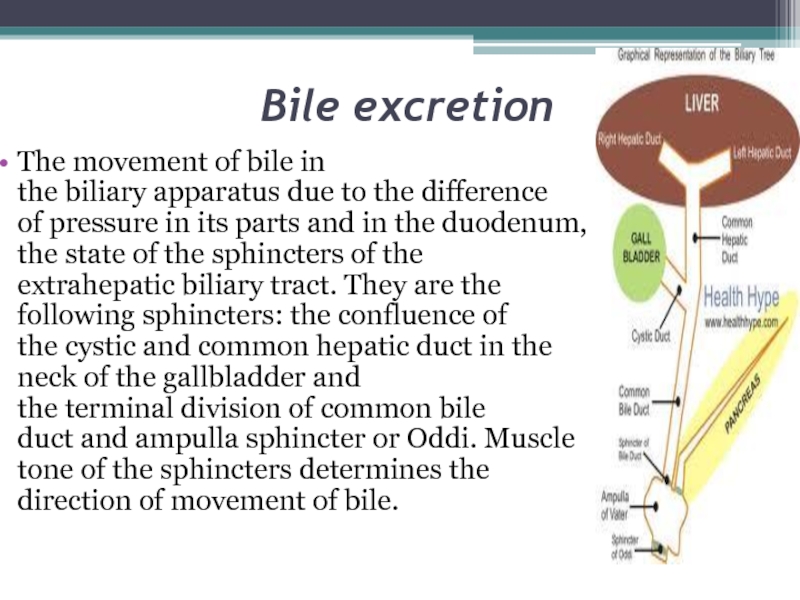
The movement of bile in the biliary apparatus due to the difference of pressure in its parts
and in the duodenum, the state of the sphincters of the extrahepatic biliary tract. They are
the following sphincters: the confluence of the cystic and common hepatic duct in the neck of the gallbladder and the terminal division of common bile duct and ampulla sphincter or Oddi. Muscle tone of the sphincters determines the direction of movement of bile.Слайд 15Bile excretion
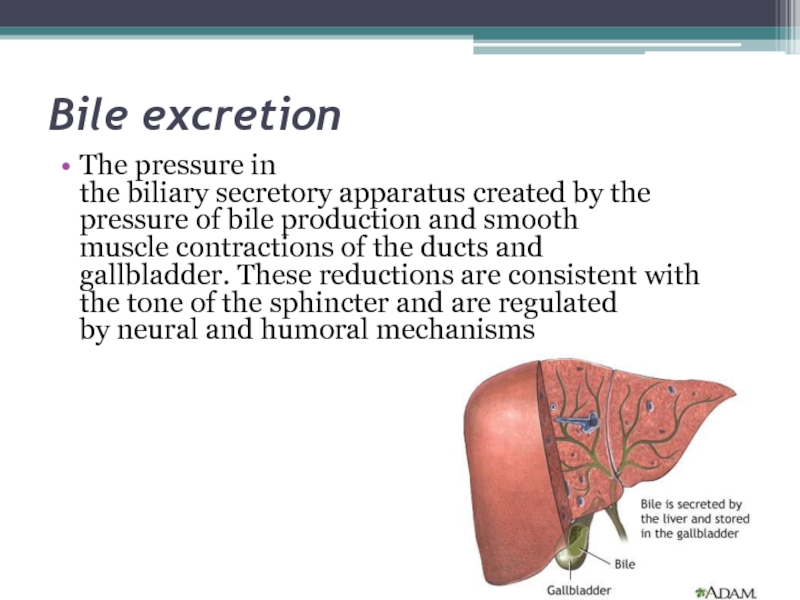
The pressure in the biliary secretory apparatus created by the pressure of bile production and smooth
muscle contractions of the ducts and gallbladder. These reductions are consistent with the tone of
the sphincter and are regulated by neural and humoral mechanismsСлайд 16For the study of bile used method of fractional duodenal sounding. In carrying out the procedure are five phases:
Basal secretion of
bile, during which outlines the contents of the duodenum and common bile duct. Duration 10
- 15 minutes.Closed sphincter of Oddi. Duration 3 - 6 min.
A portion of bile flow duration 3 - 5 minutes. During this time, released from 3 to 5 mllight brown bile. Begins with the opening of the sphincter of Oddi and ends with the opening of the sphincter Lyutkensa. During phases I and III bile released at a rate of 1 - 2ml / min.
Allocation of gallbladder bile. Portia B. It starts with the opening of the sphincterLyutkensa and emptying of the gallbladder, which is accompanied by the appearance ofdark olive bile (portion B), and ends with the appearance of amber-yellow bile (portionC). Duration 20 - 30 minutes.
Allocation of hepatic bile. Portia C. Phase begins from the moment of discontinuation ofa dark olive-bile. Duration 10 - 20 minutes. Facts Serving Size 10 - 30 ml.
Слайд 17Normal levels of bile
Basal bile (phase I and III, a portion of A) should be transparent, have
a pale straw color, density, 1007-1015, to be slightly alkaline.
Cystic bile (phase IV, a portion of B) must be transparent, have
a dark olive color, density, 1016-1035, acidity - pH 6.5-7.5.Hepatic bile (phase V, a portion of C) should be transparent, have a golden color, density, 1007-1011, acidity - pH 7,5-8,2.