Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Soil Morphology and Classification
Содержание
- 1. Soil Morphology and Classification
- 2. E horizonA horizonB horizon(Illuvial)(Elluvial)C horizonR horizonO horizonMaster HorizonsB horizonEnough information?
- 3. Sub-horizon designations
- 4. Sub-horizon designationsp – plowing/disturbancet – clay accumulationg
- 5. Subordinate distinction (p = plowed)Disturbed surface horizon
- 6. Subordinate distinction (t = clay accumulation)Translocation of
- 7. Subordinate distinction (g = gleying)Oxygen deprived or
- 8. Subordinate distinction (h = organic accumulation) Accumulation
- 9. Subordinate distinction (w = color or stucture)Non-illuvial
- 10. Subordinate distinction (o = oxic horizon)Low activity claysFew weatherable materialsLittle rock structureFe and Al oxides
- 11. Subordinate distinctions g – gleying h –
- 12. Subordinate distinctions and Organic Matter
- 13. Subordinate distinction (a, e, i)Denotes the degree
- 14. SummaryMaster: O, A, E, B, C, RSub
- 15. Other Designations
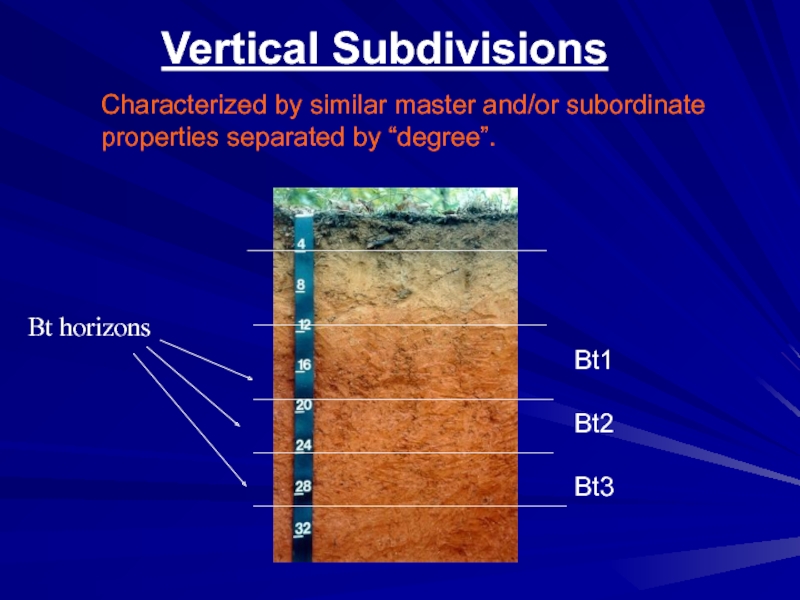
- 16. Vertical SubdivisionsCharacterized by similar master and/or subordinateproperties separated by “degree”.Bt1Bt2Bt3
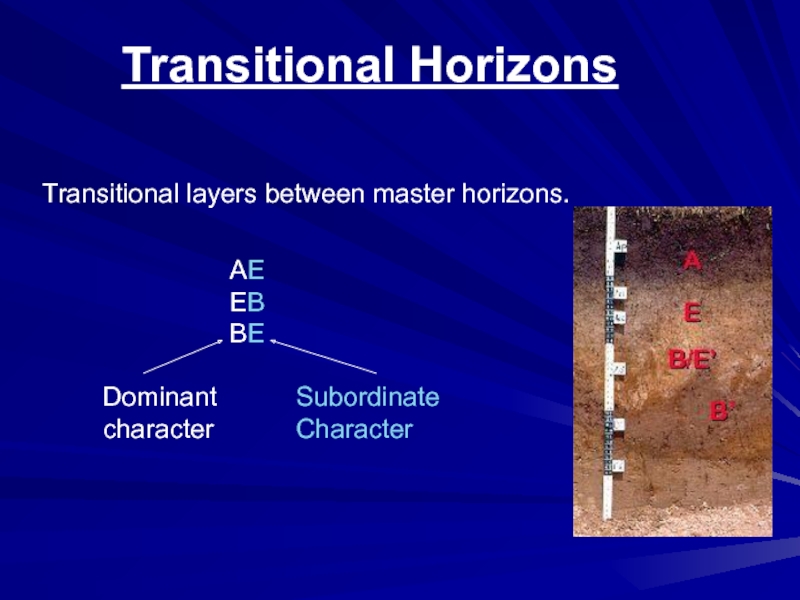
- 17. Transitional HorizonsTransitional layers between master horizons.AEEBBEDominantcharacterSubordinateCharacter
- 18. SynthesisApAEEBhBtg1Btg2
- 19. Soil Taxonomy
- 20. Soil Classification/TaxonomyBased on soil profile characteristics andthe
- 21. Soil Classification/Taxonomy Adamsville: Hyperthermic, uncoated Aquic QuartzipsammentUSDA classification systemSoil Survey Staff 1965Soil Taxonomy published 1975
- 22. OrderSuborderGreat groupSub groupFamilySeries1219,000Soil Taxonomy Hierarchy6325014008000KingdomPhylumClassOrder FamilyGenusSpecies
- 23. Units for Soil ClassificationPedon – smallest three-dimensional
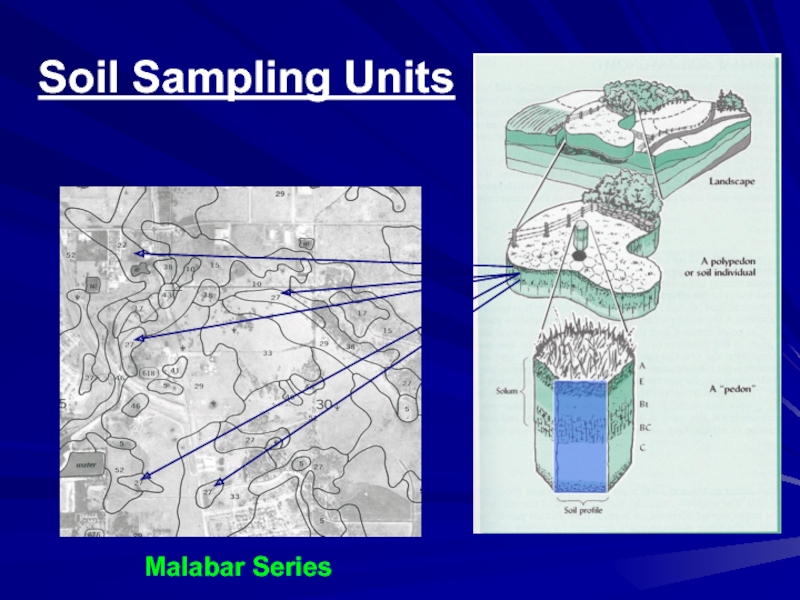
- 24. Soil Sampling Units
- 25. Diagnostic HorizonsSurfaceSubsurface
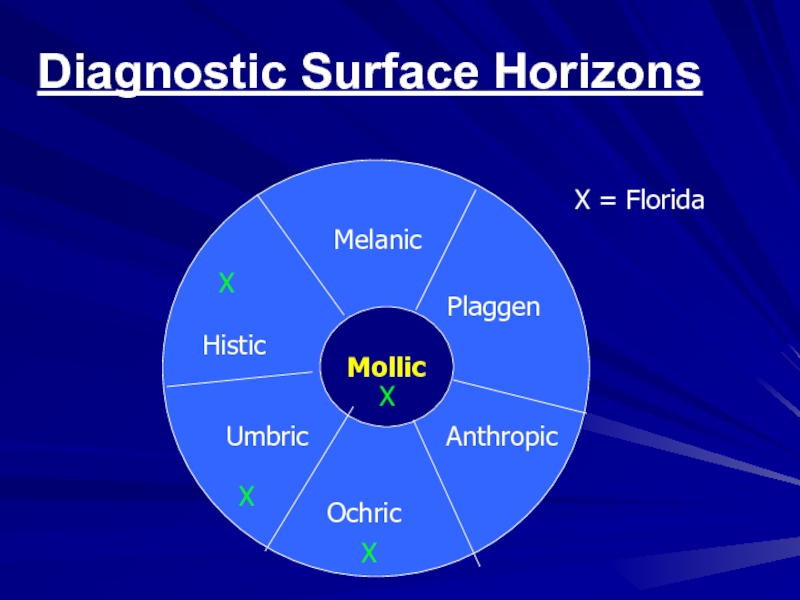
- 26. Diagnostic Surface HorizonsEpipedonsMollicUmbricOchricHisticMelanicPlaggenAnthropic
- 27. MollicHisticUmbricOchricMelanicPlaggenAnthropicXXXXX = FloridaDiagnostic Surface Horizons
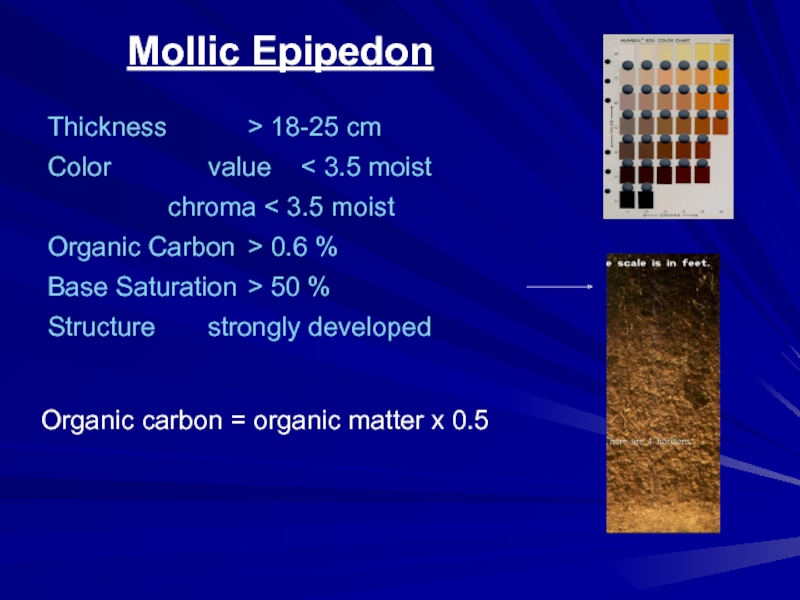
- 28. Mollic EpipedonThickness > 18-25 cmColor value < 3.5
- 29. View Tim Kiser's mapTaken in Elkhart, Iowa (See more photos here)41°27' 04" N, 93°31' 52" W41.451073-93.530988
- 30. Umbric EpipedonMeets all criteria of the Mollic epipedon,except base saturation < 50%Chemically different than Mollic
- 31. Ochric EpipedonToo: thin
- 32. Histic EpipedonOrganic horizonFormed in wet areasBlack to
- 33. Melanic EpipedonSimilar in properties to MollicFormed in volcanic ashLightweight, Fluffy
- 34. Anthropic Horizon Resembles mollic (color, o.m.) Use by humans Shells and bones Water from humans
- 35. Plaggen EpipedonProduced by long-term (100s yrs.) manuringOld, human-made surface horizonAbsent in U.S.> 50 cm thick
- 36. Diagnostic Surface HorizonsEpipedonsMollicUmbricOchricHisticMelanicPlaggenAnthropicVery commonHuman-derived“specialized”
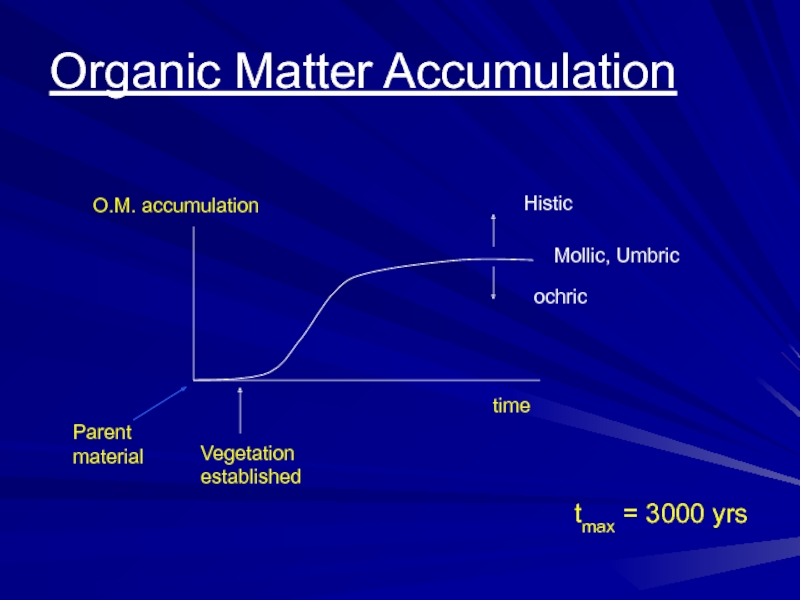
- 37. VegetationestablishedO.M. accumulationtimeOrganic Matter AccumulationParentmaterialtmax = 3000 yrs
- 38. Diagnostic Sub-surface Horizons
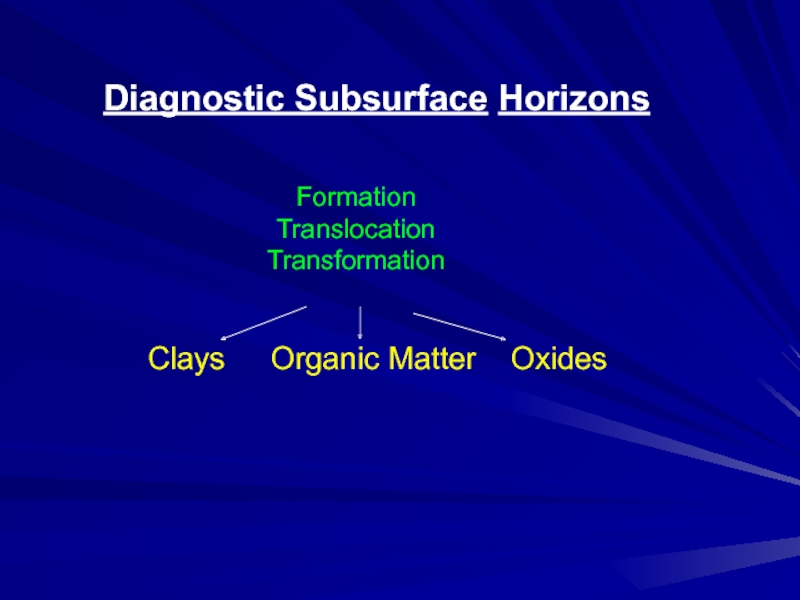
- 39. Diagnostic Subsurface HorizonsClays Organic Matter OxidesFormationTranslocationTransformation
- 40. Organic Matter Clays OxidessmectitesSubsurface HorizonsKaoliniteAlso: salts, carbonates, sulfidesDark colorsMetals (Fe, Al)IronAluminumFormationTranslocationTransformation
- 41. Diagnostic Subsurface HorizonsAlbicArgillicSpodic OxicCambicKandicSombricsulfuricNatricAgricCalcic GypsicSalicDuripanFragipanPlacicSub-Horizon Designations
- 42. Diagnostic Subsurface HorizonsAlbic (white) HorizonLight-colored (Value >
- 43. Argillic HorizonIlluvial accumulation of silicate clays Illuvial based on overlying horizonClay bridgesClay coatingsDiagnostic Subsurface Horizons
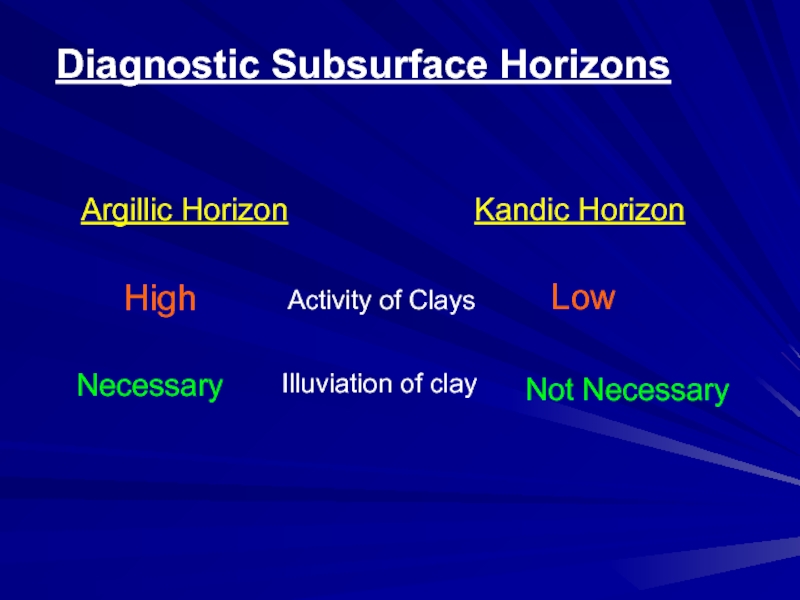
- 44. Diagnostic Subsurface HorizonsArgillic HorizonKandic HorizonActivity of ClaysHigh LowIlluviation of clayNecessaryNot Necessary
- 45. Diagnostic Subsurface HorizonsSpodic HorizonSpodic Illuvial accumulation of
- 46. Elluviation (E horizon)Organic matterClaysSpodic horizonBh horizonBt horizonArgillic horizonElluviation and IlluviationAEBhABtE
- 47. Diagnostic Subsurface HorizonsOxic horizon Highly weathered (high
- 48. AlbicKandicArgillicSpodic OxicDiagnostic HorizonsMollicUmbricOchricHisticMelanicPlaggenAnthropicEpipedonsSubsurface
- 49. Soil TaxonomyDiagnostic EpipedonsDiagnostic Subsurface horizonsMoisture RegimesTemperature Regimes
- 50. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2E horizon
A horizon
B horizon
(Illuvial)
(Elluvial)
C horizon
R horizon
O horizon
Master Horizons
B horizon
Enough information?
Слайд 4Sub-horizon designations
p – plowing/disturbance
t – clay accumulation
g – gleying
h –
illuvial organic matter
distinctions within master horizonsСлайд 5Subordinate distinction (p = plowed)
Disturbed surface horizon (cultivation, pasture, forestry)
Used
with the A master horizon (e.g. Ap horizon)
Ap horizon
Слайд 6Subordinate distinction (t = clay accumulation)
Translocation of clay or formed
in place
Coatings or discrete
Used with the B master horizon (e.g.
Bt)If reduced, can be used with the g sub horizon (Btg)
*
Слайд 7Subordinate distinction (g = gleying)
Oxygen deprived or reduced state due
to water saturation.
Reduction of iron (Fe III to Fe
II)low chroma
Often used with B master horizon (Bg horizon), also E and C horizon.
gleyed
material
oxidized
material
oxidized
Fe3+
Fe2+
Слайд 8Subordinate distinction (h = organic accumulation)
Accumulation of illuvial organic
matter-metal complexes
Coatings on sand and discrete particles
h =
“humic”value and chroma approximately 3 or less
Used with the B master horizon (e.g. Bh horizon)
Bh horizon
“spodic horizon”
*
Слайд 9Subordinate distinction (w = color or stucture)
Non-illuvial development
of color
or structure
“w” can = “weak”
Commonly used with the
B master
horizon (e.g. Bw)Bw
Слайд 10Subordinate distinction (o = oxic horizon)
Low activity clays
Few weatherable materials
Little
rock structure
Fe and Al oxides
Слайд 11Subordinate distinctions
g – gleying
h – illuvial organic matter
p – plowing/disturbance
t – clay accumulation
w – development
of color/structureo – oxic
Слайд 13Subordinate distinction (a, e, i)
Denotes the degree of organic matter
decomposition
in the O horizon.
Oa – highly decomposed (sapric)
Oe – moderately
decomposed (hemic)Oi – slightly decomposed (fibric)
Sapric –most decomposed, low plant fiber, low water content
Hemic – intermediate decompostion
Fibric – least decomposed, recognizable fibers
Слайд 14Summary
Master: O, A, E, B, C, R
Sub horizon symbols: g,
h, p, t, w and a,e,i
Examples: Oa, Oe, Oi
Bt
Bg
Btg
Bw
Ap
Слайд 16Vertical Subdivisions
Characterized by similar master and/or subordinate
properties separated by “degree”.
Bt1
Bt2
Bt3
Слайд 17Transitional Horizons
Transitional layers between master horizons.
AE
EB
BE
Dominant
character
Subordinate
Character
Слайд 20Soil Classification/Taxonomy
Based on soil profile characteristics and
the concept of soils
as a natural body.
Observable properties: color, texture, structure,
pH, O.M…Soil Profile
Hierarchical
Genesis
1883 V.V. Dukachaev: climate, vegetation, soil
1927 C.F. Marbut (USDA) applied to U.S. (1965)
Слайд 21Soil Classification/Taxonomy
Adamsville: Hyperthermic, uncoated Aquic Quartzipsamment
USDA classification system
Soil Survey
Staff 1965
Soil Taxonomy published 1975
Слайд 22Order
Suborder
Great group
Sub group
Family
Series
12
19,000
Soil Taxonomy Hierarchy
63
250
1400
8000
Kingdom
Phylum
Class
Order
Family
Genus
Species
Слайд 23Units for Soil Classification
Pedon – smallest three-dimensional unit that displays
the full range of properties characteristic of
a given
soil. (1-10 m2 of area)- the fundamental unit of soil classification
Polypedon – group of closely associated pedons in the field
Soil Series – class of soils world-wide which share a common
suite of soil profile properties
Слайд 28Mollic Epipedon
Thickness > 18-25 cm
Color value < 3.5 moist
chroma < 3.5
moist
Organic Carbon > 0.6 %
Base Saturation > 50 %
Structure strongly developed
Organic carbon =
organic matter x 0.5Слайд 29View Tim Kiser's map
Taken in Elkhart, Iowa (See more photos
here)
41°27' 04" N, 93°31' 52" W41.451073-93.530988
Слайд 30Umbric Epipedon
Meets all criteria of the Mollic epipedon,
except base saturation
< 50%
Chemically different than Mollic
Слайд 32Histic Epipedon
Organic horizon
Formed in wet areas
Black to dark brown
Low bulk
density
20-30 cm thick
Organic = > 20% - 35%
O.M.(water saturation, clay content)
Слайд 34Anthropic Horizon
Resembles mollic
(color, o.m.)
Use by humans
Shells and bones
Water from humans
Слайд 35Plaggen Epipedon
Produced by long-term (100s yrs.) manuring
Old, human-made surface horizon
Absent
in U.S.
> 50 cm thick
Слайд 36Diagnostic Surface Horizons
Epipedons
Mollic
Umbric
Ochric
Histic
Melanic
Plaggen
Anthropic
Very common
Human-derived
“specialized”
Слайд 37Vegetation
established
O.M. accumulation
time
Organic Matter Accumulation
Parent
material
tmax = 3000 yrs
Слайд 39Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons
Clays Organic Matter Oxides
Formation
Translocation
Transformation
Слайд 40Organic Matter Clays Oxides
smectites
Subsurface Horizons
Kaolinite
Also:
salts, carbonates, sulfides
Dark colors
Metals (Fe, Al)
Iron
Aluminum
Formation
Translocation
Transformation
Слайд 41Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons
Albic
Argillic
Spodic
Oxic
Cambic
Kandic
Sombric
sulfuric
Natric
Agric
Calcic
Gypsic
Salic
Duripan
Fragipan
Placic
Sub-Horizon Designations
Слайд 42Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons
Albic (white) Horizon
Light-colored (Value > 6 moist )
Elluvial
(E master horizon*)
Low in clay, Fe and Al oxides
Generally sandy
texturedLow chemical reactivity (low CEC)
Typically overlies Bh or Bt horizons
albic
*not all E horizons are albic horizons
Слайд 43Argillic Horizon
Illuvial accumulation of silicate clays
Illuvial based on overlying
horizon
Clay bridges
Clay coatings
Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons
Слайд 44Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons
Argillic Horizon
Kandic Horizon
Activity of Clays
High
Low
Illuviation of clay
Necessary
Not
Necessary
Слайд 45Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons
Spodic Horizon
Spodic
Illuvial accumulation of organic matter
and aluminum (+/- iron)
Dark colored (value, chroma < 3)
Low base saturation (acidic)Formed under humid acid conditions
Слайд 46Elluviation (E horizon)
Organic matter
Clays
Spodic horizon
Bh horizon
Bt horizon
Argillic horizon
Elluviation and Illuviation
A
E
Bh
A
Bt
E
Слайд 47Diagnostic Subsurface Horizons
Oxic horizon
Highly weathered (high temperatures, high rainfall)
-
High in Fe, Al oxides
- High in low-activity clays (kaolinite
< smectite < vermiculite)activity