Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
STRATEGY OF TREATMENT OF Presented by : Niraj Maheshwari & Shweta
Содержание
- 1. STRATEGY OF TREATMENT OF Presented by : Niraj Maheshwari & Shweta
- 2. Overview of Pulmonary HypertensionPulmonary hypertension is a
- 3. Overview of Pulmonary HypertensionA hallmark of pulmonary
- 4. Overview of Pulmonary HypertensionNB:Pulmonary Artery Hypertension (PAH)
- 5. Spotting the difference!
- 6. Pulmonary Hypertension Classification Once diagnosed with pulmonary hypertension,
- 7. Most Commonly Experienced symptoms in Pulmonary Hypertension
- 8. Pulmonary Artery Hypertension (PAH)Pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH)
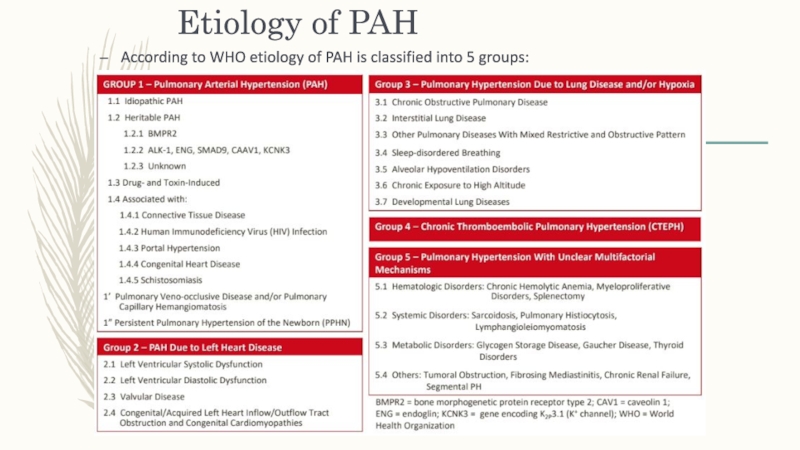
- 9. Etiology of PAHAccording to WHO etiology of PAH is classified into 5 groups:
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. Treatment StrategiesAs it is known and established
- 12. Group 1 Treatment StrategyGroup 1 PH, or
- 13. Group 1 Treatment StrategyThe current treatment strategy
- 14. Group 2 (Due to Left Heart Disease) - Pathogenesis++→+
- 15. Group 2 (Due to Left Heart Disease)
- 16. Group 3 (Due to Lung Diseases) -
- 17. Group 3 (Due to Lung Diseases) –
- 18. Group 4 (Due to Chronic Thromboembolic Hypertension)
- 19. Group 5 (Due to Multifactorial mechanisms) –
- 20. Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAHBlood
- 21. Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAHEndothelin
- 22. Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAHHigh-dose
- 23. Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAHAnticoagulants. Your
- 24. Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAHOxygen
- 25. Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAHAdvanced
- 26. Pulmonary Venous Hypertension (PVH) PVH can occur as
- 27. Treatment Strategy for PVHWith PVH, treatment is
- 28. Can Combination Therapy (CT) be used as
- 29. Can Surgeries prove to be helpful as
- 30. Can Surgeries prove to be helpful as
- 31. SUMMARY OF TREATMENT STRATEGIESRight Heart FailureUse diuretics,
- 32. Скачать презентанцию
Overview of Pulmonary HypertensionPulmonary hypertension is a type of high blood pressure that affects the arteries in your lungs and the right side of your heart.The disease is defined hemodynamically as
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1STRATEGY OF TREATMENT OF
Presented by : Niraj Maheshwari & Shweta
Burange
Olga Georgievna GoryachevaСлайд 2Overview of Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary hypertension is a type of high
blood pressure that affects the arteries in your lungs and
the right side of your heart.The disease is defined hemodynamically as a mean pulmonary artery pressure ≥ 25 mmHg at rest.
Some forms of pulmonary hypertension are serious conditions that become progressively worse and are sometimes fatal.
Although some forms of pulmonary hypertension aren't curable, treatment can help lessen symptoms and improve your quality of life.
Слайд 3Overview of Pulmonary Hypertension
A hallmark of pulmonary hypertension is an
increased pulmonary vascular resistance which leads to progressive elevations in
pulmonary artery pressure, resulting in compensatory right ventricular hypertrophy and, ultimately, heart failure.Common pathogenic features of pulmonary hypertension include sustained pulmonary vasoconstriction, vascular remodeling of the small pulmonary arteries, in situ thrombosis, and increased vascular wall stiffness, resulting in increased pulmonary arterial pressure due to increased pulmonary vascular resistance.
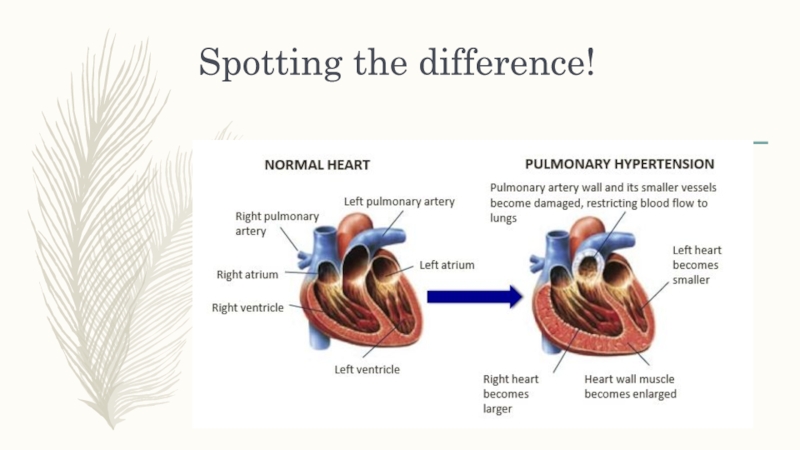
Слайд 4Overview of Pulmonary Hypertension
NB:
Pulmonary Artery Hypertension (PAH) and Pulmonary Venous
Hypertension (PVH) are included in the category of Pulmonary Hypertension
(PH)PVH
PH
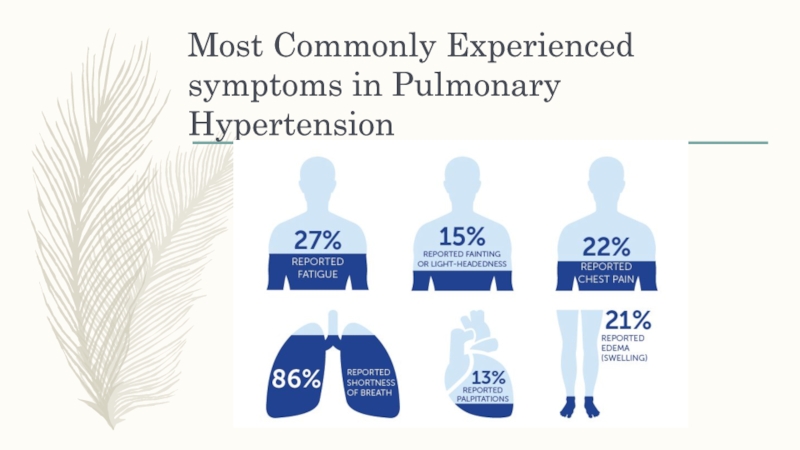
Слайд 6Pulmonary Hypertension Classification
Once diagnosed with pulmonary hypertension, your doctor might
classify the severity of your disease into one of several
classes, including:Class I. No strong symptoms with normal activity.
Class II. No symptoms at rest but with little physical activity arises symptoms like fatigue, dyspnoea, and chest pain.
Class III. No symptoms at rest but presented with strong symptoms during physical activity.
Class IV. Symptoms present during physical activity and while at rest.
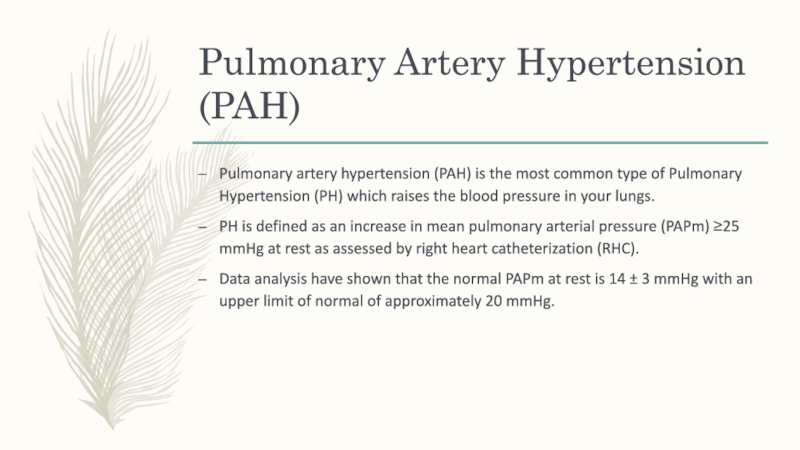
Слайд 8Pulmonary Artery Hypertension (PAH)
Pulmonary artery hypertension (PAH) is the most
common type of Pulmonary Hypertension (PH) which raises the blood
pressure in your lungs.PH is defined as an increase in mean pulmonary arterial pressure (PAPm) ≥25 mmHg at rest as assessed by right heart catheterization (RHC).
Data analysis have shown that the normal PAPm at rest is 14 ± 3 mmHg with an upper limit of normal of approximately 20 mmHg.
Слайд 11Treatment Strategies
As it is known and established for decades now,
that the permanent treatment of PAH is not possible.
So mostly
only palliative care treatment is provided for the expected result of better life expectancy for suffering individuals.That is why, we will be looking towards the treatment strategies based upon the well defined criteria of WHO of groups.
It often takes some time to find the most appropriate treatment for pulmonary hypertension. The treatments are often complex and require extensive follow-up care.
When pulmonary hypertension is caused by another condition, it is important to treat the underlying cause whenever possible.
Слайд 12Group 1 Treatment Strategy
Group 1 PH, or PAH, is a
category of diseases with the shared features of progressively increased
Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (PVR) due to obstructive changes within the pulmonary vasculature.The treatment specifically include the treatment of the underlying causes, that is treating the primary diseases which causes the secondary effect of Pulmonary Hypertension.
The treatment process of PAH patients cannot be considered as a mere prescription of drugs, but is characterised by a complex strategy that includes the initial evaluation of severity and the subsequent response to treatment.
Слайд 13Group 1 Treatment Strategy
The current treatment strategy for PAH patients
can be divided into three main steps:
The initial approach includes
general measures, and supportive therapy (oral anticoagulants, diuretics, O2, digoxin)The second step includes initial therapy with high-dose CCB in vaso-reactive patients or drugs approved for PAH in non-vaso-reactive patients according to the prognostic risk of the patient and the grade of recommendation and level of evidence for each individual compound or combination of compounds.
The third part is related to the response to the initial treatment strategy; in the case of an inadequate response, the role of combinations of approved drugs and lung transplantation are proposed.
Слайд 15Group 2 (Due to Left Heart Disease) - Treatment
The primary
goal of therapy in PH-LHD must be to improve global
management of the underlying condition prior to considering specific measures to treat PH.Systolic HF
Use: ACE inhibitors; β-blockers; diuretics
Possibly: cardiac resynchronization, implantable cardioverter defibrillator placement.
PH secondary to left valvular heart disease
Evaluation for correction of valvular disease
Слайд 16Group 3 (Due to Lung Diseases) - Examples
Group 3 (PH
due to lung diseases and/or hypoxaemia):
Mild PH is common
in both severe interstitial lung disease and severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).Whereas, severe PH is uncommon, and severe PH can be seen in the combined emphysema/fibrosis syndrome, where the prevalence of PH is high.
Слайд 17Group 3 (Due to Lung Diseases) – Treatment Strategy
Currently there
is no specific therapy for PH associated with lung diseases,
but these measures can be followed:Optimize treatment of underlying cause
Sleep apnea
COPD (Long term O2 Therapy)
Idiopathic lung disease
Use supplemental oxygen to avoid hypoxia
Enroll in pulmonary rehabilitation
Don’t use PAH therapy in PH due to lung disease
Слайд 18Group 4 (Due to Chronic Thromboembolic Hypertension) – Treatment Strategy
Prevention
of recurrent clot / embolism (anticoagulation)
Antiplatelet drugs; such as aspirin,
clopidogrel, dipyridamole.Pulmonary thromboendarterectomy (PTE)
Refer to center experienced in procedure and postop
Improves symptoms in most patients
Surgical mortality at experienced centers: <5%
Слайд 19Group 5 (Due to Multifactorial mechanisms) – Treatment Strategy
PH with
unclear and/or multifactorial mechanisms includes several disorders with multiple patho-aetiologies.
A common feature of these diseases is that the mechanisms of PH are poorly understood.These patients need careful diagnosis. Treatment is tailored for that diagnosis, ie. treatment of PH is secondary.
Слайд 20Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAH
Blood vessel dilators (vasodilators):
Vasodilators open narrowed blood vessels, and one of the most
commonly prescribed vasodilators for pulmonary hypertension is epoprostenol (Flolan)Another form of the drug, iloprost (Ventavis), can be inhaled 6-9 times a day through a nebulizer, a machine that vaporizes your medication. Because it's inhaled, it goes directly to the lungs. Side effects associated with iloprost include chest pain which is often accompanied by a headache and nausea and breathlessness.
Treprostinil (Tyvaso, Remodulin, Orenitram), another form of the drug, can be given 4 times a day. It can be inhaled, taken as oral medication or administered by injection. It can cause side effects such as a headache, nausea and diarrhea.
Слайд 21Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAH
Endothelin receptor antagonists: These medications
reverse the effect of endothelin, a substance in the walls
of blood vessels that causes them to narrow.These medications include bosentan (Tracleer), macitentan (Opsumit), and ambrisentan (Letairis).
Sildenafil and tadalafil (Phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors (PDE5 inhibitors):
Sildenafil (Viagra) and tadalafil (Cialis) are sometimes used to treat pulmonary hypertension.
These drugs work by opening the blood vessels in the lungs to allow blood to flow through more easily. Side effects can include an upset stomach, headache and vision problems.
Слайд 22Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAH
High-dose calcium channel blockers. These
drugs help relax the muscles in the walls of the
blood vessels. They include medications such as amlodipine (Norvasc), diltiazem (Cardizem, Tiazac, others) and nifedipine (Procardia, others).However, it is effective for the treatment of PH but only few number of people actually respond to them.
Soluble guanylate cyclase (SGC) stimulator. Soluble guanylate cyclase (SGC) stimulators (Adempas) interact with nitric oxide and help relax the pulmonary arteries and lower the pressure within the arteries.
They can sometimes cause dizziness or nausea.
Слайд 23Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAH
Anticoagulants. Your doctor is likely
to prescribe the anticoagulant warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven) to help prevent
the formation of blood clots within the small pulmonary arteries. Because anticoagulants prevent normal blood coagulation, they increase your risk of bleeding complications.Digoxin. Digoxin (Lanoxin) can help the heart beat stronger and pump more blood. It can help control the heart rate if you experience arrhythmias.
Diuretics. Commonly known as water pills, these medications help eliminate excess fluid from your body. This reduces the amount of work your heart has to do. They may also be used to limit fluid buildup in your lungs.
Слайд 24Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAH
Oxygen Therapy: Your doctor might
suggest that you sometimes breathe pure oxygen, a treatment known
as oxygen therapy, to help treat pulmonary hypertension, especially if you live at a high altitude or have sleep apnea.Exercise: When medically supervised, exercise can help patients improve symptoms that include shortness of breath (dyspnea); fatigue; dizziness or fainting spells (syncope); pressure or pain in the chest.
Even patients with severe PH can see improvement from exercise because toned muscles use oxygen more efficiently than flaccid muscles.
Слайд 25Recommended Drugs for the Treatment of PAH
Advanced therapies
Endothelin Antagonists (for
lower risk patients)
Phosphodiesterase-5 Inhibitors (for lower risk patients)
Prostacyclins (for higher
risk patients)Слайд 26Pulmonary Venous Hypertension (PVH)
PVH can occur as a common complication
of any type of left heart disease. One example is
as a complication of mitral valve disease.Pulmonary venous hypertension (PVH) is associated with high blood pressure in the veins of the lungs (pulmonary vein) due to the lungs being unable to efficiently carry blood to the heart.
Слайд 27Treatment Strategy for PVH
With PVH, treatment is focused on treating
the underlying cause of the disease.
For example, surgery to repair
or replace a faulty mitral valve can be an option. Medications such as beta blockers and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors may be used to prevent congestive heart failure.
Слайд 28Can Combination Therapy (CT) be used as a treatment strategy?
Sequential
addition of advanced therapies: as current model
Initial therapy: based on
illness severity + functional classIf PAH worsens: add therapies until treatment goals are met
Approach shown to improve 6-min walking distance test.
Combination therapy: Can be used
Optimum and safest approaches not yet established
Investigations ongoing
Слайд 29Can Surgeries prove to be helpful as treatment strategy for
PH?
Atrial septostomy. If medications don't control the pulmonary hypertension, this open-heart
surgery might surely be considered as an option.In an atrial septostomy, an opening is created between the left and right atrium to relieve the pressure on the right side of the heart.
Atrial septostomy can have serious complications, including heart rhythm abnormalities (arrhythmias), but it has proven to be helpful.
Слайд 30Can Surgeries prove to be helpful as treatment strategy for
PH?
Transplantation. In some cases, a lung or heart-lung transplant might be
considered as an option, especially for younger people who have idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension.Major risks of any type of transplantation include rejection of the transplanted organ and serious infection, and immunosuppressant drugs must be administered for life to help reduce the chance of rejection.
Слайд 31SUMMARY OF TREATMENT STRATEGIES
Right Heart Failure
Use diuretics, Na restriction
PH
due to left heart or chronic hypoxemic lung disease
Treat underlying
disorders (not PH primarily)Chronic thromboembolic PH
Use anticoagulants
PAH
Perform right heart catheterization with vasodilator test
Don’t treat empirically with calcium-channel blockers
Advanced therapies: prostacyclin's, endothelin-receptor antagonists,
Evaluate need for supplemental oxygen
Lung transplantation: In nonresponsive advanced disease