Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Sylvian Fissure
Содержание
- 1. Sylvian Fissure
- 2. Sylviun fissure, to whom we owe,
- 3. DefinitionThe sylvian fissure ,is the most distinct
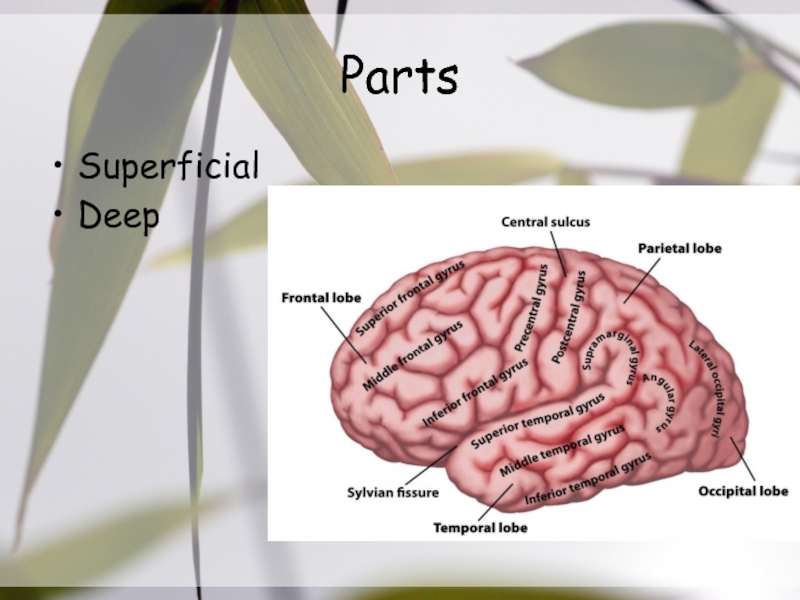
- 4. PartsSuperficialDeep
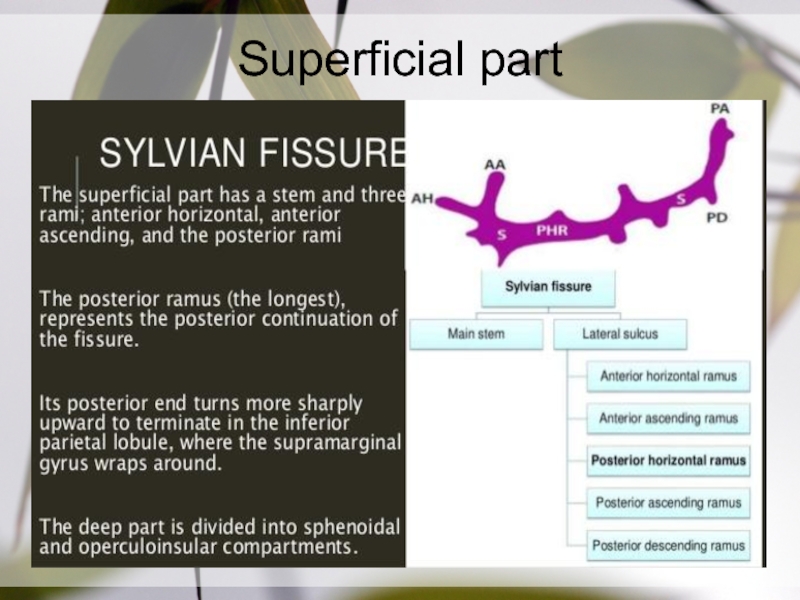
- 5. Superficial part
- 6. Deep Part (Sylvian Cistern)SphenoidalOperculoinsular compartment
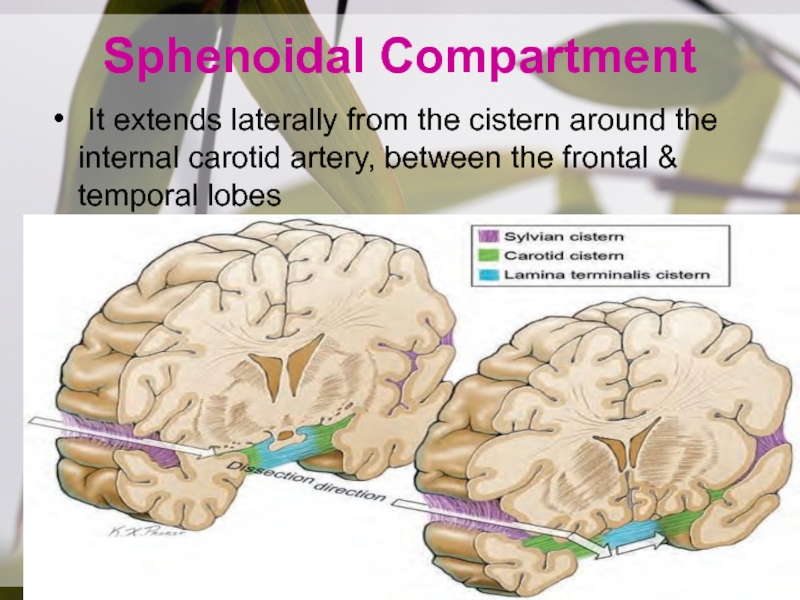
- 7. Sphenoidal Compartment It extends laterally from the
- 8. Sphenoidal CompartmentRoof is formed by: Post. orbital
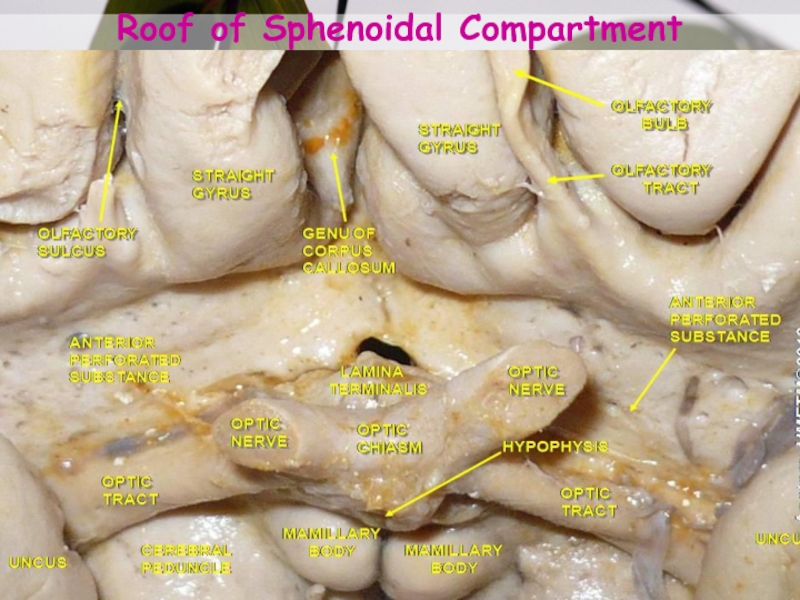
- 9. Roof of Sphenoidal Compartment
- 10. Слайд 10
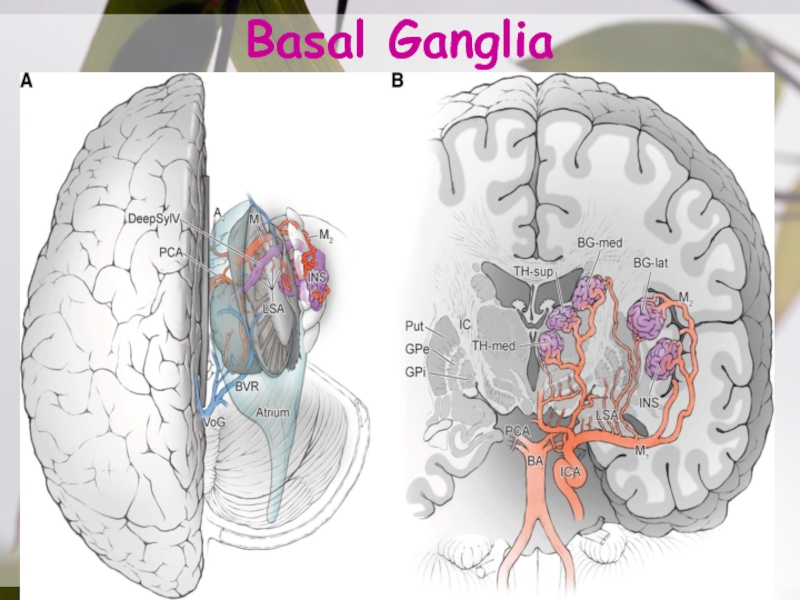
- 11. Basal Ganglia
- 12. Floor:anterior part of the planum polare, an
- 13. The operculoinsular compartmentOpercularInsular
- 14. Opercular CleftThis is situated where the sylvian
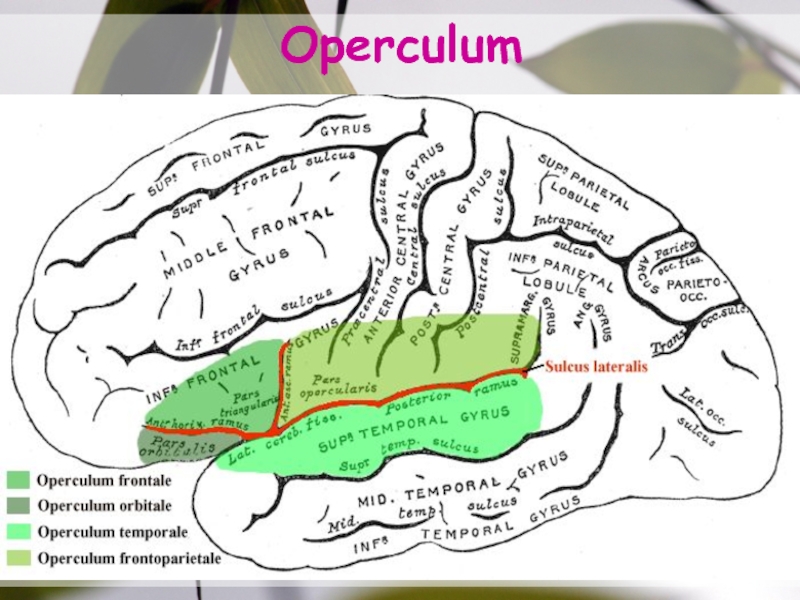
- 15. Operculum
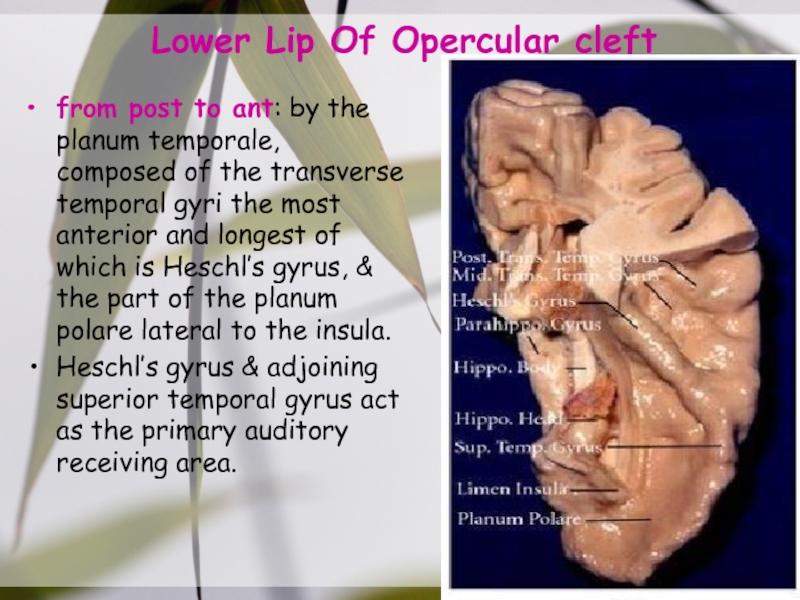
- 16. Lower Lip Of Opercular cleftfrom post to
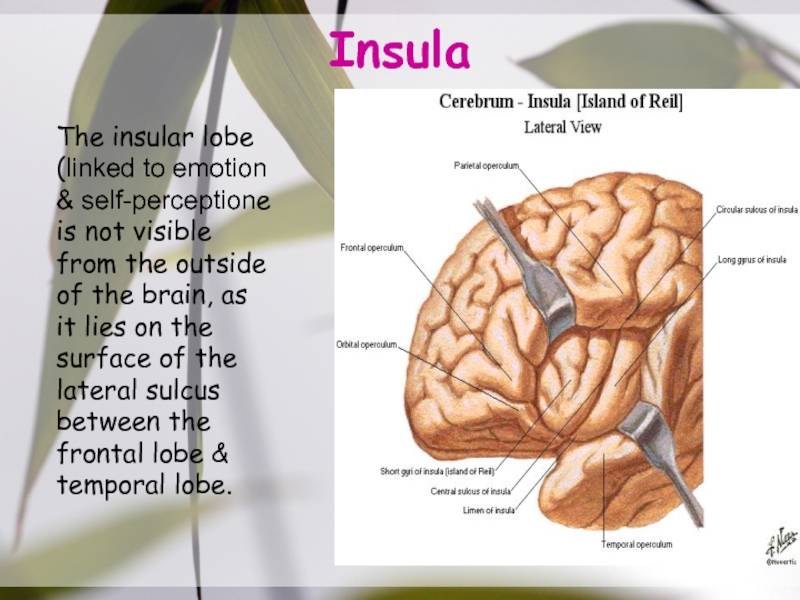
- 17. InsulaThe insular lobe (linked to emotion &
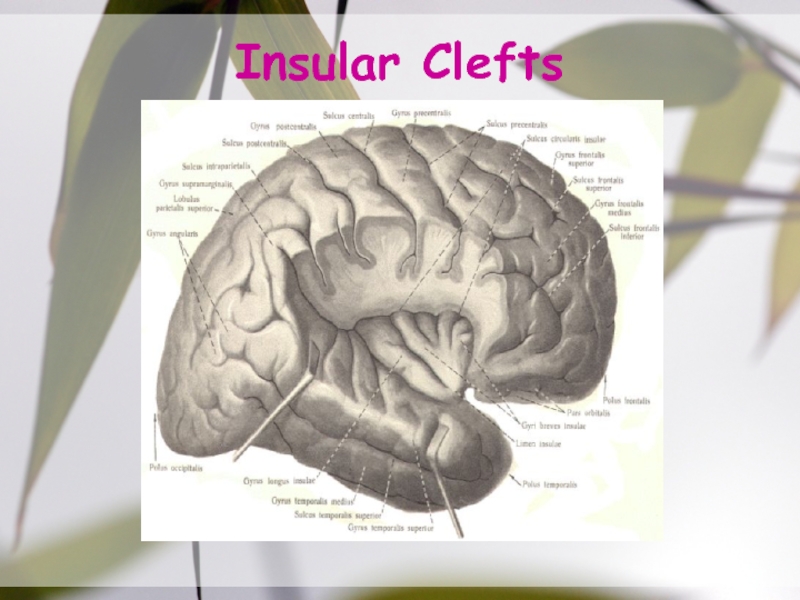
- 18. Insular Clefts
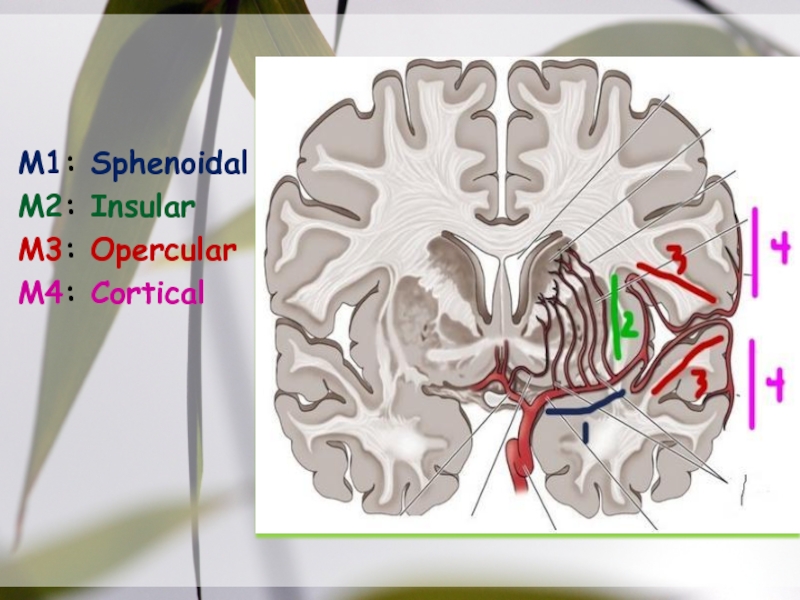
- 19. Picture slideM1: SphenoidalM2: InsularM3: OpercularM4: Cortical
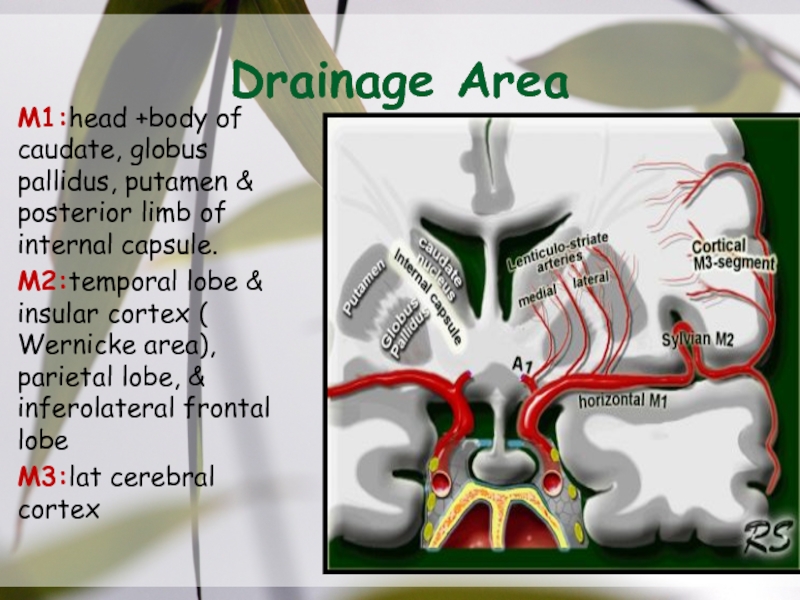
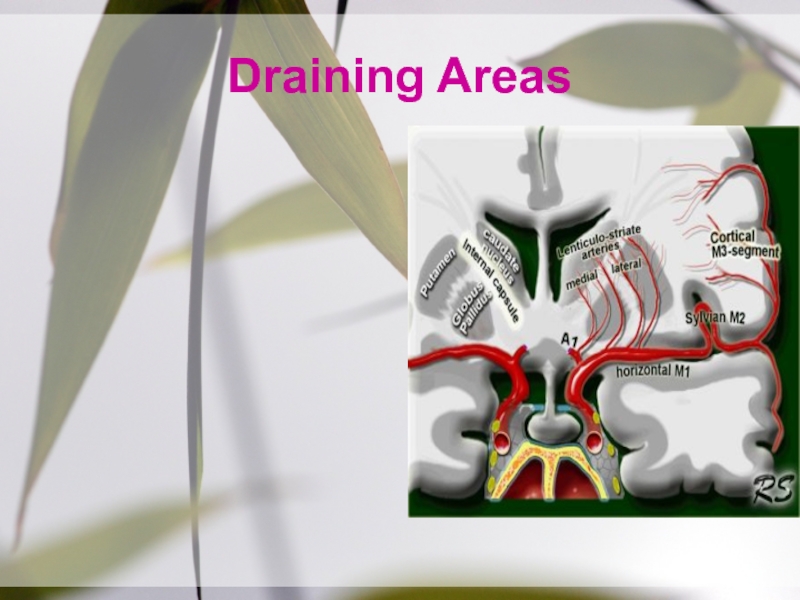
- 20. Drainage AreaM1:head +body of caudate, globus pallidus,
- 21. Radiographic ClassificationM1: before bifurcationM2: after bifurcation
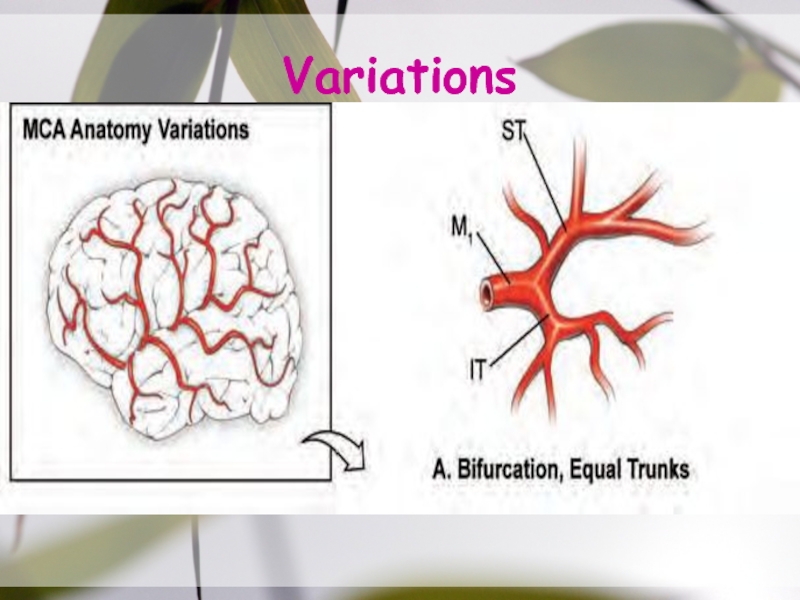
- 22. Variations
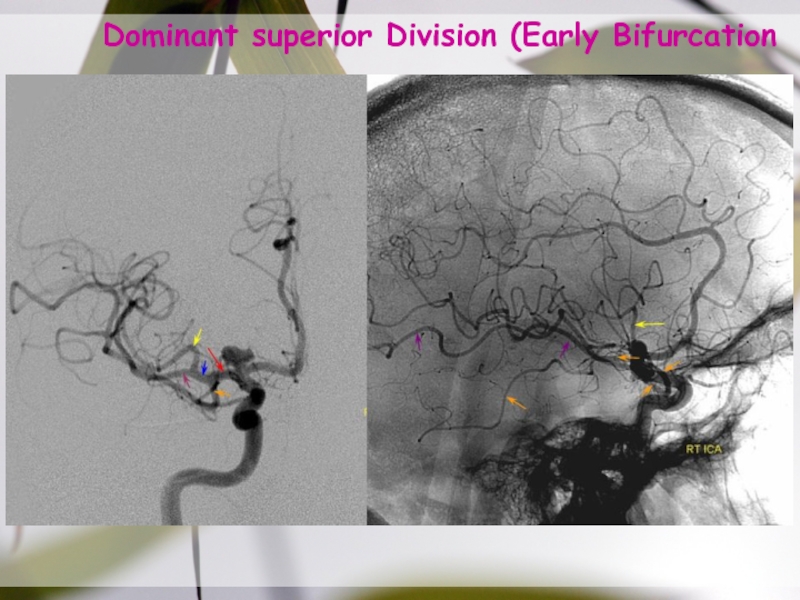
- 23. Dominant superior Division (Early Bifurcation187
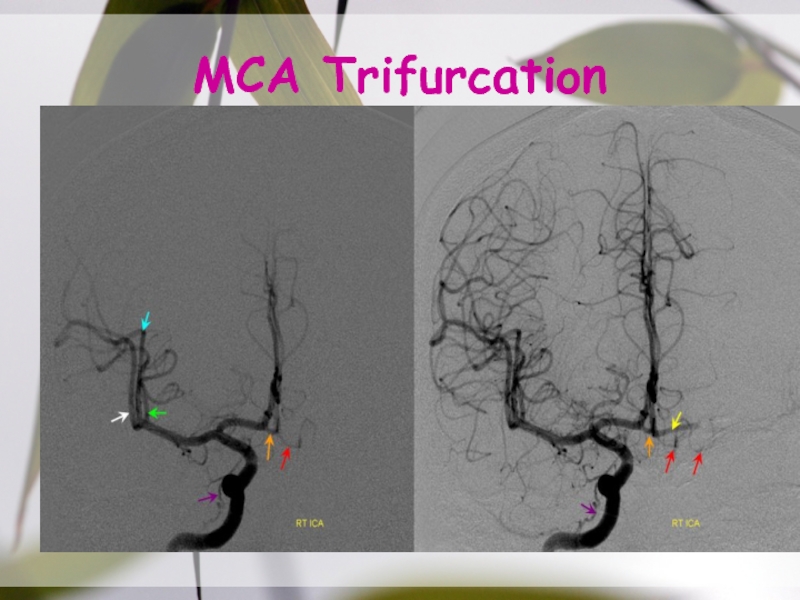
- 24. MCA Trifurcation
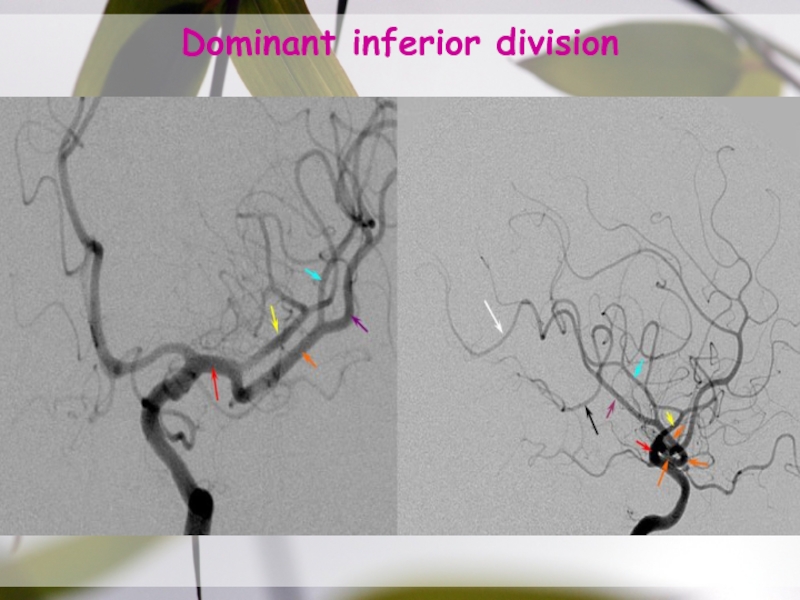
- 25. Dominant inferior division
- 26. The superior division (red) can be traced
- 27. Short M1 segment (red) with smaller superior
- 28. Acessory & Duplicated MCAaMCA configuration:both branches (purple)
- 29. Sylvian FissureSplitting
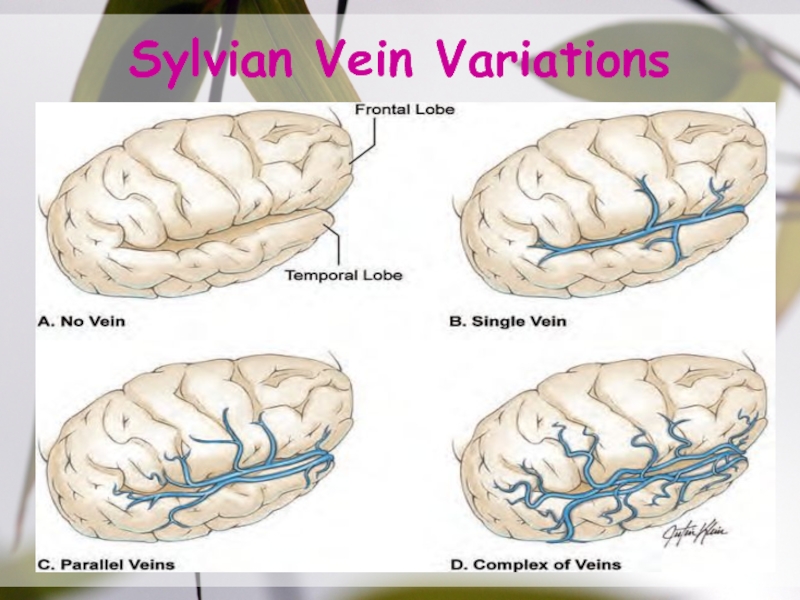
- 30. Sylvian Vein Variations
- 31. Step 1, cortical arachnoid incision; Step 2,
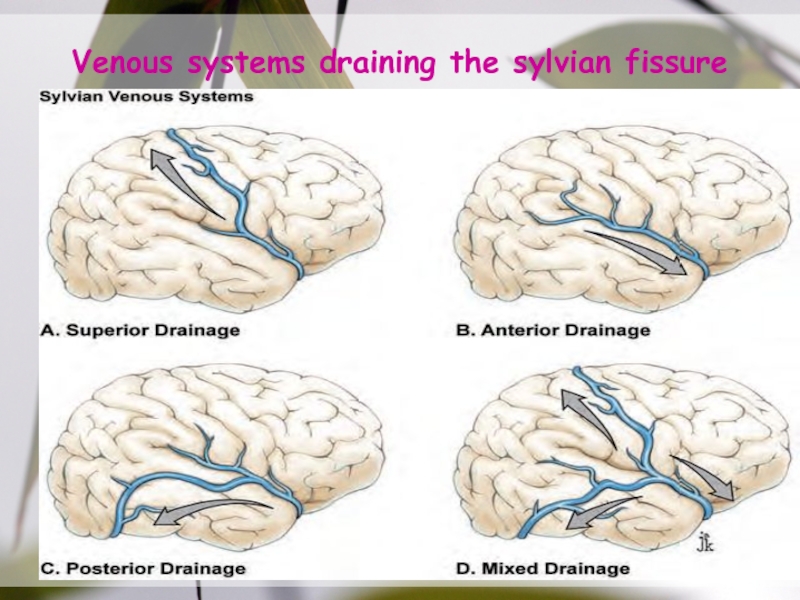
- 32. Venous systems draining the sylvian fissure
- 33. Слайд 33
- 34. Steps in splitting the sylvian fissure (arteries
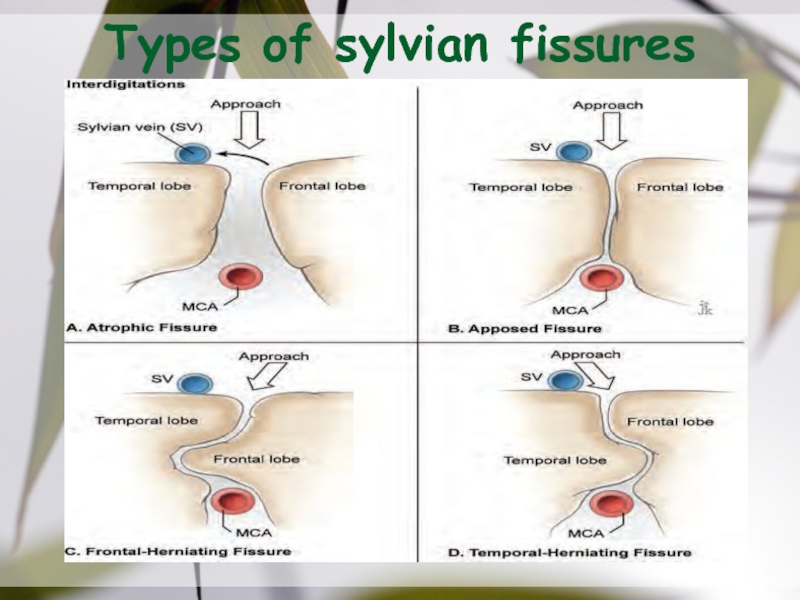
- 35. Types of sylvian fissures
- 36. Arteries branch temporally or frontally, but never
- 37. MCA aneurysm dome projectionsCoronal views: lateral (A),
- 38. MCA aneurysm dissection strategy, distal-to-proximal dissectionStep 1:
- 39. MCA aneurysm dissection strategy, proximal-to-distal dissectionStep 1,
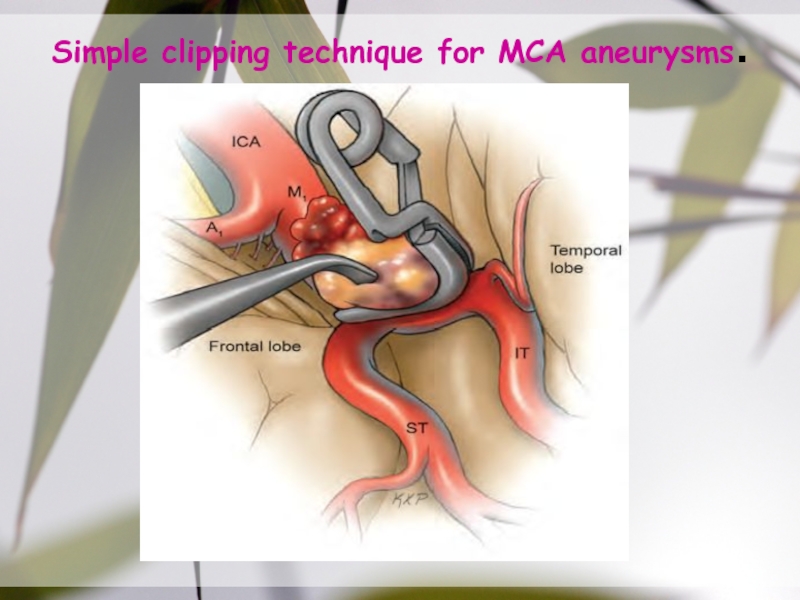
- 40. Simple clipping technique for MCA aneurysms.
- 41. Draining Areas
- 42. Thank You
- 43. Colour scheme
- 44. Sample Graph (3 colours)
- 45. Process FlowBullet 1Bullet 2Bullet 3Bullet 1Bullet 2Bullet
- 46. Example of a tableNote: PowerPoint does not
- 47. Examples of default stylesText and lines are
- 48. Use of templatesYou are free to use
- 49. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
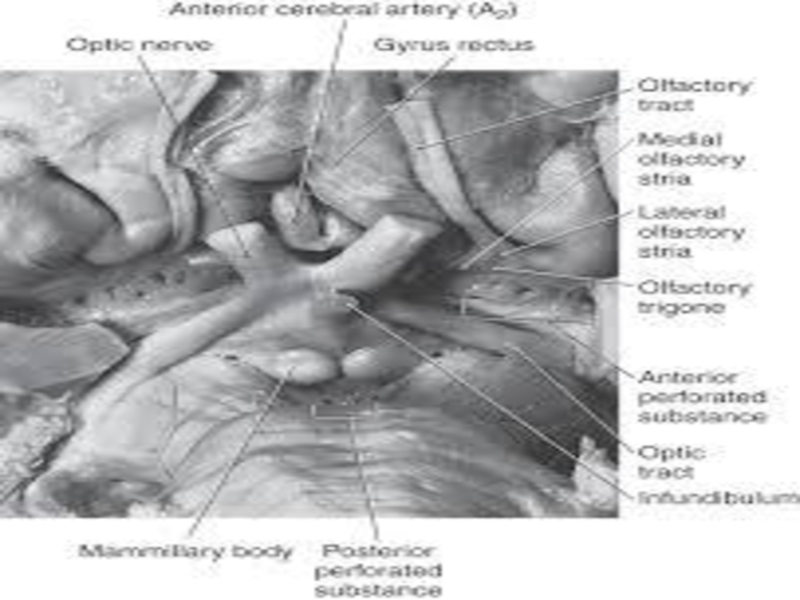
Слайд 3Definition
The sylvian fissure ,is the most distinct & consistent landmark
on the lateral surface, that carries the MCA & its
branches &provides a surgical gateway connecting the cerebral surface to the anterior part of the basal surface & cranial base.Слайд 7Sphenoidal Compartment
It extends laterally from the cistern around the
internal carotid artery, between the frontal & temporal lobes
Слайд 8Sphenoidal Compartment
Roof is formed by:
Post. orbital surface of the
frontal lobe
Anterior perforated substance.
Above Roof:
Caudate
Lentiform nuclei
Anterior limb of the internal
capsuleСлайд 12Floor:
anterior part of the planum polare, an area free of
gyri on the upper temporal pole, where a shallow cupped
trench accommodates MCA.Anterior uncal segment, amygdala, is located at the medial part of the floor.
The limen insulae, the prominence overlying the cingulum, a prominent fiber bundle connecting the frontal & temporal lobes, is located at the lateral edge of the sphenoidal compartment.
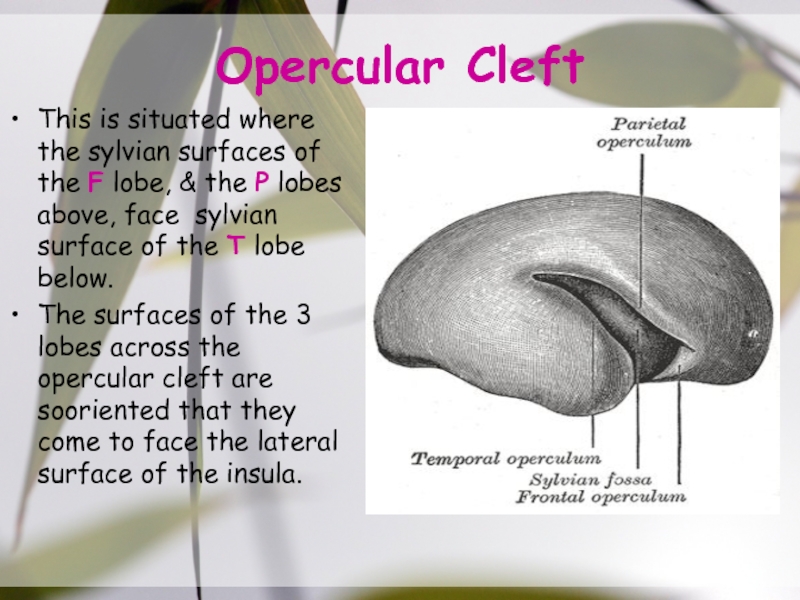
Слайд 14Opercular Cleft
This is situated where the sylvian surfaces of the
F lobe, & the P lobes above, face sylvian surface
of the T lobe below.The surfaces of the 3 lobes across the opercular cleft are sooriented that they come to face the lateral surface of the insula.
Слайд 16Lower Lip Of Opercular cleft
from post to ant: by the
planum temporale, composed of the transverse temporal gyri the most
anterior and longest of which is Heschl’s gyrus, & the part of the planum polare lateral to the insula.Heschl’s gyrus & adjoining superior temporal gyrus act as the primary auditory receiving area.
Слайд 17Insula
The insular lobe (linked to emotion & self-perceptione is not
visible from the outside of the brain, as it lies
on the surface of the lateral sulcus between the frontal lobe & temporal lobe.Слайд 20Drainage Area
M1:head +body of caudate, globus pallidus, putamen & posterior
limb of internal capsule.
M2:temporal lobe & insular cortex ( Wernicke
area), parietal lobe, & inferolateral frontal lobe M3:lat cerebral cortex
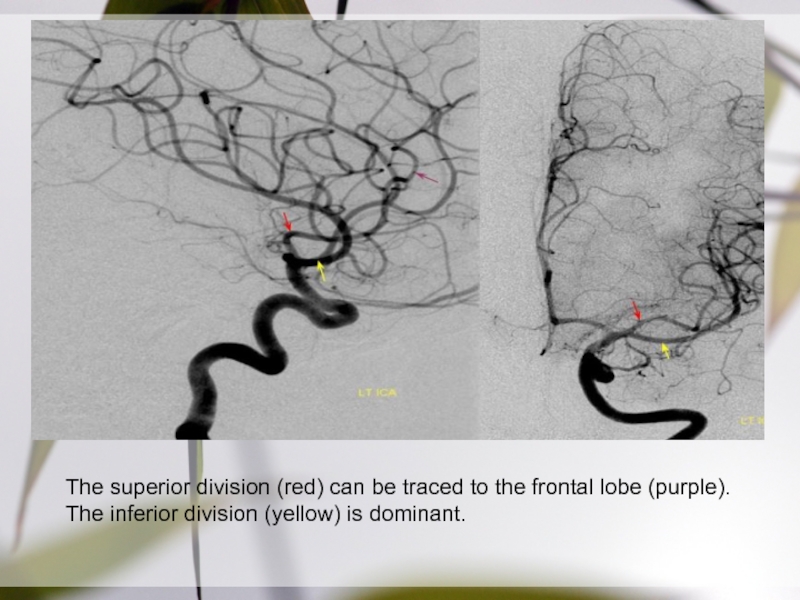
Слайд 26The superior division (red) can be traced to the frontal
lobe (purple). The inferior division (yellow) is dominant.
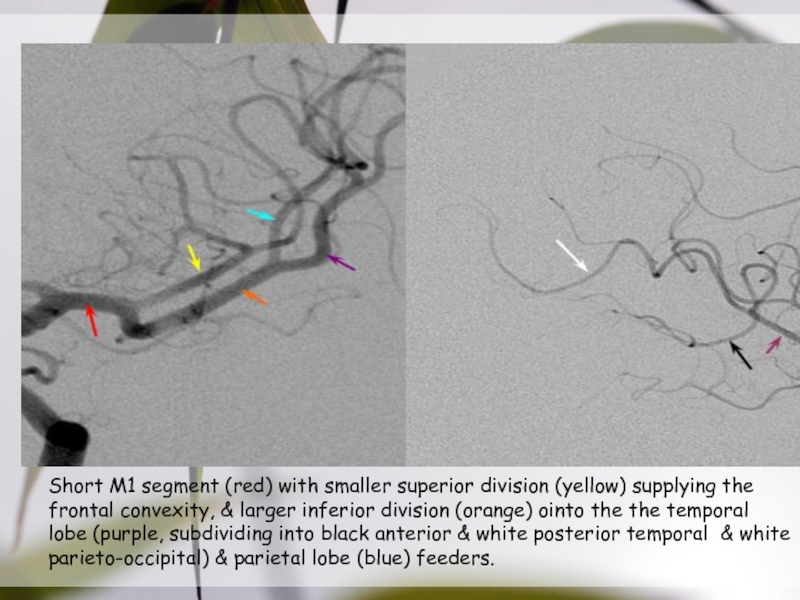
Слайд 27Short M1 segment (red) with smaller superior division (yellow) supplying
the frontal convexity, & larger inferior division (orange) ointo the
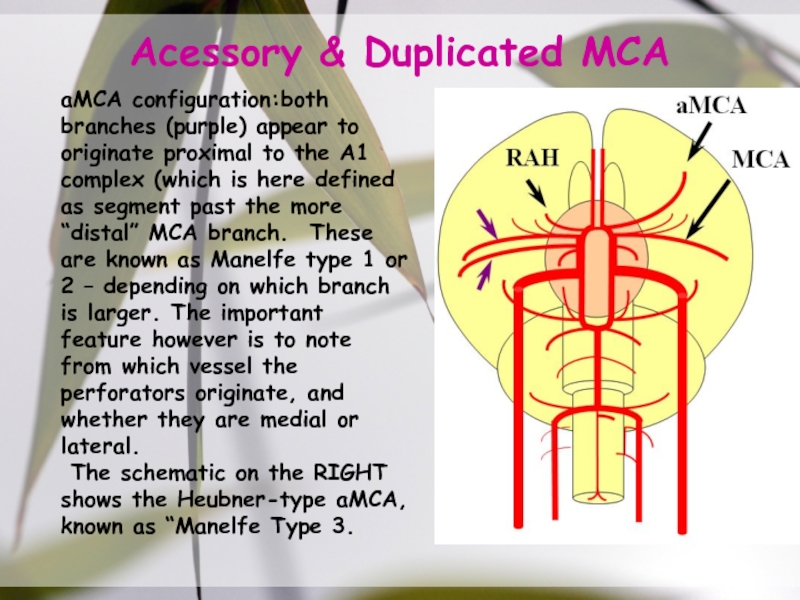
the temporal lobe (purple, subdividing into black anterior & white posterior temporal & white parieto-occipital) & parietal lobe (blue) feeders.Слайд 28Acessory & Duplicated MCA
aMCA configuration:both branches (purple) appear to originate
proximal to the A1 complex (which is here defined as
segment past the more “distal” MCA branch. These are known as Manelfe type 1 or 2 – depending on which branch is larger. The important feature however is to note from which vessel the perforators originate, and whether they are medial or lateral.The schematic on the RIGHT shows the Heubner-type aMCA, known as “Manelfe Type 3.
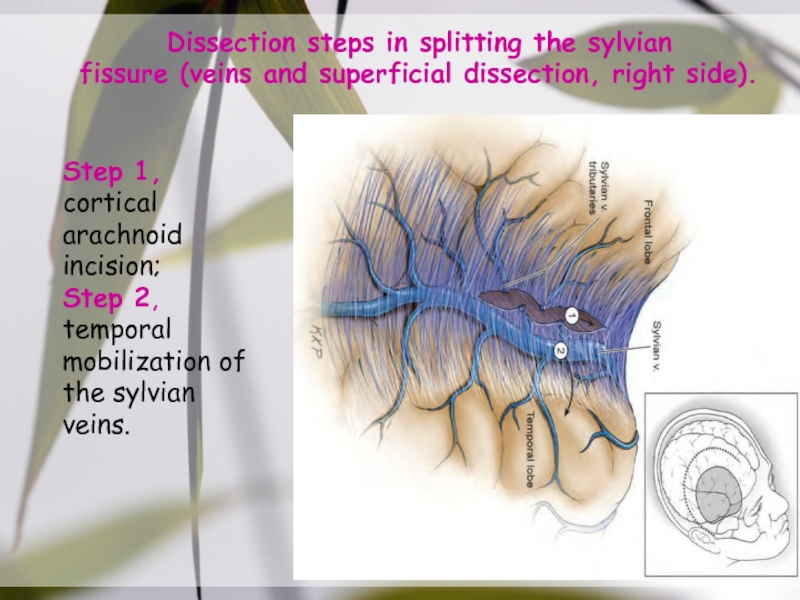
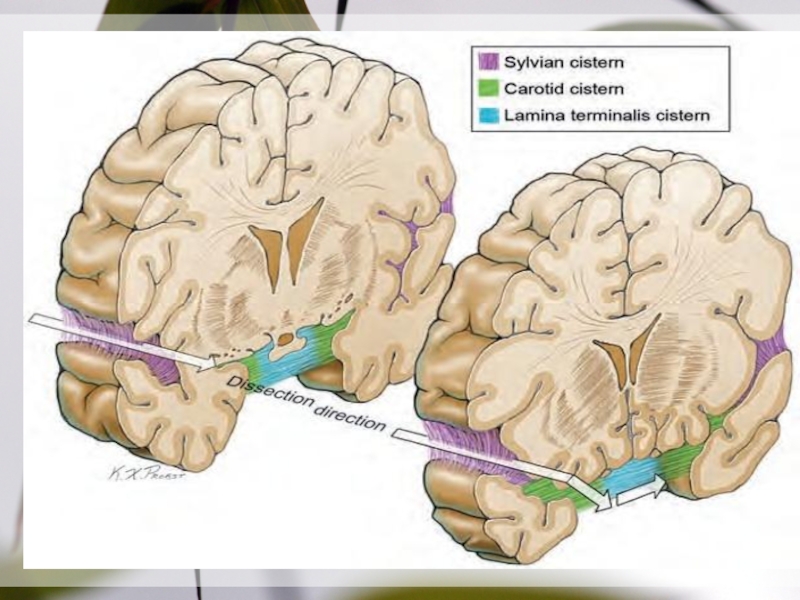
Слайд 31Step 1, cortical arachnoid incision;
Step 2, temporal
mobilization of the
sylvian veins.
Dissection steps in splitting the sylvian
fissure (veins and superficial
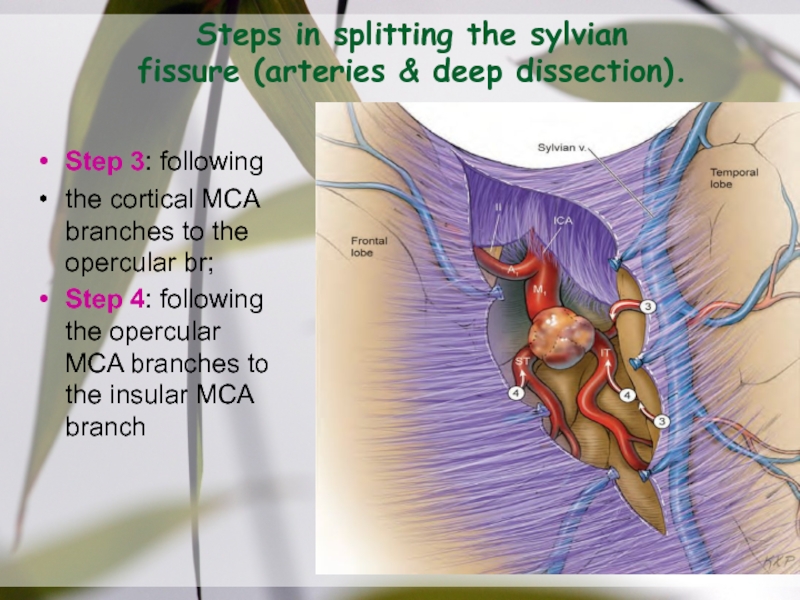
dissection, right side).Слайд 34Steps in splitting the sylvian
fissure (arteries & deep dissection).
Step 3:
following
the cortical MCA branches to the opercular br;
Step 4:
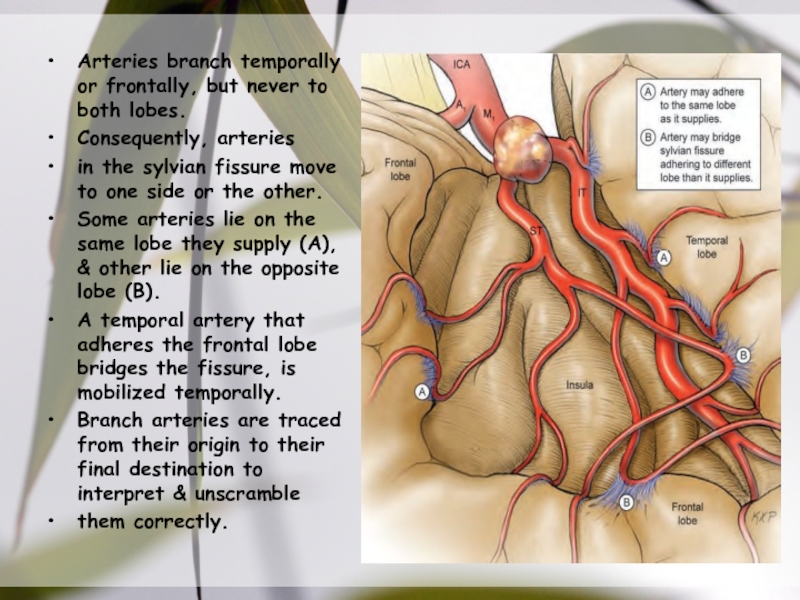
following the opercular MCA branches to the insular MCA branchСлайд 36Arteries branch temporally or frontally, but never to both lobes.
Consequently, arteries
in the sylvian fissure move to one side or
the other. Some arteries lie on the same lobe they supply (A), & other lie on the opposite lobe (B).
A temporal artery that adheres the frontal lobe bridges the fissure, is mobilized temporally.
Branch arteries are traced from their origin to their final destination to interpret & unscramble
them correctly.
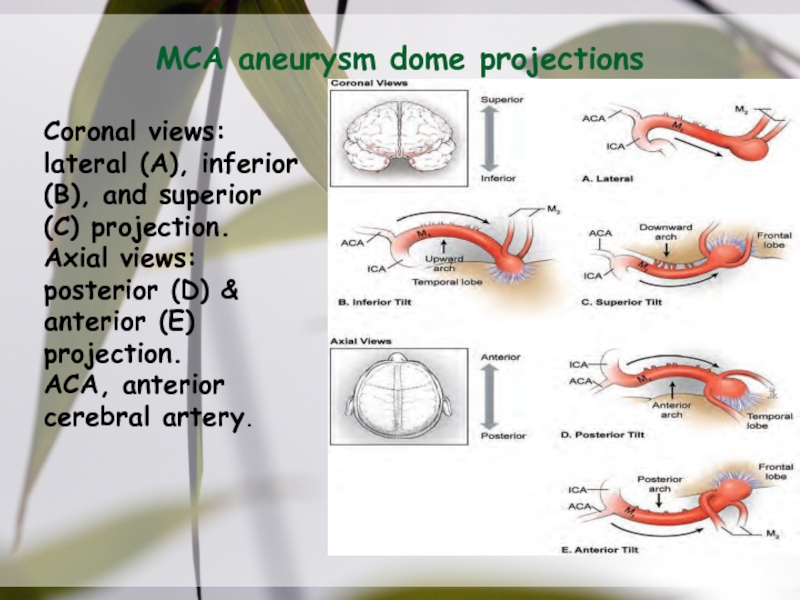
Слайд 37MCA aneurysm dome projections
Coronal views: lateral (A), inferior (B), and
superior (C) projection.
Axial views: posterior (D) & anterior (E) projection.
ACA,
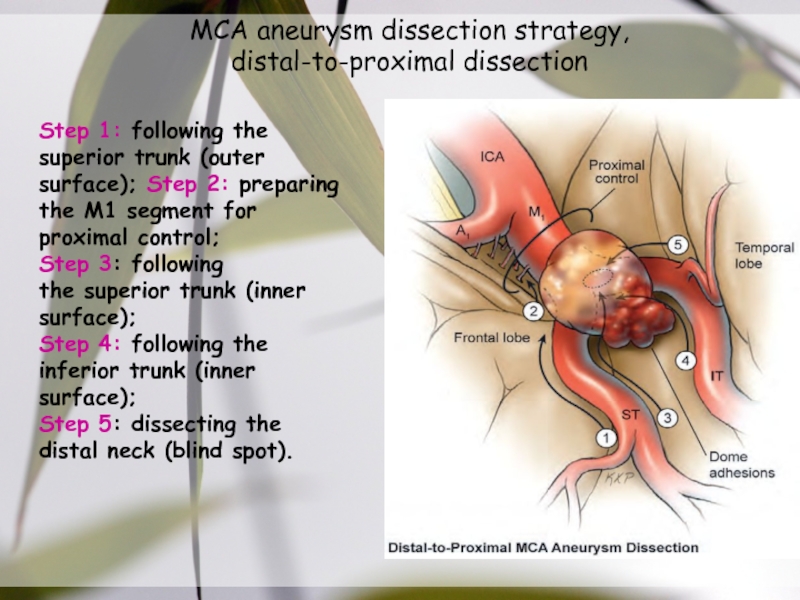
anterior cerebral artery.Слайд 38MCA aneurysm dissection strategy,
distal-to-proximal dissection
Step 1: following the
superior trunk (outer
surface); Step 2: preparing
the M1 segment for proximal control;
Step
3: followingthe superior trunk (inner surface);
Step 4: following the inferior trunk (inner surface);
Step 5: dissecting the distal neck (blind spot).
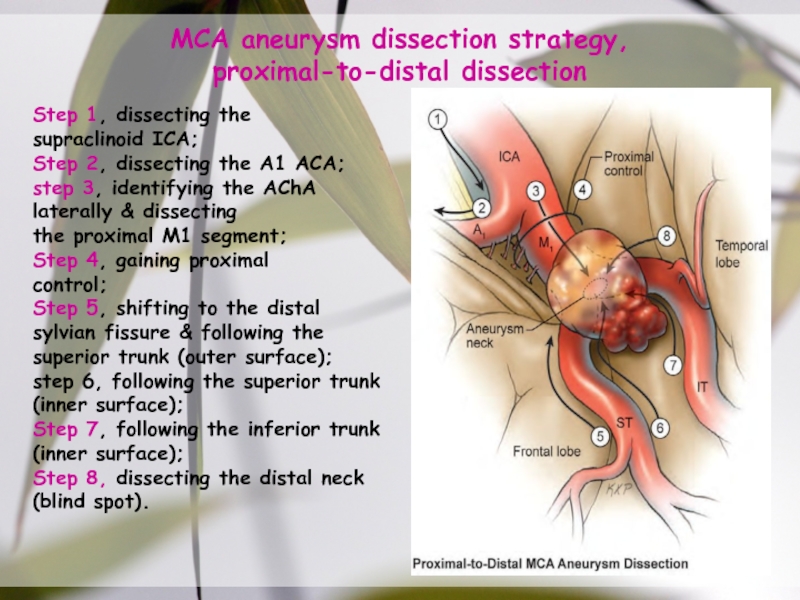
Слайд 39MCA aneurysm dissection strategy,
proximal-to-distal dissection
Step 1, dissecting the
supraclinoid ICA;
Step 2,
dissecting the A1 ACA;
step 3, identifying the AChA laterally &
dissectingthe proximal M1 segment;
Step 4, gaining proximal
control;
Step 5, shifting to the distal sylvian fissure & following the superior trunk (outer surface);
step 6, following the superior trunk (inner surface);
Step 7, following the inferior trunk (inner surface);
Step 8, dissecting the distal neck (blind spot).
Слайд 45Process Flow
Bullet 1
Bullet 2
Bullet 3
Bullet 1
Bullet 2
Bullet 3
Bullet 1
Bullet 2
Bullet
3
Bullet 1
Bullet 2
Bullet 3
Bullet 1
Bullet 2
Bullet 3
Plan
Design
Build
Test
Evaluate
Слайд 46Example of a table
Note: PowerPoint does not allow you to
have nice default tables - but you can cut and
paste this oneСлайд 47Examples of default styles
Text and lines are like this
Hyperlinks like
this
Visited hyperlinks like this
Text box
Text box
With shadow
Слайд 48Use of templates
You are free to use these templates for
your personal and business presentations.
Do
Use these templates for your presentations
Display
your presentation on a web site provided that it is not for the purpose of downloading the template.If you like these templates, we would always appreciate a link back to our website. Many thanks.
Don’t
Resell or distribute these templates
Put these templates on a website for download. This includes uploading them onto file sharing networks like Slideshare, Myspace, Facebook, bit torrent etc
Pass off any of our created content as your own work
You can find many more free PowerPoint templates on the Presentation Magazine website www.presentationmagazine.com
We have put a lot of work into developing all these templates and retain the copyright in them. You can use them freely providing that you do not redistribute or sell them.