Слайд 1The Composite Sentence
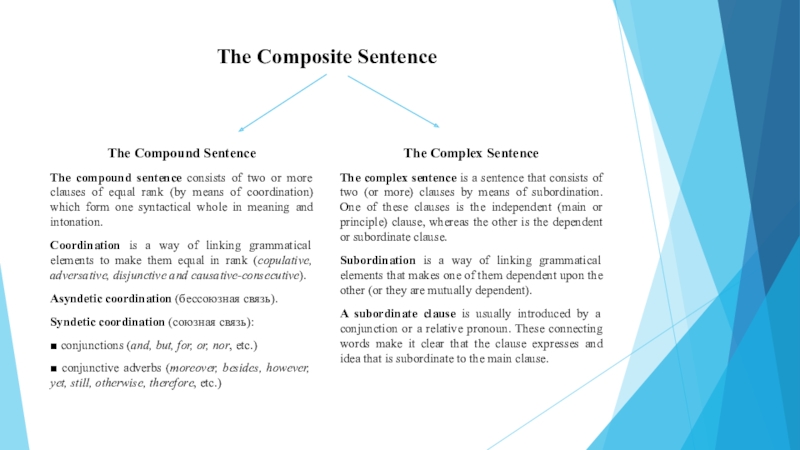
The Compound Sentence
The compound sentence consists of two
or more clauses of equal rank (by means of coordination)
which form one syntactical whole in meaning and intonation.
Coordination is a way of linking grammatical elements to make them equal in rank (copulative, adversative, disjunctive and causative-consecutive).
Asyndetic coordination (бессоюзная связь).
Syndetic coordination (союзная связь):
■ conjunctions (and, but, for, or, nor, etc.)
■ conjunctive adverbs (moreover, besides, however, yet, still, otherwise, therefore, etc.)
The Complex Sentence
The complex sentence is a sentence that consists of two (or more) clauses by means of subordination. One of these clauses is the independent (main or principle) clause, whereas the other is the dependent or subordinate clause.
Subordination is a way of linking grammatical elements that makes one of them dependent upon the other (or they are mutually dependent).
A subordinate clause is usually introduced by a conjunction or a relative pronoun. These connecting words make it clear that the clause expresses and idea that is subordinate to the main clause.
Слайд 2A clause is a group of words that has a
subject and a predicate.
There are two kinds of clauses:
■
independent or main clauses;
■ dependent or subordinate clauses.
An independent (main) clause is a group of words that has a subject and a predicate. An independent clause does not depend upon anything else for its meaning. It expresses a complete thought.
The officer blew his whistle and the cars stopped.
A subordinate clause is a group of words that has a subject and a predicate, but the clause cannot stand alone. A subordinate clause does not express a complete thought. It depends upon the main clause for its meaning. The connective, or the word that introduces the subordinate clause, plays an important part in making it a dependent clause.
The cars stopped when the officer blew his whistle.
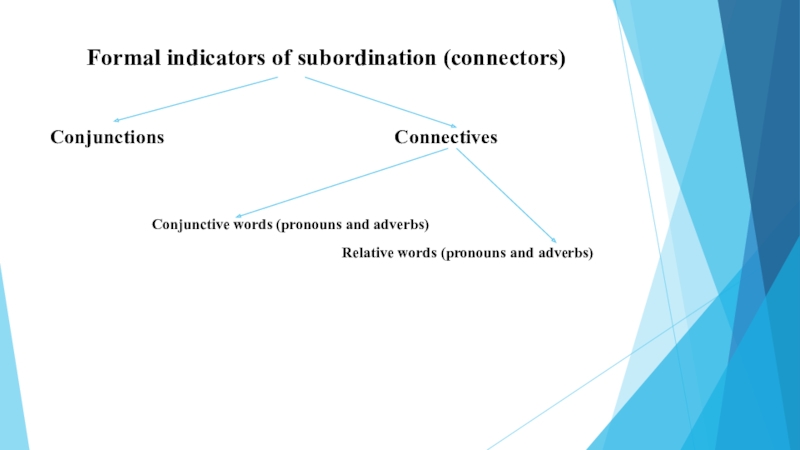
Слайд 3Formal indicators of subordination (connectors)
Conjunctions
Connectives
Conjunctive words (pronouns and adverbs)
Relative words (pronouns and adverbs)
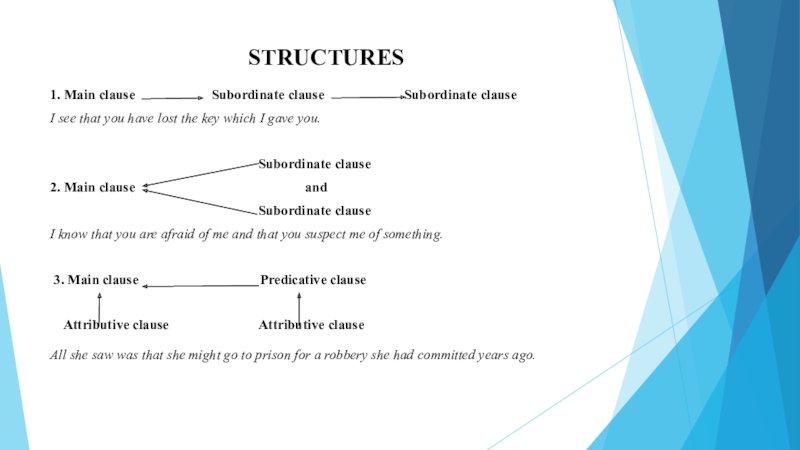
Слайд 4STRUCTURES
1. Main clause
Subordinate clause
Subordinate clause
I see that you have lost the key which I gave you.
Subordinate clause
2. Main clause and
Subordinate clause
I know that you are afraid of me and that you suspect me of something.
3. Main clause Predicative clause
Attributive clause Attributive clause
All she saw was that she might go to prison for a robbery she had committed years ago.
Слайд 5Functional classification of subordinate clauses
■ Subject clause (that, if, whether…or,
because, the way, who, whoever, what, whatever, which, where, wherever,
when, whenever, how, why)
■ Predicative clause (that, whether…or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way, who, whoever, what, whatever, which, where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why)
■ Object clause (that, if, whether, whether…or, lest, who, whoever, what, whatever, which, where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why, after, before, about, for, near, of, except, etc.)
■ Attributive clause (who, whose, whom, what, which, that, as, when, where, whence, wherein)
■ Appositive clause (that, if, whether, as if, as though, why, how)
Слайд 6■ Adverbial clauses of:
► place (where, whence, wherever, everywhere)
► time
(as, as soon as, as long as, when, whenever, while,
now that, till, until, after, before, since, every time, next time, the time, the moment, the day directly, immediately, etc.)
► manner (as, the way)
► comparison (as, like, as if, as though, than, as…as, as…as if, so…as)
► condition (if, whether, once, in case, unless, provided that, providing that, suppose that, supposing that, granted that, granting that, admitting that, considering that, given that, seeing that)
► concession (although, though, if, though…yet, whether…or, whoever, whatever, whichever, whenever, wherever, no matter how/what, despite that, in spite of the fact, even if, even though, etc.)
► purpose (that, so that, lest, so as, so, in order that, for the fear that)
► cause/reason (as, because, since, so, that, lest, seeing that, considering, for the reason that, in view of the fact that, in so far as, by reason of)
► result/consequence (so that, that, so…that, such…that)
Слайд 7Subject Clauses
1. That she understands his fault is clear.
2. Whether
we played there or not means nothing now.
3. Who spoke
at that meeting has escaped my memory.
4. What she told me yesterday proved to be correct.
5. It seemed unfair to him that he should suffer more than his wife.
Слайд 8Predicative Clauses
1. The question is whether the weather is sunny.
2.
That is what he wants you to think.
3. The fact
was that he had forgotten about it.
4. Everything remained as it used to be in this room.
5. She looks as if she were ill.
Слайд 9Object Clauses
1. We know that she is pretty.
2. Tom asked
if he could take that book.
3. I do not know).
what Peter should do now (which bag to buy/where to sleep.
4. The secretary told us how we can arrange our offers.
5. I am not certain of what he did.
Слайд 10Attributive Clauses
1. The room has a stove which faces the
door.
2. It is the same person whom we saw
last month.
3. The castle where we once had dinner has disappeared.
4. The time when Mary was young has long passed.
5. Do you know the reason why Lena was late?
Слайд 11Adverbial Clauses
1. Let me smoke a cigar before I go
(time).
2. Put the vase where it belongs (place).
3. I’m sorry
I talked the way I did at lunch (manner).
4. He was as obstinate as were most of his relatives (comparison).
5. I will read you an English fairy-tale if my friend brings the book (condition).
6. Whenever you come send me a note (concession).
7. Eva had to talk louder, so that everyone could hear her (purpose).
8. Mike can’t go to the concert because he is busy (cause/reason).
9. Light fell on her there, so that Tom could see her face, eyes and hair (result/consequence).
Слайд 12Define the type of the following subordinate clauses:
1. Which of
the knives is good for our kitchen has to be
decided.
2. The problem was that he treated us as unfamiliar people.
3. I heard that you got promoted!
4. When he arrives is not mentioned.
5. All we can do has already been done.
6. You can do whatever you want.
7. I felt as if I was guilty for all the crimes in the world.
8. Where she is hiding now is not known.
9. How you have managed to do it is very strange.
10. It happened when I was 10.
Слайд 1311. They are asking whether we are going to the party or
not.
12. Kate reserved her plane tickets earlier lest she missed her.
13. Why
they have chosen that way was known only to their guide.
14. Ann spoke in such a low voice that nobody could hear her.
15. I am not going to stop, whatever you may tell me.
16. The thing to be decided now is whether we are going to the cinema or stay home.
17. There is no child who doesn’t like playing computer games.
18. A sunset by the sea is what I love the most.
19. I don’t know what to say.
20. You can come to my house whenever you want.
21. Although she has been working since 6 a.m., she is still full of strength.
22. She ran so fast that nobody could catch up with her.
23. This is what he has done by 6 o’clock.
24. I ran away for fear that my mom would scold me.
25. Matt said there was nothing special in that restaurant.
Слайд 1426. I don’t like that kind of situations when you have
to talk to someone but don’t remember his name.
27. What
she told me yesterday turned out to be the truth.
28. They are leaving now so that they will be at home.
29. I went where you had told me to go to.
30. How he made a mistake is not clear to us.
31. We will go to the zoo after mom finishes her work.
32. I do not understand what I must do now.
33. It happened in 1998, when you were only 6.
34. Harry went to the restaurant, where some tables were on the terrace.
35. Today I slept only 2 hours, which is worse than not sleeping at all.
36. The teacher when out of the classroom, which helped Jack to crib out of Matt’s copybook.
37. Clark tried to start up his car, which was not an easy task.
38. I had some hope that Kate would come.
39. I see no reason why you should worry about it.
40. Jack’s doubts whether he had to say the truth just vanished.
Слайд 1541. Should you go to the market, buy some bread and
milk for me, please.
42. Our opinion is that facts are facts.
43. Brandon was running as fast as he
could.
44. She pointed where a group of young people stood.
45. The question is whether he knows about her betrayal or not.
46. No one will touch you provided you stay here with me.
47. It is strange that he made a mistake.
48. Kate looks bad as if she hasn’t slept for the whole week.
49. He told us that he had seen us buying a bouquet of flowers.
50. Since she was ill, she couldn’t attend her classes yesterday.