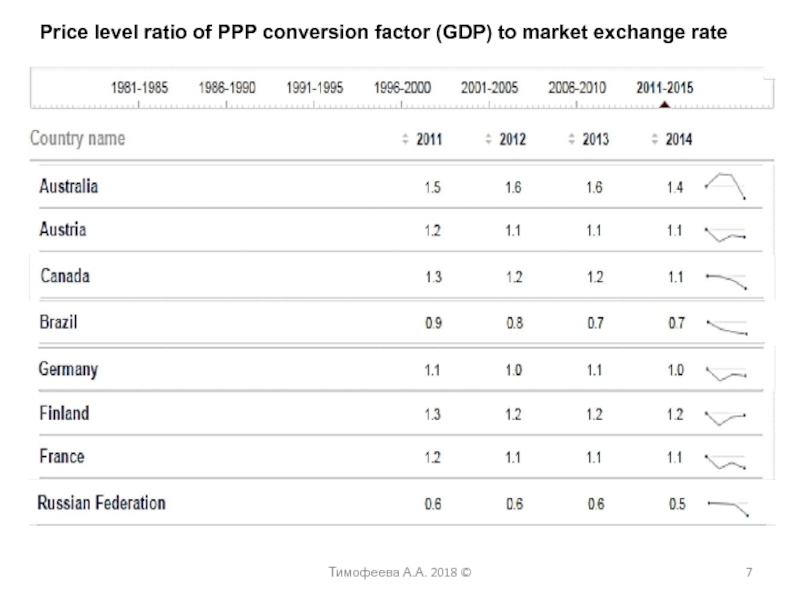
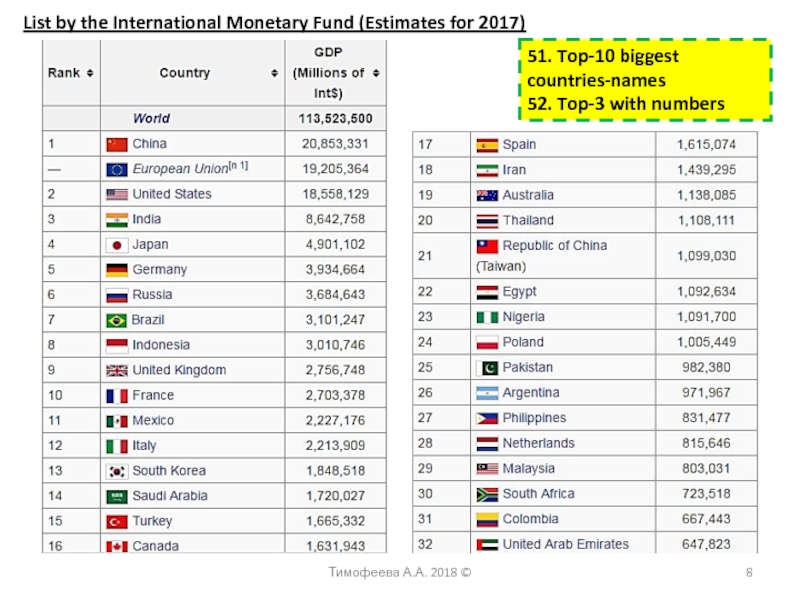
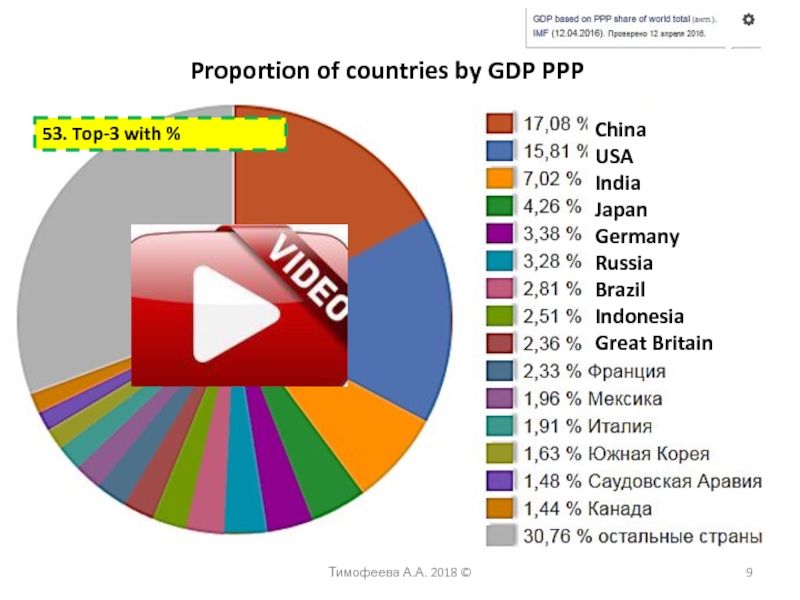
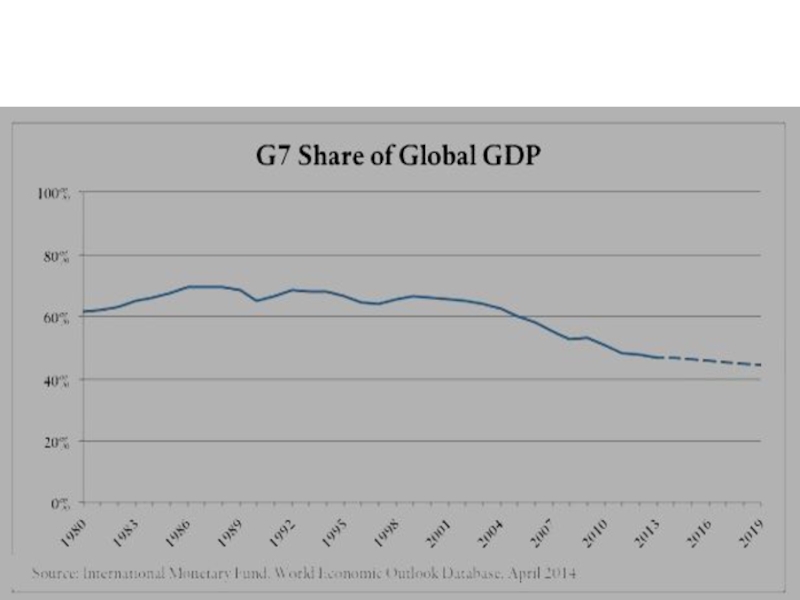
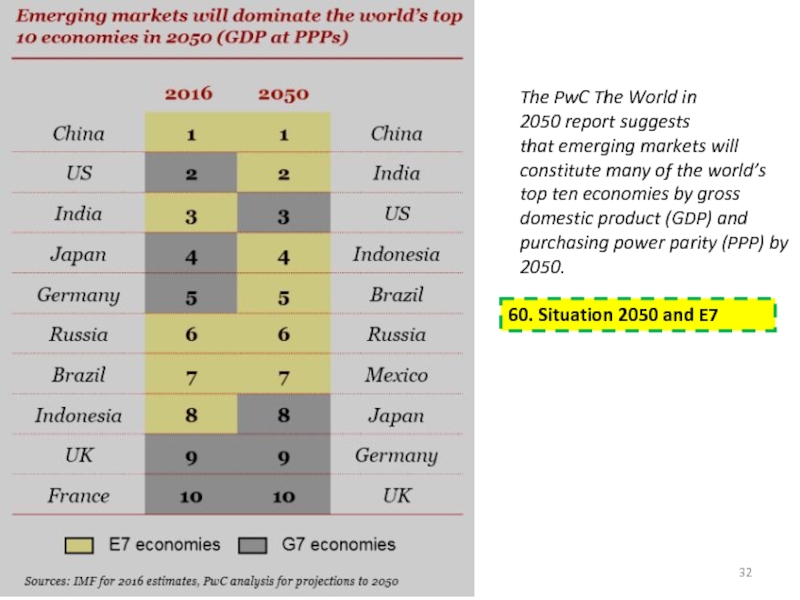
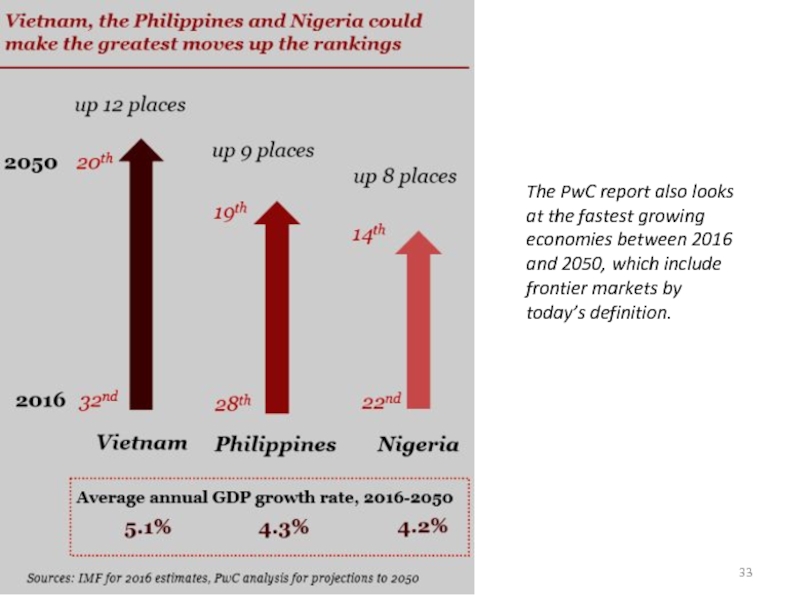
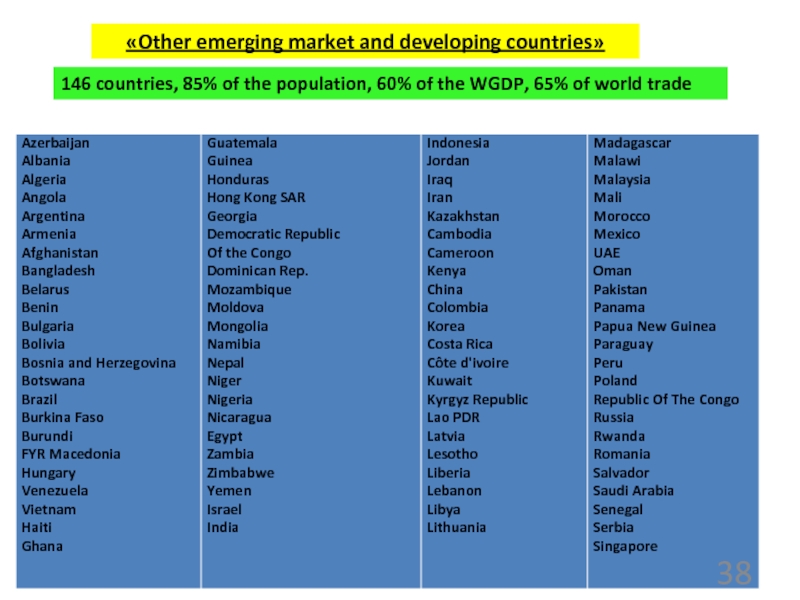
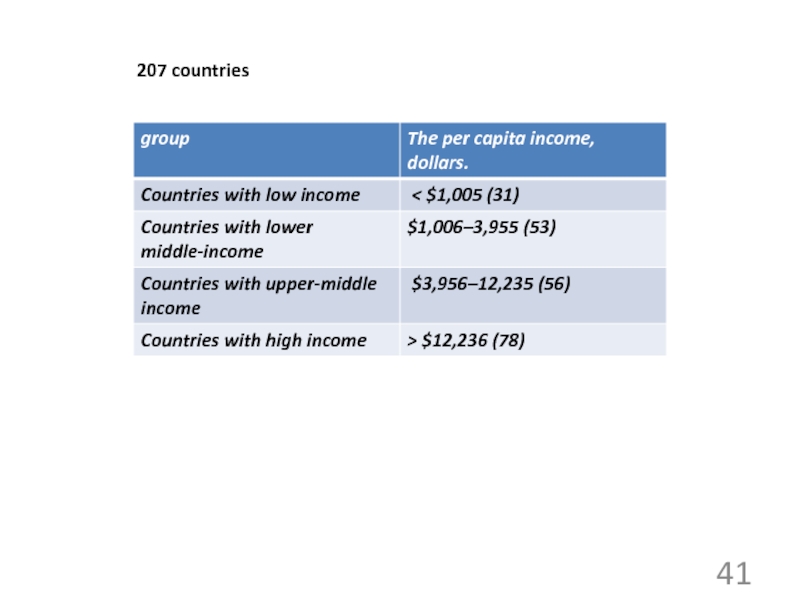
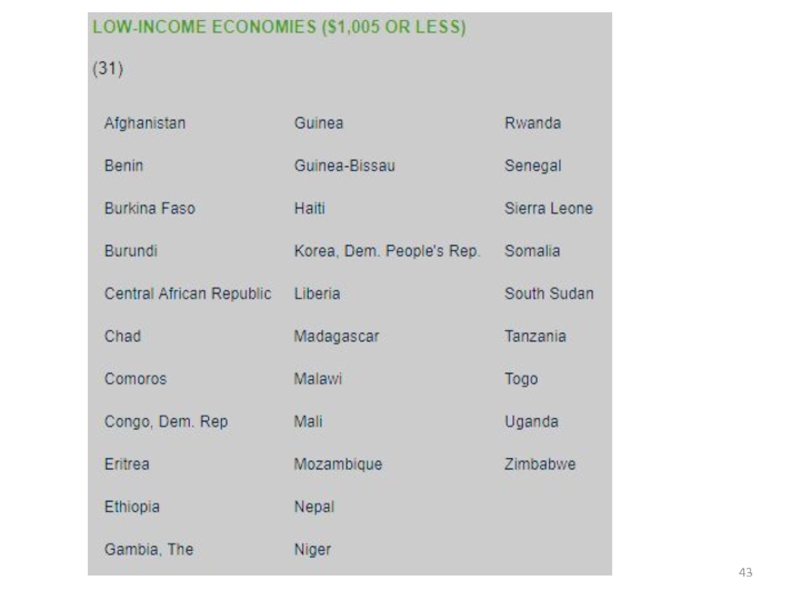
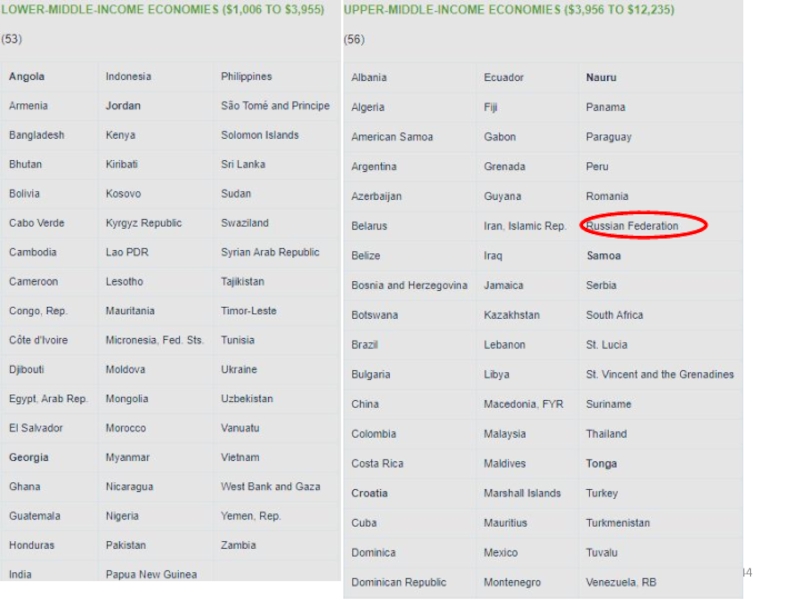
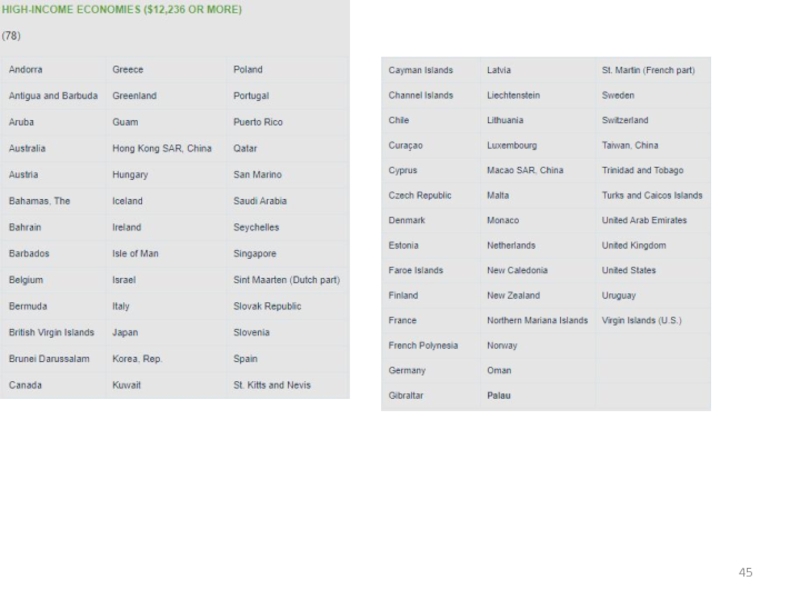
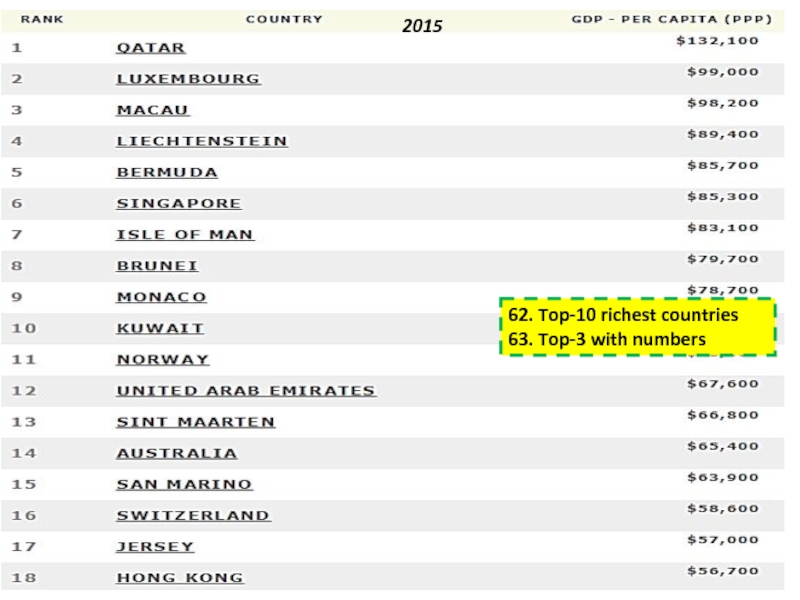
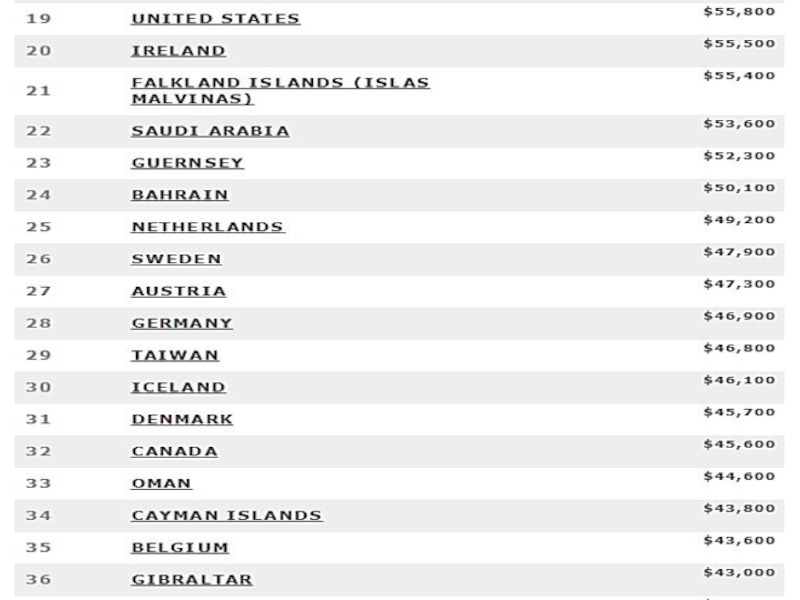
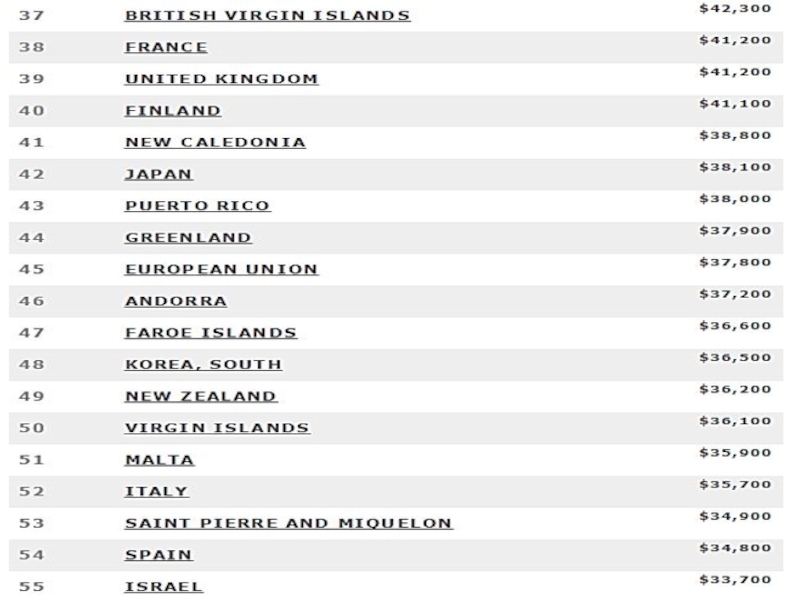
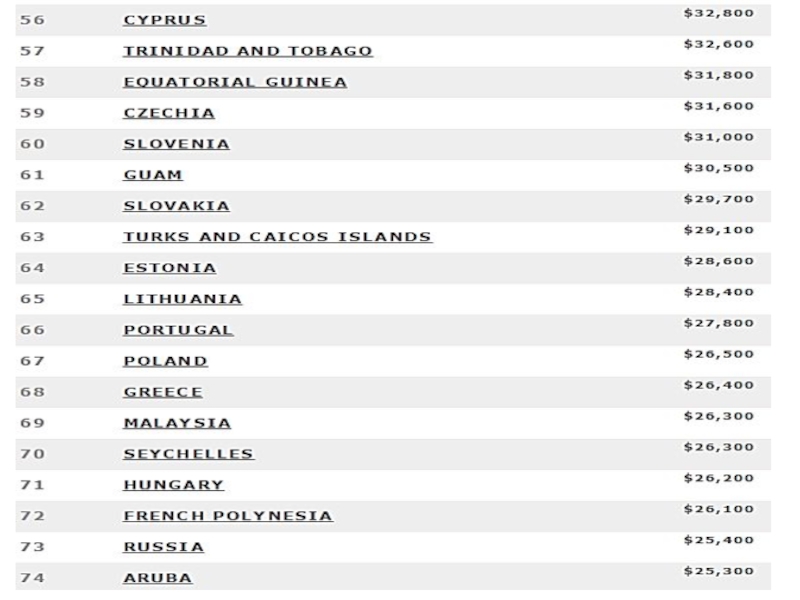
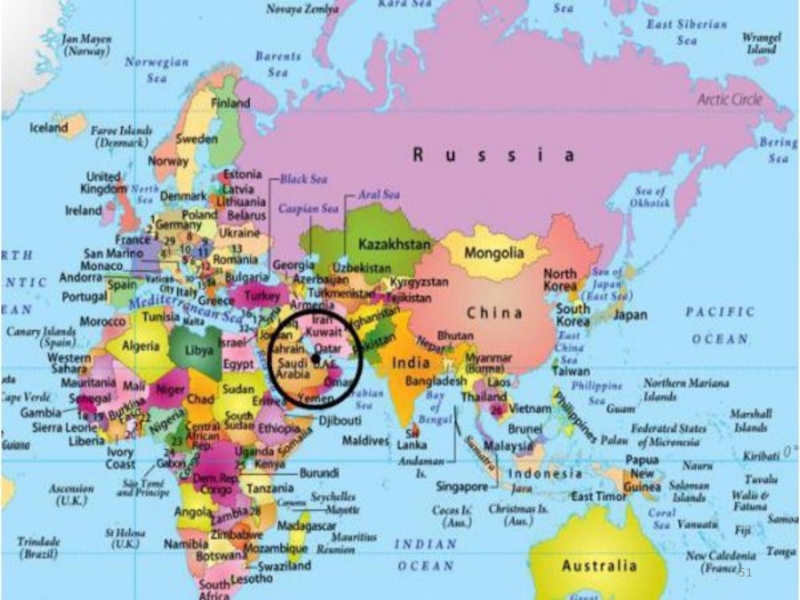
power parity
Market exchange rate
International organization
The influence of different factors
Тимофеева А.А.
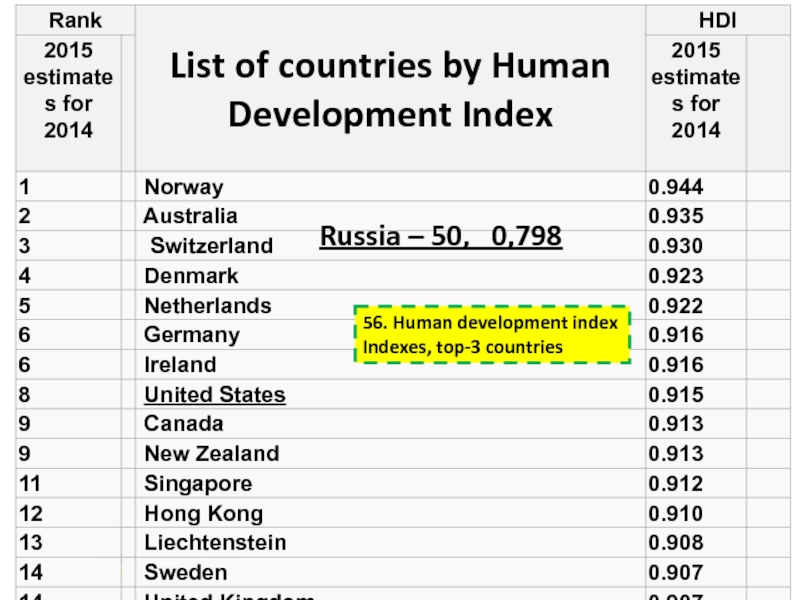
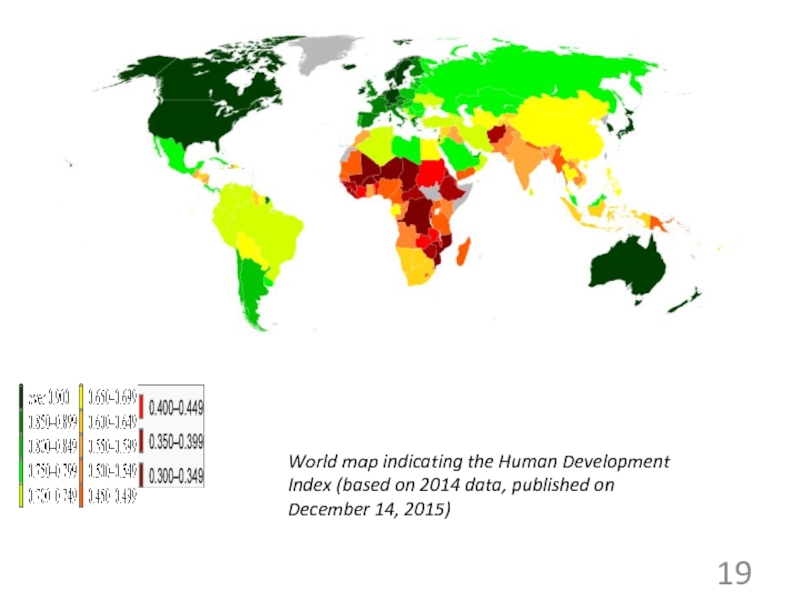
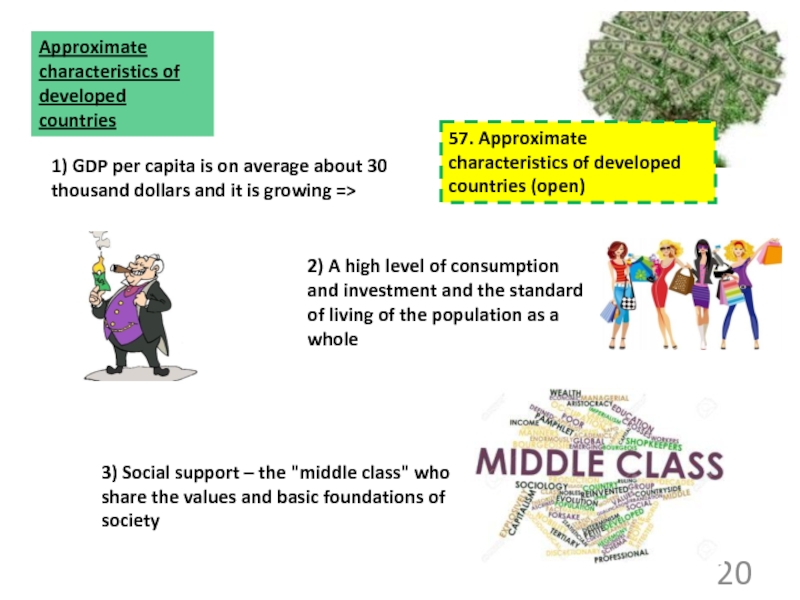
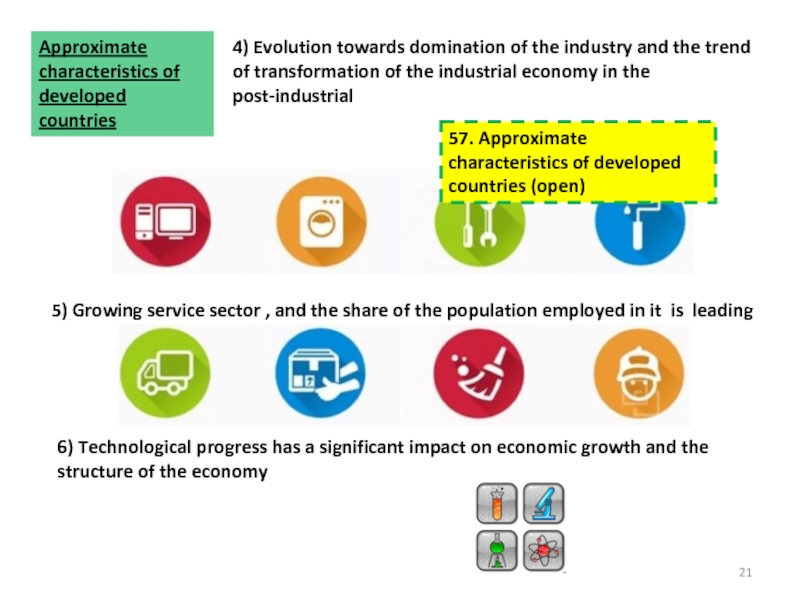
2018 ©48. Methods of comparable data obtaining (2) (open)