Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Computers. For intermediate learners Практикум
Содержание
- 1. Computers. For intermediate learners Практикум
- 2. LESSON IText A. What is a Computer
- 3. LESSON IITypes of Computer Systems:A supercomputerA mainframe computerA minicomputerA microcomputer
- 4. LESSON IIIDelete Keys – Clipboard Technology:a liquid
- 5. LESSON IVComputer Software:Systems SoftwareApplications Software
- 6. LESSON VPrograms and Programming Languages (a brief history):FORTRANCOBOLALGOLPL/1PASCALBASICC
- 7. LESSON VI Input Hardware:Using a
- 8. Keyboard Entry Input Hardware MainTypes of Terminals: A dumb terminalA smart terminalAn intelligent terminal
- 9. Popular Types of Computer TerminalsPoint-of-sale terminals (POS)Financial
- 10. LESSON VIIStorage Hardware:Primary Storage - the main
- 11. Function of Main Memory or
- 12. Data Representation: - in
- 13. TEXT VIIIThe Anatomy of a MicrocomputerKeyboardMonitor (VDU-
- 14. LESSON IX General Features of Operating SystemsAn
- 15. LESSON X Computer NetworksLink computers by communication lines and software protocols.
- 16. Text A.Types of Networks:LAN- Local Area Network
- 17. Text B: Network ConfigurationsStar - all access
- 18. LESSON XI Text A. A Brief History
- 19. LESSON XII Computer VirusesA computer virus – an
- 20. LESSON XIIIRepairsUni-medium devicesMultimedia High-end multimedia a variety
- 21. LESSON XIV Machine Translation (MT):History of development of machine translation systemsProblems and achievements
- 22. LESSON XV Multimediamultimedia the combination of
- 23. LESSON XVI Text A. Laptops, notebooks, flybooks
- 24. SUPPLEMENTARY TEXTSInternet WordsConversionComputer SecurityWorking with Victims of
- 25. Glossary of computing terms and abbreviations Explanations
- 26. USEFUL LANGUAGE FOR TECHNICIANS Names of
- 27. Скачать презентанцию
LESSON IText A. What is a Computer System?5 elements of a computer system:SoftwarePeopleHardwareProceduresData/InformationText B. The Evolution of ComputersGenerations of Computers
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3LESSON II
Types of Computer Systems:
A supercomputer
A mainframe computer
A minicomputer
A microcomputer
Слайд 4LESSON III
Delete Keys – Clipboard Technology:
a liquid crystal display and
an electronic stylus are used instead of the keyboard
Слайд 6LESSON V
Programs and Programming Languages (a brief history):
FORTRAN
COBOL
ALGOL
PL/1
PASCAL
BASIC
C
Слайд 7LESSON VI
Input Hardware:
Using a Keyboard (with keyboard entry)
Not
using a keyboard
Terminals:
A dumb terminal
E.g. A financial transaction terminal
A smart
terminalE.g. A point-of-sale terminal
An intelligent terminal
E.g.An integrated workstation
A portable terminal, a handheld terminal
Слайд 8Keyboard Entry Input Hardware
MainTypes of Terminals:
A dumb
terminal
A smart terminal
An intelligent terminal
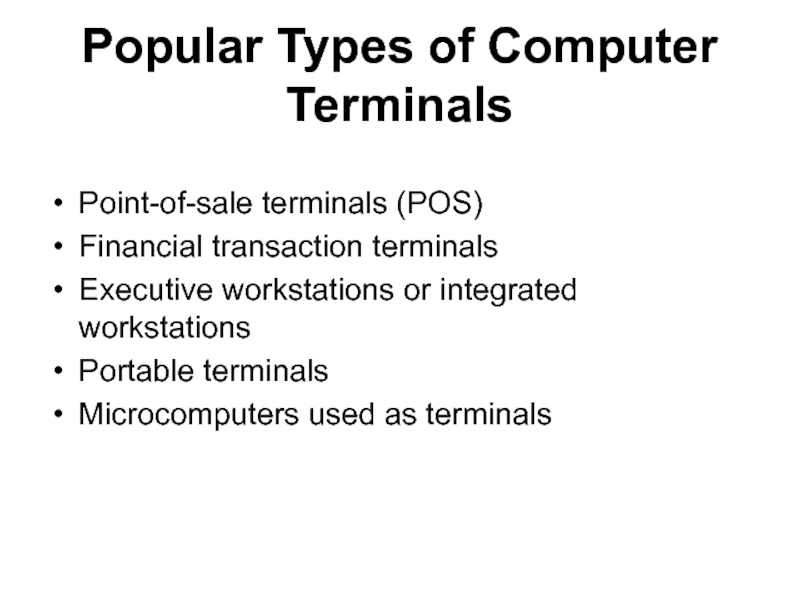
Слайд 9Popular Types of Computer Terminals
Point-of-sale terminals (POS)
Financial transaction terminals
Executive workstations
or integrated workstations
Portable terminals
Microcomputers used as terminals
Слайд 10LESSON VII
Storage Hardware:
Primary Storage - the main memory of a
computer (a volatile form of storage , i.e. the data
and instructions are lost when the computer is turned off.)Secondary (Auxiliary) Storage (a file cabinet) (a nonvolatile form of storage, i.e. the data and instructions remain intact whien the computer is turned off.)
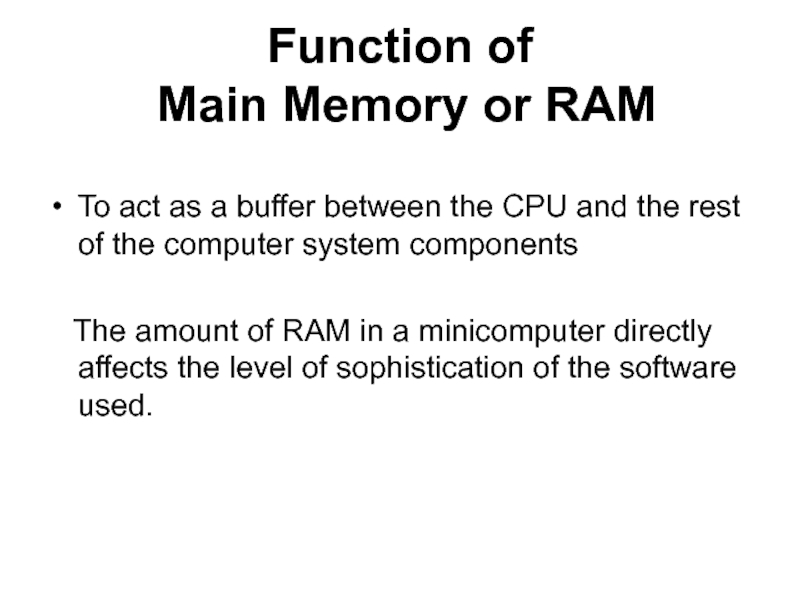
Слайд 11Function of
Main Memory or RAM
To act as a
buffer between the CPU and the rest of the computer
system componentsThe amount of RAM in a minicomputer directly affects the level of sophistication of the software used.
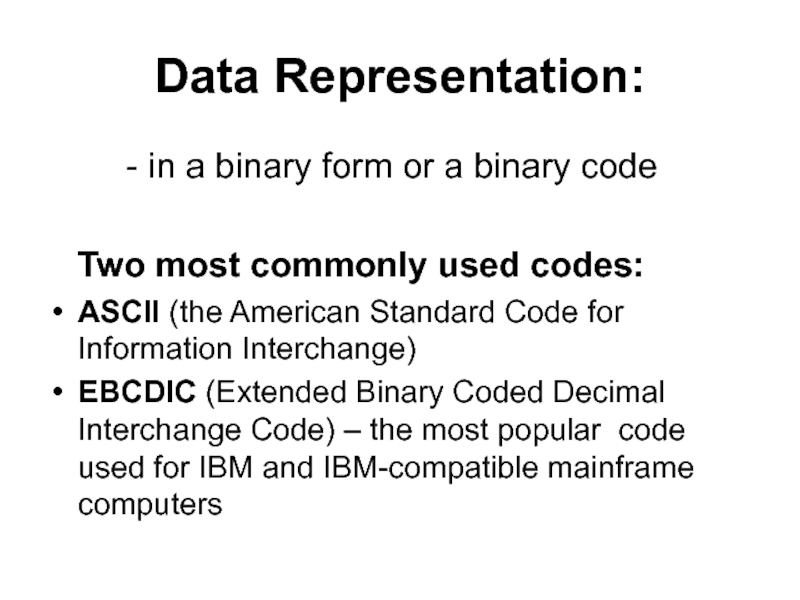
Слайд 12Data Representation:
- in a binary form
or a binary code
Two most commonly used codes:
ASCII
(the American Standard Code for Information Interchange)EBCDIC (Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code) – the most popular code used for IBM and IBM-compatible mainframe computers
Слайд 13TEXT VIII
The Anatomy of a Microcomputer
Keyboard
Monitor (VDU- visual display unit)
System
Unit which houses:
the power supply
the system board
the storage devices
additional components
Слайд 14LESSON IX
General Features of Operating Systems
An operating system - a
master control program which controls the functions of the computer
system as a whole and the running of application programs.All computers do not use the same operating systems. Some software is only designed to run under the control of specific operating systems. Some operating systems are adopted as ‘industry standards”.
Mainframe computers usually process several application programs concurrently, this is known as multiprogramming (multi-tasking in the context of microcomputers). It requires a powerful operating system incorporating work scheduling facilities to control the switching between programs. This entails reading in data for one program while the processor is performing computations on another and printing out results on yet another.
In multi-user environments an operating system is required to control terminal operations on a shared access basis as only one user can access the system at any moment of time. The operating system allocates control to each terminal in turn.
Some environments operate in concurrent batch and real-time mode.
An operating system is stored on disk and has to be booted into the internal memory (RAM)
Слайд 16Text A.Types of Networks:
LAN- Local Area Network (a localized network
usually in one building or a group of buildings close
together, but now it is possible to connect LANs remotely over telephone links so that they look as though they are a single LAN)WAN – Wide Area Network (a network connected over long distance by telephone lines)
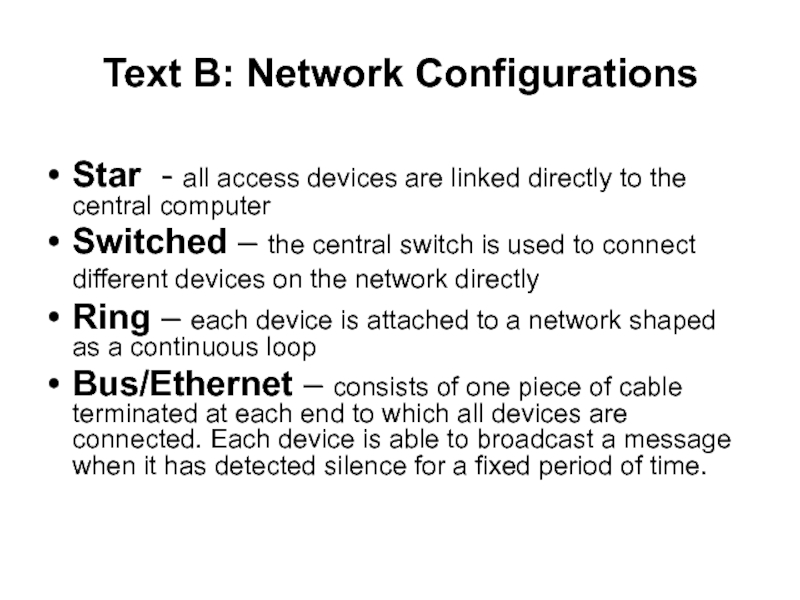
Слайд 17Text B: Network Configurations
Star - all access devices are linked
directly to the central computer
Switched – the central switch is
used to connect different devices on the network directly Ring – each device is attached to a network shaped as a continuous loop
Bus/Ethernet – consists of one piece of cable terminated at each end to which all devices are connected. Each device is able to broadcast a message when it has detected silence for a fixed period of time.
Слайд 19LESSON XII
Computer Viruses
A computer virus – an unwanted program that has
entered your system without you knowing about it. Generally consists
of two parts: the infector and the detonator. Computer virus like a disease can spread (via floppies transported from computer to computer, or networks) to other computers.Generally, the work of the virus is either damaging data on your disks, altering what you see on your computer display, or doing something else that interferes with the normal use of your computer.
Слайд 20LESSON XIII
Repairs
Uni-medium devices
Multimedia
High-end multimedia
a variety of media through
our television: full-motion video, still images, graphics, sound, and animation
School
media: the instructor's words, text, audiotapes, graphics, and a variety of visuals and videoСлайд 21LESSON XIV
Machine Translation (MT):
History of development of machine translation systems
Problems
and achievements
Слайд 22LESSON XV
Multimedia
multimedia the combination of text, graphics, animation, sound,
and video
multimedia computer a computer suitable for running multimedia
programs. It usually has a sound card and a CD-ROM drive. Computer-to-Video Conversion. How they work.
Слайд 23LESSON XVI
Text A. Laptops, notebooks, flybooks
Types
and comparison of modern
portable personal computersText B. Wired Room
Computer facilities in modern foreign hotels
Слайд 24SUPPLEMENTARY TEXTS
Internet Words
Conversion
Computer Security
Working with Victims of Computer Network Hacks
The
Case for Reporting
Debunking the Myths and Explaining the Basics
Desktop replacements
- CNET reviewsСлайд 25Glossary of computing terms
and abbreviations
Explanations of the terms and abbreviations
which
are used in the texts
Examples:
systems program a program that is
part of a computer operating system and controls a basic function of a computer systems programming the writing of systems programs
Слайд 26
USEFUL LANGUAGE FOR TECHNICIANS
Names of tools, terms and directions which
are used in manuals and in captions supplied with the
drawingsUseful for technicians, users and operators of PCs