Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Global Warming
Содержание
- 1. Global Warming
- 2. Global Warming – What is it?Rise in
- 3. The Greenhouse EffectSolar radiation from the Sun
- 4. The Greenhouse EffectWithout With
- 5. Burning of fossil fuelsThe burning of fossil
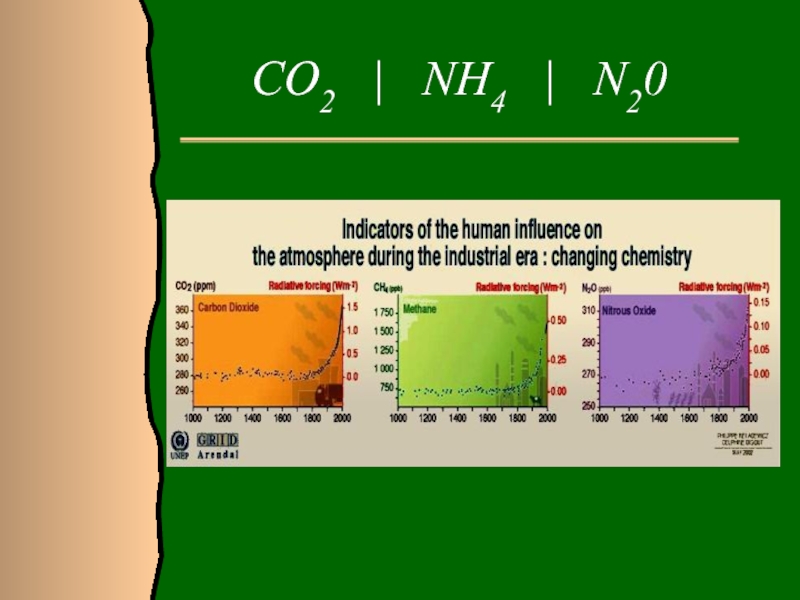
- 6. Carbon dioxide
- 7. Burning of fossil fuelsIn the last 200 years:Nitrous oxide has increased 17%.Methane has increased 150%!!
- 8. CO2 | NH4 | N20
- 9. The Ties Between Sardines & Global WarmingThe
- 10. Sardines & Global Warming (Cont.)Methane is 21
- 11. Effects of global warmingMore carbon dioxide ->
- 12. GLOBAL WARMING: Sea LifeGLOBAL WARMING’S NEGATIVE IMPACT
- 13. Rising Sea levelsThe rise of temperature, even
- 14. The Effects of Global Warming on Land
- 15. Health & Global WarmingExtreme temperatures can directly
- 16. Health & Global Warming (cont.)High temperature can
- 17. Tropical Diseases Global Warming increases drought which lessens
- 18. IMPACT ON AIRThe atmosphere’s ultimate fate is
- 19. El Niño Effect
- 20. El Niño Effect
- 21. El Niño Effect
- 22. Kyoto Protocol The Kyoto Protocol is an
- 23. Kyoto Protocol It’s Getting Warmer! TemperatureArea of Ice
- 24. It was negotiated in Kyoto, Japan in
- 25. UN Framework
- 26. The Climate Stewardship ActFirst introduced in the
- 27. How To Prevent Global Warming:Plant treesConserve
- 28. Reduce,Reuse, Recycle!3R’s of Saving Mother Nature
- 29. Скачать презентанцию
Global Warming – What is it?Rise in earth’s temperatureResults from changes in the natural environment Caused by too much carbon dioxide
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Global Warming – What is it?
Rise in earth’s temperature
Results from
changes in the natural environment
Caused by too much carbon
dioxideСлайд 3The Greenhouse Effect
Solar radiation from the Sun reaches the Earth’s
atmosphere
The surface of the Earth absorbs most of the short-rayed
insolation and later releases this heat in the form of infrared radiation into the atmosphere.Some of the heat is absorbed by particles known as “greenhouse gases.”
The heat retained by the gases acts as a “heat blanket.”
Слайд 5Burning of fossil fuels
The burning of fossil fuels releases Carbon
dioxide in the atmosphere.
In the past 150 years, burning fossil fuels has caused a 25 % increase in Carbon dioxide emissions.
Слайд 7Burning of fossil fuels
In the last 200 years:
Nitrous oxide has
increased 17%.
Methane has increased 150%!!
Слайд 9The Ties Between Sardines & Global Warming
The over-hunting of sardines
has caused higher levels of phytoplankton in the ocean.
While living,
phytoplankton release oxygen into the atmosphere and use Carbon for photosynthesisWhen they die, their decay releases large amounts of methane and the poisonous gas, hydrogen sulfide. It also uses large amounts of oxygen.
Слайд 10Sardines & Global Warming (Cont.)
Methane is 21 times more effective
than carbon dioxide in maintaining heat in the atmosphere.
This
results in the deaths of numerous marine animals.Слайд 11Effects of global warming
More carbon dioxide -> increase in
plant growth.
The increase in temperature -> rise in sea level
from melting glaciers and polar ice caps (adds 0.2 mm annually)Rising temperatures will also cause drier conditions in many important agricultural regions.
Слайд 12GLOBAL WARMING:
Sea Life
GLOBAL WARMING’S NEGATIVE IMPACT ON SEA LIFE—
Coral Reef
Bleaching—
Change in temperature and elevated sea level cause loss
of algae in the coral. Coral appears white, or “bleached.”
Result is mass death of sea animals, which are dependent on the coral reef.
The penguin population near Antarctica has been declining as the distance between them and their food has increased.
Слайд 13Rising Sea levels
The rise of temperature, even to a few
degrees, could lead to the melting of ice shelves that
hold back glaciers. This results in rising sea levelsThe Larsen area of North Antarctic, South of Chili and Argentina have lost more than 5,200 sq miles of area.
Слайд 14The Effects of Global Warming on Land animals
Global warming can
disrupt the migration, hibernation and reproductive cycles of certain types
of animals.Plants and animals will find it hard to escape or adjust to the effects of warming because humans occupy so much land.
Farmland or cities interrupt the movement of species between habitats.
Слайд 15Health & Global Warming
Extreme temperatures can directly cause the loss
of life (ex: 35,000 people died during heat wave in
Europe, Aug‘03.)Warmer weather provides an ideal breeding environment for mosquitoes. Diseases such as West Nile will be more common.
.
Слайд 16Health & Global Warming (cont.)
High temperature can increase pollution of
water and air, which harms the human body.
.
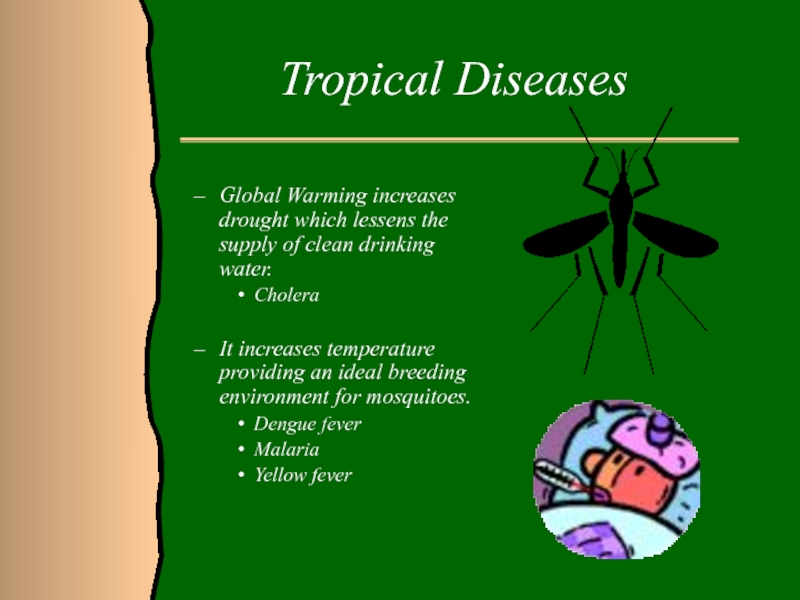
Слайд 17Tropical Diseases
Global Warming increases drought which lessens the supply of
clean drinking water.
Cholera
It increases temperature providing an ideal breeding
environment for mosquitoes. Dengue fever
Malaria
Yellow fever
Слайд 18IMPACT ON AIR
The atmosphere’s ultimate fate is unclear.
More evaporation
increase in cloud cover
How High Will the Clouds Be?
It makes a difference!Clouds close to the earth reflect sunlight cooling effect.
Clouds high in the atmosphere trap heat warmingeffect.
Generally:
Cloud cover increases
Levels of the greenhouse gas methane may increase
Hurricanes range farther north, south on warmer water
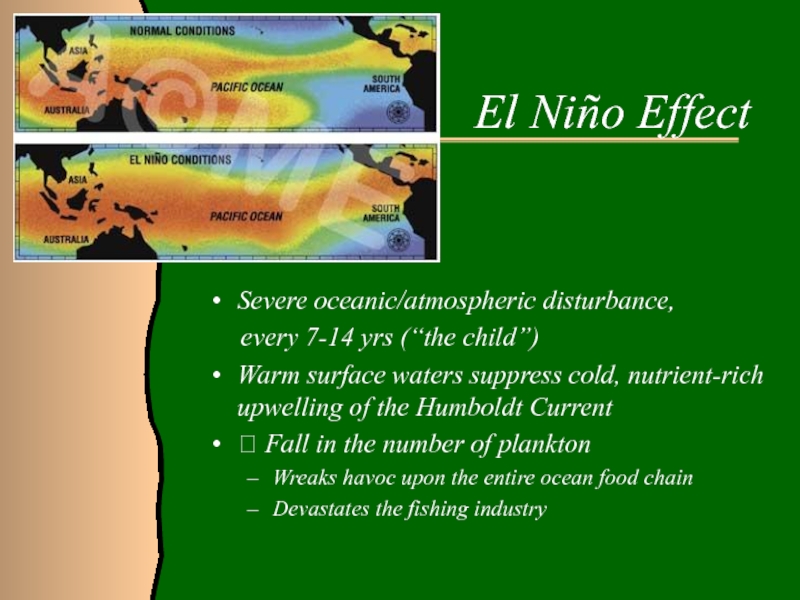
Слайд 19El Niño Effect
Severe oceanic/atmospheric disturbance,
every 7-14 yrs (“the child”)
Warm surface waters
suppress cold, nutrient-rich upwelling of the Humboldt Current Fall in the number of plankton
Wreaks havoc upon the entire ocean food chain
Devastates the fishing industry
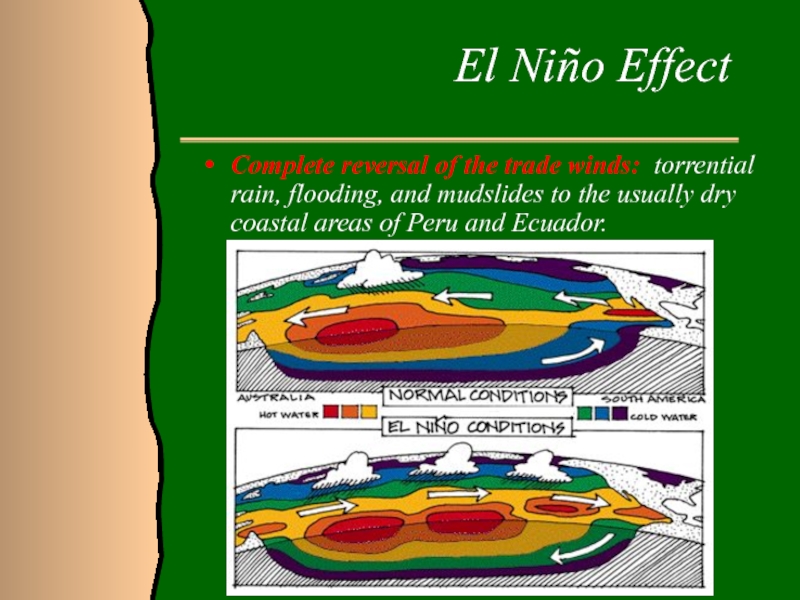
Слайд 20El Niño Effect
Complete reversal of
the trade winds: torrential rain, flooding, and mudslides to the
usually dry coastal areas of Peru and Ecuador.Слайд 21El Niño Effect
Collapse of the
monsoons in Asia severe drought to Indonesia and northern
Australia.Severe weather disturbances in other parts of the world, such as droughts in areas of Africa and central North America.
Слайд 22Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol is an amendment to the United
Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC)
UNFCCC, an international
treaty on global warmingCountries which ratify this protocol commit to reduce their emissions of carbon dioxide and five other greenhouse gases
A total of 141 countries have ratified the agreement. Notable exceptions include the United States and Australia
Слайд 24It was negotiated in Kyoto, Japan in December 1997, opened
for signature on March 16, 1998, and closed on March
15, 1999Current estimates are that even if successfully and completely implemented, the Kyoto Protocol is predicted to reduce the average global temperature by somewhere between 0.02°C and 0.28°C by the year 2050
Continued..
Слайд 25 UN Framework On
Climate Change
Article 2 (iv) Research on, and
promotion, development and increased use of, new and renewable forms of energy, of carbon dioxide sequestration technologies and of advanced and innovative environmentally sound technologies (vi) Encouragement of appropriate reforms in relevant sectors aimed at promoting policies and measures which limit or reduce emissions of greenhouse gases not controlled by the Montreal Protocol;
(viii) Limitation and/or reduction of methane emissions through recovery and use in waste management, as well as in the production, transport and distribution of energy
Слайд 26The Climate Stewardship Act
First introduced in the senate in 2003
and reintroduced in February 2005
It would reduce carbon dioxide, methane,
nitrous oxide, hydroflurocarbon and perfuorocarbons which are released by power plants to 2000 levels by 2010.The bill reduces the risk of global warming without hurting the economy.
Слайд 27How To Prevent
Global Warming:
Plant trees
Conserve energy:
(examples: 1. use low-energy,
low-water-use washing machines, 2. use a solar heated system for
hot water, 3. use an electric or push mower for gasoline powered mower)Buy energy efficient products
Buy products that have reusable or recyclable packaging
Reduce use of car (walk instead)