Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
How it develops and progresses.
Содержание
- 1. How it develops and progresses.
- 2. A few words before we start…..Haploid: half
- 3. Cell Reproductionis either sexual or asexual
- 4. Asexual Reproduction (one parent)Binary Fission-Vegetative Propagation Regeneration Advantages?Disadvantages?
- 5. Asexual reproductionAdvantages:Doesn’t require a mateTakes less timeDisadvantages:All offspring are the same (genetically)
- 6. Sexual Reproduction2 “parents” or 2 sets of DNAExamples: humans, plants, dogs
- 7. AdvantagesDIVERSITY!!!!!!!!!!Offspring are genetically different from parents.Disadvantages?Need a mateTakes longerSexual reproduction
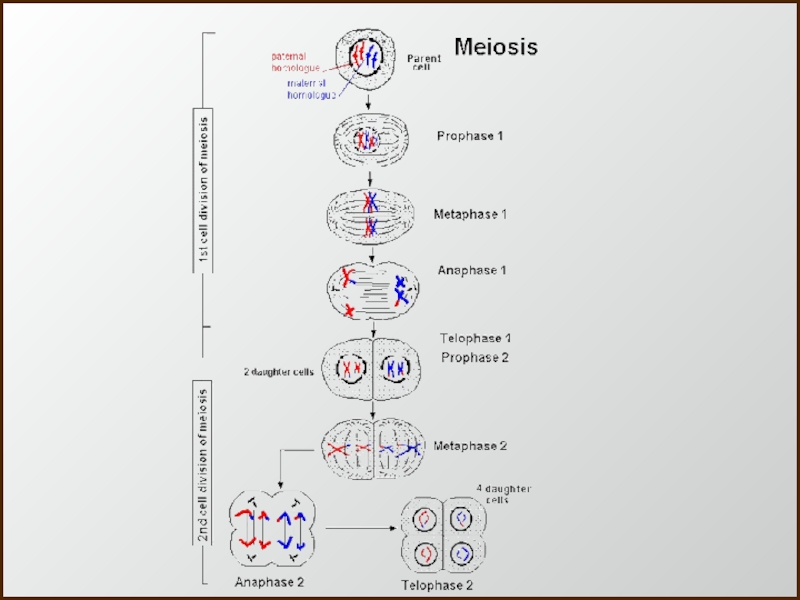
- 8. MeiosisSexual Reproduction (two parents)
- 9. Why Meiosis?Meiosis - The production of gametes
- 10. Слайд 10
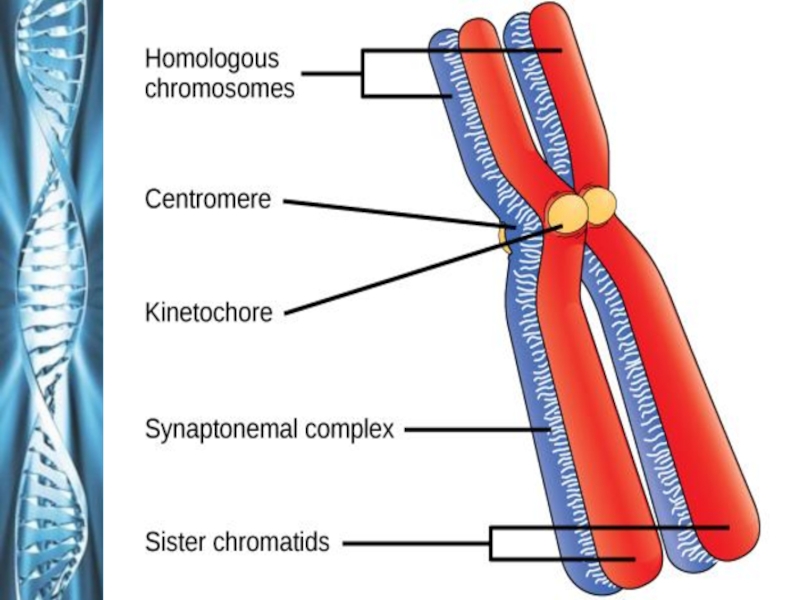
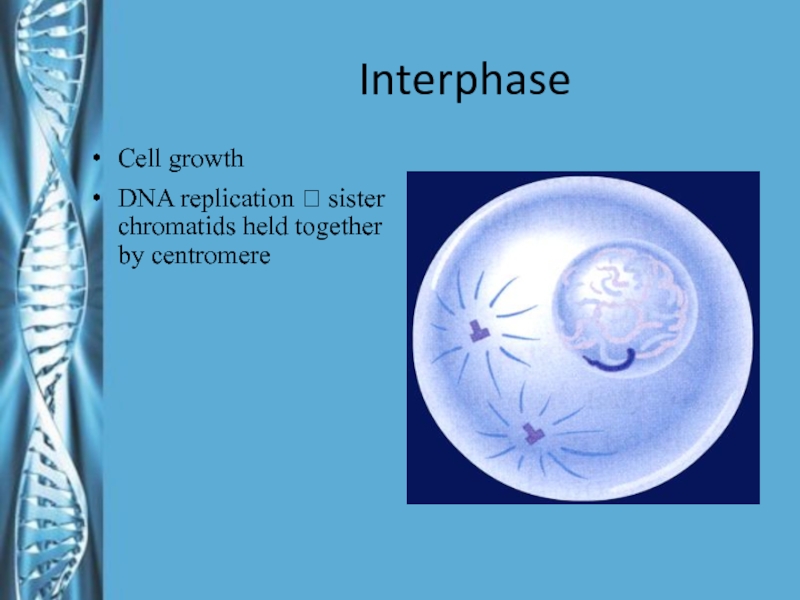
- 11. InterphaseCell growthDNA replication ? sister chromatids held together by centromere
- 12. Prophase IThe chromosomes coil up and a
- 13. Prophase I – crossing overCrossing over occurs
- 14. During prophase of meiosis I, homologous pairs
- 15. CROSSINGOVERCrossing over produces recombinant chromosomes, which combine
- 16. Crossing OverHomologous chromosomes line up during meiosisParts of maternal and paternal chromosomes migrate
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Metaphase IThe spindle fibers pull the tetrads
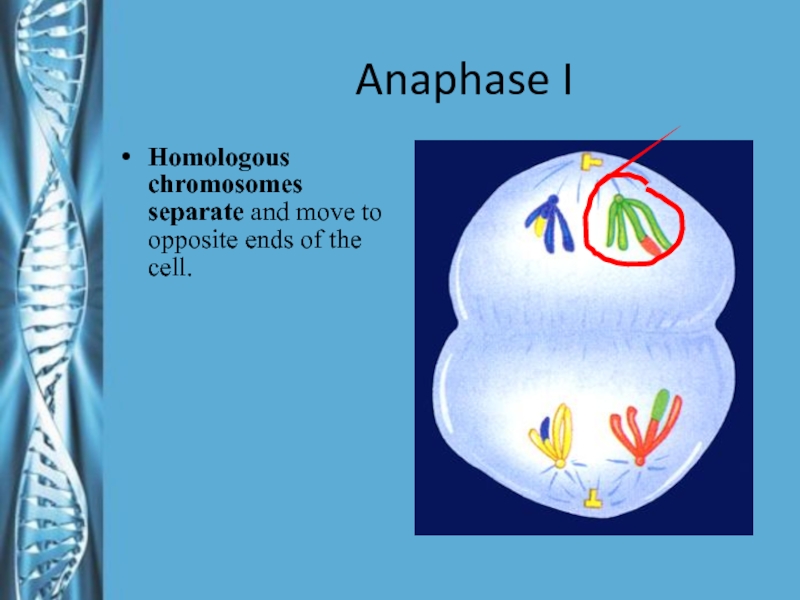
- 19. Anaphase IHomologous chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends of the cell.
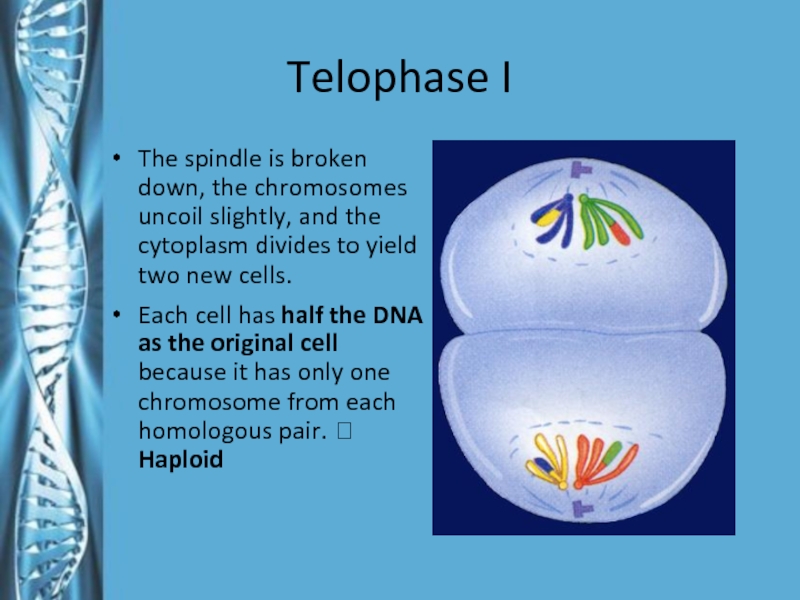
- 20. Telophase IThe spindle is broken down, the
- 21. Remember mitosis?Meiosis II looks just like mitosis except there is no DNA replication during interphase
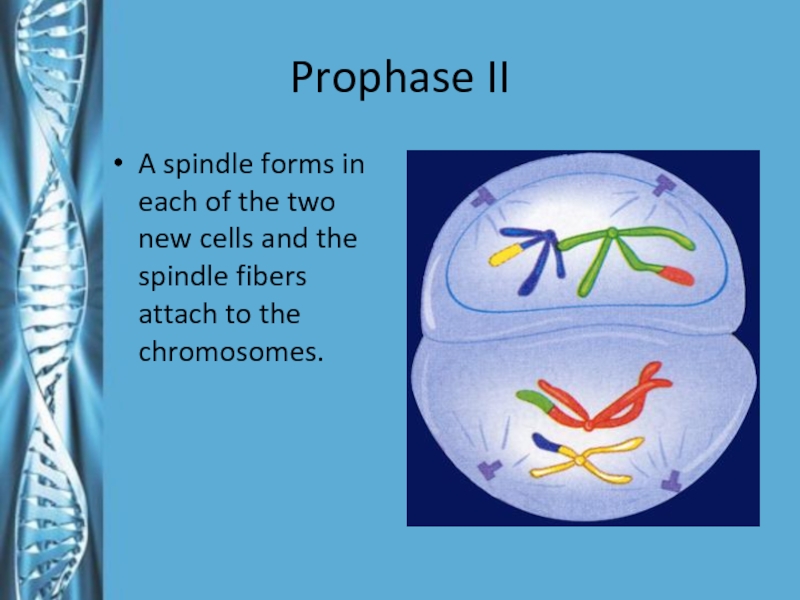
- 22. Prophase IIA spindle forms in each of
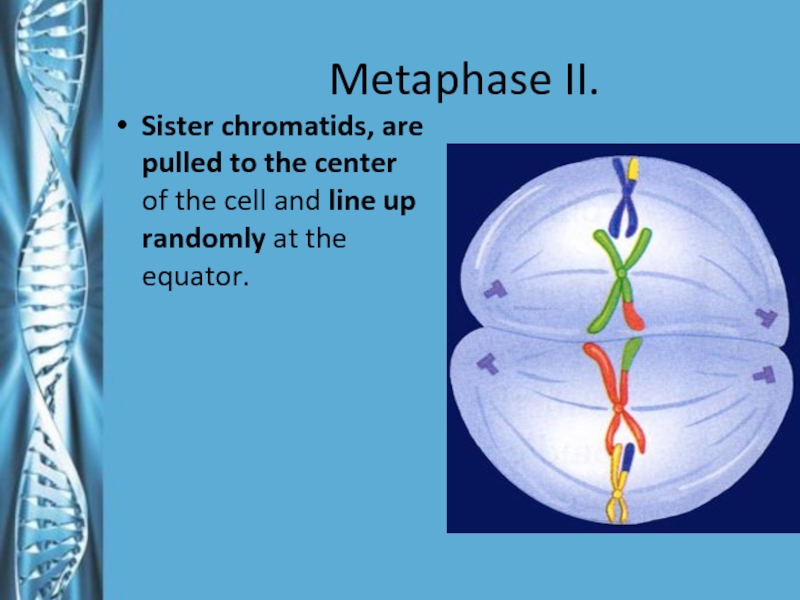
- 23. Metaphase II.Sister chromatids, are pulled to the
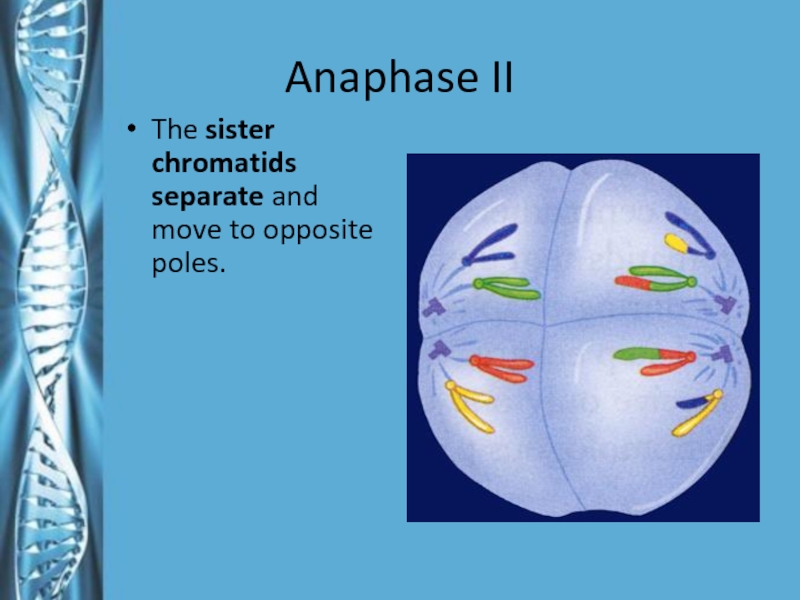
- 24. Anaphase IIThe sister chromatids separate and move to opposite poles.
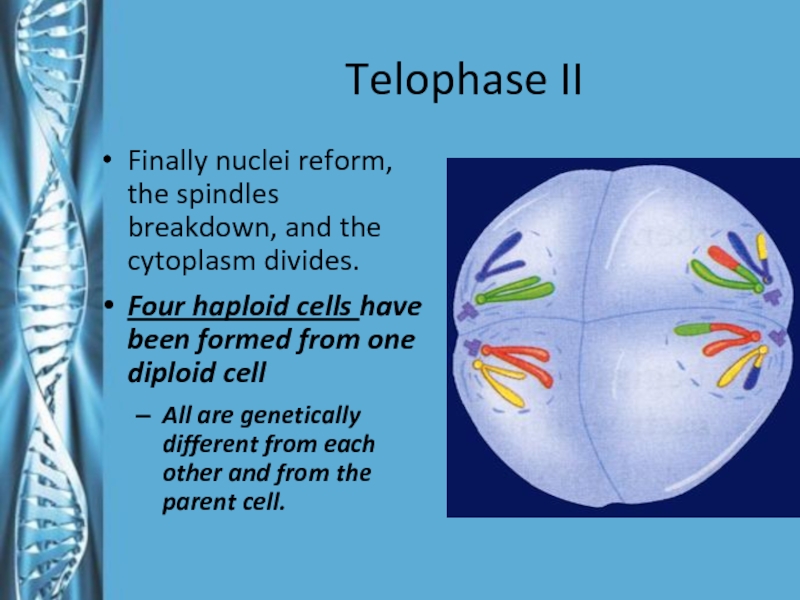
- 25. Telophase IIFinally nuclei reform, the spindles breakdown,
- 26. Слайд 26
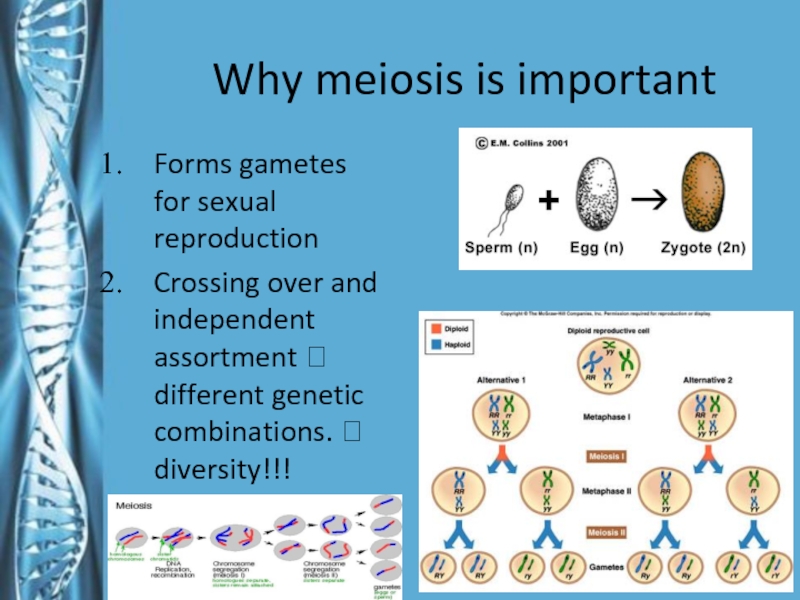
- 27. Why meiosis is importantForms gametes for sexual
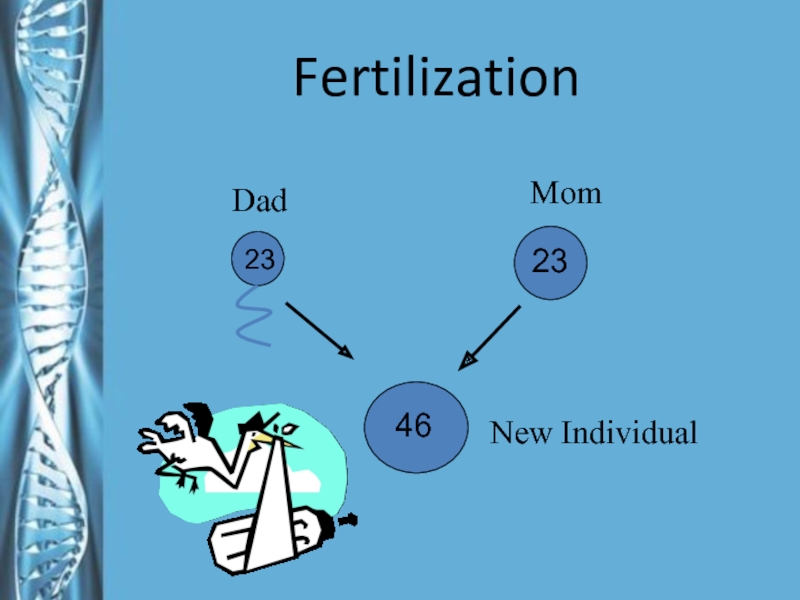
- 28. Fertilization462323
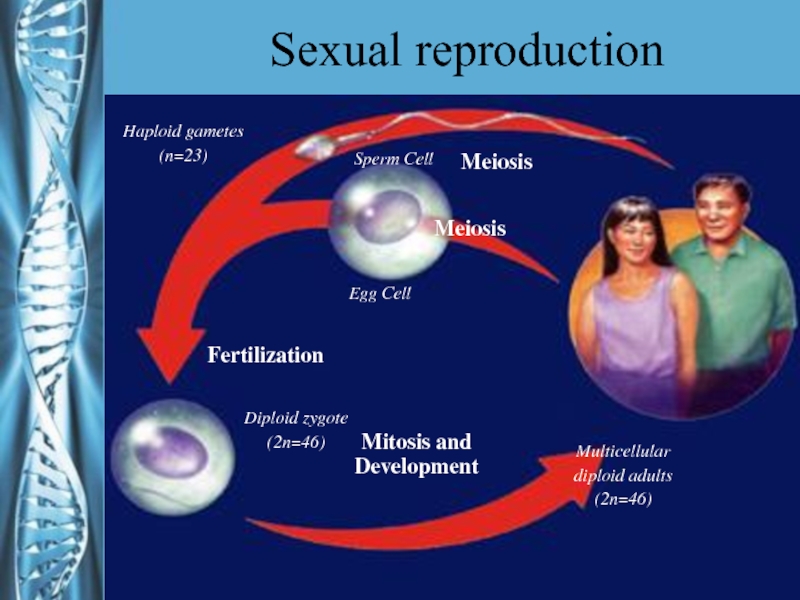
- 29. Sexual reproductionMeiosisMeiosisSperm CellEgg CellHaploid gametes(n=23)FertilizationDiploid zygote(2n=46)Mitosis and DevelopmentMulticellulardiploid adults(2n=46)
- 30. Mitosis vs. Meiosis √√√√√√
- 31. Mitosis vs. Meiosis√√√√
- 32. Скачать презентанцию
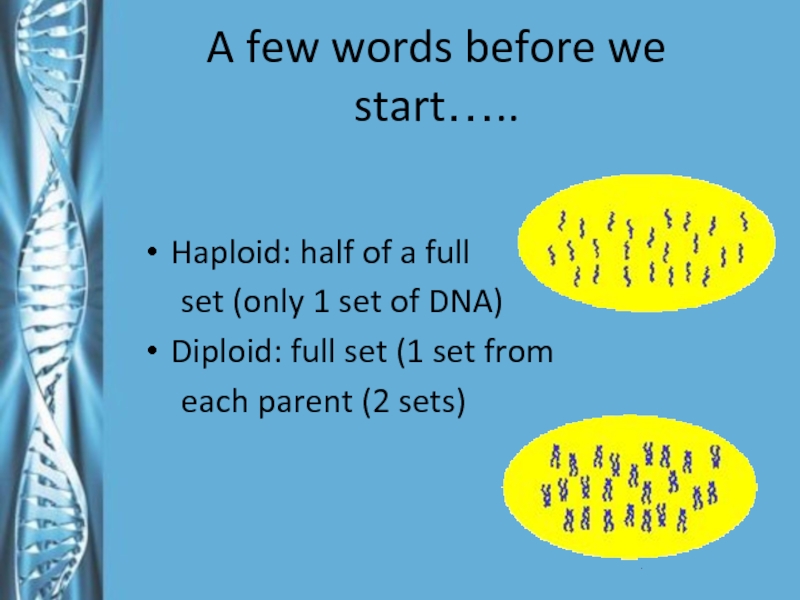
A few words before we start…..Haploid: half of a full set (only 1 set of DNA)Diploid: full set (1 set from each parent (2 sets)
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1Describe the phases of meiosis and the mechanisms of recombination
of genetic material during meiosis
Слайд 2A few words before we start…..
Haploid: half of a full
set (only 1 set of DNA)
Diploid: full set
(1 set fromeach parent (2 sets)
Слайд 4Asexual Reproduction
(one parent)
Binary Fission-
Vegetative Propagation
Regeneration
Advantages?
Disadvantages?
Слайд 5Asexual reproduction
Advantages:
Doesn’t require a mate
Takes less time
Disadvantages:
All offspring are the
same (genetically)
Слайд 7Advantages
DIVERSITY!!!!!!!!!!
Offspring are genetically different from parents.
Disadvantages?
Need a mate
Takes longer
Sexual reproduction
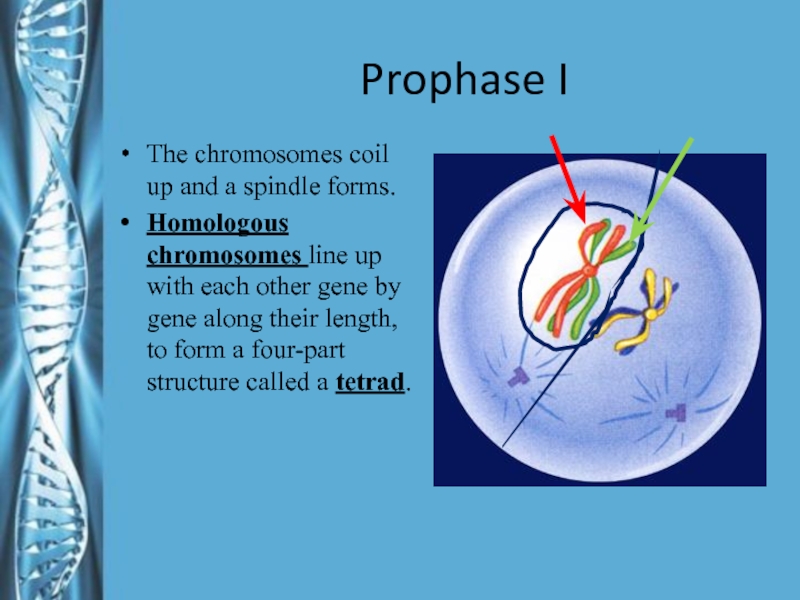
Слайд 12Prophase I
The chromosomes coil up and a spindle forms.
Homologous chromosomes
line up with each other gene by gene along their
length, to form a four-part structure called a tetrad.
Слайд 13Prophase I – crossing over
Crossing over occurs between homologous chromosomes
? new genetic combinations that are different from the parent.
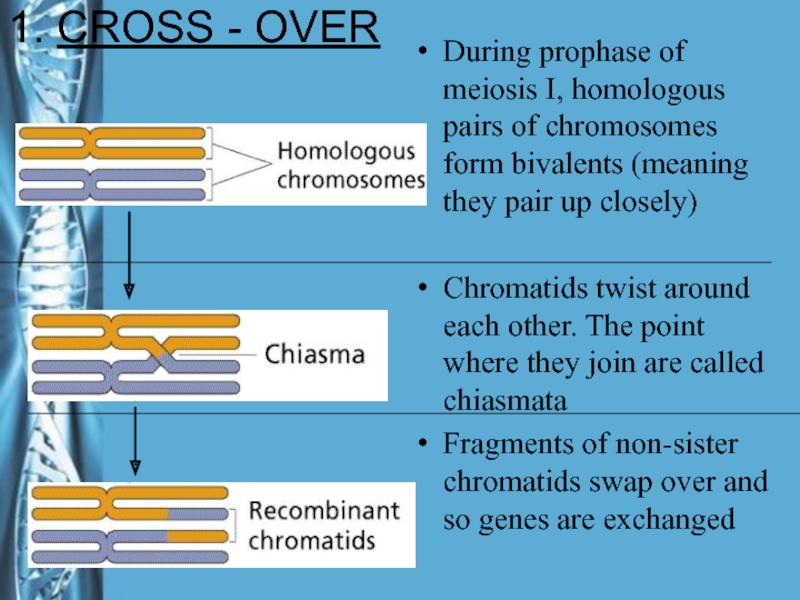
Слайд 14During prophase of meiosis I, homologous pairs of chromosomes form
bivalents (meaning they pair up closely)
Chromatids twist around each other.
The point where they join are called chiasmataFragments of non-sister chromatids swap over and so genes are exchanged
1. CROSS - OVER
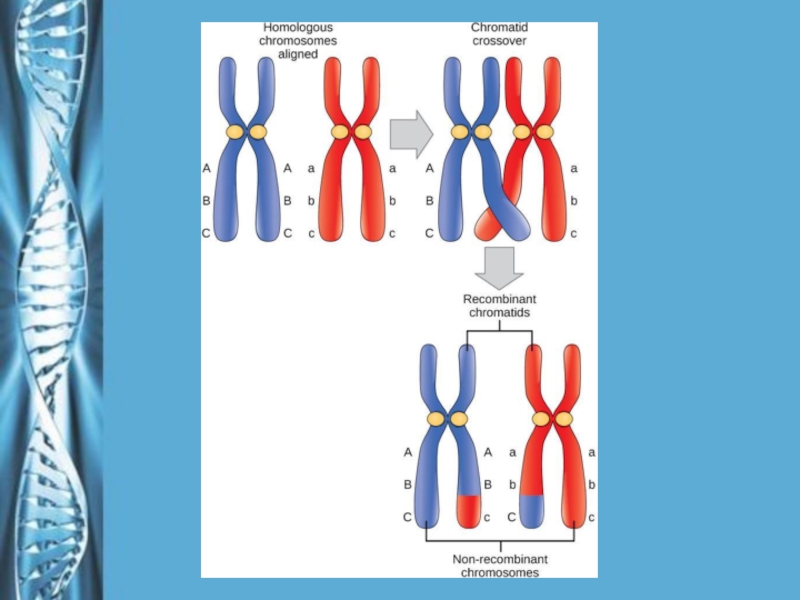
Слайд 15CROSSINGOVER
Crossing over produces recombinant chromosomes, which combine genes inherited from
each parent.
Crossing over begins very early in prophase I, as
homologous chromosomes pair up gene by gene.In crossing over, homologous portions of two nonsister chromatids trade places.
Crossing over contributes to genetic variation by combining DNA from two parents into a single chromosome.
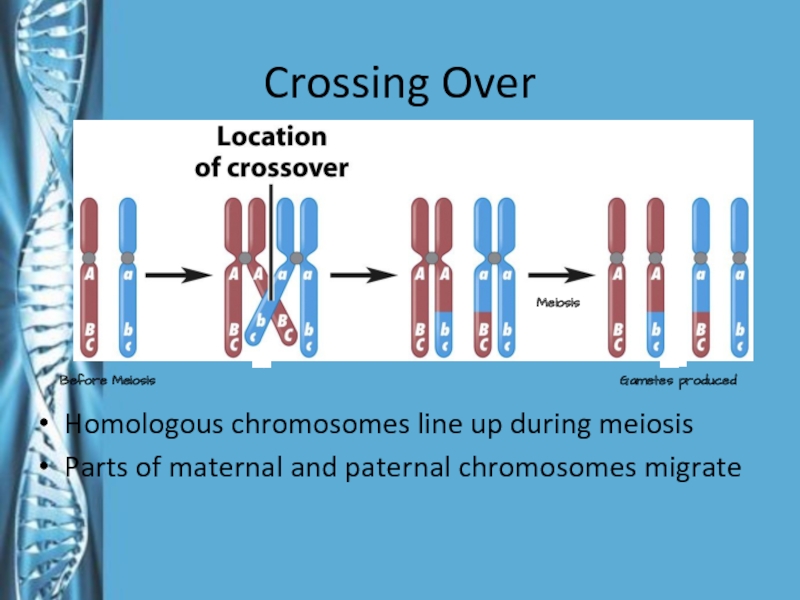
Слайд 16Crossing Over
Homologous chromosomes line up during meiosis
Parts of maternal and
paternal chromosomes migrate
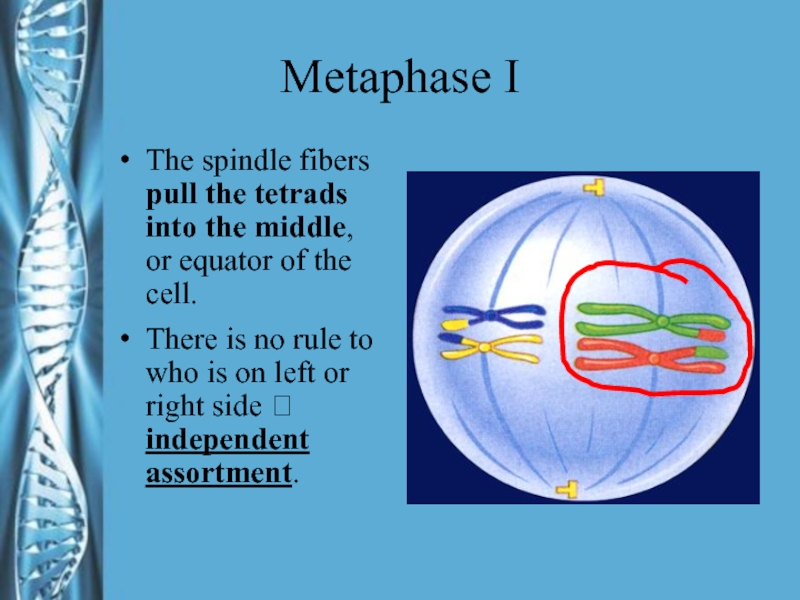
Слайд 18Metaphase I
The spindle fibers pull the tetrads into the middle,
or equator of the cell.
There is no rule to who
is on left or right side ? independent assortment.