Goals
Recognize the importance of data, their issues, and their life
cycle.Describe the sources of data, their collection, and quality issues.
Describe document management systems.
Explain the operation of data warehousing and its role in decision support.
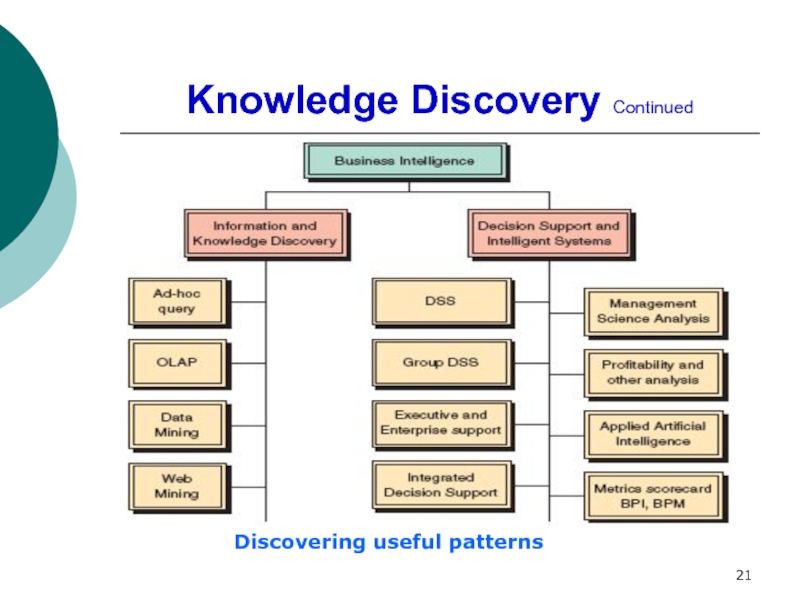
Describe information and knowledge discovery and business intelligence.
Understand the power and benefits of data mining.
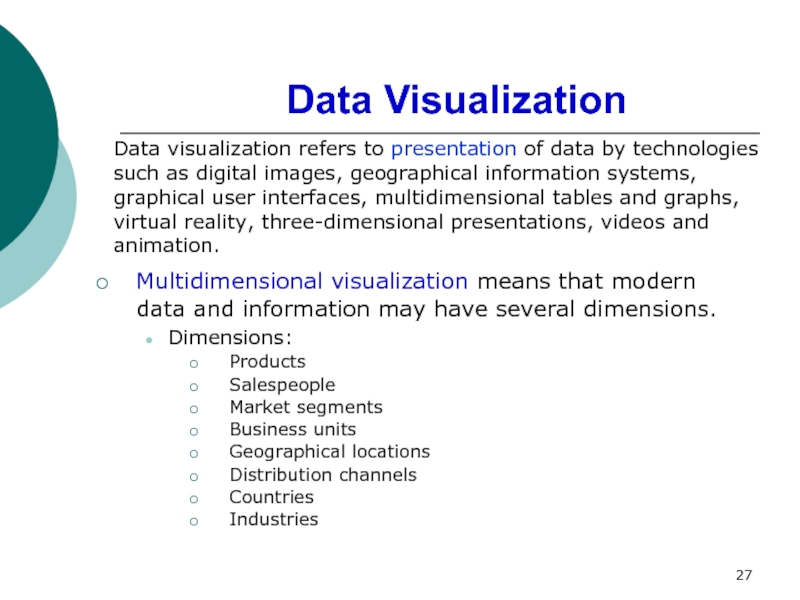
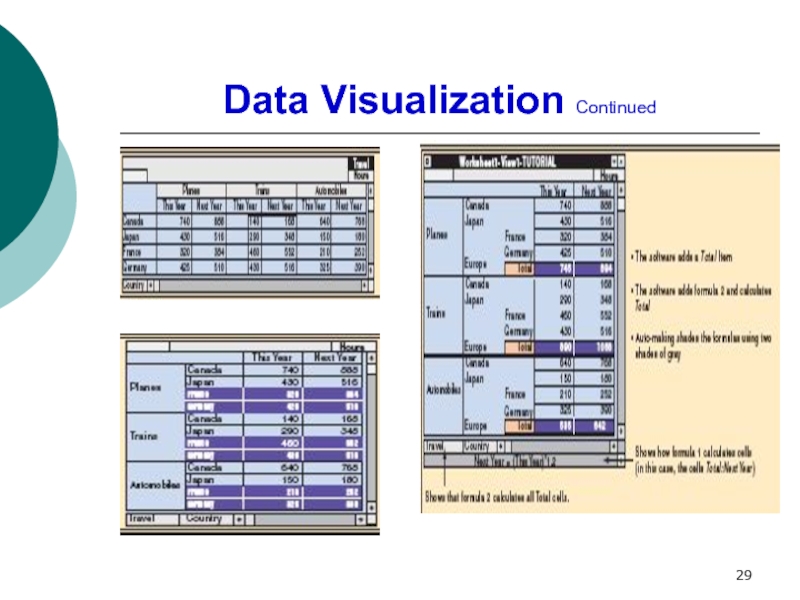
Describe data presentation methods and geoinfosystems and virtual reality as decision support tools.
Discuss the role of marketing databases
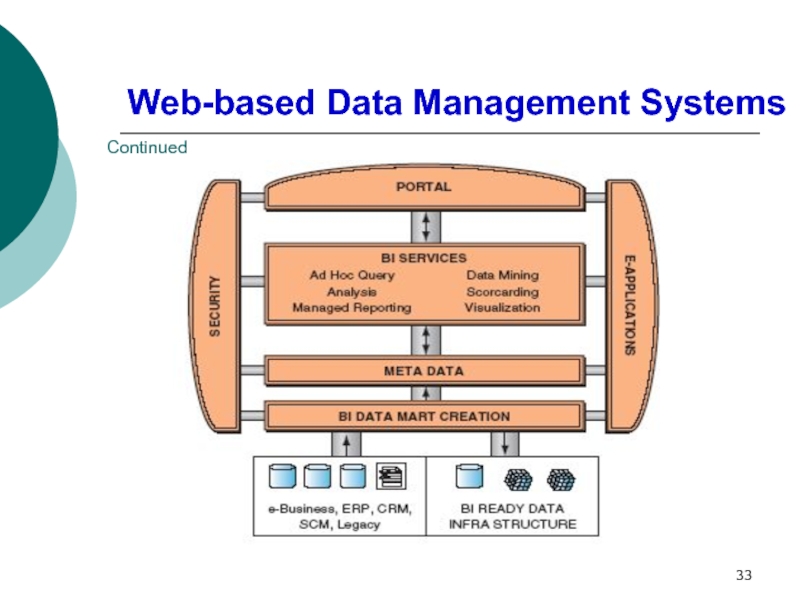
Recognize the role of the Web in data management