Слайд 12012
Economics of enterprise
KROK University
Spring 2012
Instructor Tetiana Iesypchuk
Слайд 2Home assignment for Monday 30.01.2012
Revise the first lecture for the
test
Prepare presentations which are left (it was due to 23.01)
Make
sure to have written homework for the first seminar (I’ll check it)
Revise the second lecture (1-4 questions)
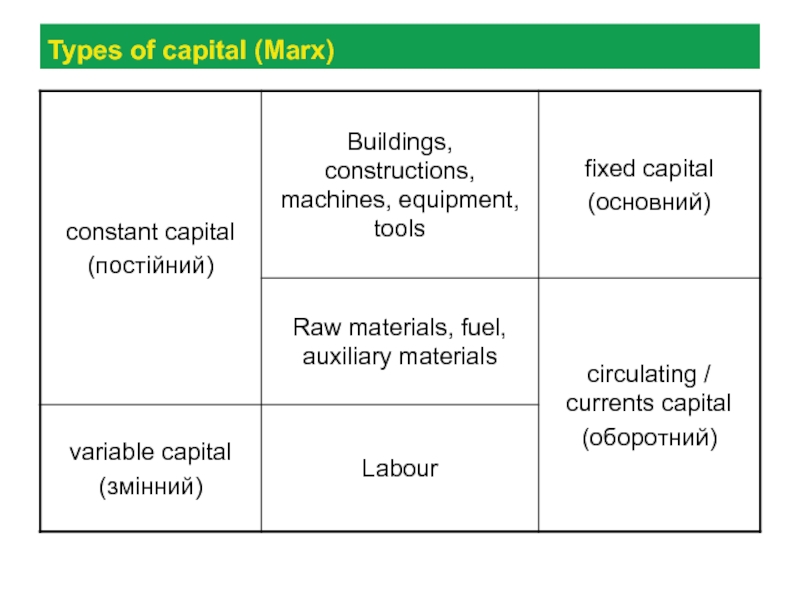
Types of capital by Marx (definitions and examples)
Production assets (funds) (definitions and structure)
Слайд 3Property of enterprise
Essence, types and functions of capital
Production Assets (funds)
Fixed
assets: Classification, Structure, and Valuation
Ageing, Depreciation and Improvement of
Fixed Assets
Efficiency of Fixed Assets
Lecture 2
Capital and Fixed assets (funds)
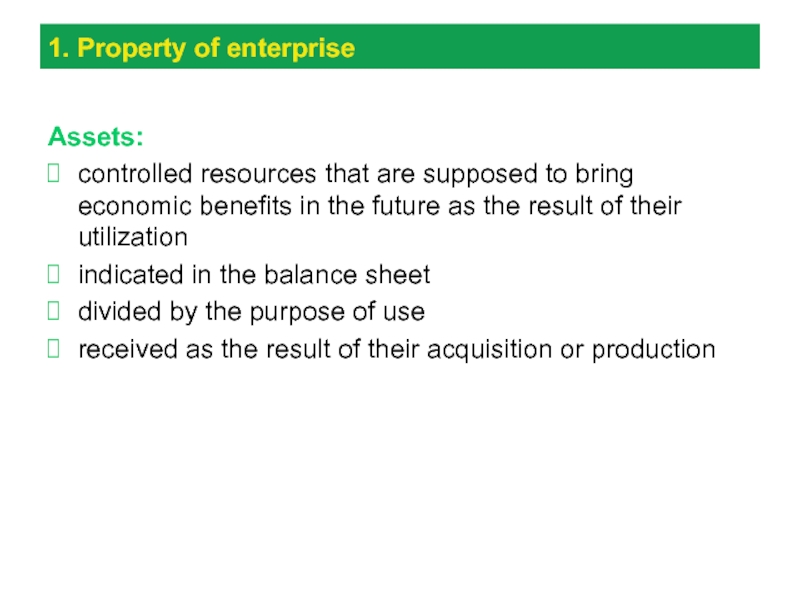
Слайд 41. Property of enterprise
Assets:
controlled resources that are supposed to
bring economic benefits in the future as the result of
their utilization
indicated in the balance sheet
divided by the purpose of use
received as the result of their acquisition or production
Слайд 5Assets
Non-negotiables
Circulating assets
Слайд 6Non-negotiables
fixed assets
intangible assets – rights for industrial and intellectual property
construction
in progress
long-term financial investments
long-term accounts receivable
future revenue derived from taxes
other
non-negotiable assets
Слайд 7Circulating (current) assets
Money and other assets that
are to be sold or used during next 12 months
Supplies (запаси)
Manufacturing stocks
Semi-finished goods
Animals
Non-finished production
Finished goods
Products
Слайд 8Circulating (current) assets
Cash, accounts and other assets
Received bills
Accounts receivable (for
goods and services; budget; prepayment; calculated revenues; internal accounts; other)
Current
(short-term) financial investments
Cash and its equivalents
Other circulating assets
Future spending
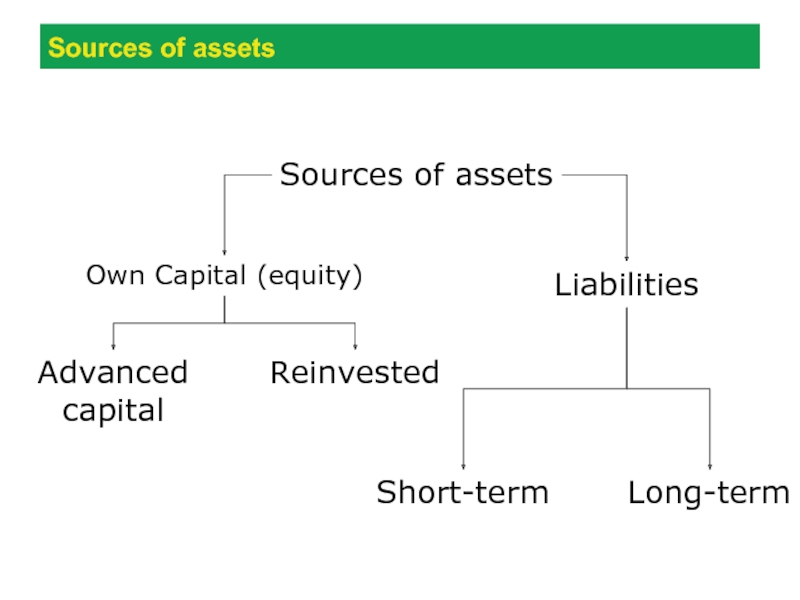
Слайд 9Sources of assets
Own Capital (equity)
Liabilities
Advanced capital
Reinvested
Short-term
Long-term
Sources of assets
Слайд 102. Essence, types and functions of capital
Capital
any form of wealth
capable of being employed in the production of more wealth
sum
of money necessary to start and run a business
Слайд 11advanced capital is
sum of money invested in the company
with the purpose of profit making
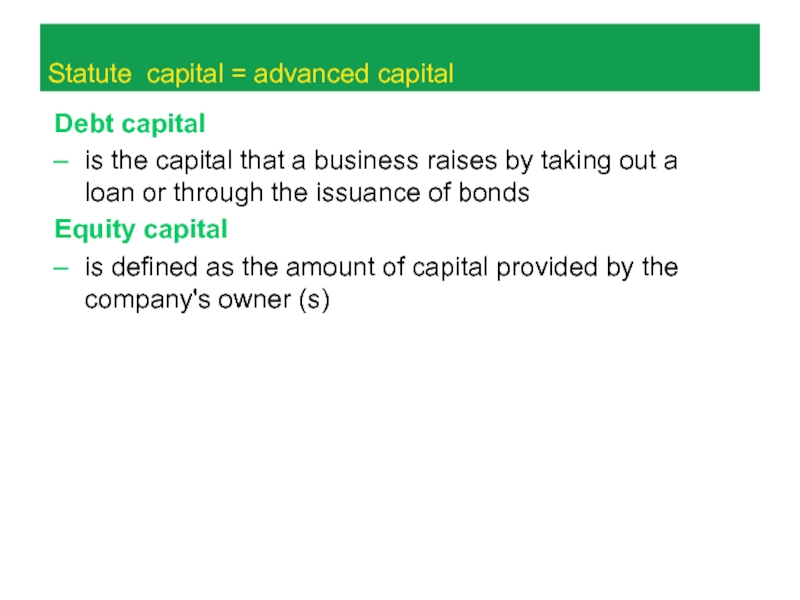
Слайд 12Statute capital = advanced capital
Debt capital
is the capital that
a business raises by taking out a loan or through
the issuance of bonds
Equity capital
is defined as the amount of capital provided by the company's owner (s)
Слайд 14Functions of equity capital
Long-term financing
Responsibility and protection of creditors
Compensation of
losses
Solvency
Financing of risky projects
Independence and power
Distribution of profits
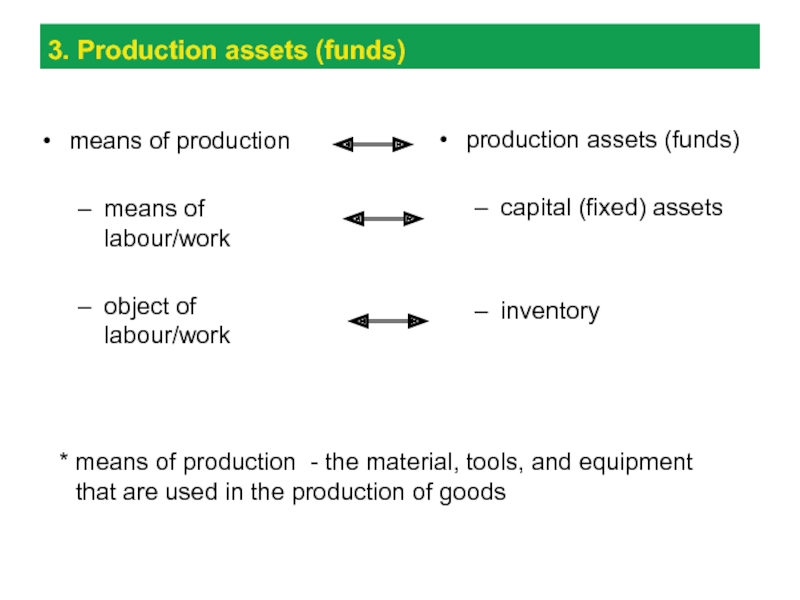
Слайд 153. Production assets (funds)
means of production
means of labour/work
object of
labour/work
production assets (funds)
capital (fixed) assets
inventory
* means of production -
the material, tools, and equipment that are used in the production of goods
Слайд 16Circulating assets is …
A part of production assets
(funds) in the form of objects of labor that are
completely used (consumed) in every production cycle, change or completely lose natural form and transfer all the value on final goods
Слайд 174. Fixed (capital) Assets: Classification, and Valuation
Means of
labor that have value and functioning in manufacturing for a
long time in unchanged consumer form.
Their value is transferred on final goods by parts.
They are used for more then 1 year or one production cycle if it is more than 1 year
Слайд 18Basics of classification (1)
Accounting Standard
#7:
Land (not agricultural land)
Capital spending to land improvement
Buildings, installations and
transmitting terminals
Machines and equipment
Vehicles
Instruments, appliances and implements (Household electric, optic, electromechanic appliances and instruments)
Working and productive animals (horses, cows etc. but not animals that are kept for meat)
Perennial plants
Others (Library funds, Furniture, office equipment )
* Transmitting terminals - land improvement, designed to perform special functions in the transmission of energy, materials, signal information, etc. of any origin and type of distance (transmission lines, pipelines, water pipelines, power and gas networks, lines, etc.).
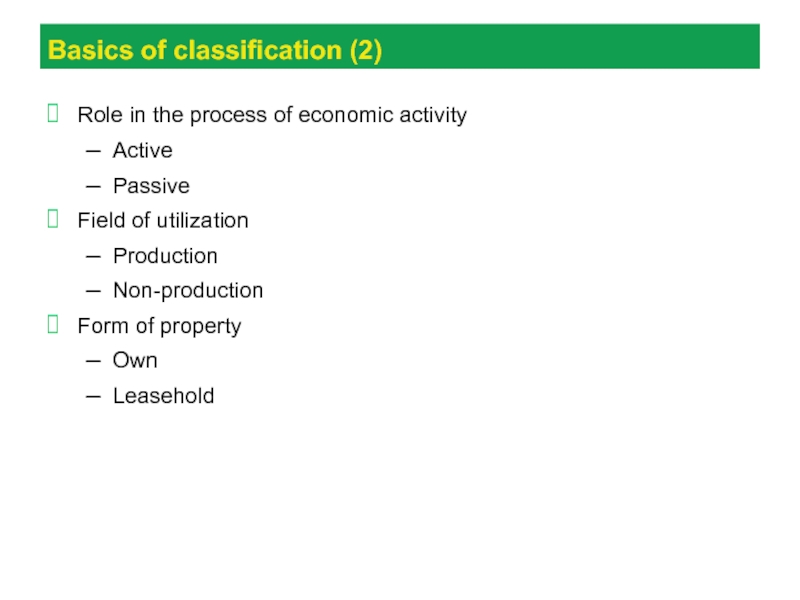
Слайд 19Basics of classification (2)
Role in the process of economic activity
Active
Passive
Field
of utilization
Production
Non-production
Form of property
Own
Leasehold
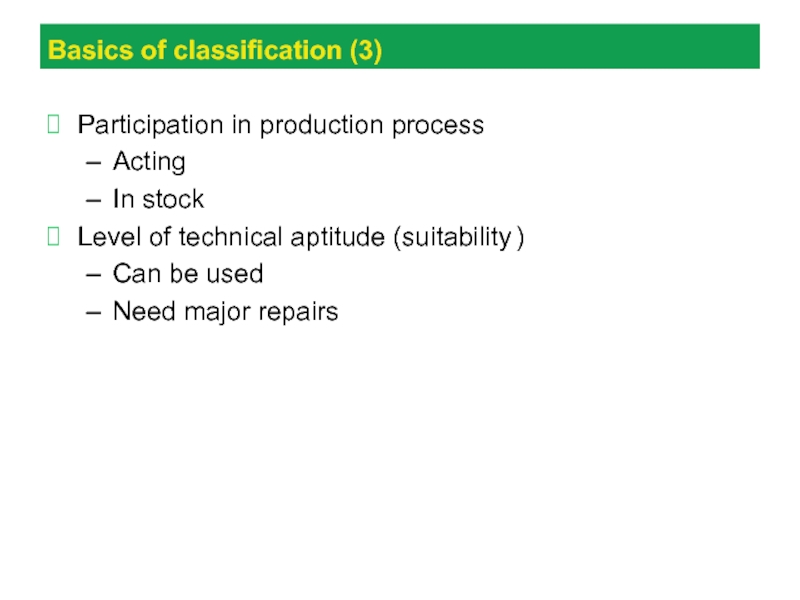
Слайд 20Basics of classification (3)
Participation in production process
Acting
In stock
Level of technical
aptitude (suitability )
Can be used
Need major repairs
Слайд 21Structure of capital assets
Ratio of certain capital assets in their
overall value
Manufacturing (functional, technological)
Active and passive
Age
Слайд 22Valuation of capital (fixed) assets
Initial value – de
facto (historical) costs of purchasing (production)
includes the
following costs:
amounts paid to suppliers and contractors for the assets of construction works (excluding indirect taxes);
registration fees, government fees and similar payments made in connection with the purchase rights to the object of fixed assets;
amount of import (customs) duty;
amount of indirect taxes in connection with the acquisition (creation) of fixed assets (if they are not reimbursed by the company);
Insurance
Costs of assembling and tooling
Other costs needed to make the capital assets usable
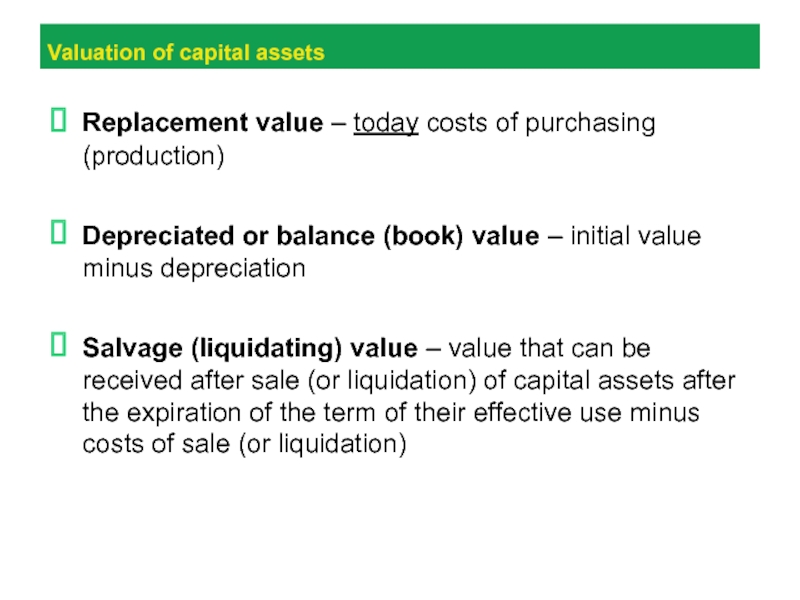
Слайд 23Valuation of capital assets
Replacement value – today costs of purchasing
(production)
Depreciated or balance (book) value – initial value minus depreciation
Salvage
(liquidating) value – value that can be received after sale (or liquidation) of capital assets after the expiration of the term of their effective use minus costs of sale (or liquidation)