Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Thermal radiation
Содержание
- 1. Thermal radiation
- 2. Quick Quiz 2Using Figure as a starting
- 3. Quick Quiz 3Cat’s eyes have pupils that
- 4. Quick Quiz 4If laser light is reflected
- 5. Course of lectures «Contemporary Physics: Part2»Lecture №5Thermal
- 6. Thermal radiationKirchhoff's lawТ(1)(2)Ratio of the emissivity of
- 7. Good model of this body is the
- 8. In 1879 Stephen on the base of
- 9. Displacement lawLocation of the maximum of spectral
- 10. (1)(2)(3)(4)(5)the Rayleigh–Jeans lawPower on unit spectral interval
- 11. Wien's lawPlanck concluded, that the radiation and
- 12. Planck equation at small x (high frequencies
- 13. Real bodies have different radiation and absorption.
- 14. Dielectic radiation coefficients for (ω/c) ηλ*L>>1Rλ
- 15. Integral radiation coefficient of several dielectrics as
- 16. Spectral radiation coefficient ελ of some metals:
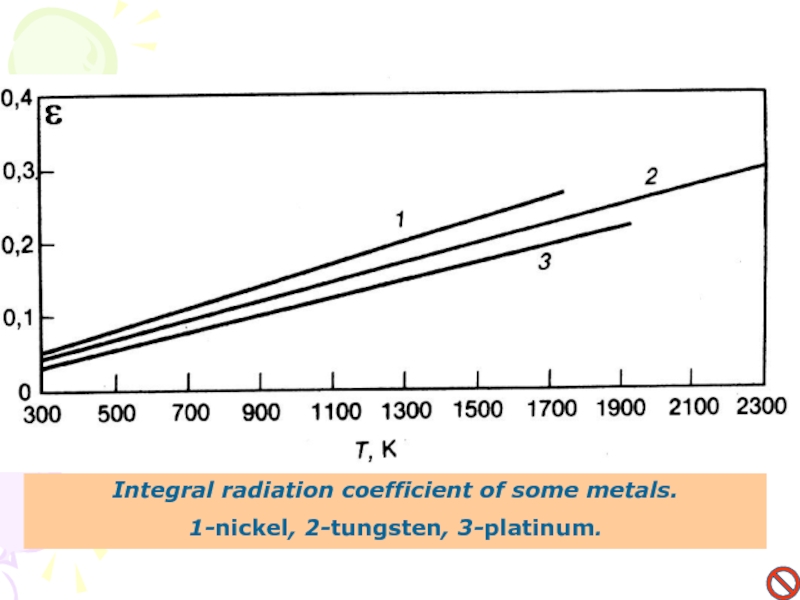
- 17. Integral radiation coefficient of some metals.1-nickel, 2-tungsten, 3-platinum.
- 18. Dependence of radiation coefficient from the angle
- 19. Selective coating are special coatings for heat
- 20. objectiveocularПриёмникgalvanometerThe hot objectRadiation pyrometersПирометры основаны на фокусировке
- 21. Яркостные пирометры. Действие пирометра основано на сравнении
- 22. Цветовые пирометры. Серое тело имеет тот же
- 23. Учебный фильм«Лучистый теплообмен»Нобелевская премия по физике в 2006 году присуждена за «абсолютно черное тело».Радиометр Крукса
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. Слайд 25
- 26. Слайд 26
- 27. Слайд 27
- 28. Quick Quiz 1If a classroom door is
- 29. Quick Quiz 2Using Figure as a starting
- 30. Quick Quiz 3Cat’s eyes have pupils that
- 31. Quick Quiz 4If laser light is reflected
- 32. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
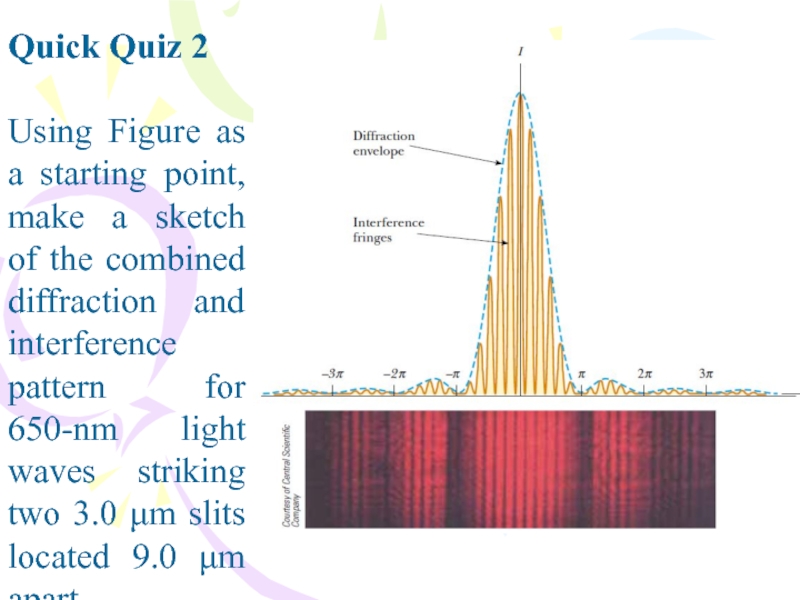
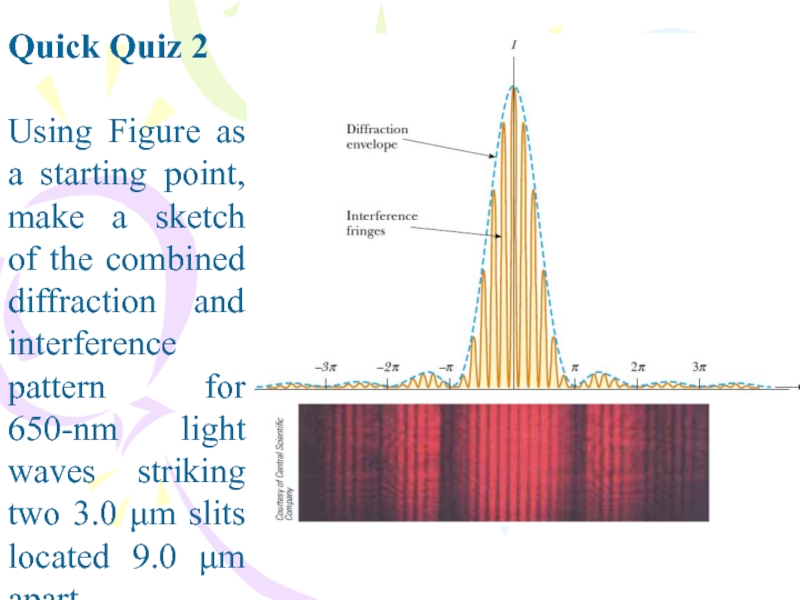
Слайд 2Quick Quiz 2
Using Figure as a starting point, make a
sketch of the combined diffraction and interference pattern for 650-nm
light waves striking two 3.0 μm slits located 9.0 μm apart.Слайд 3Quick Quiz 3
Cat’s eyes have pupils that can be modeled
as vertical slits. At night, would cats be more successful
in resolving(a) headlights on a distant car, or
(b) vertically-separated lights on the mast of a distant boat?
Слайд 4Quick Quiz 4
If laser light is reflected from a phonograph
record or a compact disc, a diffraction pattern appears. This
is due to the fact that both devices contain parallel tracks of information that act as a reflection diffraction grating. Which device, (a) record or (b) compact disc, results in diffraction maxima that are farther apart in angle?Слайд 5Course of lectures «Contemporary Physics: Part2»
Lecture №5
Thermal radiation. Emissivity and
absorptivity of the matter and their ratios. Blackbody radiation. Stefan–Boltzmann
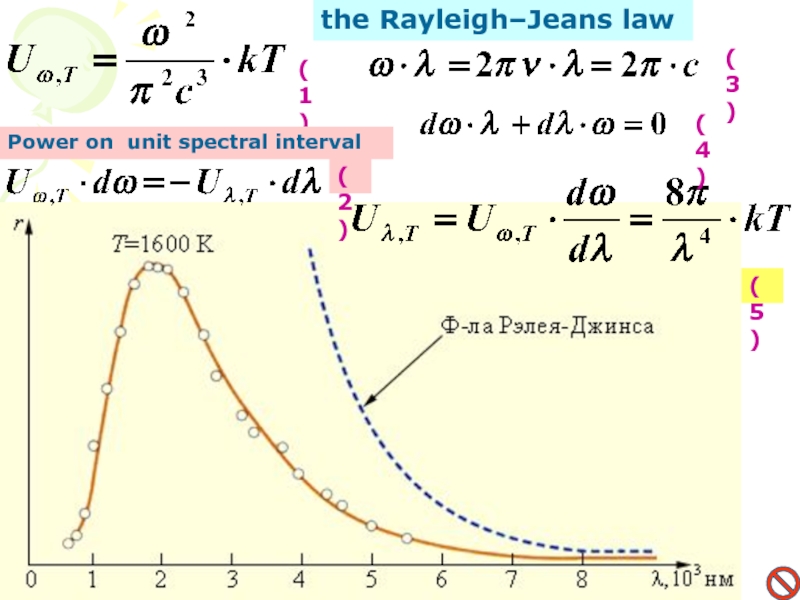
law. Derivation of the Planck Distribution Law. Wien's displacement law. The Rayleigh–Jeans law.Слайд 6Thermal radiation
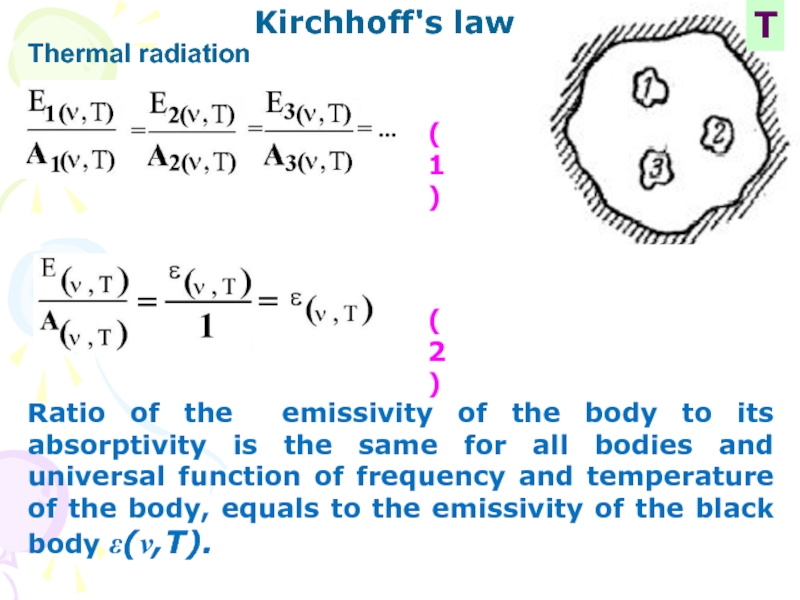
Kirchhoff's law
Т
(1)
(2)
Ratio of the emissivity of the body to
its absorptivity is the same for all bodies and universal
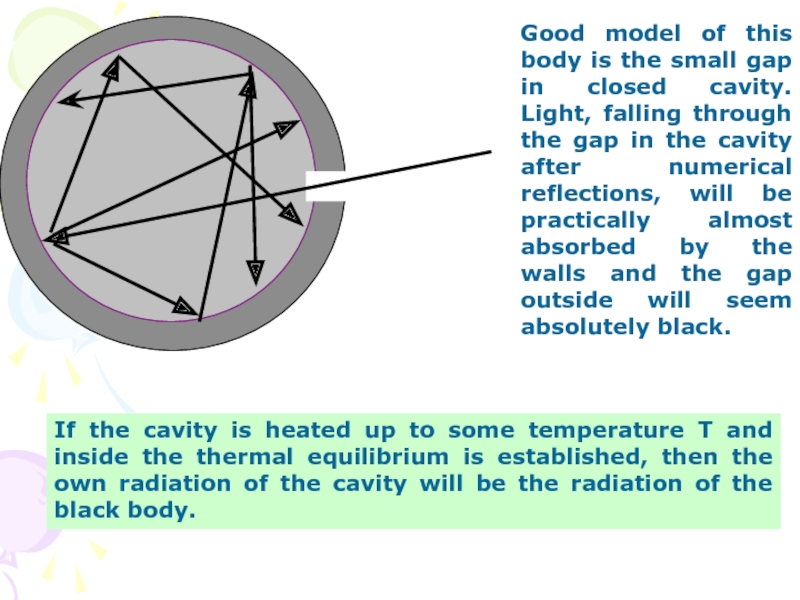
function of frequency and temperature of the body, equals to the emissivity of the black body ε(ν,T).Слайд 7Good model of this body is the small gap in
closed cavity. Light, falling through the gap in the cavity
after numerical reflections, will be practically almost absorbed by the walls and the gap outside will seem absolutely black.If the cavity is heated up to some temperature T and inside the thermal equilibrium is established, then the own radiation of the cavity will be the radiation of the black body.
Слайд 8
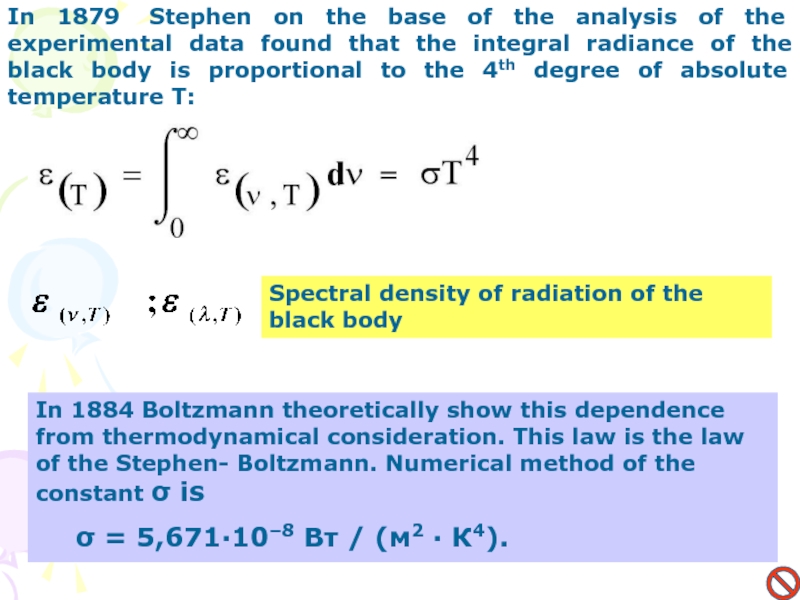
In 1879 Stephen on the base of the analysis of
the experimental data found that the integral radiance of the
black body is proportional to the 4th degree of absolute temperature T:In 1884 Boltzmann theoretically show this dependence from thermodynamical consideration. This law is the law of the Stephen- Boltzmann. Numerical method of the constant σ is
σ = 5,671·10–8 Вт / (м2 · К4).
Spectral density of radiation of the black body
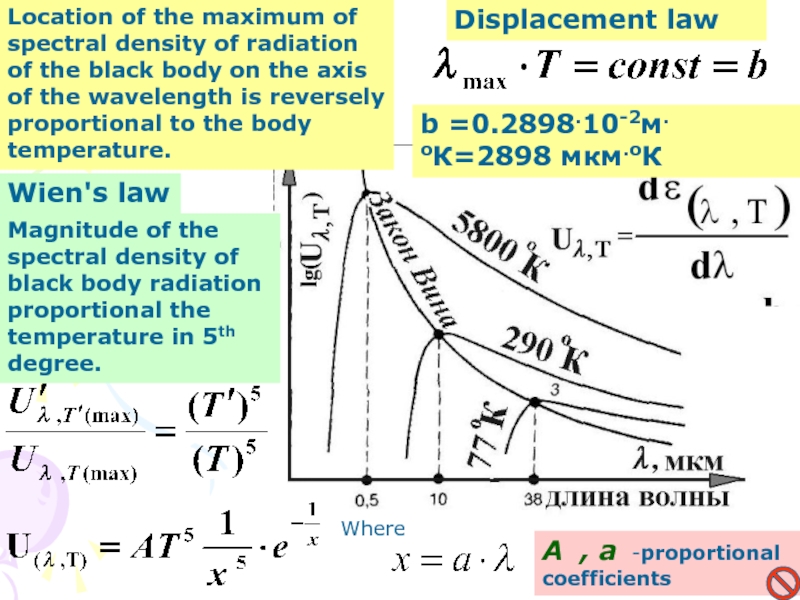
Слайд 9Displacement law
Location of the maximum of spectral density of radiation
of the black body on the axis of the wavelength
is reversely proportional to the body temperature.b =0.2898.10-2м.оК=2898 мкм.оК
Wien's law
Magnitude of the spectral density of black body radiation proportional the temperature in 5th degree.
Where
А , а -proportional coefficients
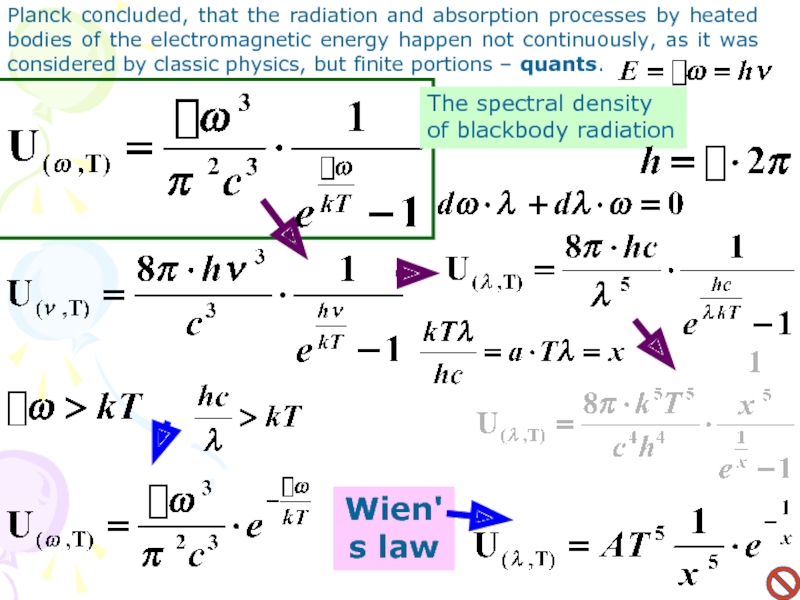
Слайд 11Wien's law
Planck concluded, that the radiation and absorption processes by
heated bodies of the electromagnetic energy happen not continuously, as
it was considered by classic physics, but finite portions – quants.The spectral density of blackbody radiation
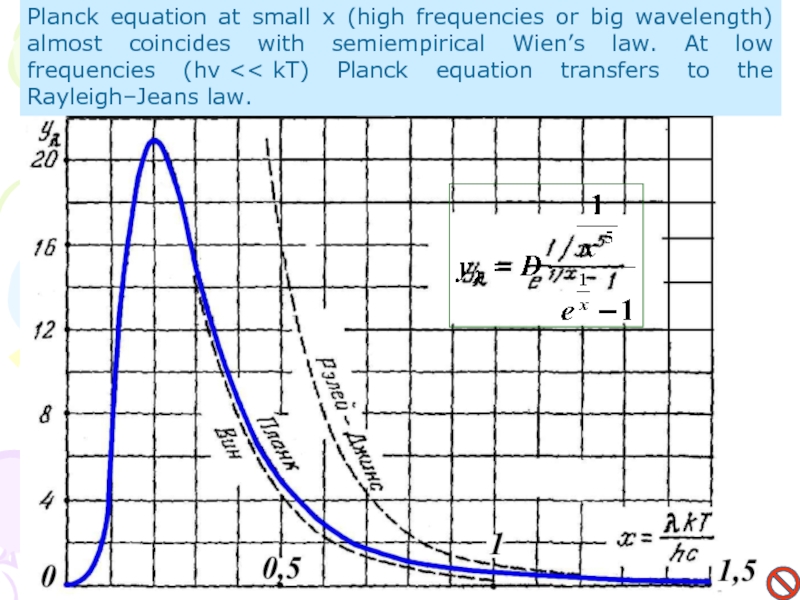
Слайд 12Planck equation at small x (high frequencies or big wavelength)
almost coincides with semiempirical Wien’s law. At low frequencies (hν
Planck equation transfers to the Rayleigh–Jeans law.
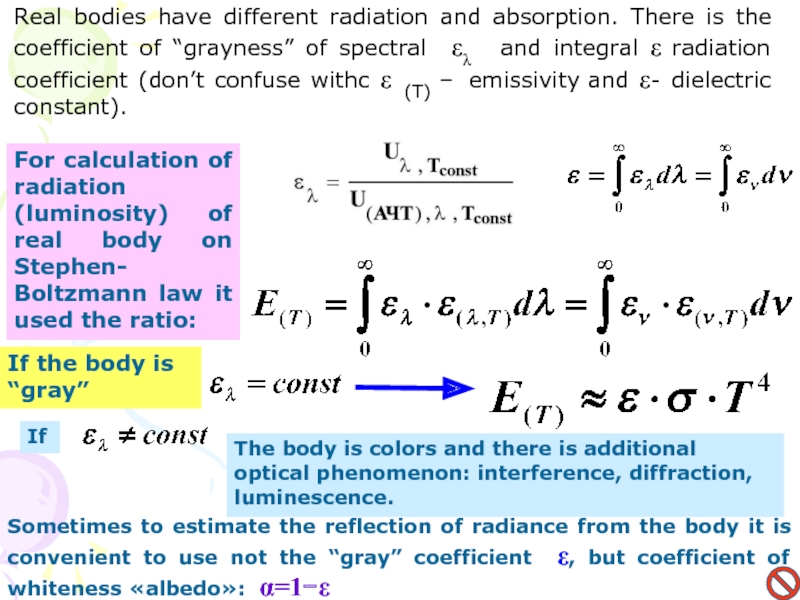
Слайд 13Real bodies have different radiation and absorption. There is the
coefficient of “grayness” of spectral ελ and integral ε
radiation coefficient (don’t confuse withс ε (Т) – emissivity and ε- dielectric constant).For calculation of radiation (luminosity) of real body on Stephen- Boltzmann law it used the ratio:
If the body is “gray”
If
The body is colors and there is additional optical phenomenon: interference, diffraction, luminescence.
Sometimes to estimate the reflection of radiance from the body it is convenient to use not the “gray” coefficient ε, but coefficient of whiteness «albedo»: α=1−ε
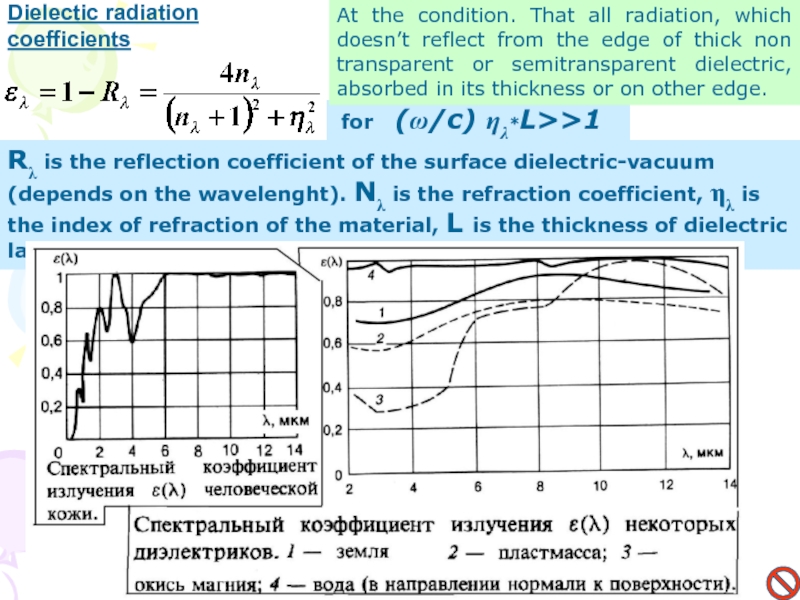
Слайд 14Dielectic radiation
coefficients
for (ω/c) ηλ*L>>1
Rλ is the reflection
coefficient of the surface dielectric-vacuum (depends on the wavelenght). Nλ
is the refraction coefficient, ηλ is the index of refraction of the material, L is the thickness of dielectric layer.At the condition. That all radiation, which doesn’t reflect from the edge of thick non transparent or semitransparent dielectric, absorbed in its thickness or on other edge.
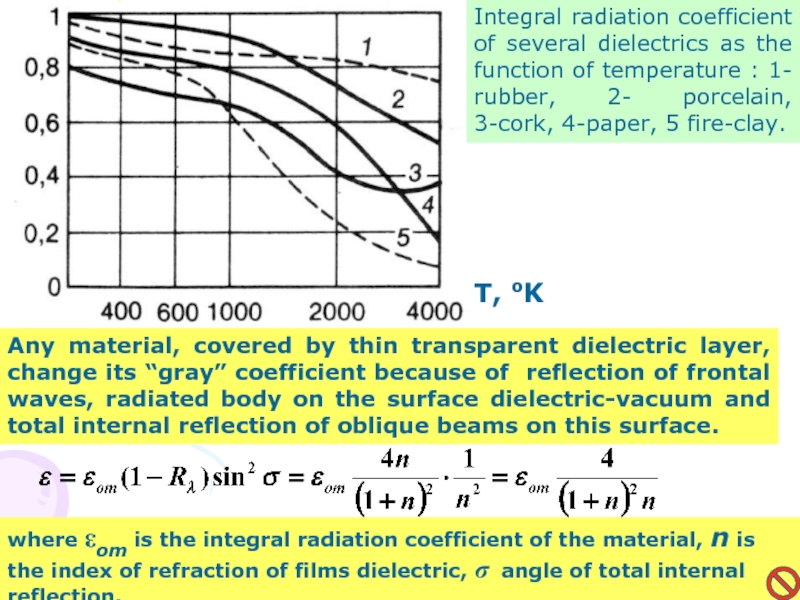
Слайд 15Integral radiation coefficient of several dielectrics as the function of
temperature : 1- rubber, 2- porcelain, 3-cork, 4-paper, 5 fire-clay.
Any
material, covered by thin transparent dielectric layer, change its “gray” coefficient because of reflection of frontal waves, radiated body on the surface dielectric-vacuum and total internal reflection of oblique beams on this surface. where εom is the integral radiation coefficient of the material, n is the index of refraction of films dielectric, σ angle of total internal reflection.
T, oK
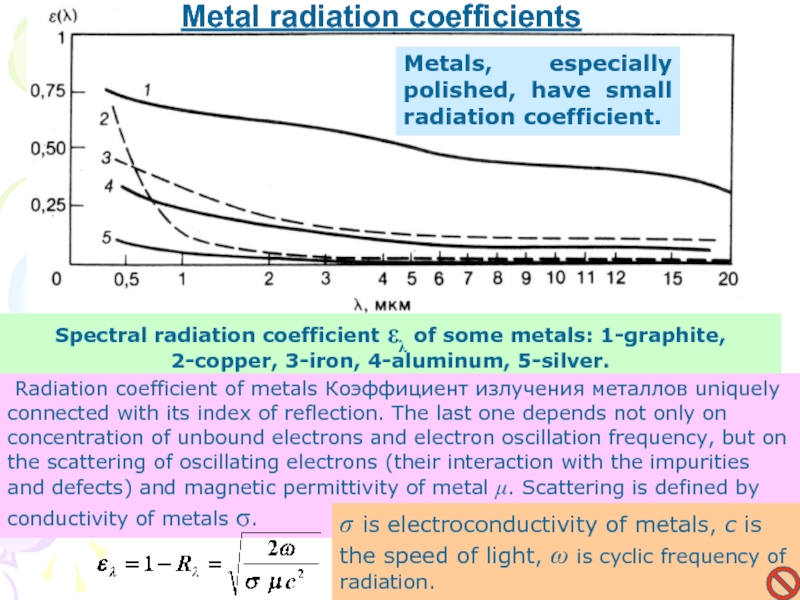
Слайд 16Spectral radiation coefficient ελ of some metals: 1-graphite, 2-copper, 3-iron,
4-aluminum, 5-silver.
Metal radiation coefficients
Metals, especially polished, have small radiation coefficient.
Radiation coefficient of metals Коэффициент излучения металлов uniquely connected with its index of reflection. The last one depends not only on concentration of unbound electrons and electron oscillation frequency, but on the scattering of oscillating electrons (their interaction with the impurities and defects) and magnetic permittivity of metal μ. Scattering is defined by conductivity of metals σ.
σ is electroconductivity of metals, с is the speed of light, ω is cyclic frequency of radiation.
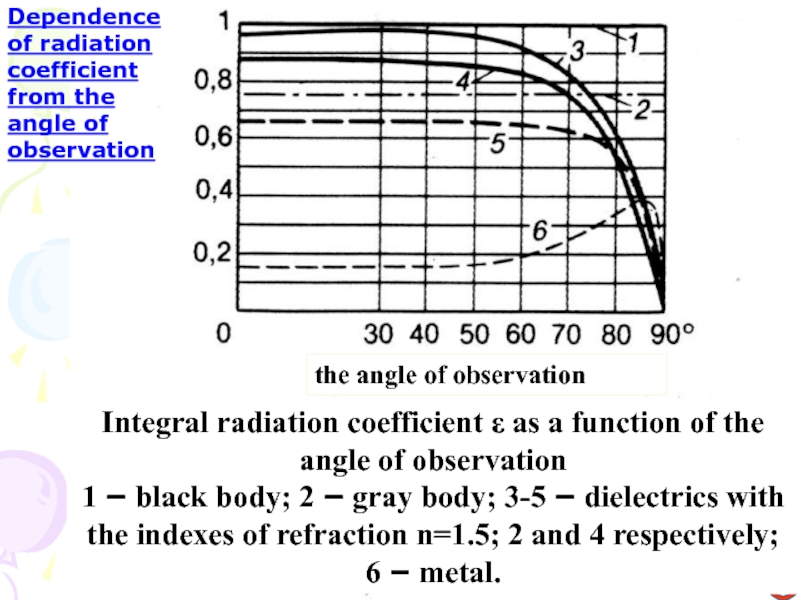
Слайд 18Dependence of radiation coefficient from the angle of observation
Integral radiation
coefficient ε as a function of the angle of observation
1
– black body; 2 – gray body; 3-5 – dielectrics with the indexes of refraction n=1.5; 2 and 4 respectively; 6 – metal.
the angle of observation
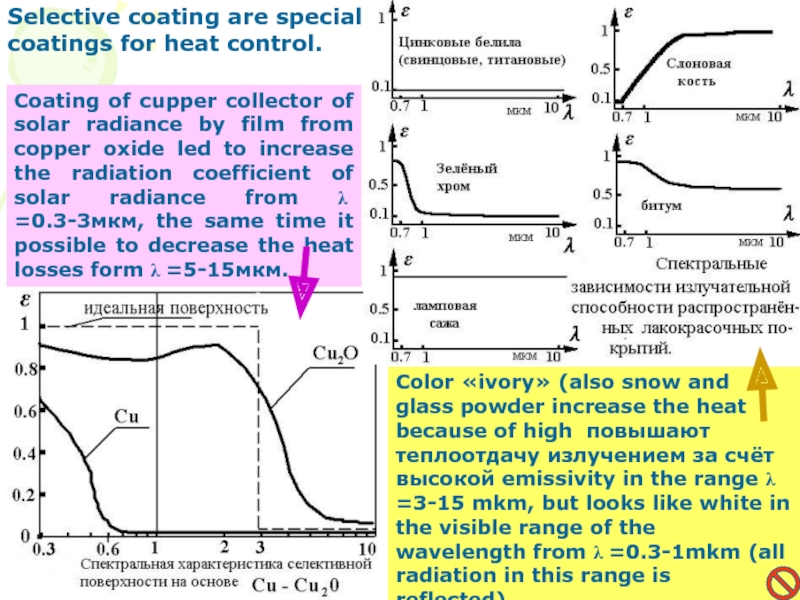
Слайд 19Selective coating are special coatings for heat control.
Coating of cupper
collector of solar radiance by film from copper oxide led
to increase the radiation coefficient of solar radiance from λ =0.3-3мкм, the same time it possible to decrease the heat losses form λ =5-15мкм.Color «ivory» (also snow and glass powder increase the heat because of high повышают теплоотдачу излучением за счёт высокой emissivity in the range λ =3-15 mkm, but looks like white in the visible range of the wavelength from λ =0.3-1mkm (all radiation in this range is reflected).
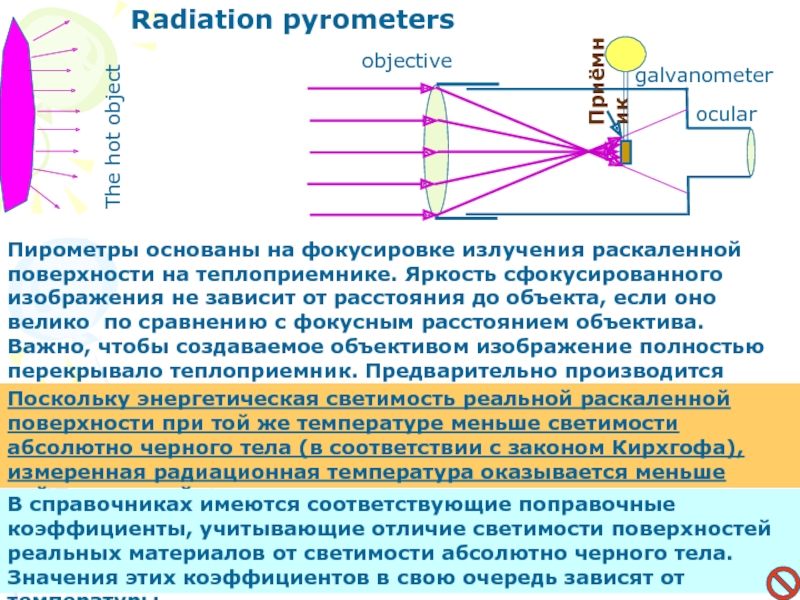
Слайд 20
objective
ocular
Приёмник
galvanometer
The hot object
Radiation pyrometers
Пирометры основаны на фокусировке излучения раскаленной поверхности
на теплоприемнике. Яркость сфокусированного изображения не зависит от расстояния до
объекта, если оно велико по сравнению с фокусным расстоянием объектива. Важно, чтобы создаваемое объективом изображение полностью перекрывало теплоприемник. Предварительно производится градуировка пирометра по абсолютно черному телу.Поскольку энергетическая светимость реальной раскаленной поверхности при той же температуре меньше светимости абсолютно черного тела (в соответствии с законом Кирхгофа), измеренная радиационная температура оказывается меньше действительной.
В справочниках имеются соответствующие поправочные коэффициенты, учитывающие отличие светимости поверхностей реальных материалов от светимости абсолютно черного тела. Значения этих коэффициентов в свою очередь зависят от температуры.
Слайд 21Яркостные пирометры.
Действие пирометра основано на сравнении яркости свечения тела,
температура которого измеряется, и нити лампы накаливания. Через красный светофильтр
производится наблюдение (λ=660 нм). Применение пирометров обычно связано с металлургией. Производится наблюдение, например, окошка в стенки доменной или мартеновской печи. На фоне изображения светящегося окошка наблюдается нить лампочки накаливания. Регулируя ток через лампочку, добиваются уравнивания их яркостей в красном цвете. При этом нить лампочки становится невидимой - потому такой пирометр называют пирометром с “исчезающей” нитью. Пирометр градуиру-ется по абсолютно черному телу - при изменении тока накала по находящейся в поле наблюдения шкале считывается температура черного тела, при котором нить должна “исчезать”.
Поскольку светимость реального тела при той же температуре меньше, для достижения равенства яркостей черного и нечерного тел это последнее должно быть нагрето сильнее, измеренная яркостная температура тоже оказывается меньше действительной (Также как и у радиационного пирометра).
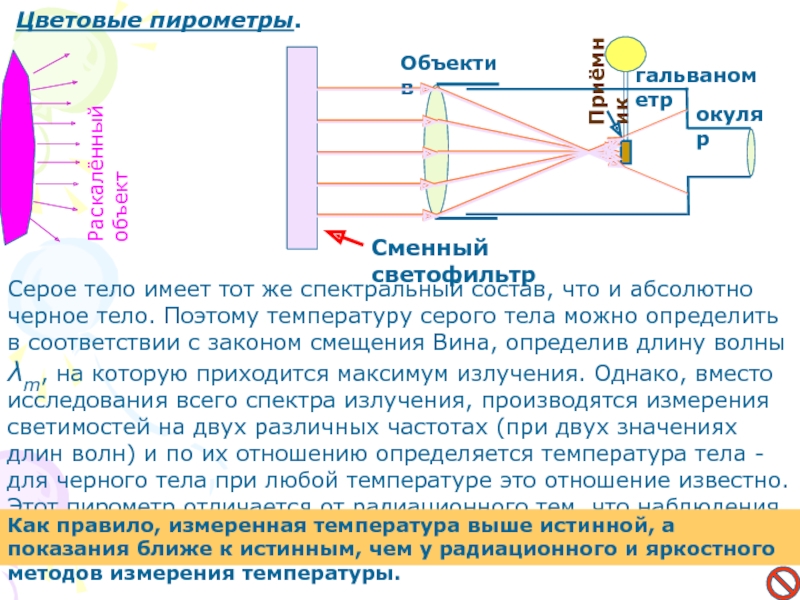
Слайд 22Цветовые пирометры.
Серое тело имеет тот же спектральный состав, что
и абсолютно черное тело. Поэтому температуру серого тела можно определить
в соответствии с законом смещения Вина, определив длину волны λm, на которую приходится максимум излучения. Однако, вместо исследования всего спектра излучения, производятся измерения светимостей на двух различных частотах (при двух значениях длин волн) и по их отношению определяется температура тела - для черного тела при любой температуре это отношение известно. Этот пирометр отличается от радиационного тем, что наблюдения производятся через сменные светофильтры.Объектив
окуляр
Приёмник
гальванометр
Раскалённый объект
Сменный светофильтр
Как правило, измеренная температура выше истинной, а показания ближе к истинным, чем у радиационного и яркостного методов измерения температуры.
Слайд 23Учебный фильм
«Лучистый теплообмен»
Нобелевская премия по физике в 2006 году присуждена
за
«абсолютно черное тело».
Радиометр Крукса
Слайд 28Quick Quiz 1
If a classroom door is open slightly, you
can hear sounds coming from the hallway. Yet you cannot
see what is happening in the hallway. Why is there this difference? (a) Light waves do not diffract through the single slit of the open doorway. (b) Sound waves can pass through the walls, but light waves cannot. (c) The open door is a small slit for sound waves, but a large slit for light waves. (d) The open door is a large slit for sound waves, but a small slit for light waves.Слайд 29Quick Quiz 2
Using Figure as a starting point, make a
sketch of the combined diffraction and interference pattern for 650-nm
light waves striking two 3.0 μm slits located 9.0 μm apart.Слайд 30Quick Quiz 3
Cat’s eyes have pupils that can be modeled
as vertical slits. At night, would cats be more successful
in resolving(a) headlights on a distant car, or
(b) vertically-separated lights on the mast of a distant boat?