Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
War for Independence
Содержание
- 1. War for Independence
- 2. King George III, and Debtsassumed the throne
- 3. Tension GrowsFarmers needed land to grow valuable
- 4. 9 major causes of the Revolutionary War,
- 5. Violence BeginsDecember 16, 1773 a group of
- 6. The Revolutionary WarFirst Continental Congress, in 1774.
- 7. The Turning PointAt Saratoga in upstate New
- 8. The Outcome May 1781, Yorktown, Virginia. February
- 9. State ConstitutionsSoon after the end of the
- 10. The Articles of Confederation The Articles provided
- 11. The Land Ordinance and The Northwest Ordinance
- 12. The ResultThe following new territories became new
- 13. The Constitutional Convention summer of 1787 Key
- 14. George Washington's Presidency the Judiciary Act of
- 15. The Presidency of John Adams served from
- 16. The formation of political partiesTariffs
- 17. Jefferson Administration Monroe : $11.25 million
- 18. The War of 1812 England invaded
- 19. The Conservative President: James Monroe In
- 20. Jacksonian Democracy 1828 was a triumph of
- 21. Slavery 1800-1840 the South feared being
- 22. Other Developments 1800-1850
- 23. "Manifest Destiny" exploration and expansion was a
- 24. Social ChangeUtopian communities in the 1840s (and
- 25. Women's rightsBegan as a social movement in
- 26. Other Milepost EventsIn 1842, the union workers'
- 27. James K. Polk and War with Mexico
- 28. Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgothe Texas-Mexico border would be
- 29. Kansas-Nebraska Act Ill-advised law to be
- 30. "Bleeding Kansas" Civil war in Kansas; In
- 31. The Debate Over SlaveryStephen Douglas and Abraham
- 32. Слайд 32
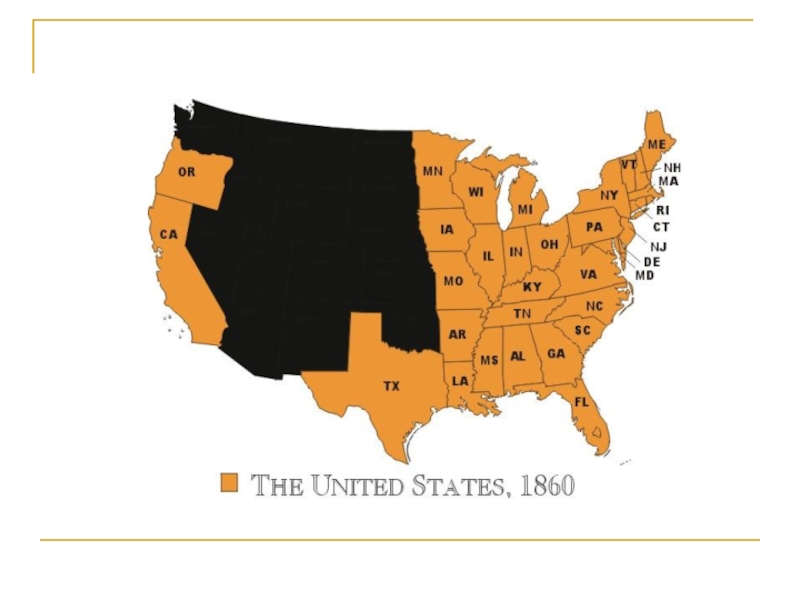
- 33. Secession In 1860, the South threatened
- 34. "Confiscation Acts"1861 - authorized the Union to
- 35. Thank you for your Attention!
- 36. Скачать презентанцию
King George III, and Debtsassumed the throne in 1760 (he ruled until 1820). The ruling sentiment was that the colonies should be obliged to pay for their own expenses, rather than
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 1War for Independence and First Constitution
1800 - 1850s: Jacksonian Democracy;
Social Movements, Manifest Destiny and Expansion
Слайд 2King George III, and Debts
assumed the throne in 1760 (he
ruled until 1820). The ruling sentiment was that the colonies
should be obliged to pay for their own expenses, rather than depending on the mother county (England).the Proclamation Act of 1763, forbidding colonists from settling west of Appalachians and forcing them to stop buying land from Indians. The logic behind the Proclamation Act - as long as the colonists stayed in the colonies and had nothing to do with Indians, there should be peace.
Слайд 3Tension Grows
Farmers needed land to grow valuable crops of tobacco,
corn, rice, indigo, and wheat, but the Proclamation Act confined
them to the land they already had in the colonies- was detrimental to their growth.The first true crisis began around 1763 when Parliament allocated money to maintain a standing army in the colonies. More than 1500 ships began to patrol American waters.
Слайд 49 major causes of the Revolutionary War, also called the
"American Revolution":
(1) Colonists were accustomed to much independence and self-determination,
and British efforts (led by the Tory political party in England) to regulate and tax were bitterly opposed by the colonies (and by the Whig political party in England; the conservative Edmund Burke was a British politician who sided with the American colonists). (2) British burdens hurt nearly all the colonists in all walks of life.
(3) Taxes hit at a bad time: postwar depression.
(4) Legally, colonies disagreed with "virtual representation."
(5) Religious reasons: many colonists disliked Anglicans (and Catholics), and feared England would install an Anglican bishop.
(6) Colonists disliked English class distinctions.
(7) 1/3 of colonists were not even English, and thus felt no attachment to the British.
(8) Colonists accepted John Locke's philosophy of natural rights and a social contract, which conflicted with rule by a monarchy.
(9) Colonists saw a bright prospect for their future.
Слайд 5Violence Begins
December 16, 1773
a group of colonists led by
Samuel Adams disguised themselves as Indians;
Result - the Coercive Acts
or the Intolerable Acts. These laws revoked Massachusetts' charter, closed Boston Harbor, installed a British general as governor, and repealed liberties like the right to hold town meetings.In Boston today, there is still no tax on tea as a tribute to the Boston Tea Party.
Слайд 6The Revolutionary War
First Continental Congress, in 1774. The colonies agreed
to end all trade with Britain in a final effort
to have her alter her policies. All of these plans were carried out.Parliament officially declared that Massachusetts was in rebellion.
Patrick Henry “give me liberty or give me death!"
On July 4, 1776, the Declaration of Independence was formally announced.
Слайд 7The Turning Point
At Saratoga in upstate New York in October
1777, 6,000 British soldiers surrendered; the French then ended its
neutrality and entered on American side.Benjamin Franklin was instrumental in obtaining French backing for the American cause and forging the Franco-American Alliance in 1778 (+Franklin stove for heating, and starting the first library).
Слайд 8The Outcome
May 1781, Yorktown, Virginia.
February 1783, the Treaty
of Paris. In it the British gave up their claim
to land east of the Mississippi, from Canada to Florida. The Americans promised to treat fairly the Loyalists and English creditors.Слайд 9State Constitutions
Soon after the end of the Revolution, all but
two of the states adopted new constitutions. Rhode Island and
Connecticut continued to use their charters, after removing all references to Britain.opposition to concentrating power in one person was reflected in the states' constitutions by concentrating power – where? Governers’ positions? state courts?
Слайд 10The Articles of Confederation
The Articles provided for a unicameral (one
body) Congress to govern the states. There was no ___?
Just to imagine!a very weak national government: why?
The federal government under the Articles did not have enough power to operate effectively in its foreign policy .
more than 35 million dollars in debt
There were no national taxes, and requests for money from the states were ignored.
Слайд 11The Land Ordinance and The Northwest Ordinance
The Land Ordinance of
1785 provided for surveying and dividing territories west of the
colonies into towns 6 miles square, and selling 640 acre chunks at public auctions for a minimum of $1 per acre.The Northwest Ordinance established a way to create no less than three and no more than five new states. It established a three-stage process based on population for new states to be created and join the Confederation of colonies. It also specified what type of government the new territories and states must have, a requirement that would later become part of the U.S. Constitution.
Слайд 12The Result
The following new territories became new states due to
the success of the Northwest Ordinance :Ohio (1803), Indiana (1816),
Illinois (1818), Michigan (1837), Wisconsin (1848), and Minnesota (1858).Слайд 13The Constitutional Convention
summer of 1787
Key participants :James Madison, George
Washington, Alexander Hamilton , Benjamin Franklin, George Washington
the Connecticut
Compromise: Congress would have one house with equal representation and one house with representation based on population. (part of the Constitution, and today Americans have both the House of Representatives and the Senate). The "Three-Fifths Compromise“
Sept. 17, 1787 – Constitution day
Слайд 14George Washington's Presidency
the Judiciary Act of 1789, which established
federal court system.
1791 Hamilton was successful in persuading Congress
to establish the First Bank of the United States "Washington's Neutrality Proclamation,"
"Executive Privilege" of President
The Bill of Rights passed in 1791 to limit the federal government
an unwritten tradition of a maximum of two terms for presidents
+Eli Whitney invented the cotton gin = ‘King Cotton’
Слайд 15The Presidency of John Adams
served from 1797-1801
The Alien &
Sedition Acts – blatantly unconstitutional
"lame duck" action: case of Marbury
v. Madison (1803), where the Supreme Court held in Jefferson's favor by declaring a federal law to be unconstitutional: the first time the new Supreme Court declared an Act of Congress to be unconstitutional and thus void. Слайд 16
The formation of political parties
Tariffs + North/South friction
The Federalist
Party - a strong national government, friendly dealings with England,
a liberal interpretation of the Constitution (known as "loose constructionism),Democratic-Republican Party - the opposite: a weak national government (keeping the power at a local level, which Virginia preferred), friendly dealings with France, and a strict interpretation of the Constitution ("strict constructionism").
"Revolution of 1800," victory by Jefferson and Burr against Adams was a victory for limited government and a "strict constructionist"
Слайд 17Jefferson Administration
Monroe : $11.25 million to France for all
of the property (which translates to only a few pennies
per acre), not merely West Florida and New Orleans. This enormous tract of land was as large as the entire United States at the time.In 1812, Louisiana because the first state admitted to the United States from this new territory. Only one additional state joined the United States during Jefferson's presidency: Ohio, in 1803. Jefferson is credited with eliminating unnecessary taxes such as the whiskey tax and decreasing the size of the federal government.
Слайд 18The War of 1812
England invaded D.C. itself and burned
down the Capitol and the White House
Francis Scott Key
- the Star-Spangled Banner; In 1931, over 100 years later, it became the official National Anthem.Treaty of Ghent (negotiated by the Czar of Russia!) arranged for the long, open Canadian-U.S. border that remains to this day
Слайд 19The Conservative President: James Monroe
In 1820, the successful "Missouri
Compromise" : 11 free states and 11 slave states
So the
Missouri Compromise added Maine as a free state (which would side with the North), and Missouri as a slave state (which would side with the South until the Civil War, when it refused to join the southern Confederacy). The other new states to be added from the Louisiana Purchase (once they had enough population) would be free: slavery was banned by this Compromise above the latitude of 36 degrees, 30 minutes. The most lasting contribution of James Monroe - "Monroe Doctrine" in 1823 – Which? Works to this day.
Слайд 20Jacksonian Democracy
1828 was a triumph of democracy
the "spoils
system,"
the "Indian Removal."
the powerful tools of the modern
presidency: vetoing bills of Congress to prevent them from becoming law (Jackson vetoed more bills than all the presidents before him combined), removing people from office when the President disagreed with them, and using executive orders as President to give his views the power of law.“the president was not merely a member of the government's symphony: he was its conductor”
Слайд 21Slavery 1800-1840
the South feared being outvoted by the North
in the Senate if the States abolishing slavery outnumbered the
States using it. Slavery became caught up in politicsIn 1831, Nat Turner led slave revolt in Virginia, and 57 whites died; William Lloyd Garrison, a fiery Puritan abolitionist in Massachusetts, started the "Liberator" newspaper to demand an end to slavery. 1833 - the American Antislavery Society
Congress instituted a "gag rule" from 1836 to 1844 to prohibit its members from circulating proposals concerning slavery, especially abolitionism
Слайд 22Other Developments 1800-1850
Counting California, which
joined the Union in 1850, five new states were added
to the United States: Florida, Texas, Iowa, Wisconsin and California. This included the two largest states in area in the continental United States (California and Texas), and what are now three of the four largest in population (California, Texas and Florida). This was the greatest addition of new states since the 1810s. The nation as we know it today was taking shape.Слайд 23"Manifest Destiny"
exploration and expansion was a mission from God
on the Oregon Trail.
1843- the Oregon territory, and 1000
pioneers traveled all the way from Missouri to Willamette Valley (a trip that took 4 to 6 months then). From 1811 to 1818, the first national road was built
In 1836, Texas fought and won its independence from Mexico
the "gold rush" - in 1848 , hit a fever pitch in 1849, attracting many to California (the football team the "San Francisco 49ers" is named after those settlers)
Слайд 24Social Change
Utopian communities in the 1840s (and earlier) the Shakers,
Brook Farm, the Rappites, the Oneida Community ;
David Thoreau!
the Church
of Jesus Christ of Latter Day Saints (the Mormon Church), the only major church founded in America, was established in 1830 by Joseph Smith in western New York. The Seventh Day Adventist Church began 1844 -developed an approach to good health that included building hospitals
Слайд 25Women's rights
Began as a social movement in 1848 in Seneca
Falls, New York: a Declaration of Sentiments that called for
granting women the right to voteIn 1849, the English-born Elizabeth Blackwell became the first woman to receive a medical degree in America, which she obtained from Geneva College in New York.
Слайд 26Other Milepost Events
In 1842, the union workers' movement; it became
legal for workers to organize a union and to strike.
The unionization of government workers recently became a national controversy("prohibition", or the "temperance movement") began in 1826 and lasted until the 18th Amendment passed in 1919 to ban alcohol nationwide (it was later repealed by the 21st Amendment during the Great Depression);
public school education. Horace Mann - the first state school board.
Слайд 27James K. Polk and War with Mexico
instigated, fought and won
the Mexican War (also called the Mexican-American War) (ended in
1848 with the Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo)annexed Texas (1845)
settled a dispute with British (Canada) by establishing the northwest boundary in Oregon Treaty (1846)
reduced tariffs
reestablished an independent treasury (bank)
admitted Iowa as a free state in 1846 (under the Missouri Compromise), with Iowa having the highest percentage of farmland of any State
set off the gold rush by announcing there was gold in California (1849)
Слайд 28Treaty of Guadalupe-Hidalgo
the Texas-Mexico border would be set at the
Rio Grande River
Mexico would grant to the United States
about 525,000 square miles (55% of its prewar territory) the United States would pay Mexico $15 million
the United States government would pay off up to $3.25 million worth of debts owed by Mexico to U.S. citizens, relieving Mexico of those obligations
Слайд 29Kansas-Nebraska Act
Ill-advised law to be the greatest single
step towards Civil War
each new region could decide for itself
whether to allow slavery. anti-slavery activists founded the Republican Party in 1854 on the moral grounds of ending slavery :
stop the expansion of slavery
repeal the Kansas-Nebraska Act
repeal the Fugitive Slave Law
end slavery in D.C.
Слайд 30"Bleeding Kansas"
Civil war in Kansas; In early 1856, pro-slavery forces
burned down the "Free State Hotel" and destroyed the offices
and presses of antislavery newspapers. A man was killed.John Brown - the Pottawatomie Massacre.
Слайд 31The Debate Over Slavery
Stephen Douglas and Abraham Lincoln
The Dred Scott
ruling
The South: tremendous economy, had strategic advantages: it controlled
the mouth of the Mississippi and had better generals.The North benefited from the railroad system, heavy immigration and a much more balanced economy. The population of the North was 22 million compared with only 9 million in the South, 3.5 million of whom were slaves; control of the United States Navy; was politically successful in keeping border slave states -- Delaware, Kentucky, Maryland, Missouri and the to-be-formed West Virginia -- from joining the Confederacy to fight against the North.
Слайд 33Secession
In 1860, the South threatened to secede (break away)
from the United States if the Republican Abraham Lincoln were
elected president.By the end of January 1861, six other southern states imitated South Carolina and declared their independence from the United States. They were Mississippi, Florida, Alabama, Georgia, Louisiana and Texas. "We are divorced, North and South, because we have hated each other so."
Слайд 34"Confiscation Acts"
1861 - authorized the Union to seize any property,
including slaves, which were being used to aid the South
in its "insurrection" against the NorthThe Second Confiscation Act was next passed in 1862, taking the additional step of ordering freedom for any slaves belonging to slave-owners engaged in "treason" against the United States.