Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Accounting 1 Accounting Lecture 1: Accounting and Business Environment Lisa, Li
Содержание
- 1. Accounting 1 Accounting Lecture 1: Accounting and Business Environment Lisa, Li
- 2. Join the Tencent Meeting ClassPlease enter your
- 3. Materials of the CourseTextbook:Horngren’s Accounting, Pearson, 10th
- 4. Materials of the Course (cont’d)Textbook:Noble, L.Tracie; Mattison,
- 5. Materials of the Course (cont’d) Accounting
- 6. Слайд 6
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. Unit Assessment TaskIn class
- 9. Tips for success
- 10. Chapter 1: Learning ObjectivesIntroductionImportance of AccountingGoverning
- 11. Introduction of Accounting
- 12. Users of Accounting InformationExternal UsersCreditorsShareholdersTax AuthoritiesOutside InvestorsExternal AuditorsCustomersBankersInternal UsersManagersBoard of DirectorsInternal AuditorsSales StaffBudget OfficersControllersCEO, CFO
- 13. Multiple Choices 2mins
- 14. True or False Questions 5mins Shareholders
- 15. Importance of Accounting
- 16. Importance of Accountingaccounting positions for the
- 17. BIG 4 Auditors - How Big ?leading
- 18. Importance of Accounting
- 19. How to govern accounting?I. Governing Organizations
- 20. I. Governing Organizations Governing organizations are:Securities
- 21. I. Governing OrganizationsSecurities and Exchange Commission SEC
- 22. I. Governing OrganizationsFASB in USAthe Financial Accounting
- 23. II. Guidelines for accounting information Generally Accepted
- 24. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)Issued by the
- 25. II. Guidelines for accounting information International Financial
- 26. Multiple ChoiceThe guidelines for accounting information are
- 27. III. Basic Accounting Assumption and Principle 1.
- 28. 1. Economic Entity AssumptionProprietorship (sole trader) means
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. 2. Going Concern AssumptionFinancial statements are prepared
- 31. 3. Monetary Unit AssumptiomThe assumption that requires
- 32. 4. The Cost
- 33. Accounting AssumptionsAccounting Economic Entity AssumptionCost PrincipleGoing Concern AssumptionMonetary Unit Assumption
- 34. Multiple Choices 2mins The
- 35. Multiple Choices 2mins According
- 36. TRY IT!
- 37. Accounting FieldsFinancial AccountingManagerial AccountingAuditing Public Sector Accounting – governmentsAccounting
- 38. Accounting FieldsManagerial AccountingFinancial Accounting Public Sector Accounting Auditing
- 39. Two basic branches of accountingManagement accounting(MA)special requirement
- 40. Comparison of FA and MA
- 41. Comparison of FA and MA
- 42. Users of Financial Information1-©2014 Pearson Education, Inc. Publishing as Prentice Hall
- 43. Multiple Choices 2mins Managerial accounting information is used by:taxing authorities.auditors.lenders.internal decision makers.
- 44. Relationship between MA and FABoth of
- 45. 3Accounting Homework-Matching
- 46. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
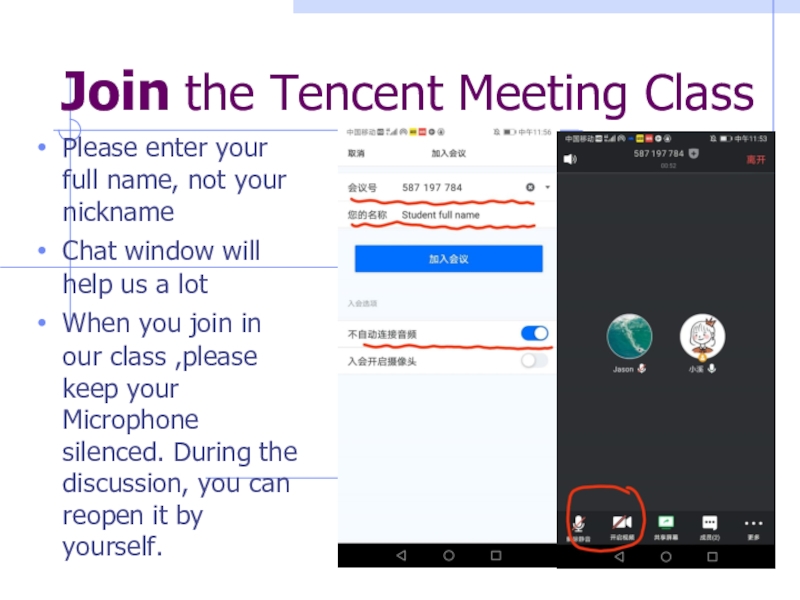
Слайд 2Join the Tencent Meeting Class
Please enter your full name, not
your nickname
Chat window will help us a lot
When you join
in our class ,please keep your Microphone silenced. During the discussion, you can reopen it by yourself.Слайд 3Materials of the Course
Textbook:
Horngren’s Accounting, Pearson, 10th Global edition
Learning Objectives,
Chapter
Summary handout (preview)
PPT slides(preview)
‘Try it’ Questions,
Chapter Overview,
10-mins quizzes
and Review Q (homework)Short Exercises, and critical thinking cases
Accounting
2
Слайд 4Materials of the Course (cont’d)
Textbook:Noble, L.Tracie; Mattison, L. Brenda &
Matsumura Mae Ella, Horngren’s Accounting, Pearson, 10th edition, Global edition
Other
Reference Books:Randall & Hopkins, Cambridge International AS and A Level Accounting
Warren,C. Reeve, J.& Fess P. Principles of Accounting(23rd ed)
by and Wild, J. Financial Accounting Fundamentals
Accounting
Слайд 6 Study Guide
Part 1:
Introduction of accounting
Accounting and Business Environment
Financial Accounting vs. Managerial
Accounting Five Groups (elements)of Accounts
Basic Accounting Principles
The Accounting Process
Mid-term exam
Accounting
Слайд 7 Study Guide
Part 2:
Prepare Financial Statement
Adjusting process
Closing process
The Accounting cycle
Common Accounting ratios
Final examination
Accounting
Слайд 8 Unit Assessment Task
In class practice
15%
multiple choices, ‘try it’
Q, practices in classMid-term Exam 15%
textbook and PowerPoint
Final Exam 70%
-textbook, PowerPoint and practices in class
-multiple choices, short answers and accounting cases
More than 60% of total marks will pass
Accounting
Слайд 9 Tips for success in the course
Experience of Learning Accounting
Spend more time on the beginning part
(Chapter 1,2)Theory → Practice → Theory
professional business language
Materials: textbook, PPTs and reference books
Download IAS,IFRS and AASB from official website
Accounting
Слайд 10 Chapter 1: Learning Objectives
Introduction
Importance of Accounting
Governing Organizations and Guidelines
Basic
Accounting assumptions
Accounting Principles
Two basic branches of accounting:
MA and FAAccounting
Слайд 11 Introduction of Accounting
What Is Accounting?
Accounting is an information
process, which is related with collecting and recording financial information from business organizations, and communicating relevant financial information to stakeholders. information process: identifying, collecting, classifying, recording and communicating
stakeholders: persons or entities have interest in the economic performance of the business. e.g. managers, creditors, bankers
Global and professional business language
Accounting
Слайд 12Users of Accounting Information
External Users
Creditors
Shareholders
Tax Authorities
Outside Investors
External Auditors
Customers
Bankers
Internal Users
Managers
Board of
Directors
Internal Auditors
Sales Staff
Budget Officers
Controllers
CEO, CFO
Слайд 13Multiple Choices 2mins
Which of
the following are external users of a business’s financial information?
A. Taxing authorities
B. Customers
C. Employees
D. Creditors
E. Board of Directors
(tip: two or more than two correct answers)
Слайд 14True or False Questions 5mins
Shareholders primarily use accounting
information for decision-making purposes.
Local, state, and federal governments use
accounting information to calculate firm’s income tax. A creditor is a person who owes money to the business.
Different users of financial statements focus on the different parts of the financial statements for the information they need.
Слайд 15 Importance of Accounting
For individual
Saving and Managing money
Statement of Financial Performance (oversea student)
Accounting
Слайд 16 Importance of Accounting
accounting positions for the careers
External auditors, BIG
4 Accounting Firms
Internal auditors,
Controllers,
finance and accounting specialists in bank,
Tax accountants(CPAs)
cost
accountants(CMAs),Business system analysts, Financial analysts
Accounting
Слайд 17BIG 4 Auditors - How Big ?
leading firms: Account for
¾ auditing markets,
Company’s Income : more than $20 billion/year
“Famous
customers”: majority customers are world's top 500 enterprises.Eg. Walmart, Albaba, Google, HSBC
Employment: 17,000-20,000
staffs in 70 countries, including
10,000 Chinese employees.
Departments: auditing, taxes, advisory
Tax
Advisory
Auditing
Слайд 18 Importance of Accounting
for Business Firms
All the businesses and organizations need accountants.
Financial
Annual Reports—public firms Budegt, project plan,Managerial report
Internal Control – accounting information system
Financial and Strategic Decisions
Accounting
Слайд 19How to govern accounting?
I. Governing Organizations
SEC
FASB in USA IASB in
UKII. Guidelines for Accounting Information
GAAP IFRS
III. Basic Accounting assumption and Principles
Accounting
Слайд 20 I. Governing Organizations
Governing organizations are:
Securities and Exchange Commission
(SEC)
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB)
International Accounting Standard Board (IASB), which
publish International Financial Report Standard (IFRS) the importance of the convergence of accounting standards at a global level.
Accounting
Слайд 21I. Governing Organizations
Securities and Exchange Commission
SEC is an U.S.
governmental agency that oversees the US financial markets. It also
oversees FASB.The SEC was established by the Securities Act of 1934
the SEC requires that all publicly traded companies have an annual financial statement audit that is conducted by a Certified Public Accountant.
The SEC delegated that standard-setting responsibility to the accounting profession.
Слайд 22I. Governing Organizations
FASB in USA
the Financial Accounting Standard Board (FASB)
is a private organazation.
Creates the rules and standards that
govern financial accountingIt oversees the creation and governance of U.S.GAAP (accounting standards).
IASB in UK
the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB), located in London, has established a body of International Financial Reporting Standards, IFRS, that are used by a majority of other countries.
Accounting
Слайд 23II. Guidelines for accounting information
Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
It
is the main US accounting rule book and is issued
by the FASB.GAAP rests on a conceptual framework that identifies the objectives, characteristics, elements and implementation of FS and create the acceptable accounting practices.
The SEC requires that American businesses follow U.S. GAAP.
Accounting
Слайд 24Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP)
Issued by the FASB.
Establishes the rules
for recording transactions and preparing financial statements.
Published online as part
of the Accounting Standards Codification.Requires that information be useful.
Relevant = The info allows users to make a decision.
Faithfully Representative = The info is complete, neutral, and free from material error.
Accounting
Слайд 25II. Guidelines for accounting information
International Financial Report Standards
(IFRS)
A set of global accounting guidelines , formulated by the
International Accounting Standard Board.IFRS is a set of global accounting standards that are used or required by more than 120 nations.
A publicly traded company in the United States come under SEC regulations as long as it follows the rules of GAAP.
Accounting
Слайд 26Multiple Choice
The guidelines for accounting information are called:
Globally Accepted and
Accurate Policies.
Global Accommodation Accounting Principles.
Generally Accredited Accounting Policies.
Generally Accepted Accounting
Principles.Слайд 27III. Basic Accounting Assumption and Principle
1. Economic Entity Assumption
2.
Goning Concern Assumption
3. Monetary Unit assumptiom
4. The Cost principle
5. The
Accounting Equation6. Profit Determination
7. Double-entry bookkeeping
8. Matching principle
9. Reporting Principle
Accounting
Слайд 281. Economic Entity Assumption
Proprietorship (sole trader) means one person or
a family owns the firm and control business,small business such
as laundries, repair shop,newsstand.Partnership multiple individuals, called general partners, manage the business and are equally liable for its debts.e.g.dentist office, law firms.
Corporation Firm that meets certain legal requirements to be recognized as having a legal existence, as an entity separate and distinct from its owners. e.g. General Motor, IBM
Limited-Liability Company (LLC) a company in which each member is only liable for his or her own actions. Indefinite life. e.g. Big 4 Auditors
Accounting
Слайд 302. Going Concern Assumption
Financial statements are prepared under the assumption
that the entity will continue to operate for the foreseeable
future.This assumption is essential if we expect businesses to engage in long term agreements. For example, a manufacturer would not likely enter into a long-term sales agreement with a customer, if it believed that that customer would soon be out of business.
Accounting
Слайд 313. Monetary Unit Assumptiom
The assumption that requires the items on
the financial statements to be measure in terms of a
monetary unit.In the United States, we record transaction in American dollars($).
In UK, we record transaction in Yuan (¥). Pound(£).
In china, we record transaction in Chinese Yuan (¥)
Albaba, big multinational Chinese company, should be record in American dollars or
Chinese Yuan? And why?
Accounting
Слайд 32 4. The Cost Principle
assets should be
recorded at their actual cost (historical cost) on the date
of acquisition.all liabilities should be recorded at their actual cost, when it happened.
We record a transaction at the amount shown on the receipt(or contracts)- actual amount paid.
Not at “expected cost” or “current relevant market value”.
Eg. the company bought the Land with building at $300,000 20 years age, now the land price increases dramatically.
Accounting
Слайд 33Accounting Assumptions
Accounting
Economic Entity Assumption
Cost Principle
Going Concern Assumption
Monetary Unit Assumption
Слайд 34Multiple Choices 2mins
The formation of
a partnership firm requires a minimum of:
A) four partners.
B) three
partners.C) one partner.
D) two partners.
Слайд 35Multiple Choices 2mins
According to which of
the following accounting concepts should the acquired assets be recorded
at the amount actually paid rather than at the estimated market value?Monetary unit assumption
Cost principle
Economic entity assumption
Going concern assumption
Слайд 37 Accounting Fields
Financial Accounting
Managerial Accounting
Auditing
Public Sector Accounting
– governments
Accounting
Слайд 38Accounting Fields
Managerial
Accounting
Financial
Accounting
Public Sector
Accounting
Auditing
Слайд 39Two basic branches of accounting
Management accounting(MA)
special requirement for the purposes
to make better decisions for the organization and improve the
efficiencyIMA: large U.S. professional organization of accountants, focus on internal accounting
Licensed as Certified Management Accountant(CMA)
Financial accounting(FA)
Stakeholders, particular external parties - comply with IASs, GAAP;external users
Licensed as Certified Public Accountant(CPA)