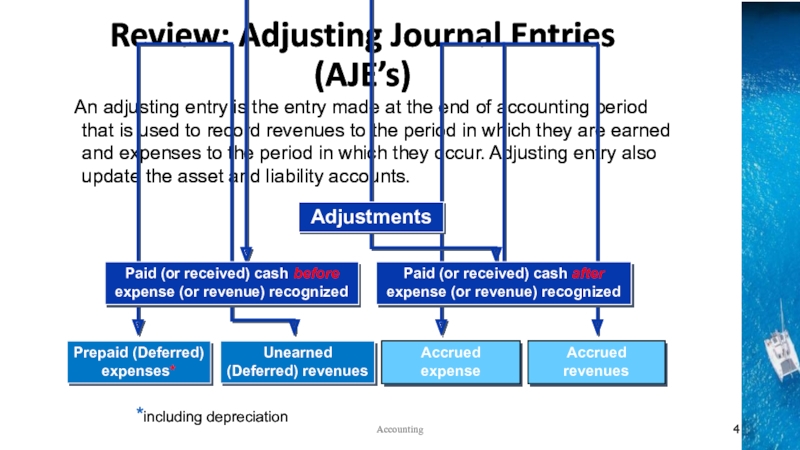
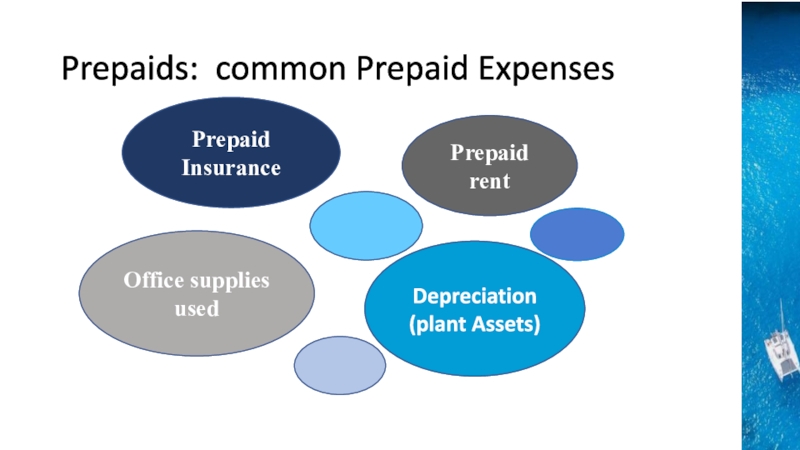
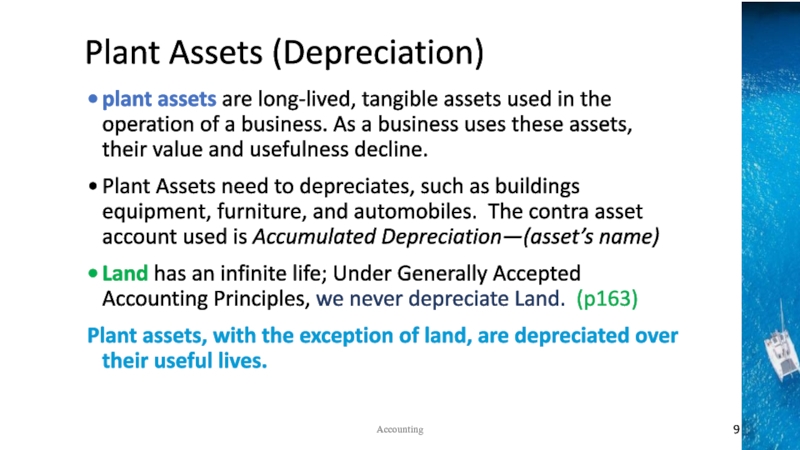
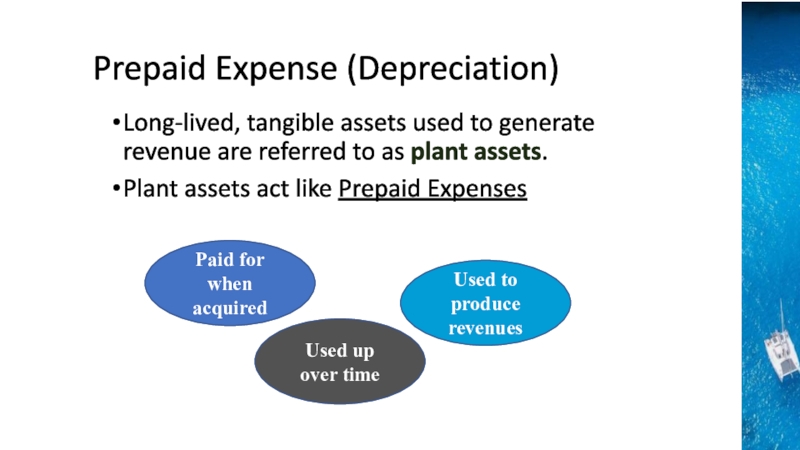
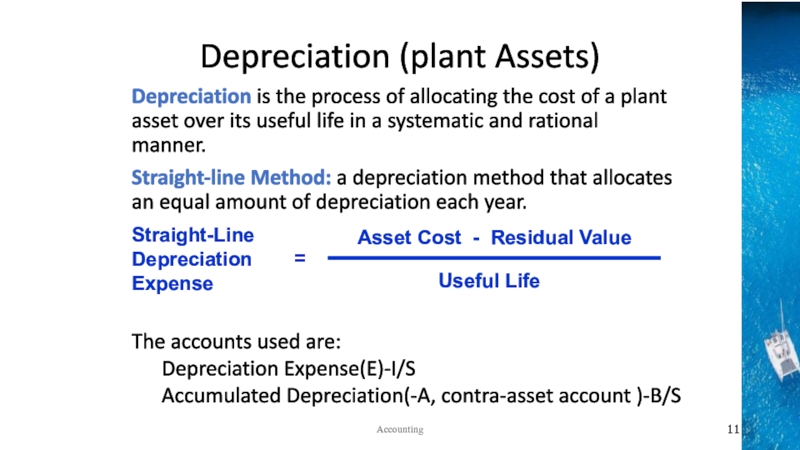
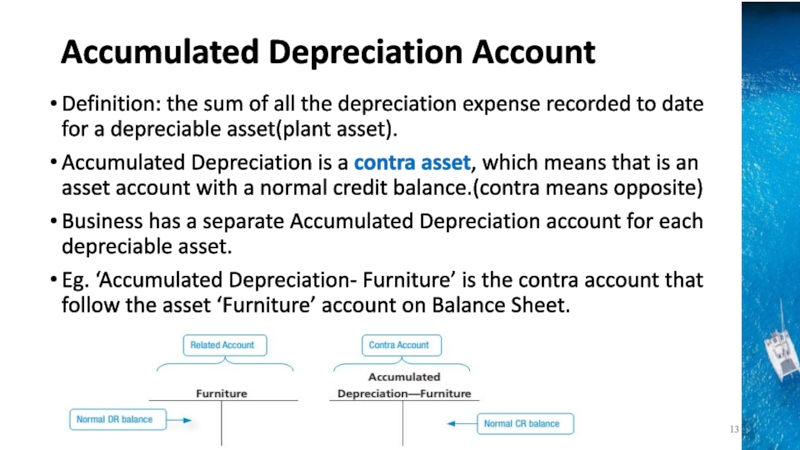
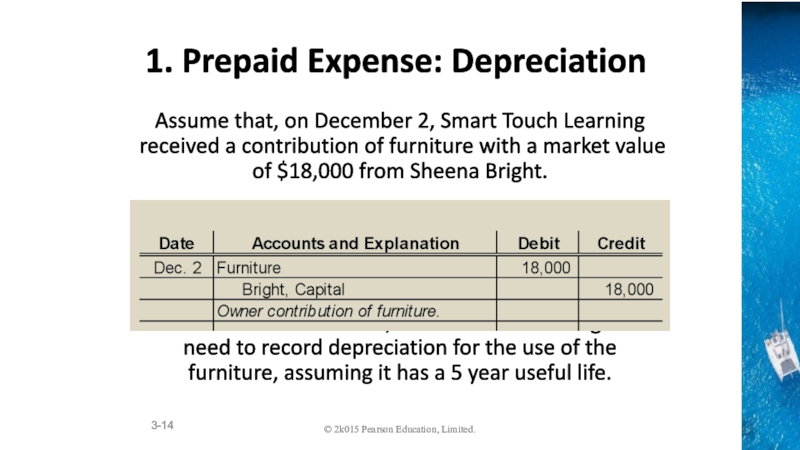
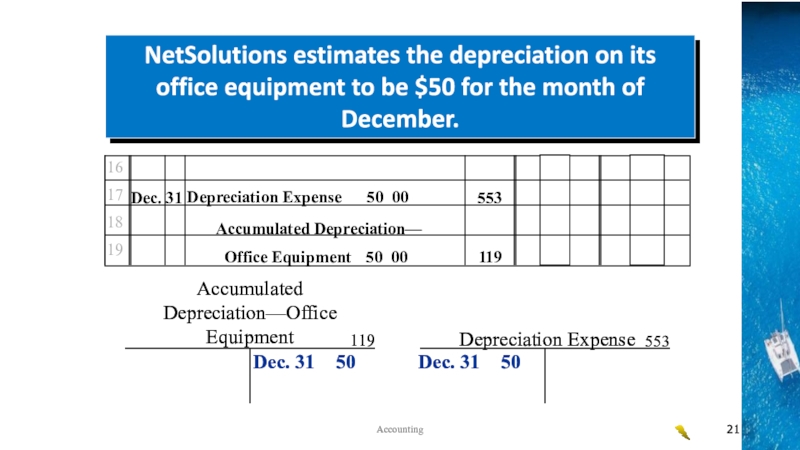
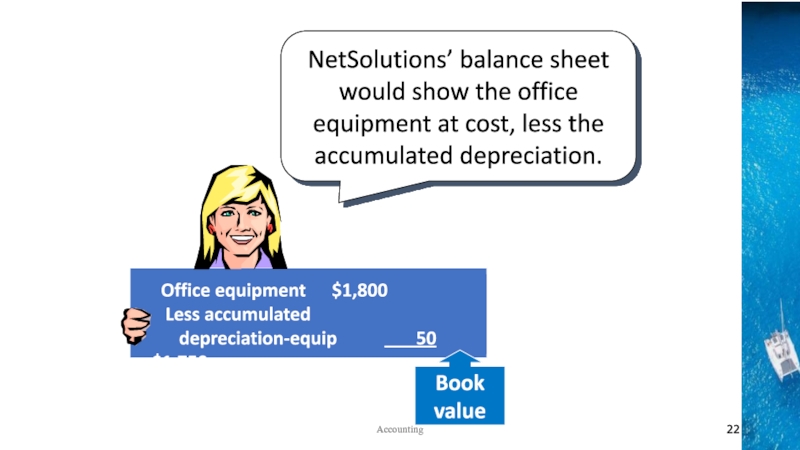
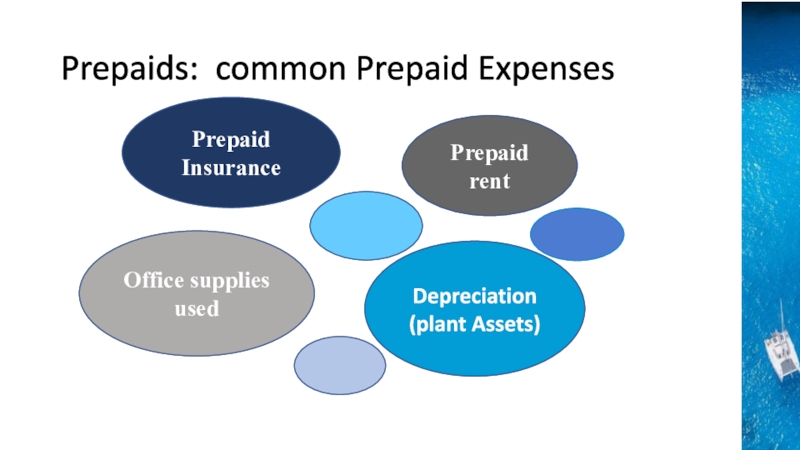
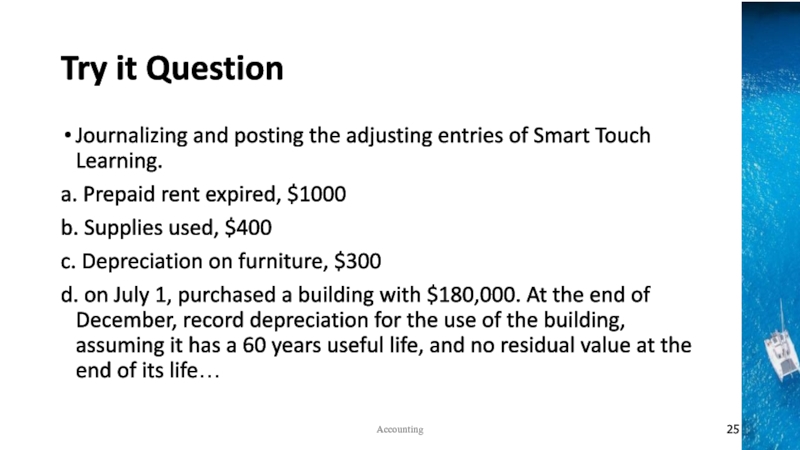
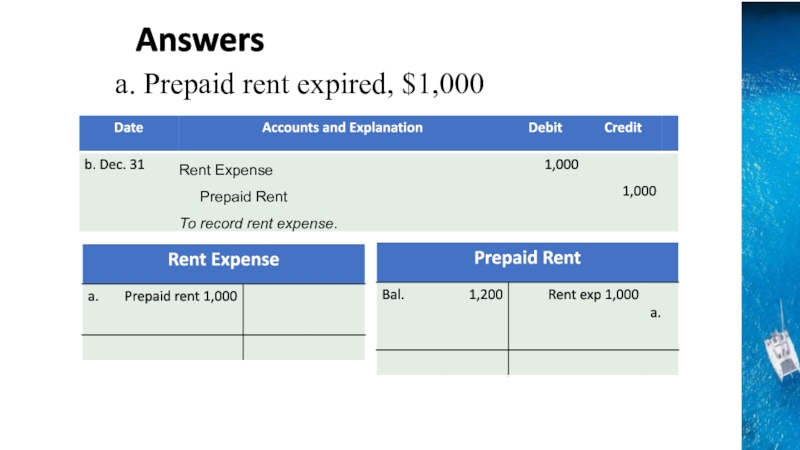
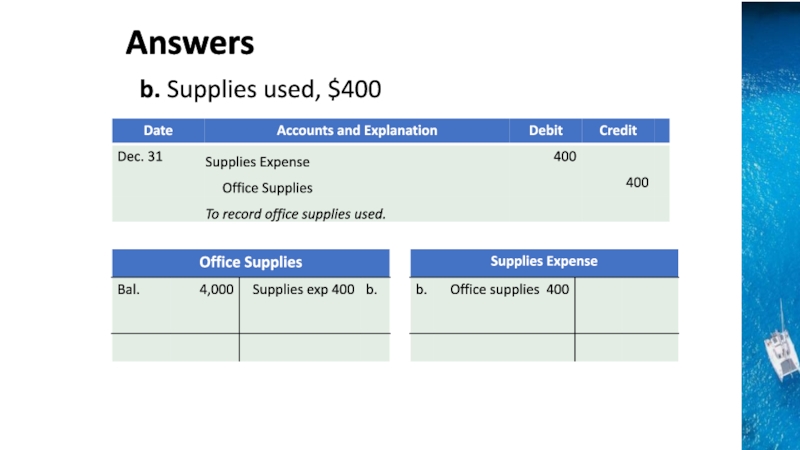
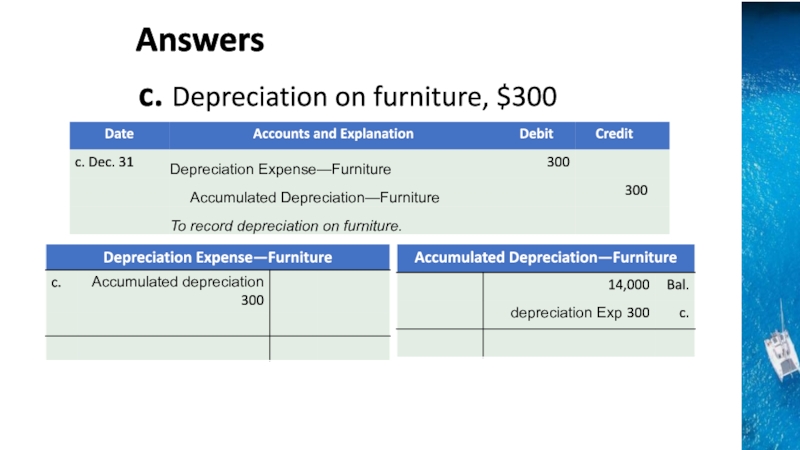
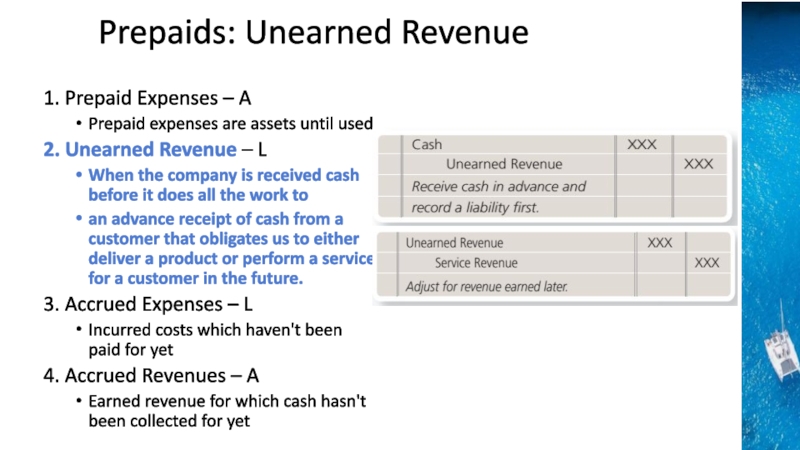
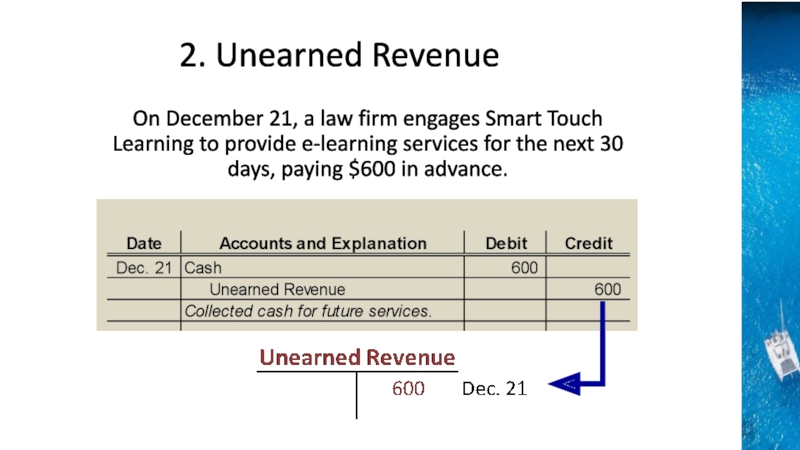
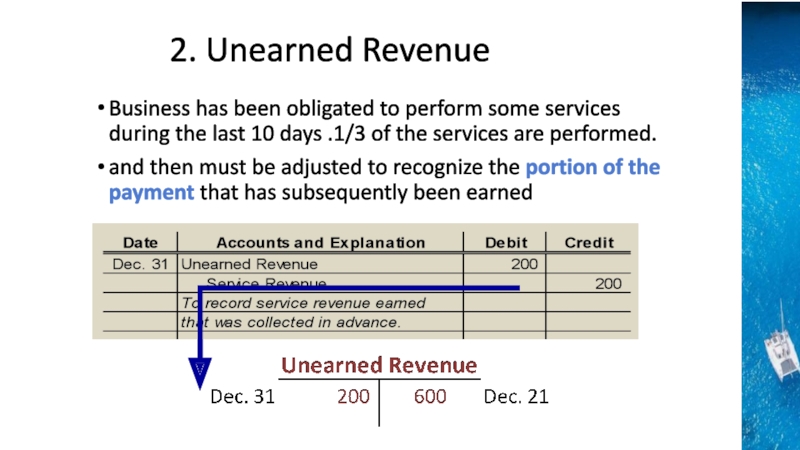
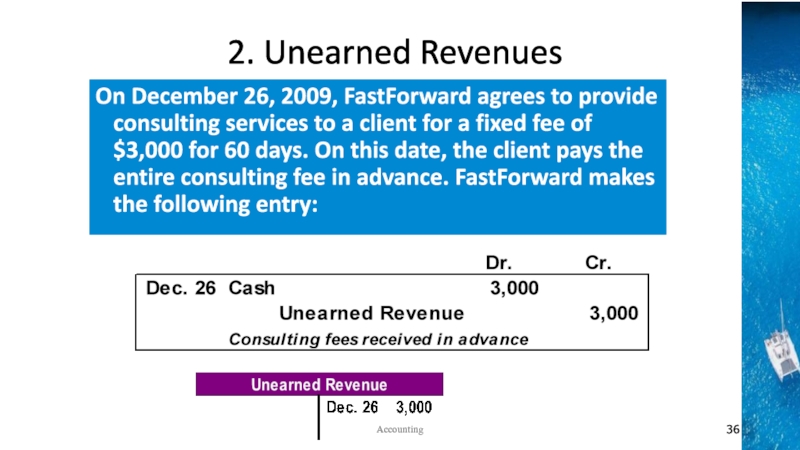
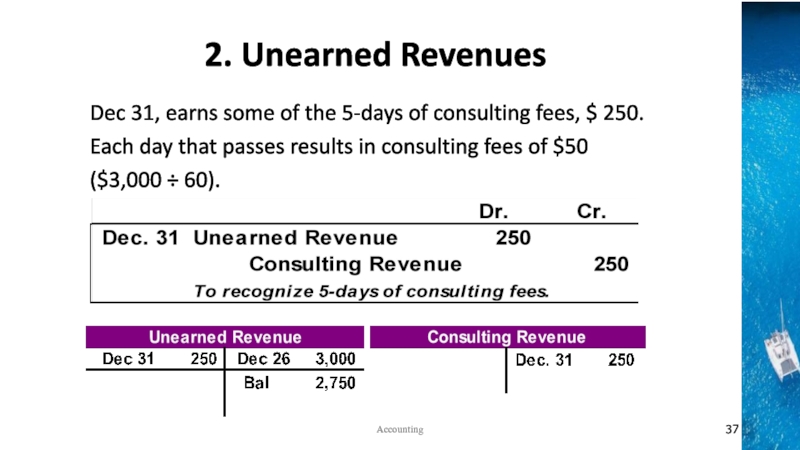
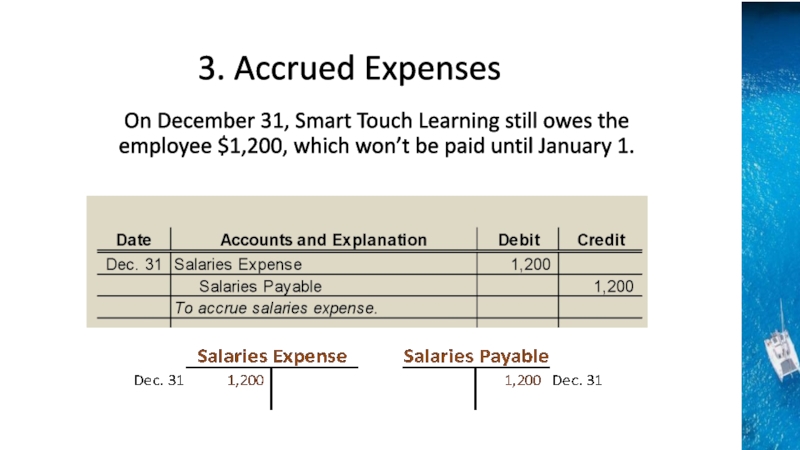
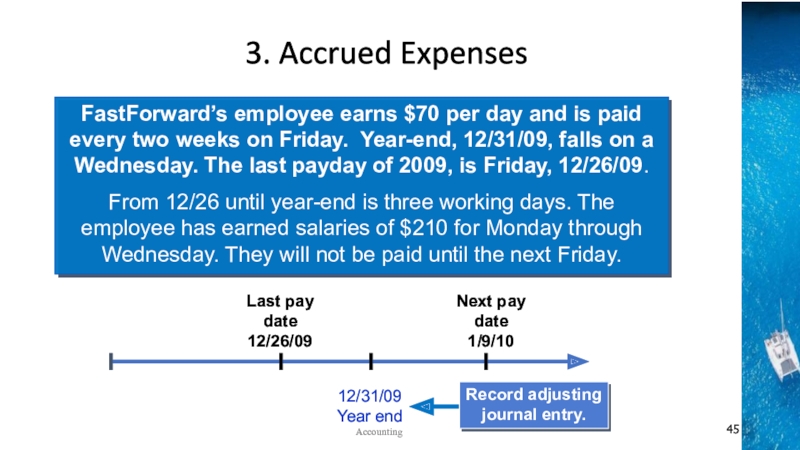
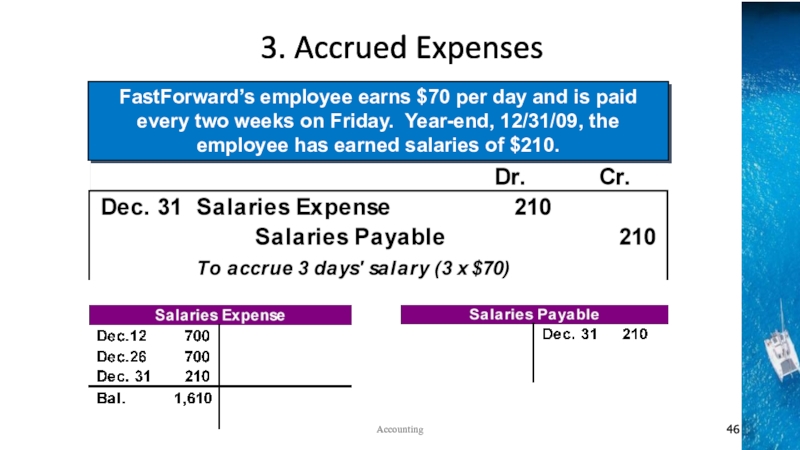
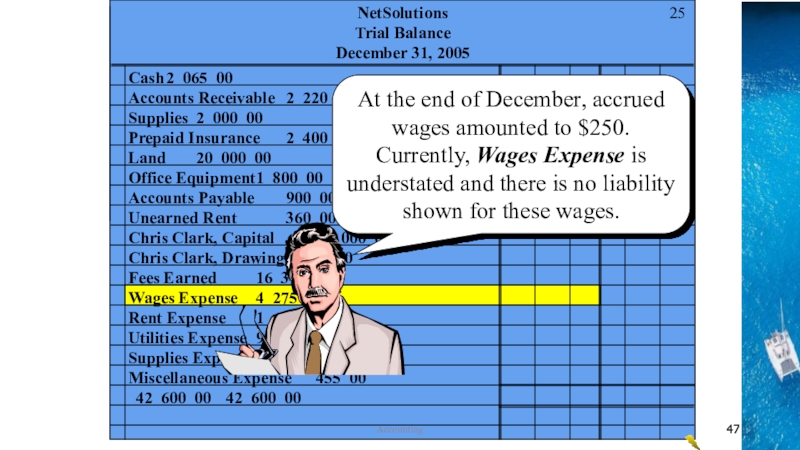
the time period concept, revenue recognition, and matching principles
Explain the
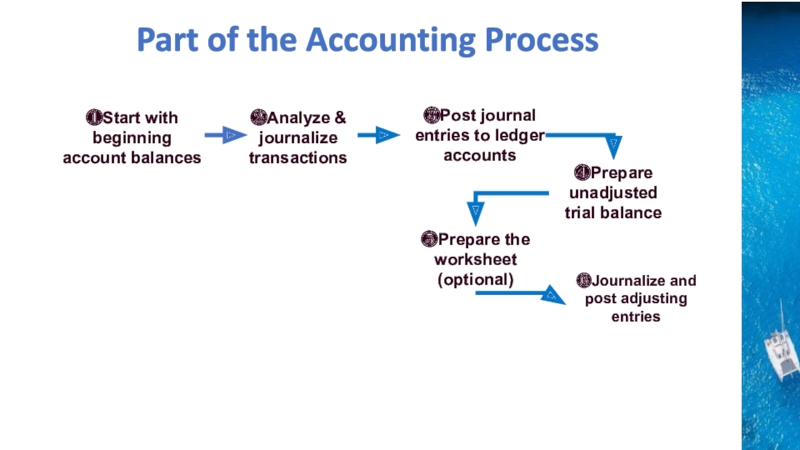
purpose of and journalize and post adjusting entriesPrepare an adjusted trial balance
Identify the impact of adjusting entries on the financial statements
use a worksheet to prepare the adjusted trial balance
Accounting