Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Amplifier
Содержание
- 1. Amplifier
- 2. AmplifierAn amplifier is an electronic device or
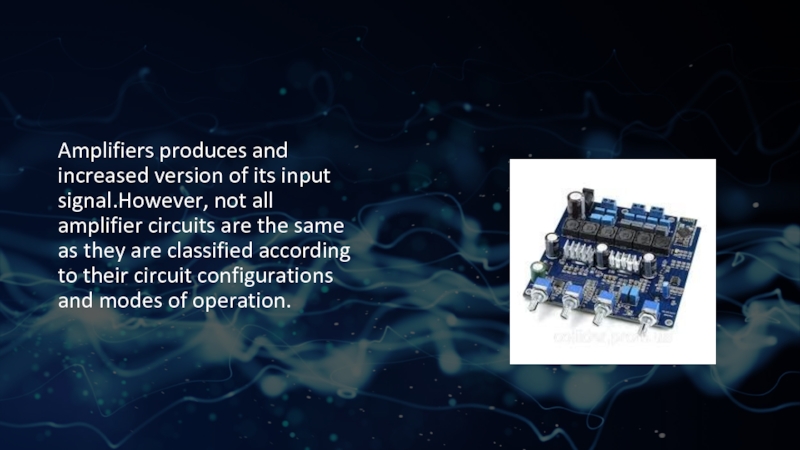
- 3. Amplifiers produces and increased version of its input
- 4. Types of Power AmplifiersThere are three categories
- 5. Voltage AmplifierThese amplifiers increase the amplitude of
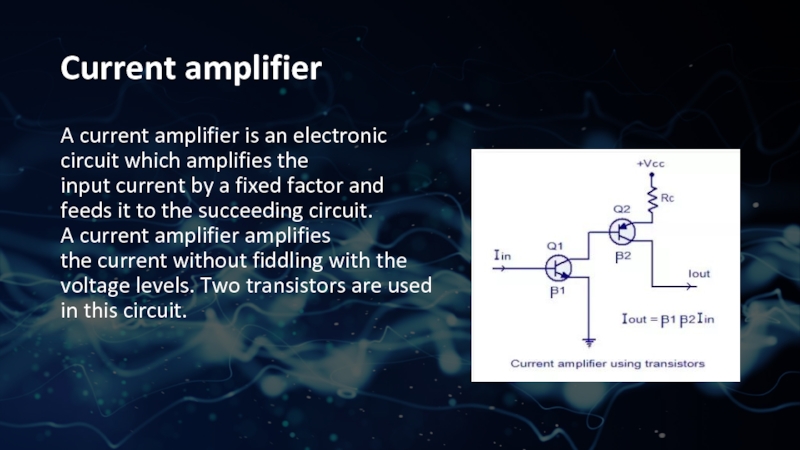
- 6. Current amplifierA current amplifier is an electronic circuit which
- 7. Power amplifierA power amplifier produces maximum power
- 8. AmplifiesAmplifies can be further classified based on the signal they amplify: Audio Frequency AmplifiersUltrasonic AmplifiersWide band AmplifiersVideo AmplifiersOperational Amplifiers
- 9. Audio Frequency AmplifiersAudio voltage amplifiers is an electronic amplifier that amplifies low-power electronic audio signals such as the signal.
- 10. Ultrasonic AmplifiersThey are used for specific purposes such as ultrasonic cleaning, ultrasound scanning, remote control systems.
- 11. Wide band AmplifiersThese amplifiers are used in measuring equipment such as oscilloscopes.
- 12. Video AmplifiersVideo signals carry all the picture information on TV sets, video and radar systems.
- 13. Operational AmplifiersOperational Amplifiers are linear devices that are
- 14. ClassesThe class gives a broad indication of
- 15. Class AClass A amplifiers generally provide the
- 16. Class BClass B offer poorer linearity but are cheaper, run cooler, and are much more efficient.
- 17. Class ABClass AB are a compromise solution,
- 18. Class CClass C amplifiers have much higher efficiency but much poorer output quality.
- 19. Thanks for your attention!
- 20. Скачать презентанцию
AmplifierAn amplifier is an electronic device or circuit which is used to increase the magnitude of the signal applied to its input.