Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Antifungal agents are used for superficial and deep (systemic) fungal
Содержание
- 1. Antifungal agents are used for superficial and deep (systemic) fungal
- 2. AntibioticsPolyenes: Amphotericin B (AMB), Nystatin, HamycinEchinocandins: Caspofungin,
- 3. Слайд 3
- 4. Polyenes have double-bonded structure. Amphotericin B binds
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. Amphotericin B is administered by slow, intravenous
- 7. Nystatin is used only locally in superficial
- 8. Caspofungin inhibits the synthesis of β-1, 3-glucan
- 9. Azoles are predominantly fungistatic, but may be
- 10. Clotrimazole is effective in the topical treatment.
- 11. Fluconazole is well absorbed after oral administration
- 12. Griseofulvin is fungistatic for most dermatophytes, including
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. Terbinafine inhibits a fungal enzyme squalene epoxidase.
- 15. Antiviral Chemotherapy ProphylaxisAs obligate intracellular parasites,
- 16. Слайд 16
- 17. Слайд 17
- 18. Acyclovir is a guanosine analog active against
- 19. Слайд 19
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Acyclovir can be administered by the topical,
- 22. Ribavirin is an analogue of guanosine. It
- 23. Idoxuridine is a synthetic analog of thymidine.
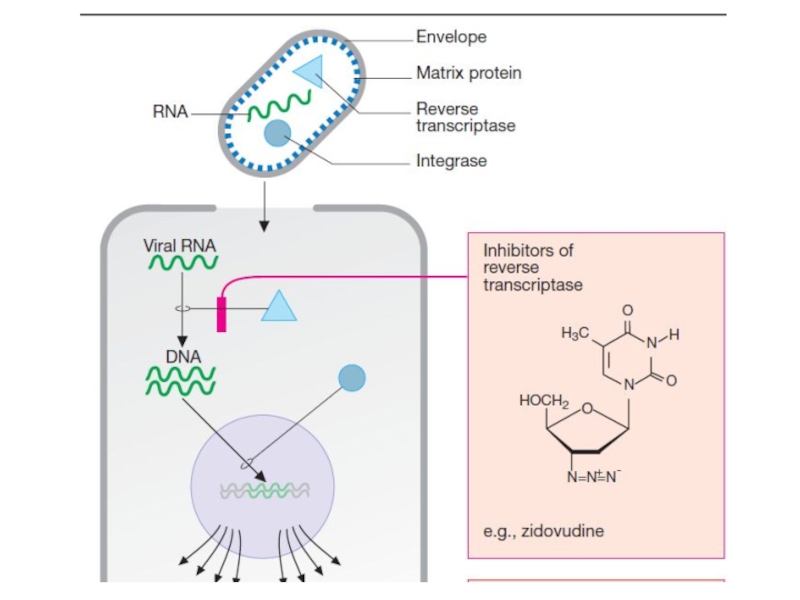
- 24. Zidovudine is a nucleoside derivative. It is
- 25. It is used for the treatment of
- 26. Слайд 26
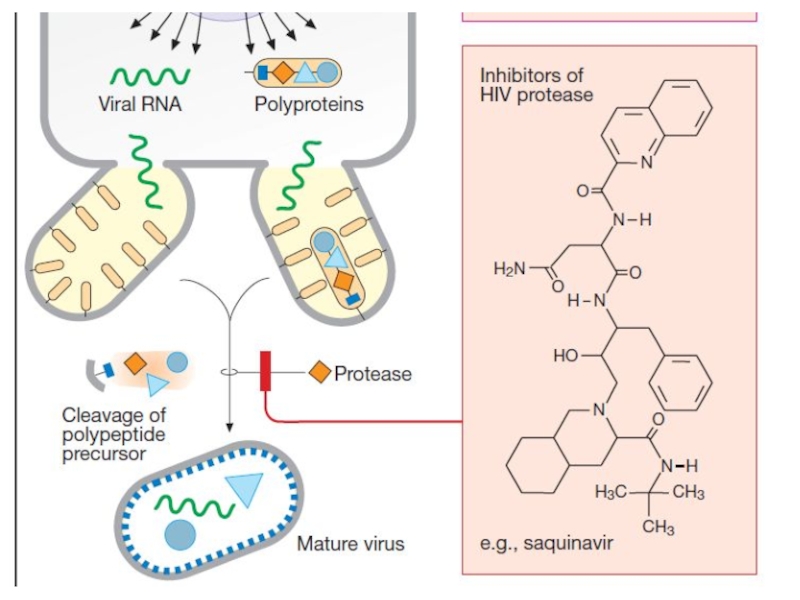
- 27. Saquinavir selectively inhibits the HIV protease. It
- 28. Слайд 28
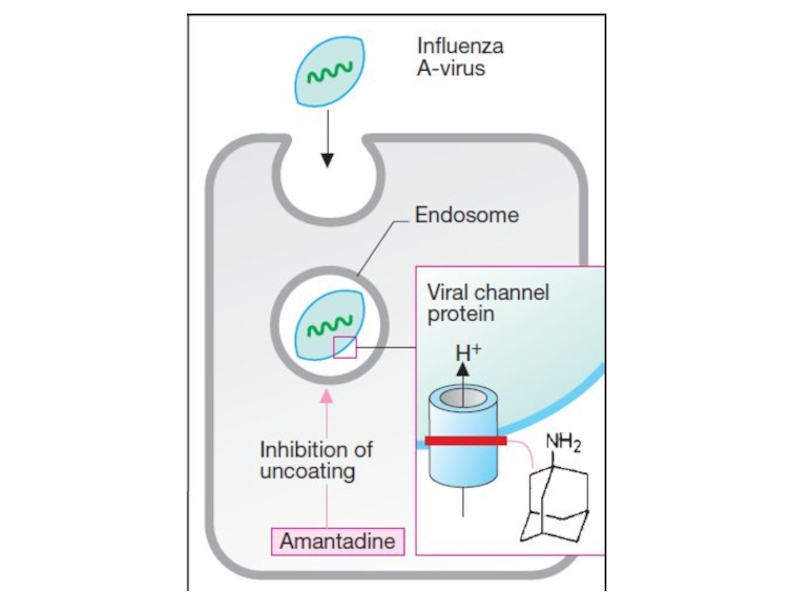
- 29. Remantadin and midantan reduce the penetration of
- 30. Слайд 30
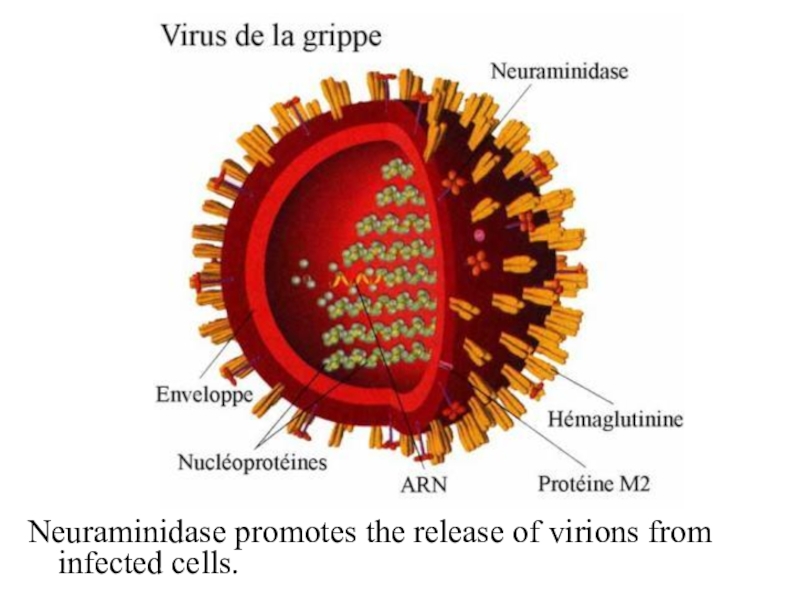
- 31. Oseltamivir inhibits neuraminidase on the surface of
- 32. Neuraminidase promotes the release of virions from infected cells.
- 33. Arbidol and oxoline reduce the penetration of
- 34. Слайд 34
- 35. Interferons-glycopeptides, which are produced by leukocytes (α),
- 36. Drugs are obtained from cells and by
- 37. Side effects of interferon: fever, chills, headache,
- 38. Слайд 38
- 39. Слайд 39
- 40. Amixin has an immunostimulatory effect, it increases
- 41. Literature1. Tripathi K.D. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology.
- 42. Скачать презентанцию
AntibioticsPolyenes: Amphotericin B (AMB), Nystatin, HamycinEchinocandins: Caspofungin, MicafunginHeterocyclic benzofuran: GriseofulvinSynthetic drugs:Antimetabolite - Flucytosine (5-FC)Azoles: Imidazoles1.Topical: Clotrimazole, Miconazole, Oxiconazole2.Systemic: KetoconazoleTriazoles: Fluconazole (systemic), IntraconazoleAllylamine - Terbinafine
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Antibiotics
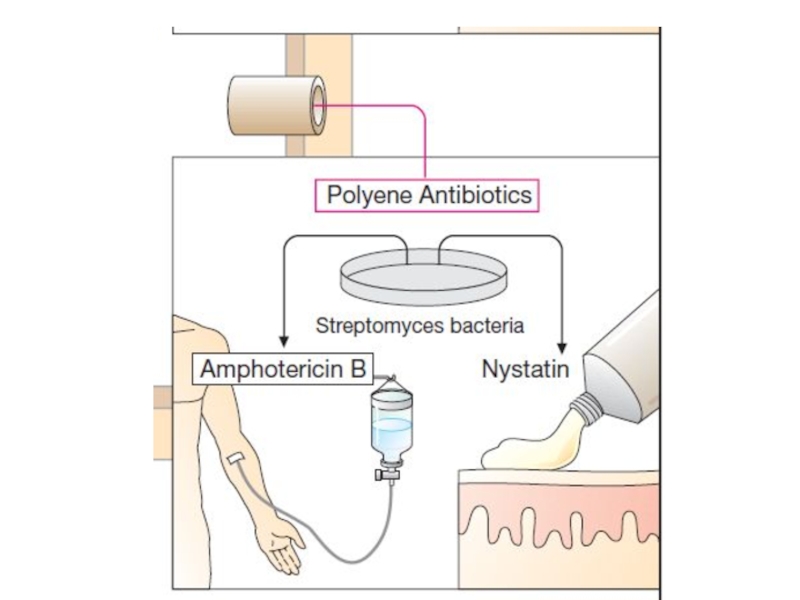
Polyenes: Amphotericin B (AMB), Nystatin, Hamycin
Echinocandins: Caspofungin, Micafungin
Heterocyclic benzofuran: Griseofulvin
Synthetic
drugs:
Antimetabolite - Flucytosine (5-FC)
Azoles:
Imidazoles
1.Topical: Clotrimazole, Miconazole, Oxiconazole
2.Systemic: Ketoconazole
Triazoles: Fluconazole
(systemic), IntraconazoleAllylamine - Terbinafine
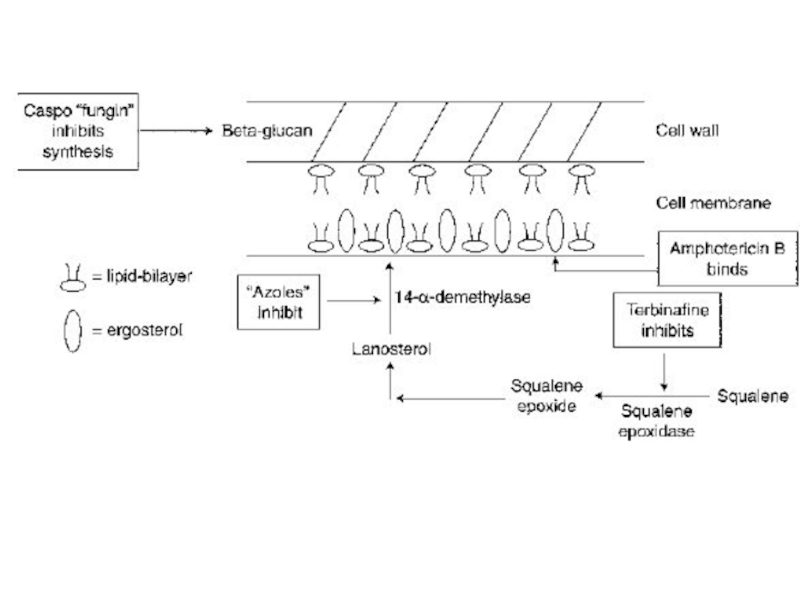
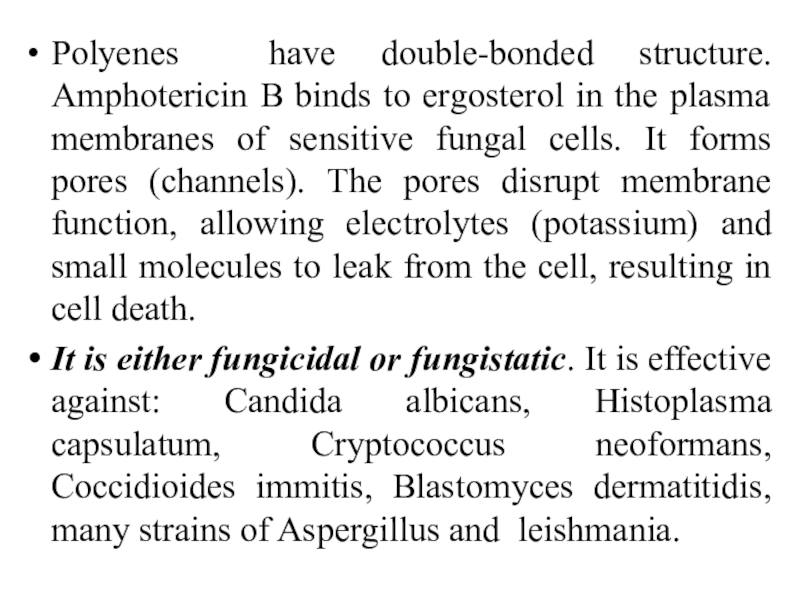
Слайд 4Polyenes have double-bonded structure. Amphotericin B binds to ergosterol in
the plasma membranes of sensitive fungal cells. It forms pores
(channels). The pores disrupt membrane function, allowing electrolytes (potassium) and small molecules to leak from the cell, resulting in cell death.It is either fungicidal or fungistatic. It is effective against: Candida albicans, Histoplasma capsulatum, Cryptococcus neoformans, Coccidioides immitis, Blastomyces dermatitidis, many strains of Aspergillus and leishmania.
Слайд 6Amphotericin B is administered by slow, intravenous (IV) infusion, It
is extensively bound to plasma proteins and is distributed throughout
the body. But it does not pass BBB.Adverse effects: fever and chills, renal impairment, hypotension, thrombophlebitis.
Hamycin is used to topical application for oral thrush, cutaneous candidiasis, monilial and trichomonas vaginitis and otomycosis by Aspergillus.
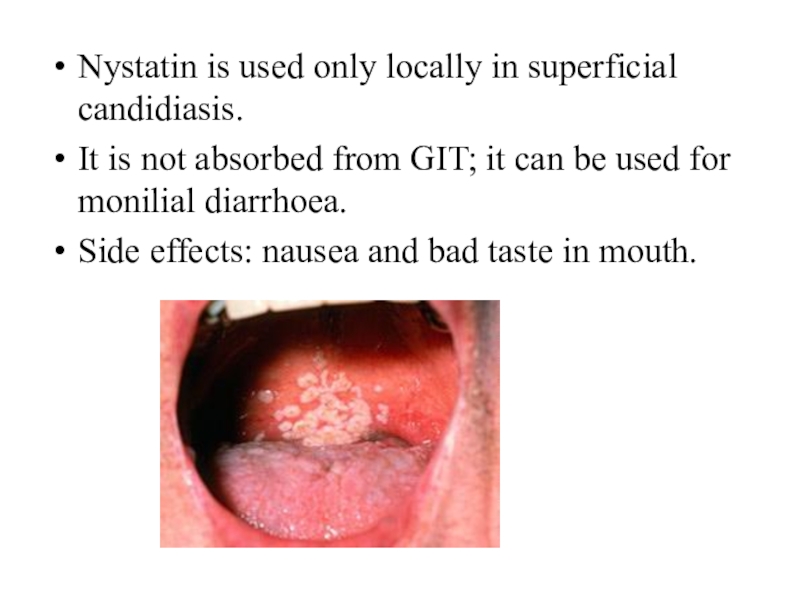
Слайд 7Nystatin is used only locally in superficial candidiasis.
It is
not absorbed from GIT; it can be used for monilial
diarrhoea.Side effects: nausea and bad taste in mouth.
Слайд 8 Caspofungin inhibits the synthesis of β-1, 3-glucan (a unique component
of the fungal cell wall. It is active mainly against
Candida and Aspergillus.Uses: deep and invasive candidiasis, invasive aspergillosis.
It is infused i.v., distributed into tissues, but does not enter CSF.
Adverse effects: rash, vomiting, dyspnoea, hypokalemia and joint pain, acute febrile reaction.
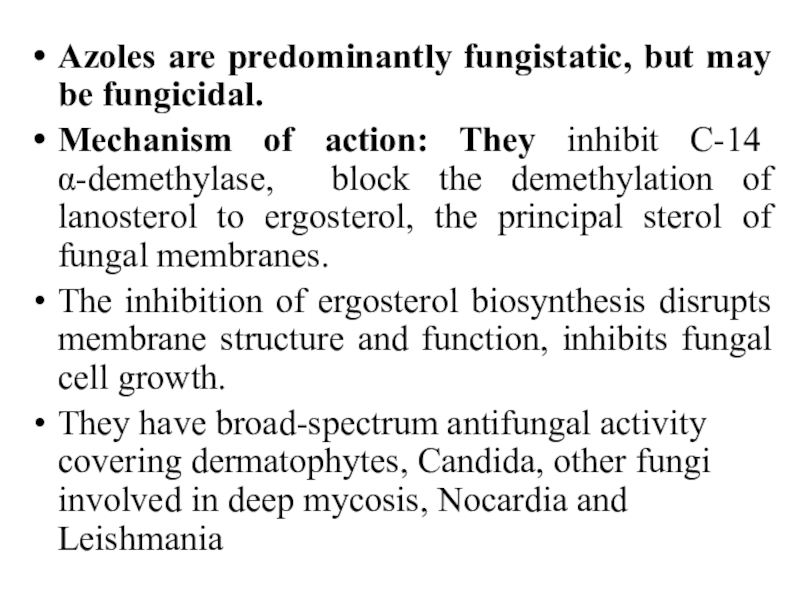
Слайд 9Azoles are predominantly fungistatic, but may be fungicidal.
Mechanism of
action: They inhibit C-14 α-demethylase, block the demethylation of lanosterol
to ergosterol, the principal sterol of fungal membranes.The inhibition of ergosterol biosynthesis disrupts membrane structure and function, inhibits fungal cell growth.
They have broad-spectrum antifungal activity covering dermatophytes, Candida, other fungi involved in deep mycosis, Nocardia and Leishmania
Слайд 10Clotrimazole is effective in the topical treatment. Uses: tinea infections,
ringworm, Athletes’ foot, otomycosis, oropharyngeal candidiasis, vaginal candidiasis.
Adverse effects: local
irritation with stinging.Ketoconazole is the broad-spectrum antifungal drug, useful in both dermatophytosis and deep mycosis.
Adverse effects: nausea and vomiting; loss of appetite, headache, paresthesia, rashes and hair loss.
Слайд 11Fluconazole is well absorbed after oral administration and distributes widely
to body fluids and tissues. The majority of the drug
is excreted unchanged via the urine. It is used orally, IV .It is highly active against Cryptococcus neoformans and certain species of Candida, including C. albicans
Uses: deep fungal infections (including meningitis), ringworm, mucocutaneous candidiasis (the oral cavity, gastrointestinal tract, vagina).
Side effects: dyspepsia, liver dysfunction, skin rash.
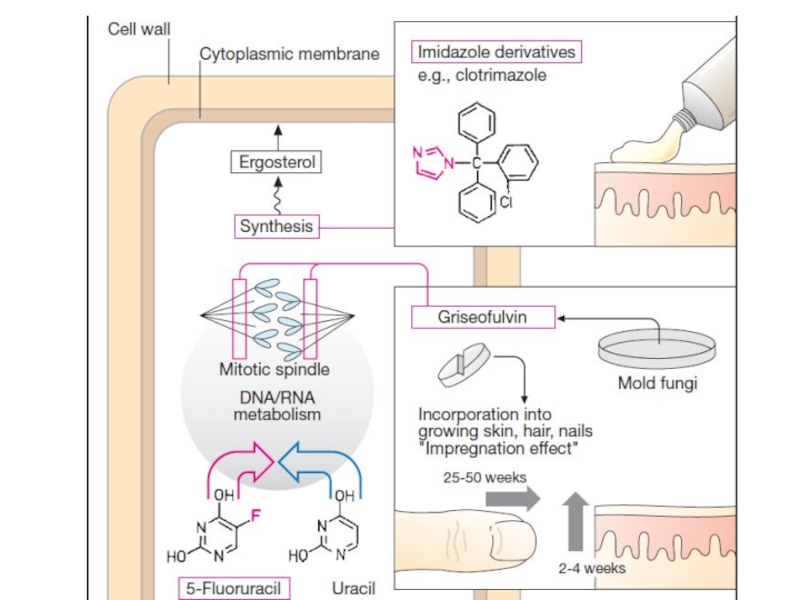
Слайд 12Griseofulvin is fungistatic for most dermatophytes, including Epidermophyton, Trichophyton, Microsporum.
Griseofulvin interferes with microtubule function in dermatophytes and may also
inhibit the synthesis and polymerization of nucleic acids.Griseofulvin is fungistatic.
The oral formulation of the drug is indicated for dermatophytoses of the skin and hair.
Adverse effects: headaches, mental confusion, gastrointestinal irritation, photosensitivity and changes in liver function.
Слайд 14Terbinafine inhibits a fungal enzyme squalene epoxidase. It causes accumulation
of toxic levels of squalene, which can interfere with ergosterol
synthesis.Terbinafine is fungicidal.
Terbinafine is available in both oral and topical forms. It accumulates in keratin, but it is much more effective than griseofulvin in onychomycosis.
Adverse effects include gastrointestinal upsets, rash, headache, and taste disturbances.
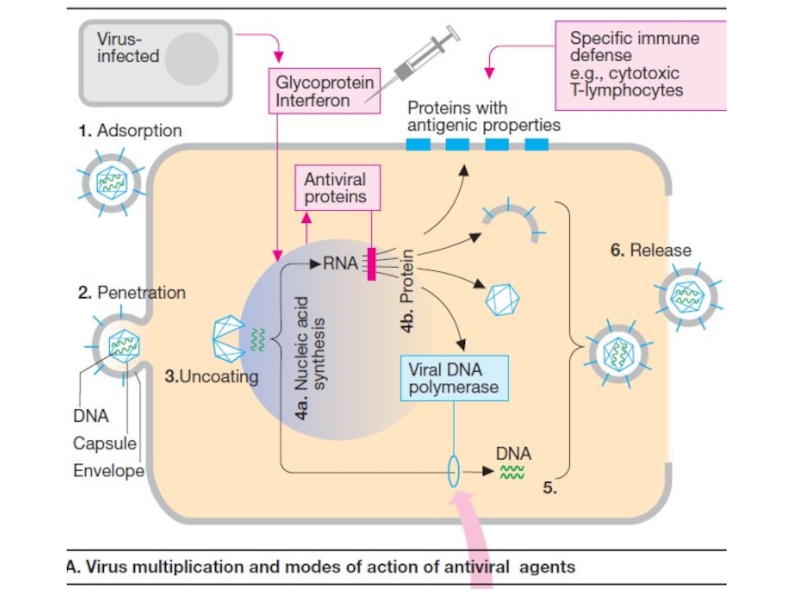
Слайд 15Antiviral Chemotherapy
Prophylaxis
As obligate intracellular parasites, the replication of viruses
depends on synthetic processes of the host cell.
Antiviral
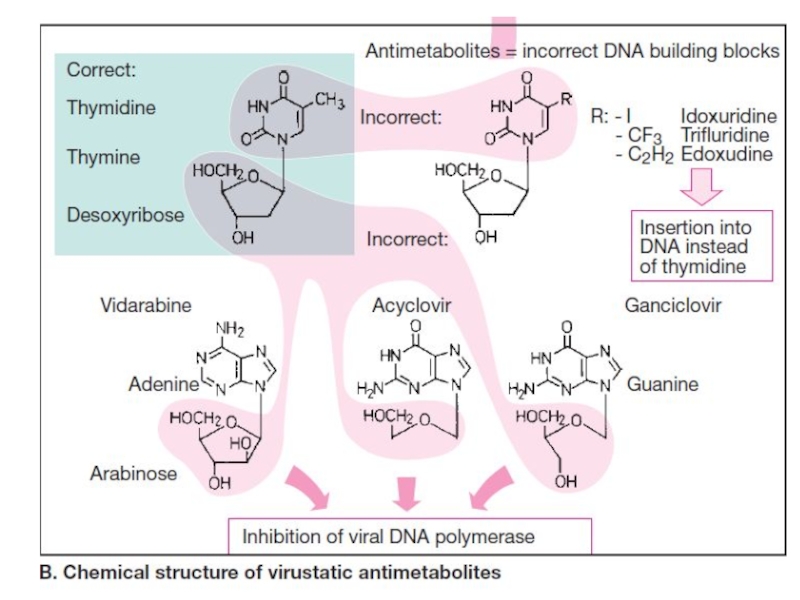
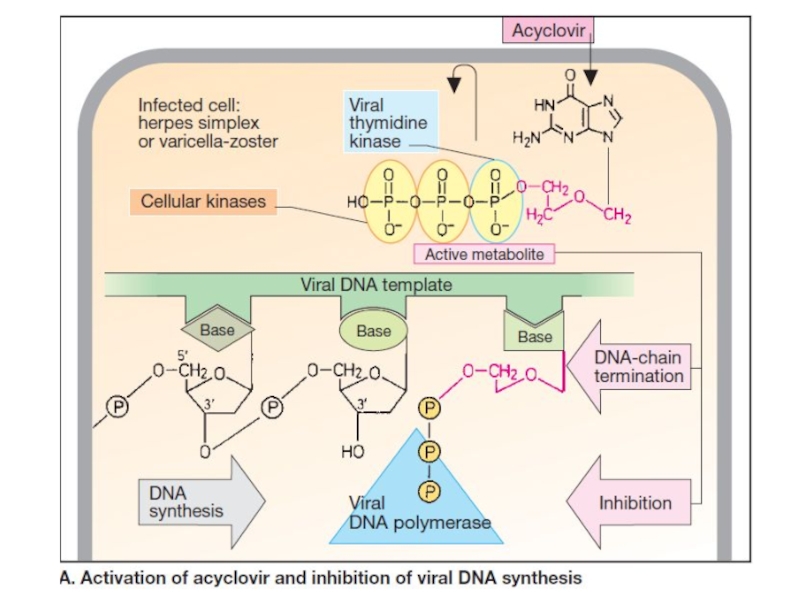
drugs can exert their actions at several stages of viral replication including viral entry, nucleic acid synthesis, late protein synthesis and processing, and in the final stages of viral packaging and virion release.Слайд 18Acyclovir is a guanosine analog active against herpes simplex virus,
varicella-zoster virus and some Epstein-Barr virus.
Acyclovir is monophosphorylated in the
cell by the herpes virus-encoded enzyme thymidine kinase .Virus-infected cells are most susceptible. The monophosphate analog is converted to the di- and triphosphate forms by the host cell kinases. Acyclovir triphosphate competes with deoxyguanosine triphosphate as a substrate for viral DNA polymerase and is itself incorporated into the viral DNA, causing premature DNA chain termination. Слайд 21Acyclovir can be administered by the topical, and oral routes
for the treatment of mucocutaneous and genital herpes lesions.
The oral
drug is well tolerated but may cause gastrointestinal distress and headache. Intravenous administration is used for severe herpes disease, including encephalitis, and for neonatal HSV infection.
Toxic effects with parenteral administration include delirium, tremor, seizures, hypotension and nephrotoxicity
Слайд 22Ribavirin is an analogue of guanosine. It is phosphorylated in
monophosphate, reduces the synthesis of nucleotides.
It turns into
triphosphate, inhibits viral dehydrogenase, disrupts the formation of RNA, proteins and virus replication.It is used for influenza, herpes.
It can cause allergic reactions.
It is contraindicated in pregnancy.
Слайд 23Idoxuridine is a synthetic analog of thymidine.
It is embedded
in the DNA molecule, suppresses the replication of some DNA
viruses.It is used locally for herpetic skin lesions
Слайд 24Zidovudine is a nucleoside derivative. It is phosphorylated in the
cells and is converted to thymidine triphosphate. It inhibits the
reverse transcriptase of virion, prevents the formation of DNA from viral RNA.This DNA can be stored in human cells and become a source of RNA virus synthesis.
Zidovudine inhibits the synthesis of mRNA and viral proteins.
HIV reverse transcriptase is 20-30 times more sensitive to the inhibitory effect of the drug than DNA polymerase of macroorganism cells.
Слайд 25It is used for the treatment of HIV infection.
It
is effective during the first 6 to 8 months from
the start of disease and it delays the development of the disease.It is used orally and IV, passes well into the tissue, through the BBB. It is excreted by the kidneys in the active form and in the form of metabolites.
Side effects: anemia, neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, headache, insomnia, myalgia, renal dysfunction, dyspepsia.
Слайд 27Saquinavir selectively inhibits the HIV protease. It disrupts the formation
of structural proteins and enzymes of HIV virions, which are
necessary for reproduction.Immature virion precursors are formed. The development of infection is delayed.
Saquinavir is used orally for HIV-1 infection (causes HIV infection and AIDS) and HIV-2.
Side effects: dyspepsia, increased activity of liver enzymes, lipid metabolism disorders, hyperglycemia.
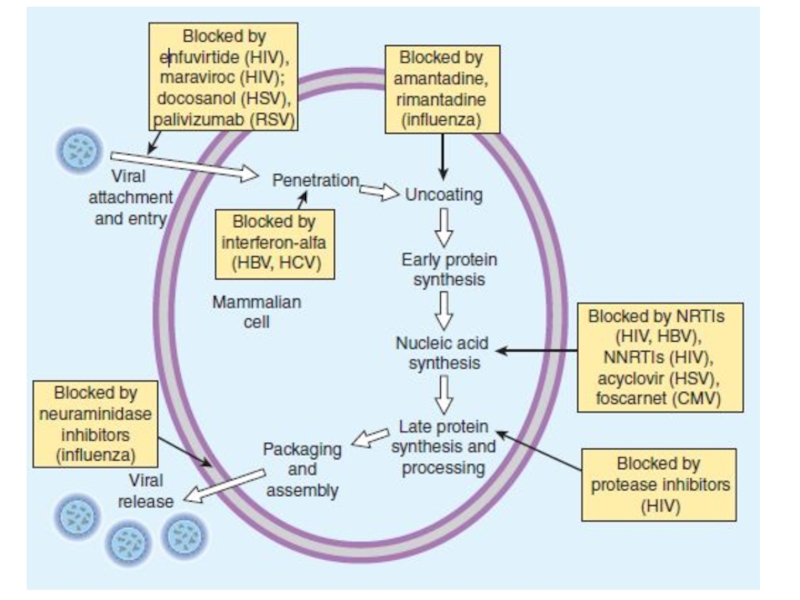
Слайд 29Remantadin and midantan reduce the penetration of the virus into
the cell.
They block the membrane protein M2, violate
the deproteinization of virus of influenza A, suppress the replication of this virus. They are used to prevent influenza according to the scheme.
Side effects: irritability, anxiety, drowsiness, tremor, hypotension, dyspepsia, allergy, development of resistance.
Слайд 31Oseltamivir inhibits neuraminidase on the surface of virus of influenza
A and B.
It reduces the release of viruses, the
spread of infection to healthy cells.It violates the replication of the viruses.
It reduces the production of cytokines and prevents the development of local and systemic inflammatory response.
It is used inside.
Side effects: nausea, vomiting
Слайд 33Arbidol and oxoline reduce the penetration of the virus into
the cells.
Arbidol is active in influenza A and B, adenovirus
infection. It increases humoral and cellular immunity, resistance to infections.It is used orally.
Oxoline is used in drops or ointments for prevention of influenza, herpetic, adenovirus infection.
It can cause irritating effect.
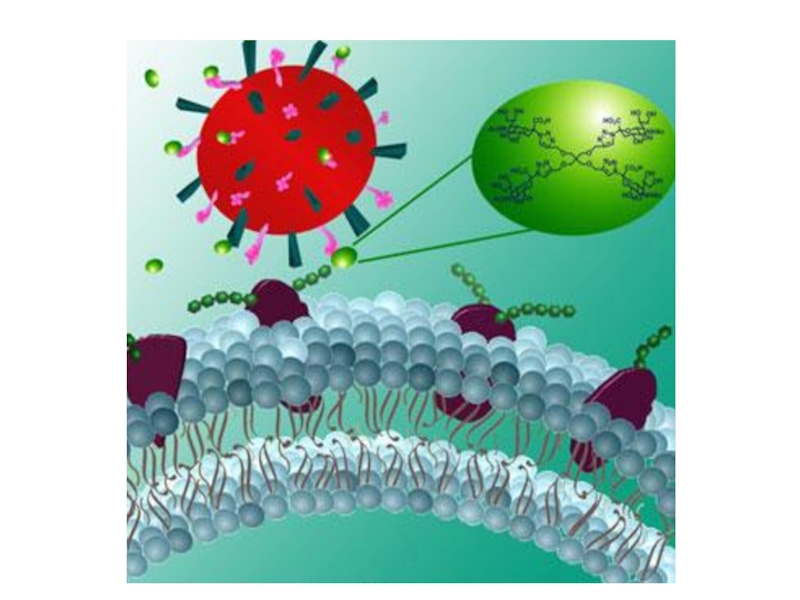
Слайд 35Interferons-glycopeptides, which are produced by leukocytes (α), fibroblasts (β), lymphocytes
(γ).
They bind to specific receptors on the surface of
cells infected with the virus, activate protein kinases. They increase the synthesis of endonucleases that destroy RNA of viruses.They reduce virus replication.
Interferons increase immunity, macrophage activity, cytotoxicity of T-killers.
They are used in viral diseases: hepatitis, encephalitis, rabies, herpes, influenza, adenovirus infections, etc. They reduce the risk of cancer.
Слайд 36Drugs are obtained from cells and by genetic engineering.
Preparations of
α-interferon: Reaferon, Viferon
β-interferon: Betaferon
γ-interferon: Gammaferon.
They are used locally for
the treatment and prevention of influenza, adenovirus infection, herpes. They are administered IV, IM, SC in severe forms of influenza, viral hepatitis, measles, herpes, multiple sclerosis.
They penetrate into the tissues poorly, they quickly collapse.
Слайд 37Side effects of interferon: fever, chills, headache, soreness, hyperemia at
the injection site, tachycardia, hypotension, dyspepsia, muscle pain.
In very high
doses, they cause violation of hematopoiesis, paresis, paralysis, hepatotoxicityСлайд 40Amixin has an immunostimulatory effect, it increases the production of
α, β, γ interferons.
It is used for influenza, acute
respiratory viral infections, hepatitis, neuroinfection, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection. It can cause dyspepsia, chills, intermittent fever, allergic reactions.
Слайд 41Literature
1. Tripathi K.D. Essentials of Medical Pharmacology. Eighth Edition. -2019.-
Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers. The Health Sciences Publisher. -New Delhi.
London. Panama2. D.A.Kharkevich. Pharmacology. Textbook for medical students. Translation of 12th edition of Russion textbook “Pharmacology” (2017). – М., ГЭОТАР-Медиа, 2017.
3. Review of pharmacology. Gobind Rai Garg, Sparsh Gupta. 13th edition. - 2019.- Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers. The Health Sciences Publisher. -New Delhi. London. Panama
4. Whalen Karen. Lippincott Illustrated Reviews: Pharmacology. Sixth Edition. - Wolters Kluwer. - 2015.-Philadelphia
5. Color Atlas of Pharmacology. 2nd edition, revised and expanded. Heinz Lüllmann.- 2000 Thieme
6. Pharmacology Examination & Board Review. Tenth Edition. Trevor Anthony J., Katzung Bertram G., Kruidering-Hall Marieke, Susan B. Masters. - a LANGE medical book. - 2013.-New York
7. Medical Pharmacology at a Glance. Eighth Edition. Neal Michael J. – 2016. John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.
8. USMLE Step 1. Lecture Notes. Pharmacology. Lionel P.Raymon and others.- Kaplan Medical.Inc. -2009