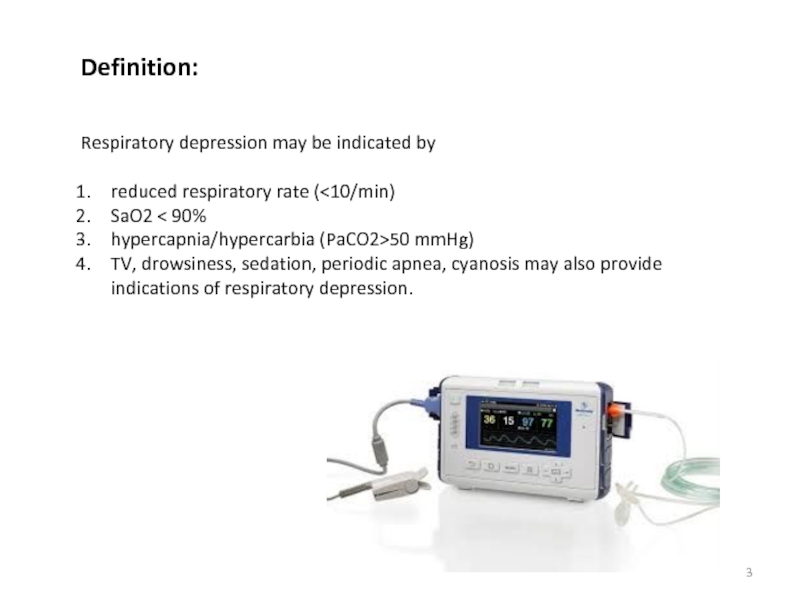
Opioids:
RCTs indicate less respiratory depression when continuous infusion of epidural
opioids are compared with IV infusion of opioids (Category A1-B).
RCTs evaluating differences in hypercarbia somnolence and sedation are equivocal (Category A2-E).
RCT reports no difference in the frequency of respiratory depression when extended release epidural morphine is compared with IV PCA morphine (Category C2-E)
RCTs report no significant differences in respiratory depression, hypoxia, and sedation or somnolence when extended-release epidural morphine is
compared with conventional (immediate-release) epidural morphine (Category C2-E)
ASA consultants agree that extended-release epidural morphine may be used in place of IV or conventional epidural morphine, although extended monitoring may be required.