Слайд 1
Business Statistics
Shirley SHAO
2020.3
Слайд 2Brief Introduction of the lecturer
Shirley SHAO
Bachelor of Finance, Liaoning University
Master
of Finance, University of Sydney, Australia
Ph.D. of Economics, Liaoning University
Visiting
scholar, Fort Hays State University, USA
Visiting scholar, Middlesex University, UK
Email:shaoruo2008@163.com
Chap 1-
Слайд 3In Today’s Business World You Cannot Escape From Data
In today’s
digital world ever increasing amounts of data are gathered, stored,
reported on, and available for further study.
You hear the word data everywhere.
Data are facts about the world and are constantly reported as numbers by an ever increasing number of sources.
Слайд 4Each Business Person Faces A Choice Of How To Deal
With This Explosion Of Data
They can ignore it and hope
for the best.
They can count on other people’s summaries of data and hope they are correct.
They can develop their own capability and insight into data by learning about statistics and its application to business.
Слайд 5Statistics Is Evolving So Businesses Can Use The Vast Amount
Of Data Available
The emerging field of Business Analytics makes
“extensive use of:
Data
Statistical and quantitative analysis
Explanatory & predictive models
Fact based management
to drive decisions and actions.”
Слайд 6What is Meant by Statistics?
Statistics is the science of collecting,
organizing, presenting, analyzing, and interpreting numerical data to assist in
making more effective decisions.
Chap 1-
Слайд 7Why Study Statistics?
Numerical information is everywhere
•2.5 EB bytes of data
is created every day. •2,500,000,000,000,000,000 bytes
•More than 30 million
sensors are being used. •More than 5 billion people were using mobile phones in 2017.
Chap 1-
Слайд 8Why Study Statistics?
Today, there are 1.8 billion young people between
the ages of 10 and 24 in the world.
One point
eight billion young women and young men are standing at the door of adulthood.
Are they ready?
Right now, too few of them are.
Chap 1-
Слайд 9Why Study Statistics?
Every month, 10 million young people reach working
age. It’s a staggering number. Some will go on for
further education, but many will enter the workforce.
And our world is not creating 10 million new jobs each month. The competition is fierce for the jobs that are available.
So, imagine being a young person today, needing a job, seeking a livelihood, ready to build a future, and opportunities are hard to find.
Chap 1-
Слайд 10Why Study Statistics?
We are finding ourselves at a time in
the world
when the world is changing so fast for work.
We’re
in the fourth industrial revolution.
Young people do not want to be on the farms and in rural communities. They want to go to the cities.
They want to learn future skills for future work.
They want to learn digital technology.
They want to learn business and entrepreneurship, so that they can create a business of their own.
Chap 1-
Слайд 11Who Uses Statistics?
A teacher?
A researcher?
A coach?
A businessman?
A government policy maker?
etc...
Chap
Слайд 12Who Uses Statistics?
Statistical techniques are used extensively by marketing, accounting,
finance, quality control, consumers, professional sports people, hospital administrators, educators,
politicians, physicians, etc...
Chap 1-
Слайд 13How
shall we learn for this lesson ?
1. To get
the principal knowledge through the lesson. (Take down lecture notes)
2.
To consolidate the knowledge through self-learning with supplementary materials, and by doing exercises after lesson.
3. To have discussions on the subject between students, or between students and the teacher in the lesson or after the lesson.
PPT & Textbook
Слайд 14Business Statistics(6th Edition)
(美)莱文,克雷比尔,贝伦森,
中国人民大学出版社,2017.
1. Class Participation 10%
2. Test 10%
3. Homework/ Quiz 10%
4. Final Exam 70%
Total 100%
Assessment
Your participation is warmly welcomed !
Слайд 16Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Business Statistics: A First Course
6th Edition
Chapter 1
Introduction
Слайд 17Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Learning Objectives
In this chapter you learn:
What statistics is
How statistics
is fundamental to business
The basic concepts and vocabulary of statistics
Слайд 18GOALS
1.Understand why we study statistics.
2.Explain what is meant by descriptive
statistics
and inferential statistics.
3.Distinguish between a qualitative
variable and a
quantitative variable.
4. Describe how a discrete variable is different
from a continuous variable.
Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Слайд 19Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
In Business, Statistics Helps
Transform numbers into useful information for decision
makers
Quantify & identify the risks in a business decision
You understand and reduce the variation in a decision making process
Слайд 20Slide 1-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which is correct?
The data is . . .
The data are
. . .
Слайд 21Slide 1-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which of the
following is not a step in using statistics to make
business decisions?
Plan
Repeat
Do
Report
Слайд 22Slide 1-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Statistics can be
used for
Assessing risk
Predicting results
Understanding our world
All of the above
Слайд 23Slide 1-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Statistics is a
way of reasoning.
True
False
Слайд 24Slide 1-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Statistics helps us
make sense of this so we can learn from data?
Variation
Constancy
Numbers
World
Слайд 25Slide 1-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Which of the
following is not an objective of Business Statistics: A First
Course 1/e :
Develop the insights to think clearly about questions
Use tools to show what the data are saying
Give formulas to memorize
Acquire skills to interpret what it all means
Слайд 26Chap 1-
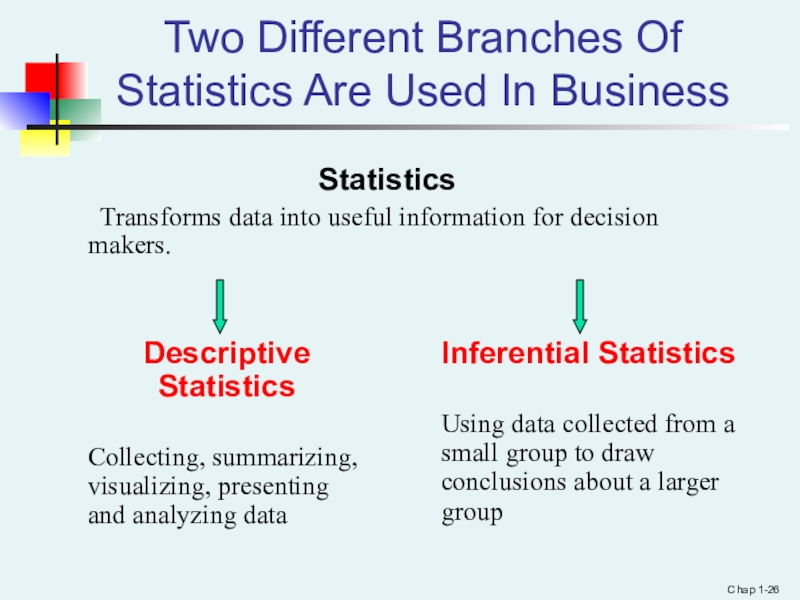
Two Different Branches Of Statistics Are Used In Business
Statistics
Transforms data into useful information for decision makers.
Descriptive Statistics
Collecting,
summarizing, visualizing, presenting and analyzing data
Inferential Statistics
Using data collected from a small group to draw conclusions about a larger group
Слайд 27Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
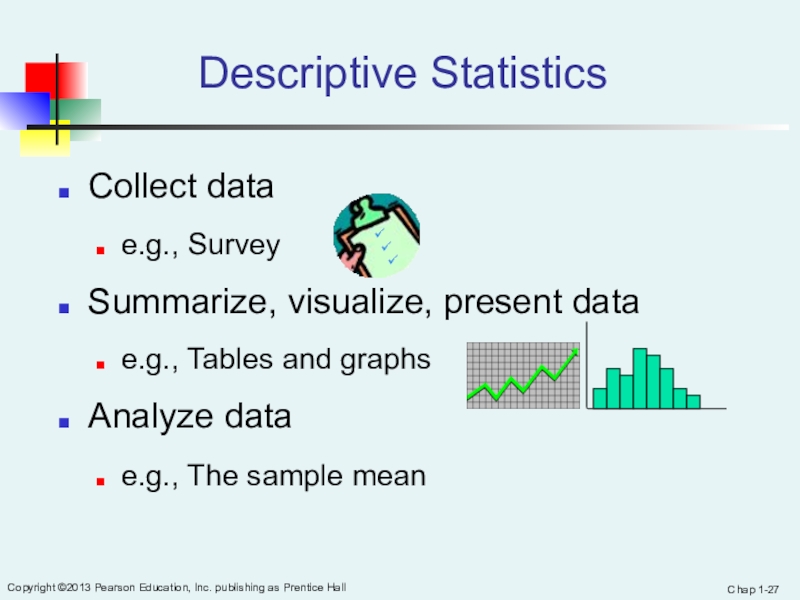
Descriptive Statistics
Collect data
e.g., Survey
Summarize, visualize, present data
e.g., Tables and graphs
Analyze
data
e.g., The sample mean
Слайд 28Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
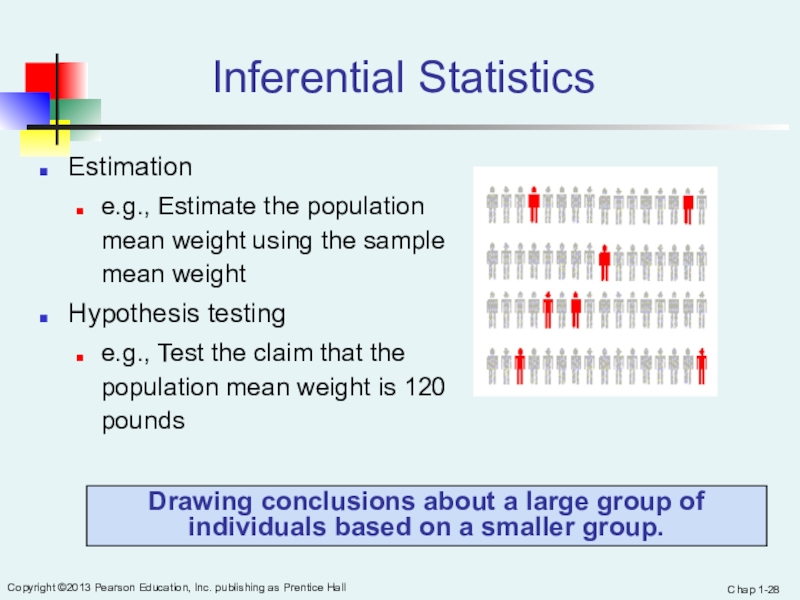
Inferential Statistics
Estimation
e.g., Estimate the population mean weight using the sample
mean weight
Hypothesis testing
e.g., Test the claim that the population mean weight is 120 pounds
Drawing conclusions about a large group of individuals based on a smaller group.
Слайд 29Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Understanding Statistics Enhances A Person’s Numerical Literacy
When do numbers presented
represent useful information?
When are differences in numbers presented meaningful versus simply due to chance?
When are claims of causality in numbers presented valid?
When are patterns observed in large amounts of data meaningful?
Слайд 30Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
In Business, Statistics Plays A Fundamental & Important Role
To visualize
& summarize business data
Descriptive methods used to create charts & tables
To draw conclusions from business data
Inferential methods used to reach conclusions about a large group based on data from a smaller group
To make reliable forecasts about business activities
Inferential methods utilizing statistical models based on business data
To improve business processes
Involves managerial approaches like Six Sigma
Слайд 31Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Two Trends Are Driving The Increasing Importance Of Statistics In
Business
The increasing amount of data that businesses can collect, store, & manage
The increasing accessibility of computerized statistical tools
Слайд 32Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Basic Vocabulary Of Statistics
Слайд 33Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Types of Variables
Categorical (qualitative) variables have values that can only
be placed into categories, such as “yes” and “no.”
Numerical (quantitative) variables have values that represent quantities.
Discrete variables arise from a counting process
Continuous variables arise from a measuring process
Слайд 34Chap 1-
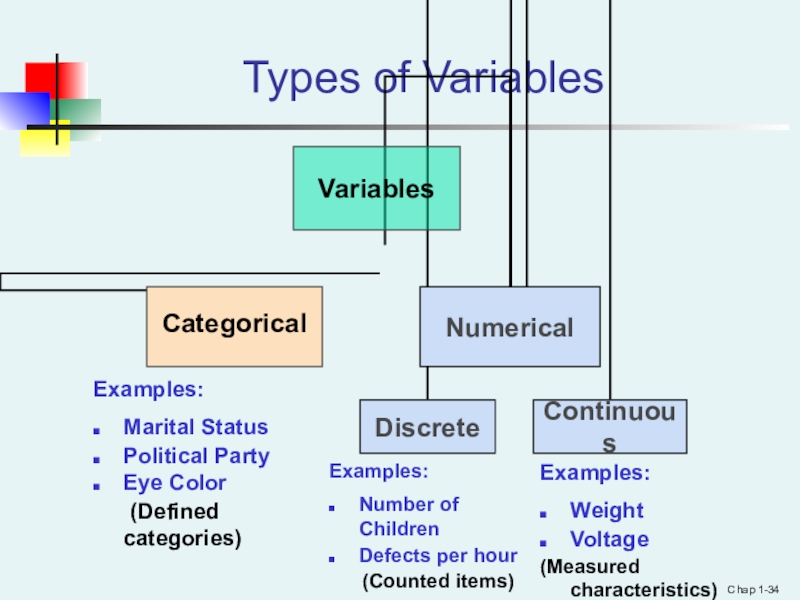
Types of Variables
Examples:
Marital Status
Political Party
Eye Color
(Defined
categories)
Examples:
Number of Children
Defects per hour
(Counted items)
Examples:
Weight
Voltage
(Measured characteristics)
Слайд 35Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Basic Vocabulary of Statistics (Con’t)
Слайд 36Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
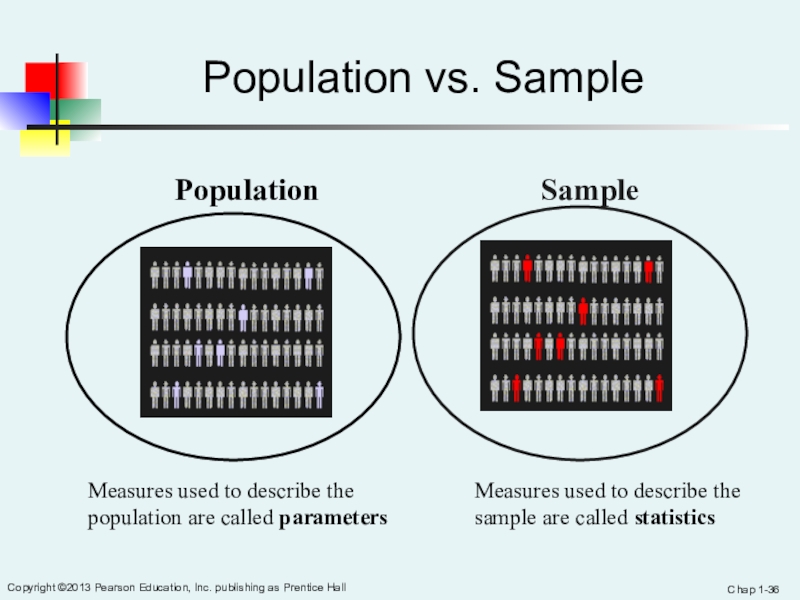
Population vs. Sample
Population
Sample
Measures used to describe the population are called
parameters
Measures used to describe the sample are called statistics
Слайд 37Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
This Book Is Organized To Show The Four Uses Of
Statistics
To summarize business data (Chapters 2 & 3)
To draw conclusions from business data (Chapters 4 – 11)
To make reliable forecasts about business activities (Chapters 12 & 13)
To improve business processes (Chapter 14)
Слайд 38Slide 1-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
What are
data?
A bunch of numbers
Values along with context
Words
only
Слайд 39Slide 2-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Variables that
are numbers are always quantitative.
True
False
Слайд 40Slide 2-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
Individuals who
answer a survey are called:
Subjects
Participants
Respondents
Units
Слайд 41Slide 2-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
The SPCA
collects data about the dogs they house. Which is categorical?
Breed
Age
Weight
Veterinary costs
Слайд 42Slide 2-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
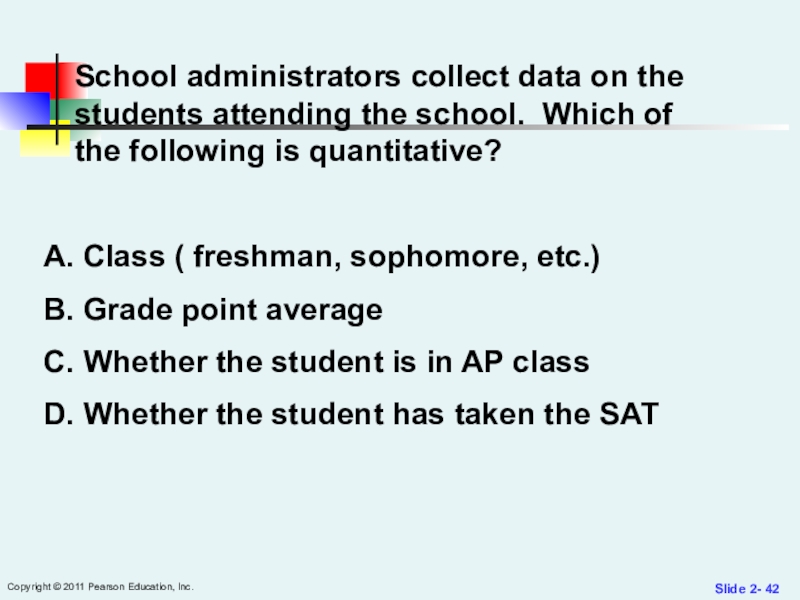
School administrators
collect data on the students attending the school. Which of
the following is quantitative?
Class ( freshman, sophomore, etc.)
Grade point average
Whether the student is in AP class
Whether the student has taken the SAT
Слайд 43Slide 2-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
We collect
these data from 50 students. Which variable is categorical?
Eye
color
Head circumference
Hours of homework last week
Number of TV sets in at home
Слайд 44Slide 2-
Copyright © 2011 Pearson Education, Inc.
The W’s
(Who, What, When, Where, Why) provide ___________ for data values.
Cases
Records
Context
Subjects
Слайд 45Chap 1-
Copyright ©2013 Pearson Education, Inc. publishing as Prentice Hall
Chapter Summary
In this chapter we have:
Described what statistics is
Discussed
why & how statistics is fundamental to business
Defined the basic concepts and vocabulary of statistics
Слайд 46Exercise
1. The process of using sample statistics to draw conclusions
about true population parameters is called
A. statistical inference.
B. the scientific
method.
C. sampling.
D. descriptive statistics.
Слайд 472. Those methods involving the collection, presentation, and characterization of
a set of data in order to properly describe the
various features of that set of data are called
A. statistical inference.
B. the scientific method.
C. sampling.
D. descriptive statistics.
Слайд 483. The collection and summarization of the socioeconomic and physical
characteristics of the employees of a particular firm is an
example of
A. inferential statistics.
B. descriptive statistics.
C. a parameter.
D. a statistic.
Слайд 494. The estimation of the population average family expenditure on
food based on the sample average expenditure of 1,000 families
is an example of
A. inferential statistics.
B. descriptive statistics.
C. a parameter.
D. a statistic.
Слайд 505. The universe or "totality of items or things" under
consideration is called
A. a sample.
B. a population.
C. a parameter.
D. a
statistic.
Слайд 51 6. The portion of the universe that has been
selected for analysis is called
A. a sample.
B. a frame.
C. a
parameter.
D. a statistic.
Слайд 527. A summary measure that is computed to describe a
characteristic from only a sample of the population is called
a
parameter.
a census.
a statistic.
the scientific method.
Слайд 538. A summary measure that is computed to describe a
characteristic of an entire population is called
A. a parameter.
B. a
census.
C. a statistic.
D. the scientific method.
Слайд 549. Which of the following is most likely a population
as opposed to a sample?
A. respondents to a newspaper survey.
B.
the first 5 students completing an assignment.
C. every third person to arrive at the bank.
D. registered voters in a county.
Слайд 5510. Which of the following is most likely a parameter
as opposed to a statistic?
A. The average score of the
first five students completing an assignment.
B. The proportion of females registered to vote in a county.
C. The average height of people randomly selected from a database.
D. The proportion of trucks stopped yesterday that were cited for bad brakes.
Слайд 5611. Which of the following is not an element of
descriptive statistical problems?
A. An inference made about the population based
on the sample.
B. The population or sample of interest.
C. Tables, graphs, or numerical summary tools.
D. Identification of patterns in the data.
Chap 1-
Слайд 57 12. A study is under way in Yosemite National
Forest to determine the adult height of American pine trees.
Specifically, the study is attempting to determine what factors aid a tree in reaching heights greater than 60 feet tall. It is estimated that the forest contains 25,000 adult American pines. The study involves collecting heights from 250 randomly selected adult American pine trees and analyzing the results. Identify the population from which the study was sampled.
The 250 randomly selected adult American pine trees
The 25,000 adult American pine trees in the forest.
All the adult American pine trees taller than 60 feet.
All American pine trees, of any age, in the forest.
Chap 1-
Слайд 5813. A study is under way in Yosemite National Forest…
Identify the variable of interest in the study.
A. The age
of an American pine tree in Yosemite National Forest.
B. The height of an American pine tree in Yosemite National Forest.
C. The number of American pine trees in Yosemite National Forest.
D. The species of trees in Yosemite National Forest.
Chap 1-
Слайд 5914. Identify the sample in the study.
A. The 250 randomly
selected adult American pine trees.
B. The 25,000 adult American pine
trees in the forest.
C. All the adult American pine trees taller than 60 feet.
D. All American pine trees, of any age, in the forest.
Chap 1-