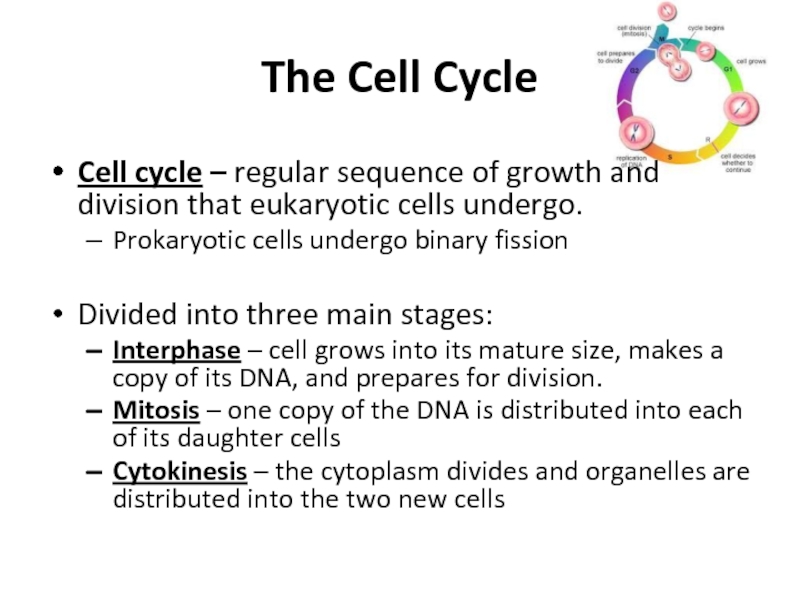
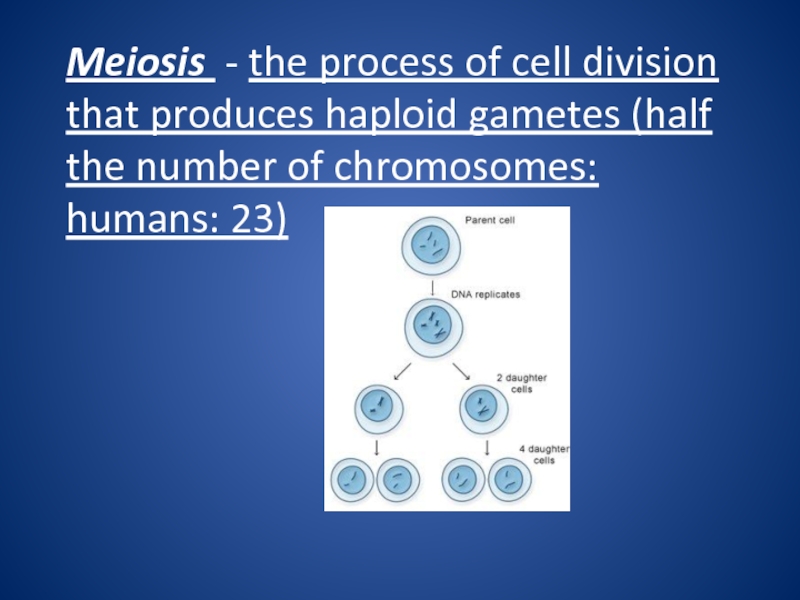
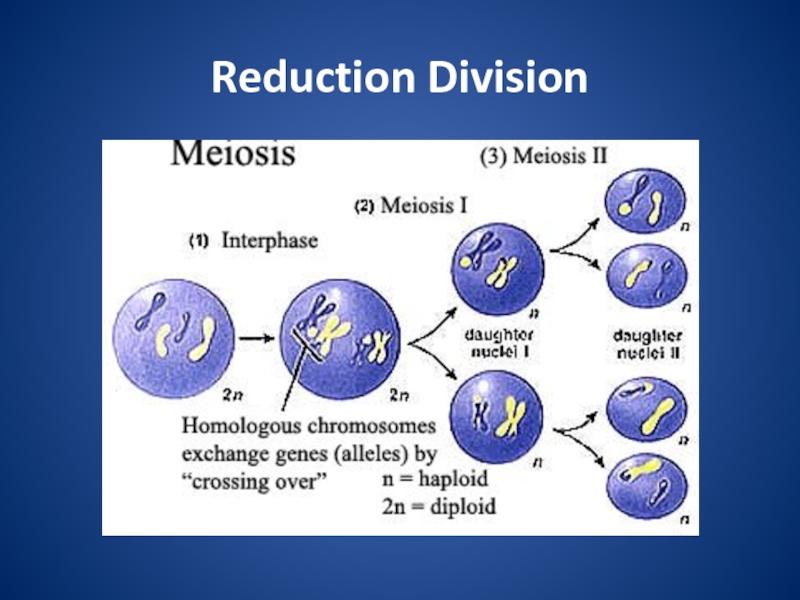
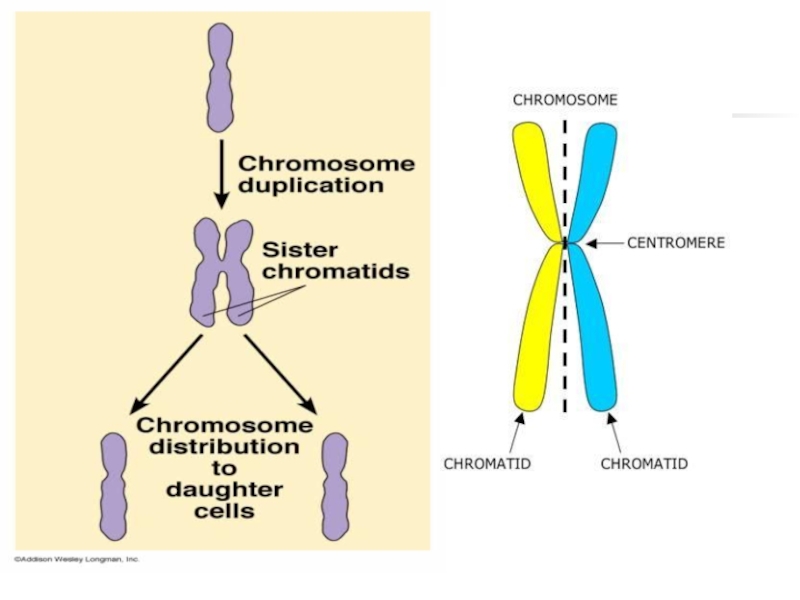
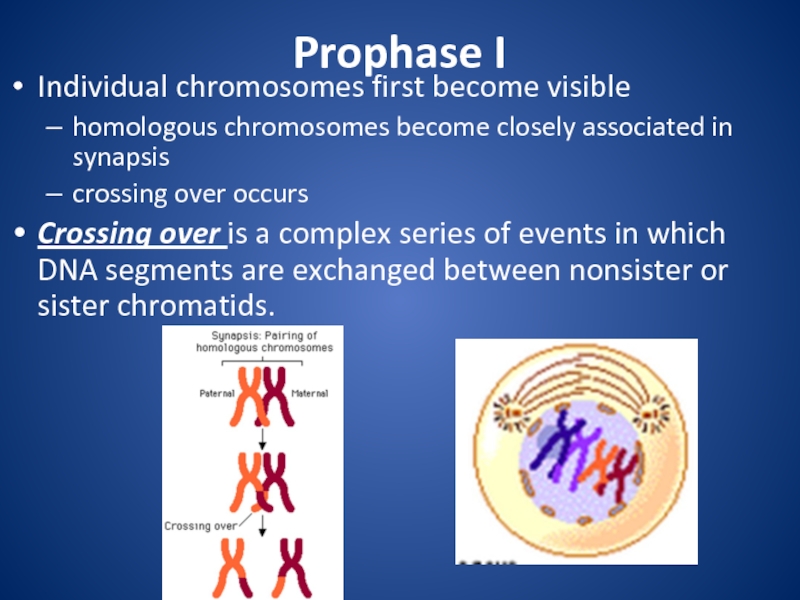
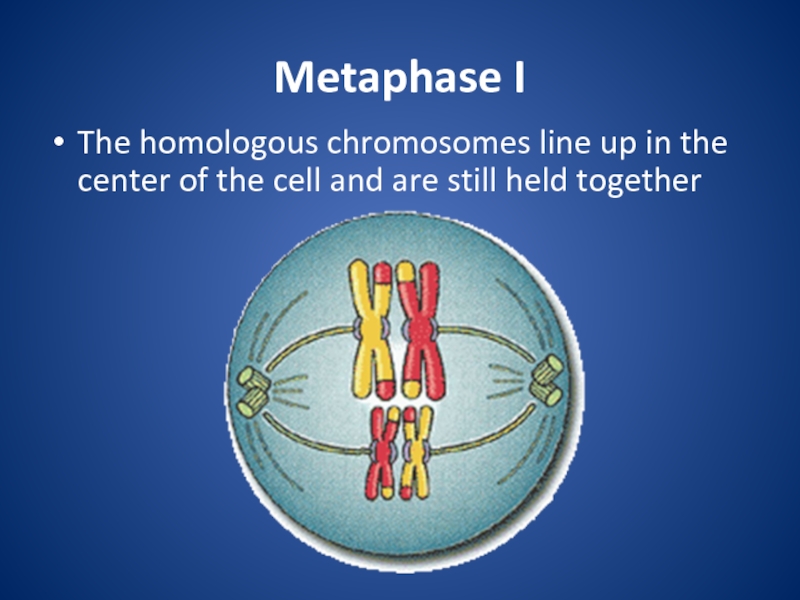
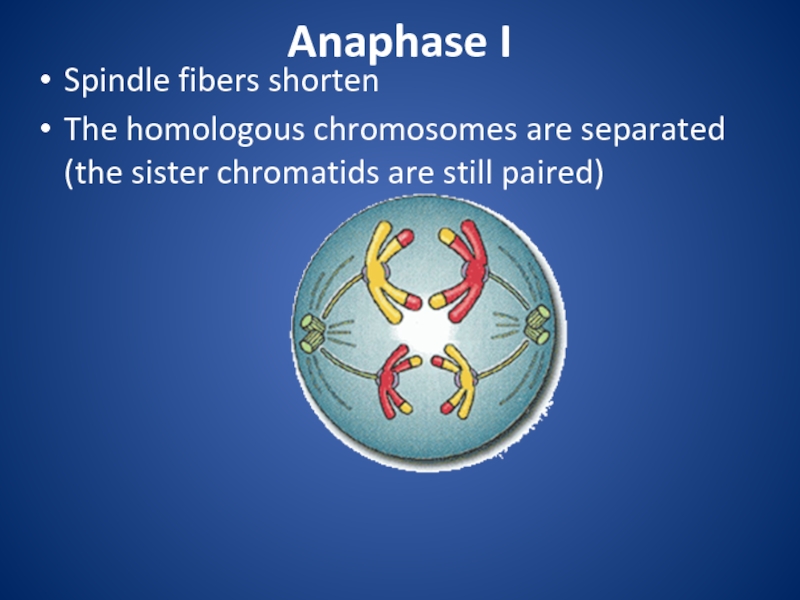
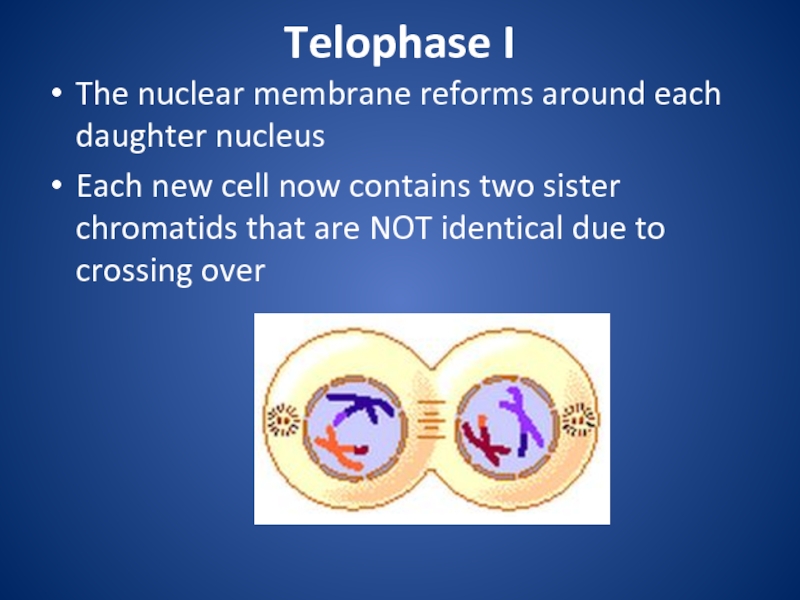
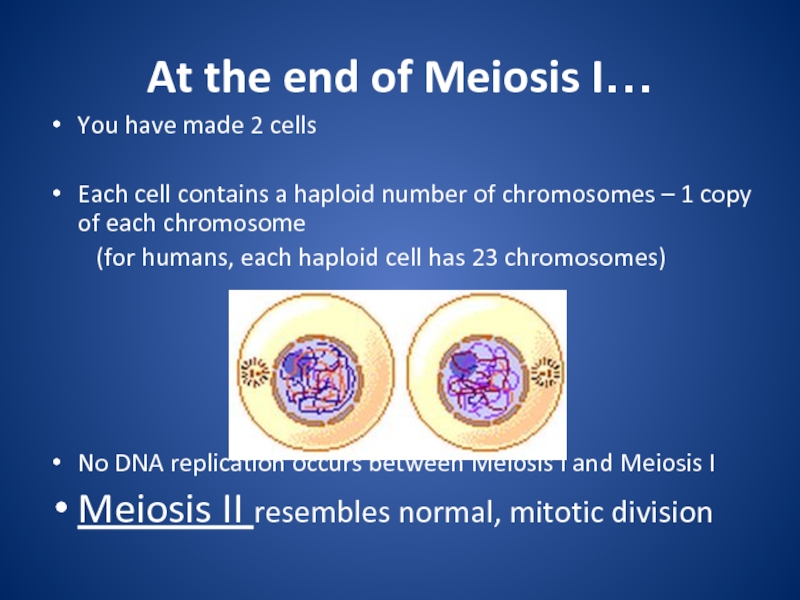
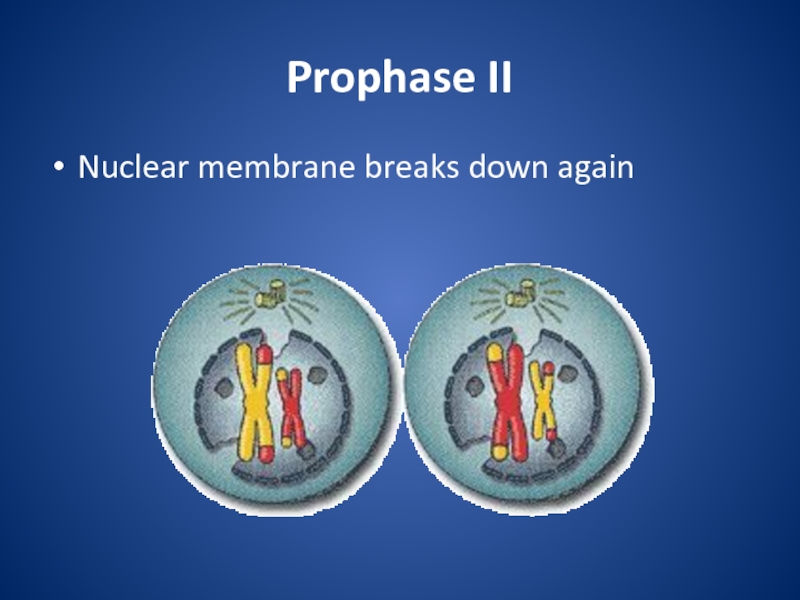
division that eukaryotic cells undergo.
Prokaryotic cells undergo binary fission
Divided into
three main stages:Interphase – cell grows into its mature size, makes a copy of its DNA, and prepares for division.
Mitosis – one copy of the DNA is distributed into each of its daughter cells
Cytokinesis – the cytoplasm divides and organelles are distributed into the two new cells