Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Cholinoblockers
Содержание
- 1. Cholinoblockers
- 2. Anticholinergics block the cholinergic receptors, prevents their
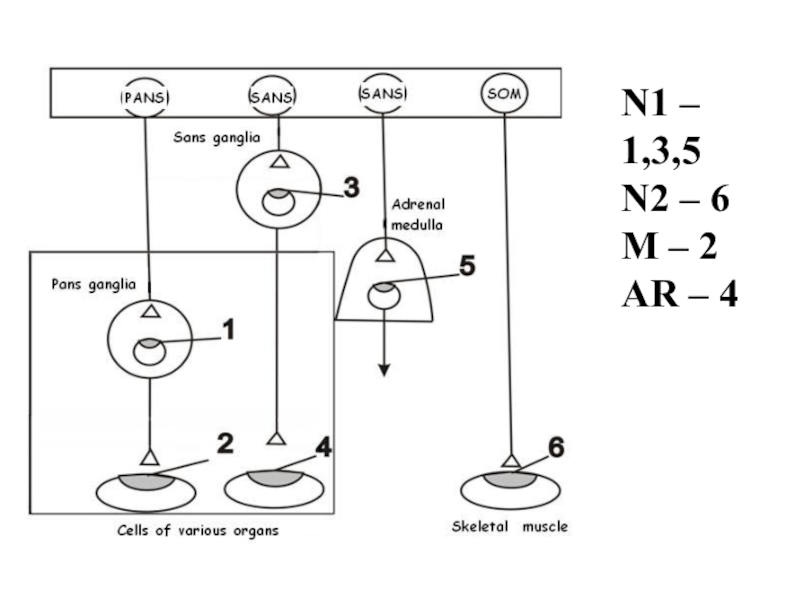
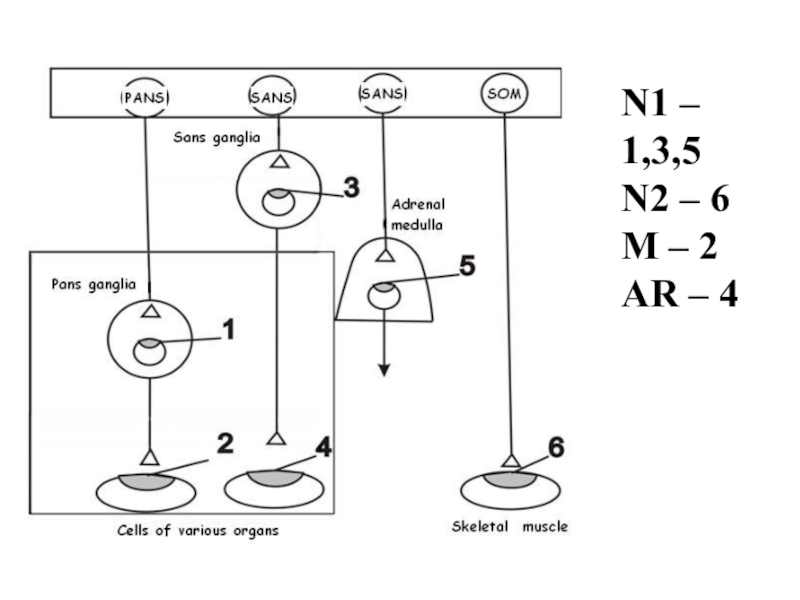
- 3. N1 – 1,3,5N2 – 6M – 2AR – 4
- 4. M-cholinoblockers block the peripheral M-cholinoceptors of the
- 5. B. Alkaloids: Atropine, Scopolamine, Platyphilline2.Semisynthetic derivatives: Homatropine,
- 6. Alkaloids are tertiary amines and pass well
- 7. Слайд 7
- 8. CNSAtropine stimulates many medullary centres —vagal, respiratory,
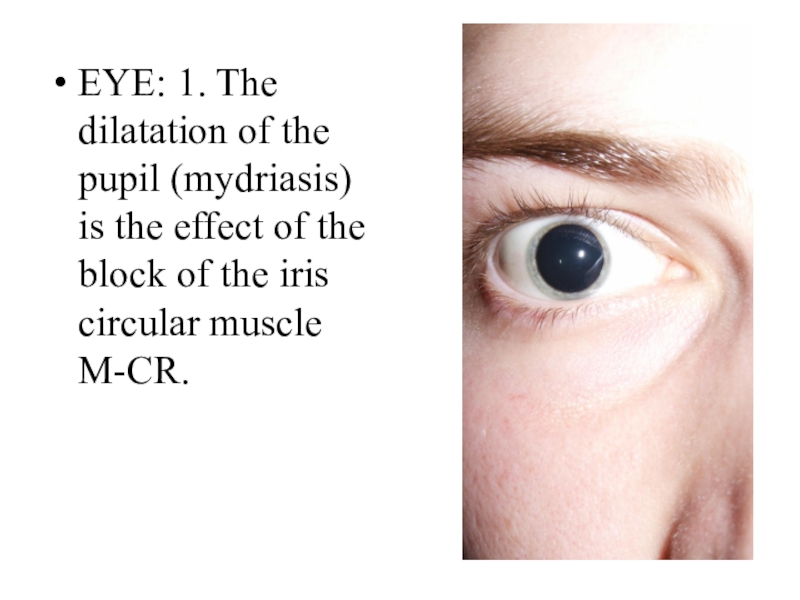
- 9. EYE: 1. The dilatation of the pupil
- 10. 2. The fluid outflow from the anterior
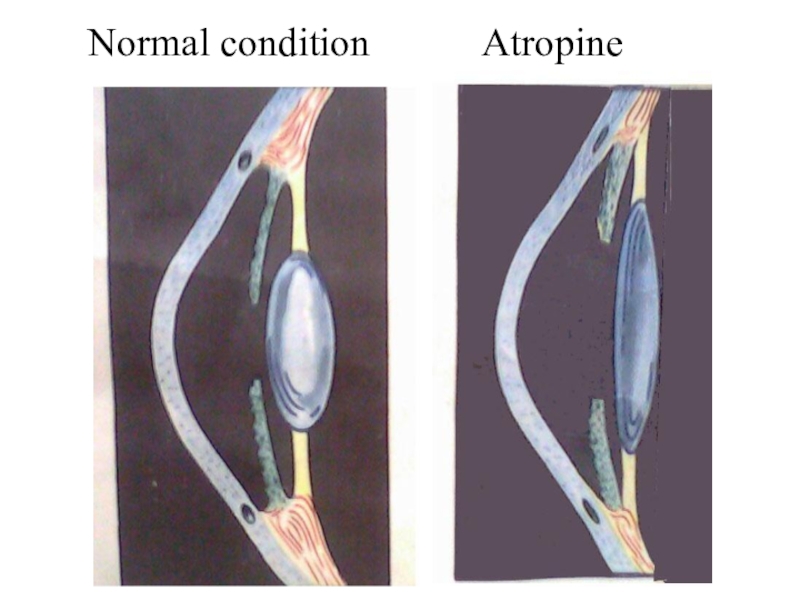
- 11. Normal conditionAtropine
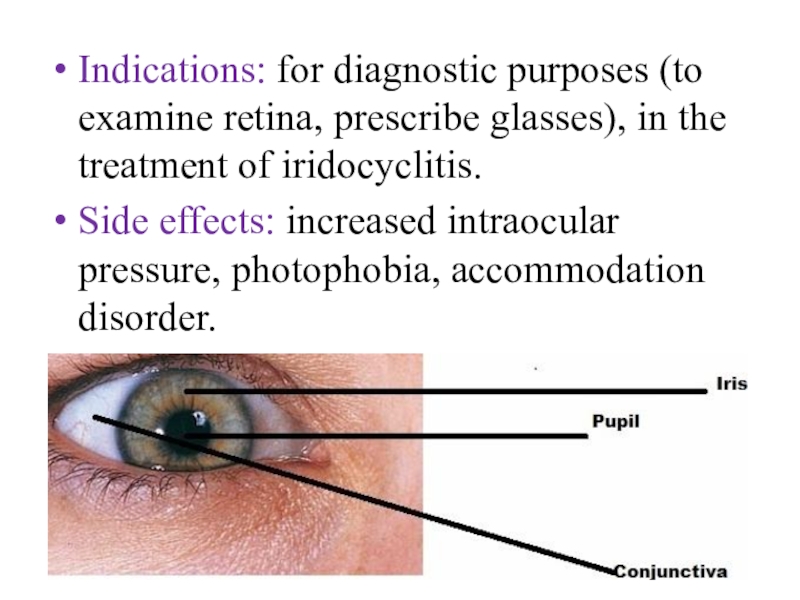
- 12. Indications: for diagnostic purposes (to examine retina,
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. Heart. The main effect is tachycardia. It
- 15. Exocrine glands. It inhibits glandular secretion: bronchial,
- 16. Indications:Bradyarrhythmia, atrioventricular block;Stomach and duodenal ulcer, hyperacid
- 17. Wide use of atropine for premedication before
- 18. Side effects of atropine:Dryness of oral mucosa,Accommodation disorder, Tachycardia, An increase in intraocular pressure,Constipation,Urination difficulty.
- 19. Symptoms of atropine poisoning (usually children):Dryness of
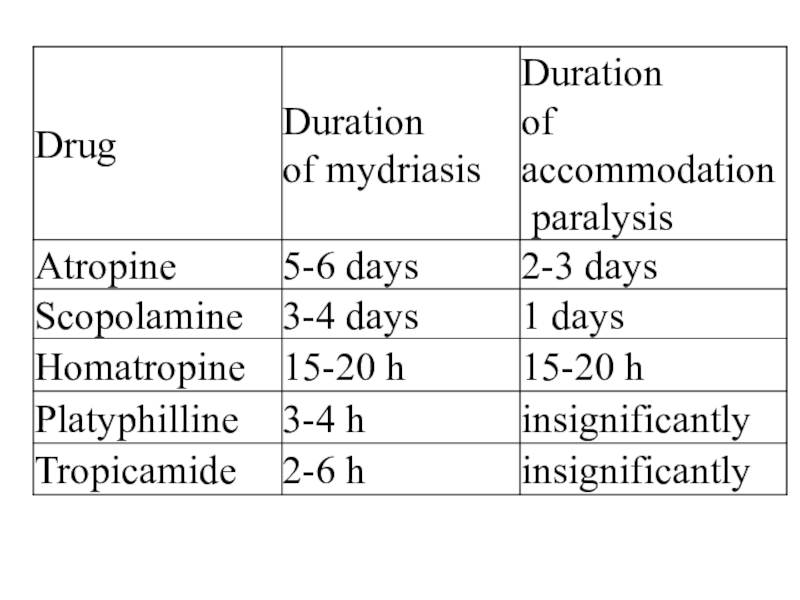
- 20. Scopolamine more strongly affects the eyes and
- 21. Platyphilline has moderate ganglioblocking and direct myotropic
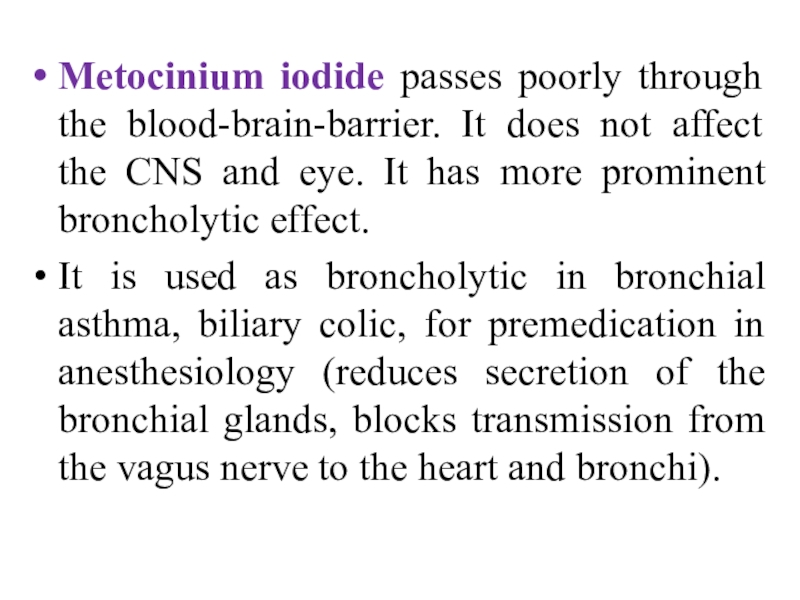
- 22. Metocinium iodide passes poorly through the blood-brain-barrier.
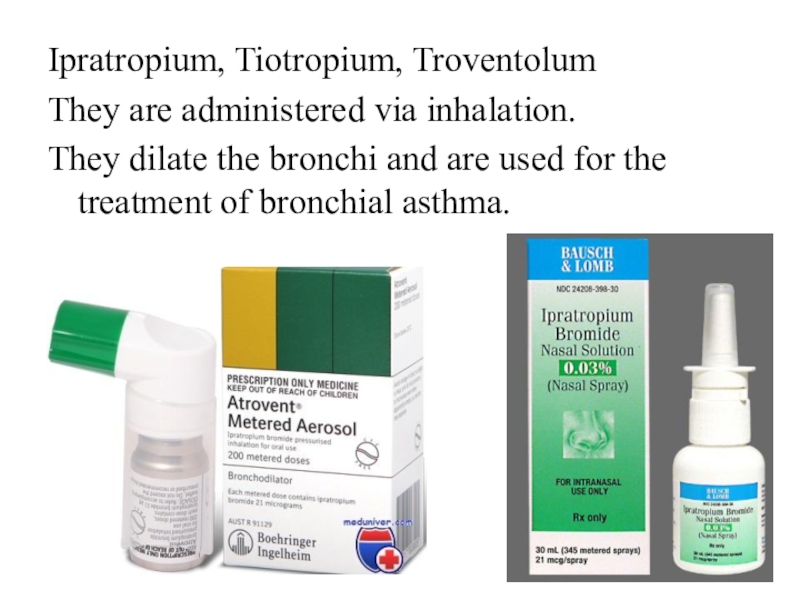
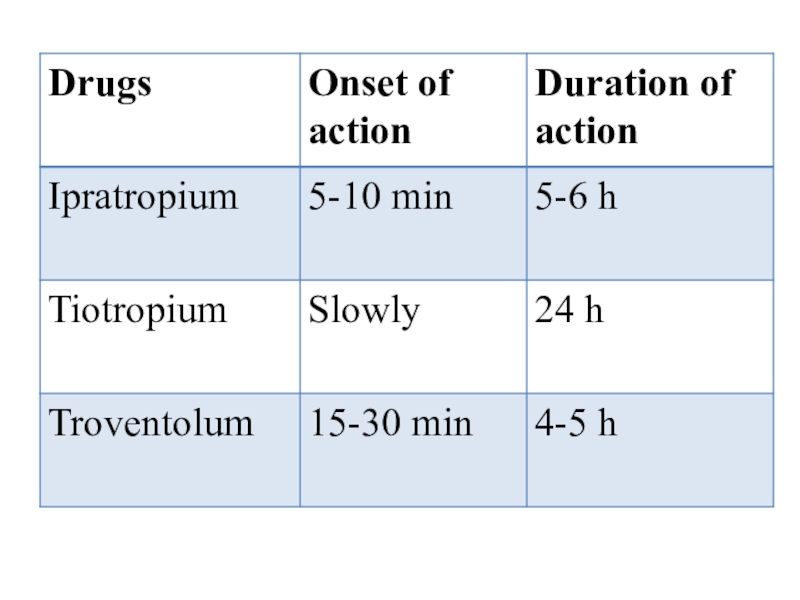
- 23. Ipratropium, Tiotropium, TroventolumThey are administered via inhalation.
- 24. Слайд 24
- 25. Pirenzepine blocks M1-CR of the enterochromaffin cells
- 26. Ganglionic blockers block sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia,
- 27. They dilate arterial and venous vessels, decrease
- 28. Indications for the use:Obliterating endarteritis, pulmonary edema,
- 29. Side effects:Orthostatic collapse develops after an abrupt
- 30. Drugs blocking neuromuscular transmission (neuromuscular relaxants, peripheral
- 31. Слайд 31
- 32. N1 – 1,3,5N2 – 6M – 2AR – 4
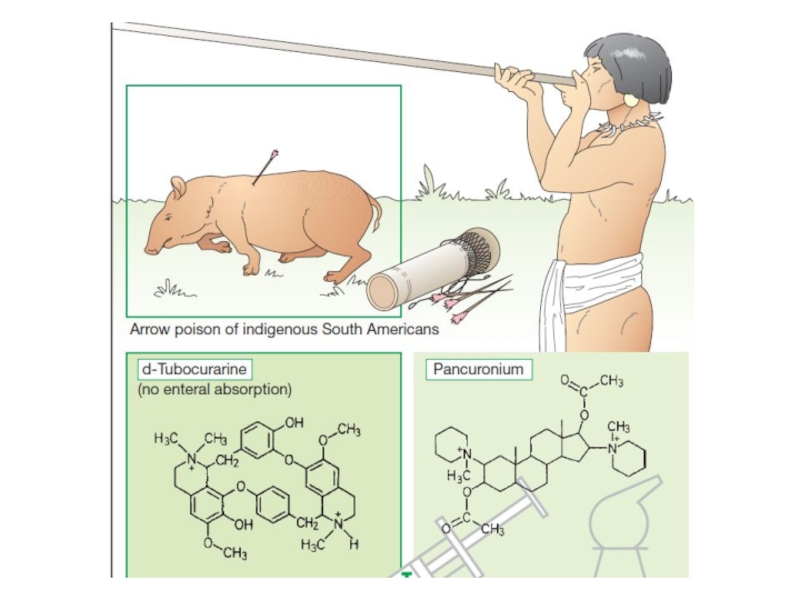
- 33. ClassificationAntidepolarizing (nondepolarizing) drugs: Tubocurarine, Pancuronium, Pipecuronium bromide, Atracurium besilate, Mivacurium chlorideDepolarizing drug – Suxamethonium iodide
- 34. Duration of action:Short-acting: Mivacurium chloride (15 min),
- 35. Antidepolarizing drugs block N-ChR and prevent depolarizing
- 36. Слайд 36
- 37. Слайд 37
- 38. Слайд 38
- 39. Muscles are relaxed in a certain sequence:Muscles
- 40. The sequence shutdown of skeletal muscle during intravenous curare-like drugs
- 41. Antagonists: Antagonists of the antidepolarizing drugs are
- 42. Indications for the use:In anaesthesiology during the
- 43. Side effects:Tachycardia (pancuronium), fluctuations in blood pressure,
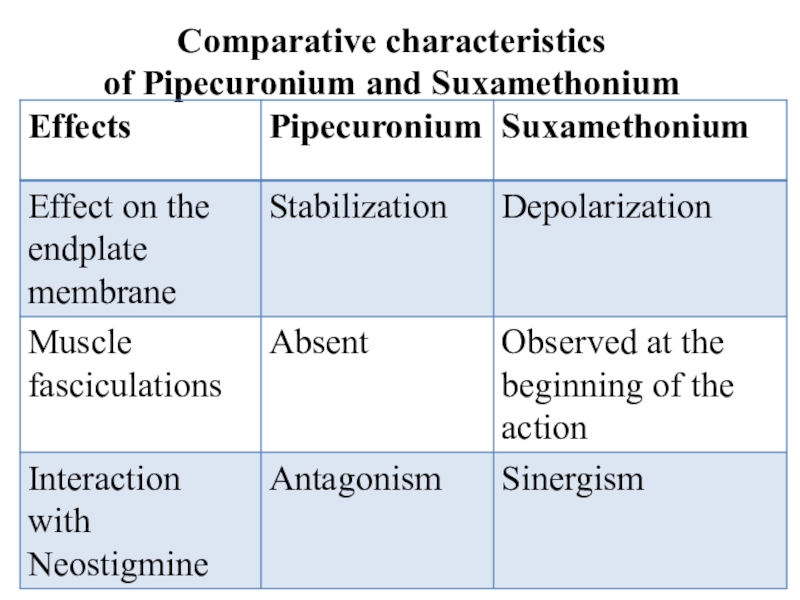
- 44. Comparative characteristics of Pipecuronium and Suxamethonium
- 45. Скачать презентанцию
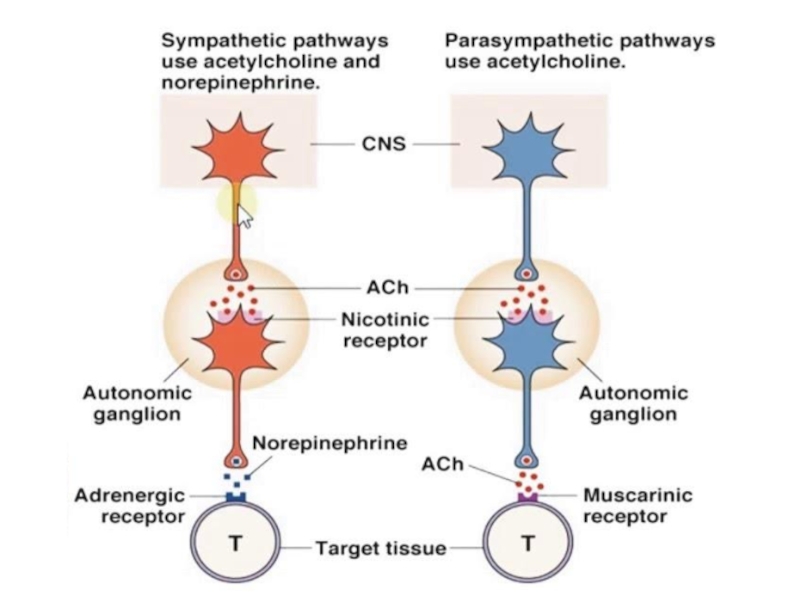
Anticholinergics block the cholinergic receptors, prevents their interaction with acetylcholine and disrupts the conduction of nerve impulses.Cholinoblockers:M-cholinoblockersM,N-cholinoblockersN-cholinoblockersGanglionblockersNeuromuscular relaxants (curare-like drugs)
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Anticholinergics block the cholinergic receptors, prevents their interaction with acetylcholine
and disrupts the conduction of nerve impulses.
Слайд 4M-cholinoblockers block the peripheral M-cholinoceptors of the effectors' cell membranes
(on the terminals of postganglionic cholinergic fibers) and M-cholinoceptors in
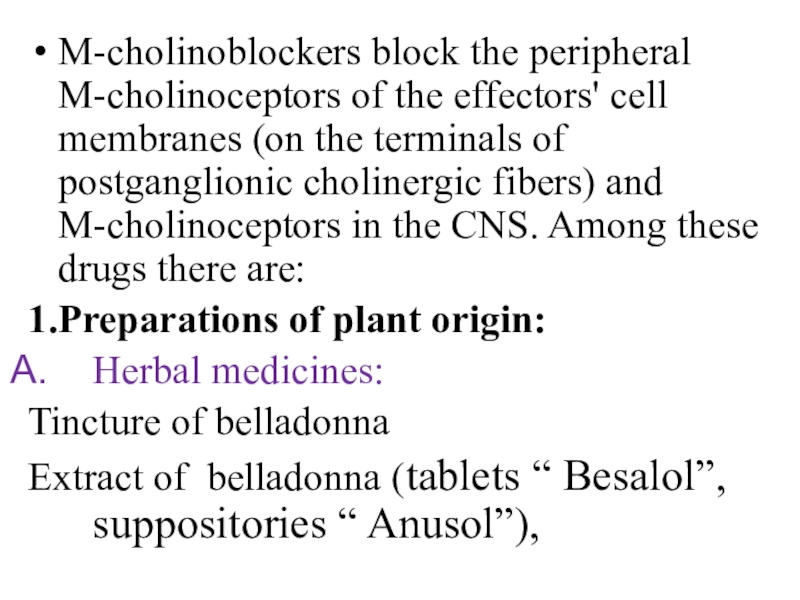
the CNS. Among these drugs there are:1.Preparations of plant origin:
Herbal medicines:
Tincture of belladonna
Extract of belladonna (tablets “ Besalol”, suppositories “ Anusol”),
Слайд 5B. Alkaloids: Atropine, Scopolamine, Platyphilline
2.Semisynthetic derivatives: Homatropine, Tiotropium bromide, Ipratropium
bromide
3. Synthetic drug: Tropicamide, Metocinium iodide,
Pirenzepine hydrochloride,
4. Antiparkinsonian:
TrihexyphenidylСлайд 6Alkaloids are tertiary amines and pass well through the BBB,
synthetic drugs (Quaternary ammonium compounds) pass poorly.
M-cholinoblockers block receptors
differently.Selective blocker of M1-cholinoceptors of stomach – pirenzepin
N, m blocker - Platyphylline
Non-selective blockers – all other drugs
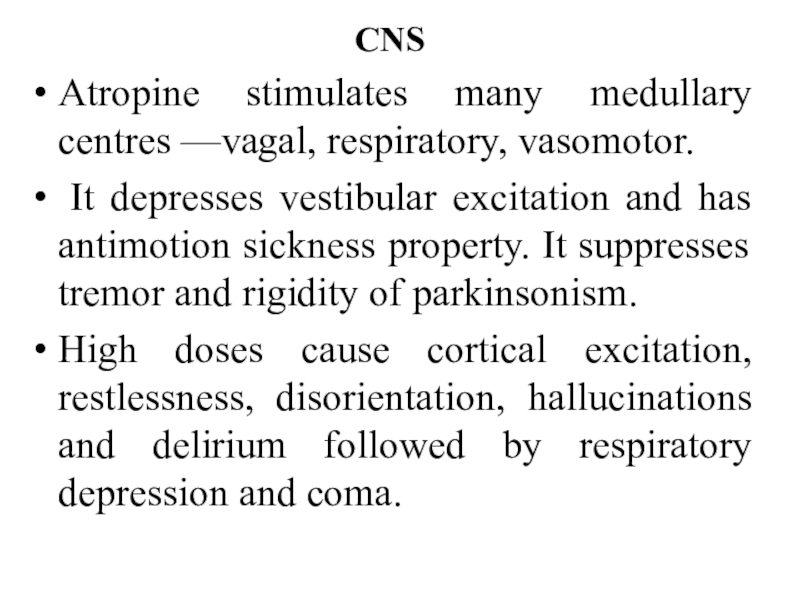
Слайд 8CNS
Atropine stimulates many medullary centres —vagal, respiratory, vasomotor.
It depresses
vestibular excitation and has antimotion sickness property. It suppresses tremor
and rigidity of parkinsonism.High doses cause cortical excitation, restlessness, disorientation, hallucinations and delirium followed by respiratory depression and coma.
Слайд 9EYE: 1. The dilatation of the pupil (mydriasis) is the
effect of the block of the iris circular muscle M-CR.
Слайд 102. The fluid outflow from the anterior chamber of the
eye is decreased and intraocular pressure can increase (especially in
glaucoma).3. Blocking M-CR of the ciliary muscle leads to its relaxation, which results in an increase of the ciliary zonule (ligament of Zinn) tension and a reduction of lens curvative. Accommodation paralysis occurs and the eye become adjusted to the distant point of vision.
Слайд 12Indications: for diagnostic purposes (to examine retina, prescribe glasses), in
the treatment of iridocyclitis.
Side effects: increased intraocular pressure, photophobia, accommodation
disorder.Слайд 14Heart. The main effect is tachycardia. It is due to
blockade of M2 receptors on the SA node through which
vagal tone decreases HR. Atropine facilitates A-V conduction.Smooth muscles. A. decreases muscular tone of the gastrointestinal tract, bile ducts, gallbladder, bronchi, bladder.
Слайд 15Exocrine glands. It inhibits glandular secretion: bronchial, nasopharyngeal, digestive (especially
salivary), sweat and lacrimal. It leads to a dryness of
oral mucous membrane (xerostomia), skin (xerodermia) and a change in the timbre of the voice. A decrease in sweating may leads to a rise in body temperature.Слайд 16Indications:
Bradyarrhythmia, atrioventricular block;
Stomach and duodenal ulcer, hyperacid gastritis; acute pancreatitis;
Spastic
pain or colic (intestinal, hepatic, renal);
Bronchial asthma, bronchospasm;
Hypersalivation (in Parkinsonism,
poisoning with heavy metals salts); Overdose of cholinomimetics, anticholinesterase drugs, cardiac glycosides
Слайд 17Wide use of atropine for premedication before surgical interventions is
linked to its ability to inhibit secretion of salivary, nasopharyngeal
and thracheobrochial glands. Moreover, blocking MCR of the heart (vagolytic action), A. prevents negative effects on the heart, including the possibility of its reflectory arrest (for example, in administration of inhalation anesthetics that irritate the upper respiratory tract).Слайд 18Side effects of atropine:
Dryness of oral mucosa,
Accommodation disorder,
Tachycardia,
An
increase in intraocular pressure,
Constipation,
Urination difficulty.
Слайд 19Symptoms of atropine poisoning (usually children):
Dryness of the mucous membranes
of the mouth and nasopharynx, difficulty with swallowing and speech,
dry skin, rise of temperature,
dilated pupils, photophobia,
motor and verbal agitation, impairment of memory and orientation, hallucinations (acute psychosis).
Help: anticholinesterase drugs
Слайд 20Scopolamine more strongly affects the eyes and the secretion of
a number of excretory glands. It causes calming, drowsiness, sleep.
It inhibits the extrapyramidal system and transmission from pyramidal pathways to motorneurons.It can be used for the prevention of seasickness and airsickness and for Parkinson treatment.
Слайд 21Platyphilline has moderate ganglioblocking and direct myotropic spasmolytic (papaverine-like) actions.
It inhibits the vasomotor center.
It is used as a
spasmolytic drug in spasm of the stomach, intestine, biliary ducts, gallbladder and uretes. It is administered to reduce pathologically increased tone of cerebral and coronary vessels. Слайд 22Metocinium iodide passes poorly through the blood-brain-barrier. It does not
affect the CNS and eye. It has more prominent broncholytic
effect.It is used as broncholytic in bronchial asthma, biliary colic, for premedication in anesthesiology (reduces secretion of the bronchial glands, blocks transmission from the vagus nerve to the heart and bronchi).
Слайд 23Ipratropium, Tiotropium, Troventolum
They are administered via inhalation.
They dilate the
bronchi and are used for the treatment of bronchial asthma.
Слайд 25Pirenzepine blocks M1-CR of the enterochromaffin cells and parasympathetic ganglia
of the stomach. It suppresses basal and induced secretion of
hydrochloric acid and pepsinogen, causes a decrease in gastrin release in response to food.It increases the resistance of gastric mucosal sells to injury (gastroprotective effect).
P. causes a slight decrease in salivary glands secretion.
It is used for the treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers.
Слайд 26Ganglionic blockers block sympathetic and parasympathetic ganglia, N-CR of the
adrenal medulla and carotid body.
Classification
Bis-Quaternary ammonium salts do not
penetrate the BBB1. Short-acting drugs (5-20 minutes): Trepirium iodide
2. Average duration (3-4 hours): Azametonium bromide, Hexamethonium benzolsulfonate
3. Long-acting (tertiary amines): Pachycarpine (6-8 hours)
Слайд 27They dilate arterial and venous vessels, decrease blood pressure, reduce
preload and postload of the heart, improve blood circulation in
organs (lower limbs), improve tissue trophism .They reduce smooth muscle tone (intestine, bronchi, except myometrium), secretion of exocrine glands (salivary, gastric). But they can increase tone of uterine and stimulate labor.
Слайд 28Indications for the use:
Obliterating endarteritis, pulmonary edema, arterial embolism, hypertensive
crisis.
Short-acting drugs can be used for controlled hypotension during operation.
They are administered IV drip, dilate vessels, decrease arterial pressure and reduce hemorrhage during thyroidectomy and mastectomy. In neurosurgery they reduce the possibility of the development of brain edema.Spastic pain (colic), bronchospasm, gastric and duodenal ulcer.
Слайд 29Side effects:
Orthostatic collapse develops after an abrupt change of the
body’s position in space. Marked and rapid decrease in the
arterial pressure develops after transition from horizontal to vertical position.Syncope.
Constipation, urinary retention.
Accommodation disorder, mydriasis.
Dysarthria, dysphagia.
Слайд 30Drugs blocking neuromuscular transmission (neuromuscular relaxants, peripheral muscles relaxants)
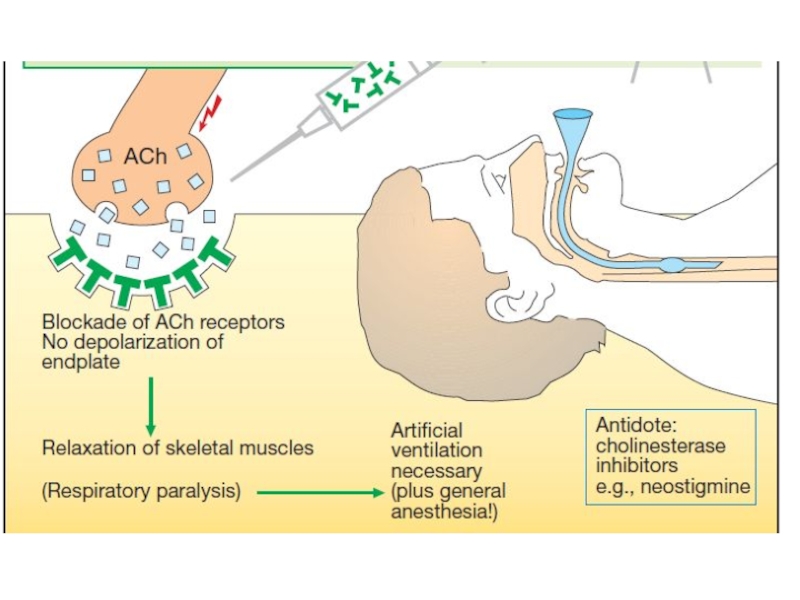
They inhibit
neuromuscular transmission on the level of postsynaptic membrane, interacting with
N-cholinoceptors of the endplates.Curare was the first muscle relaxant. Its extract was obtained from plants in South America and used as an arrow poisoning.
Слайд 33Classification
Antidepolarizing (nondepolarizing) drugs: Tubocurarine, Pancuronium, Pipecuronium bromide,
Atracurium besilate,
Mivacurium
chloride
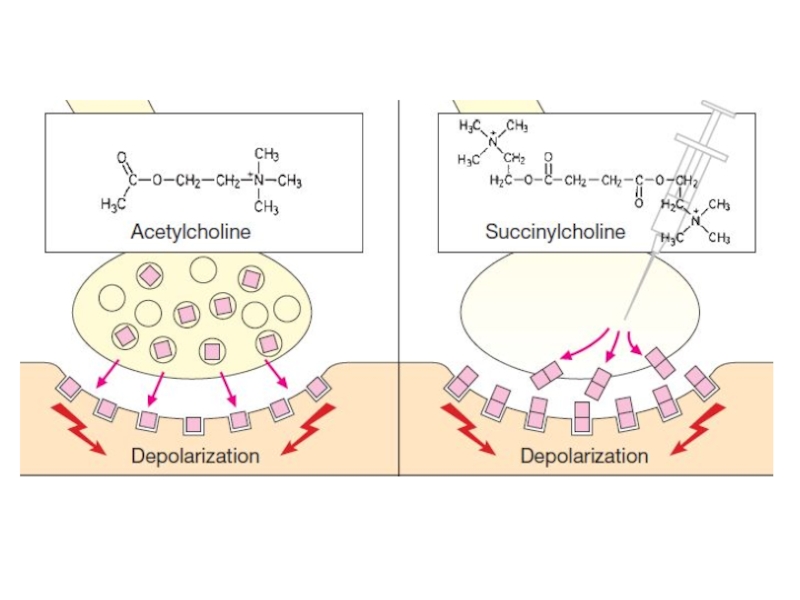
Depolarizing drug – Suxamethonium iodide
Слайд 34Duration of action:
Short-acting:
Mivacurium chloride (15 min), Suxamethonium iodide (5-8
min)
Average duration:
Atracurium besilate(15-35 min)
Long-acting:
Pipecuronium bromide (50-120 min)
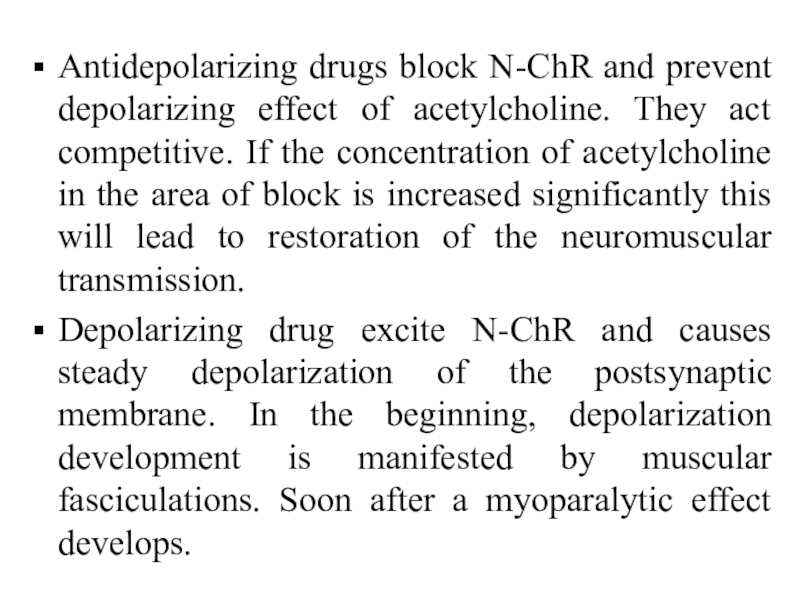
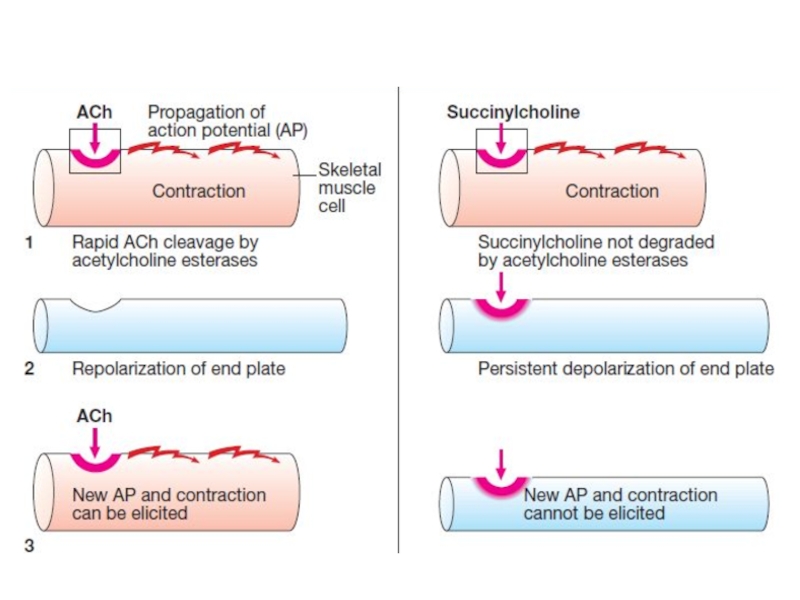
Слайд 35Antidepolarizing drugs block N-ChR and prevent depolarizing effect of acetylcholine.
They act competitive. If the concentration of acetylcholine in the
area of block is increased significantly this will lead to restoration of the neuromuscular transmission.Depolarizing drug excite N-ChR and causes steady depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane. In the beginning, depolarization development is manifested by muscular fasciculations. Soon after a myoparalytic effect develops.
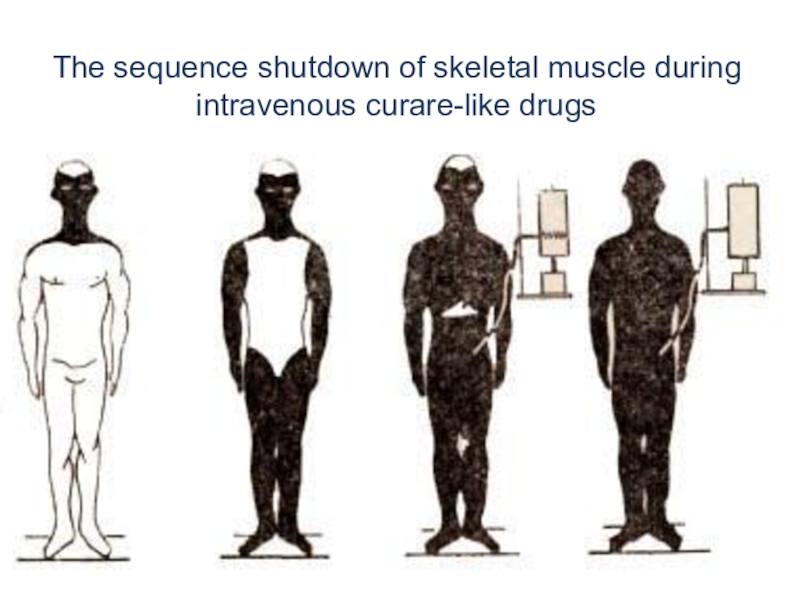
Слайд 39Muscles are relaxed in a certain sequence:
Muscles of the face
and neck;
The lower and upper limbs;
Muscles of the trunk;
Respiratory muscles;
The
diaphragm.Myoparalytic action range: the range between doses in which drugs paralyze more sensitive muscles, and doses that cause respiratory arrest.
Artificial ventilation of the lungs is required when using muscle relaxants
Слайд 41Antagonists:
Antagonists of the antidepolarizing drugs are anticholinesterase drugs (Neostigmine,
Galanthamine).
The action of depolarizing drug (suxamethonium) can be reversed by
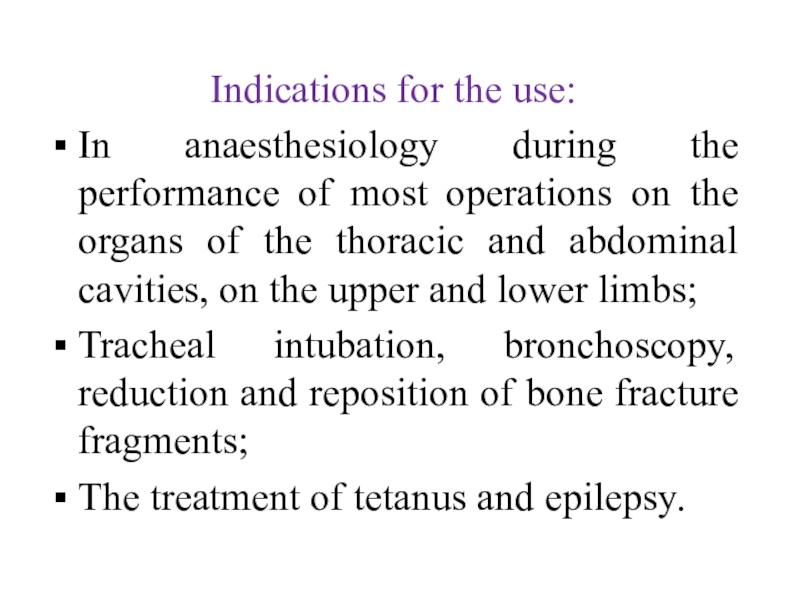
the administration of fresh citrated blood, containing plasma cholinesterase, which hydrolyzes suxamethonium.Слайд 42Indications for the use:
In anaesthesiology during the performance of most
operations on the organs of the thoracic and abdominal cavities,
on the upper and lower limbs;Tracheal intubation, bronchoscopy, reduction and reposition of bone fracture fragments;
The treatment of tetanus and epilepsy.