Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
ClassificationSeizures-2017-Scheffer
Содержание
- 1. ClassificationSeizures-2017-Scheffer
- 2. Classification of the EpilepsiesPurpose: for clinical diagnosisTransparent language: use words that mean what they say
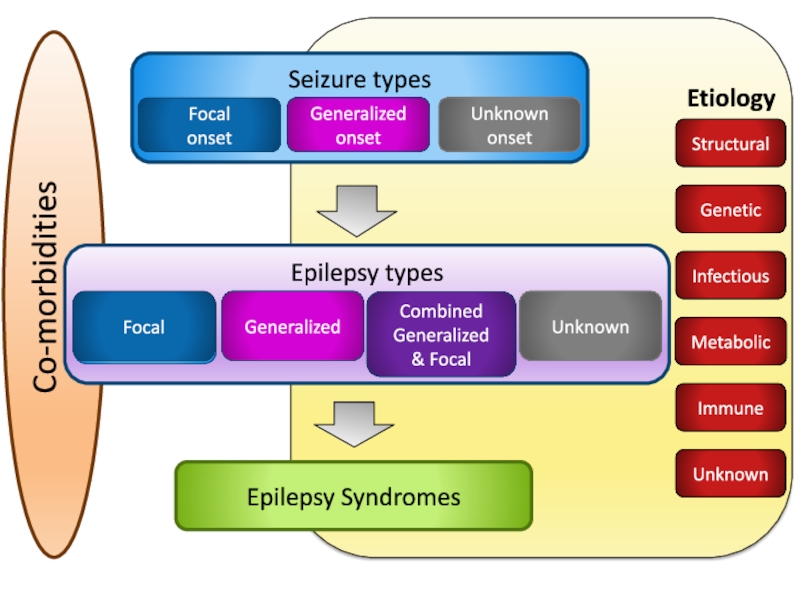
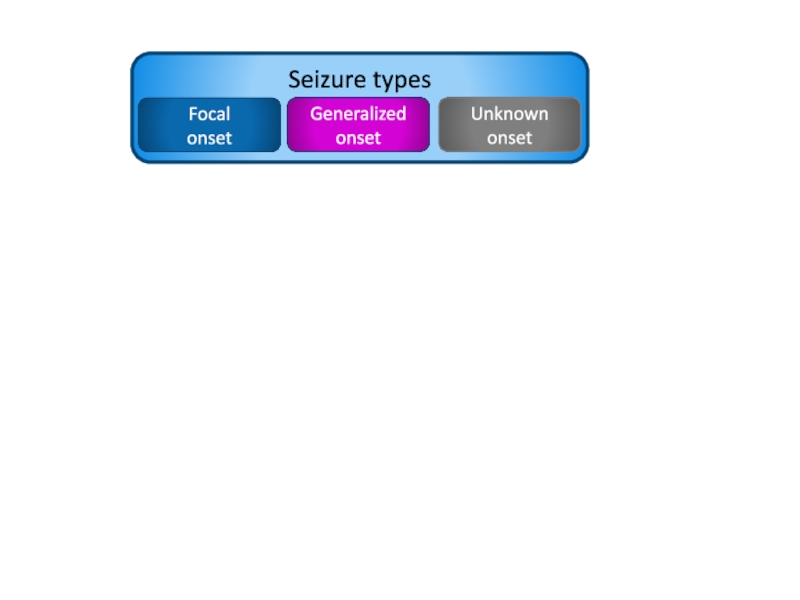
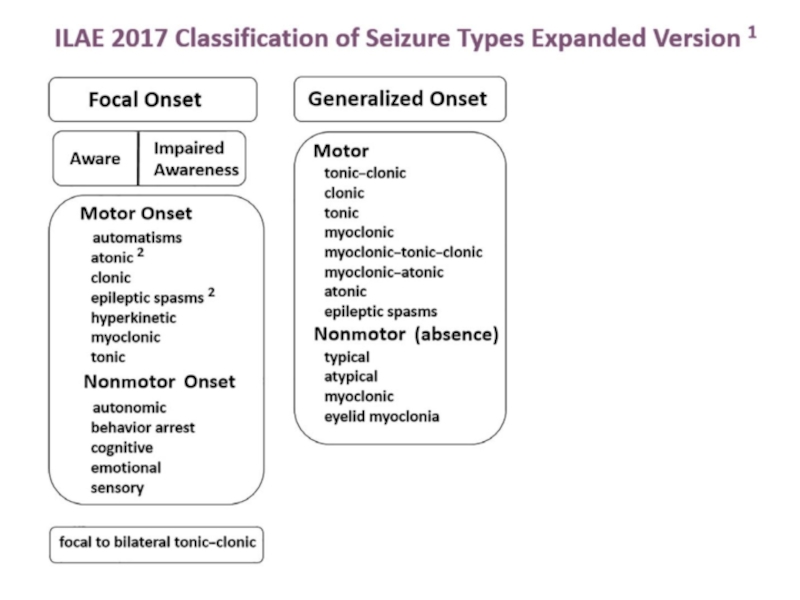
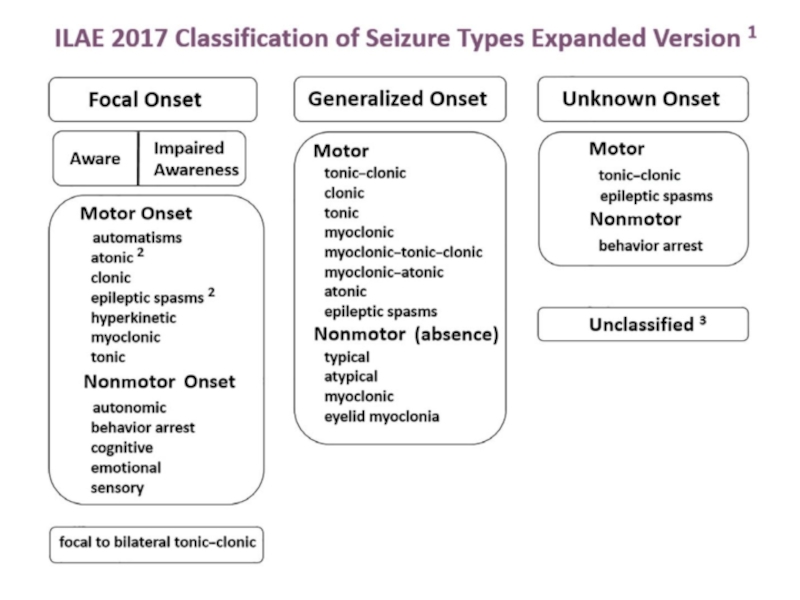
- 3. Co-morbiditiesSeizure typesGeneralized onsetUnknown onsetFocal onset
- 4. 1. Seizure typesCertain that events are epileptic
- 5. Слайд 5
- 6. Generalized seizures Originate at some point within
- 7. Слайд 7
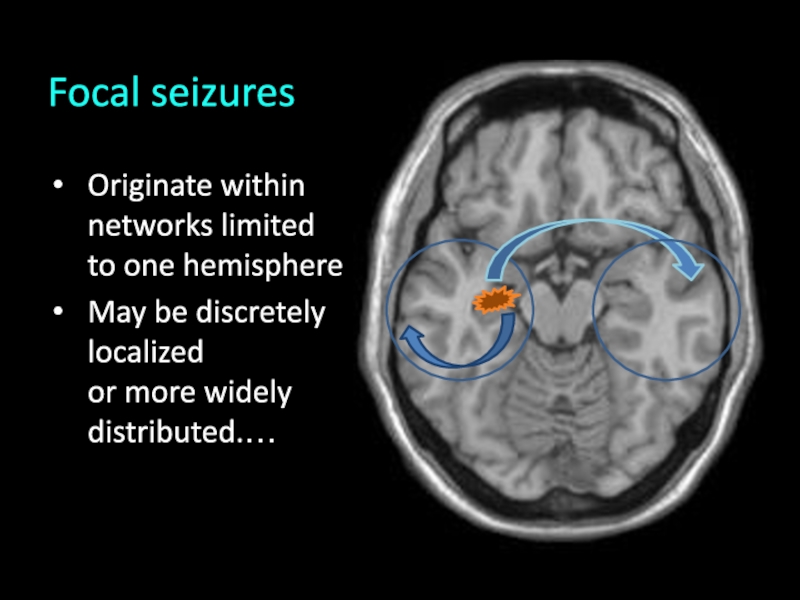
- 8. Originate within networks limited to one hemisphereMay be discretely localized or more widely distributed.…Focal seizures
- 9. Слайд 9
- 10. NotesAtonic seizures and epileptic spasms would not
- 11. Слайд 11
- 12. Слайд 12
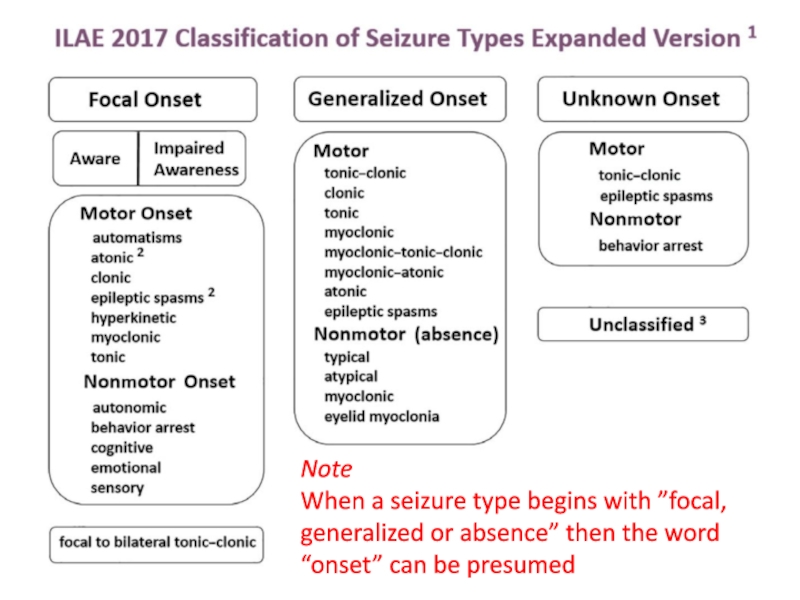
- 13. NoteWhen a seizure type begins with ”focal,
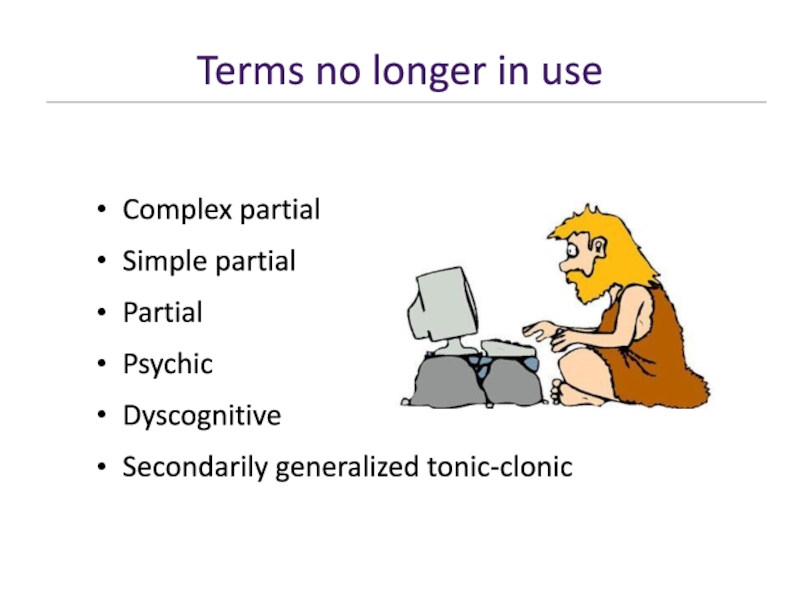
- 14. Terms no longer in use Complex partialSimple partialPartialPsychic DyscognitiveSecondarily generalized tonic-clonic
- 15. Слайд 15
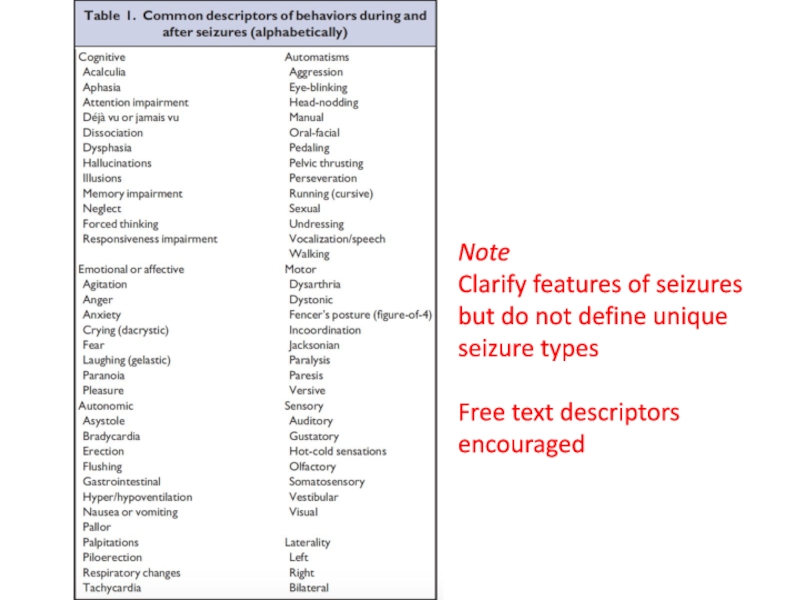
- 16. NoteClarify features of seizures but do not define unique seizure typesFree text descriptors encouraged
- 17. Слайд 17
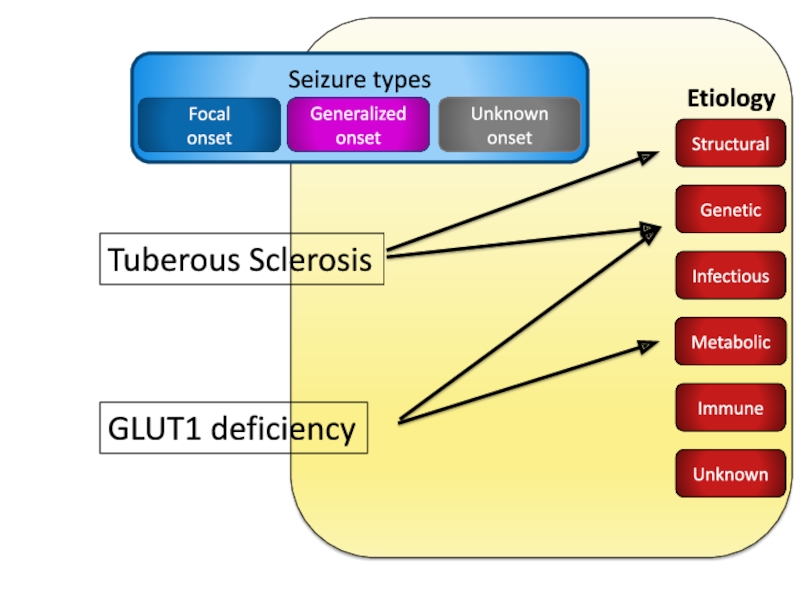
- 18. Tuberous SclerosisGLUT1 deficiencyUnknownImmuneInfectiousStructuralMetabolicGenetic
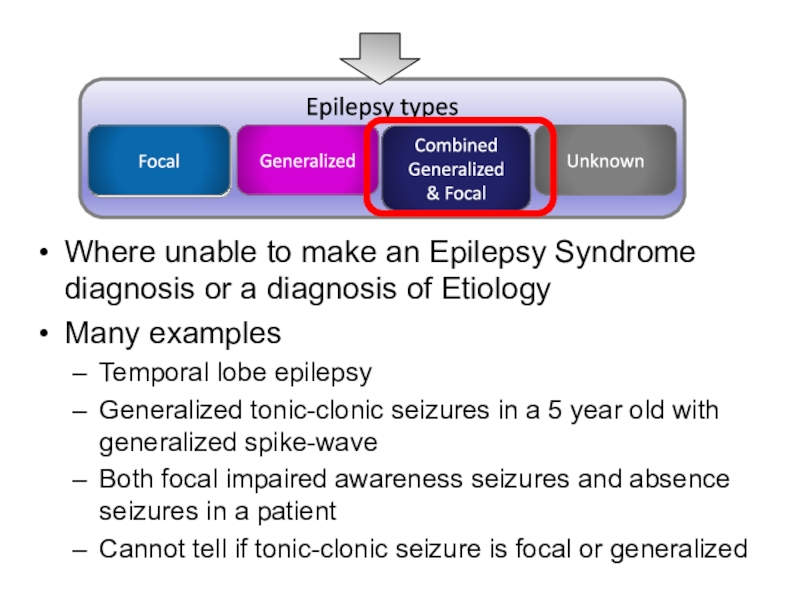
- 19. Where unable to make an Epilepsy Syndrome
- 20. Generalized and Focal EpilepsiesCombined focal and generalized epilepsiesExamplesDravet syndrome What do withMultifocal epilepsies?Hemispheric epilepsies? focal focal
- 21. Epilepsy SyndromesSeizure typesGeneralized onsetUnknown onsetFocal onset
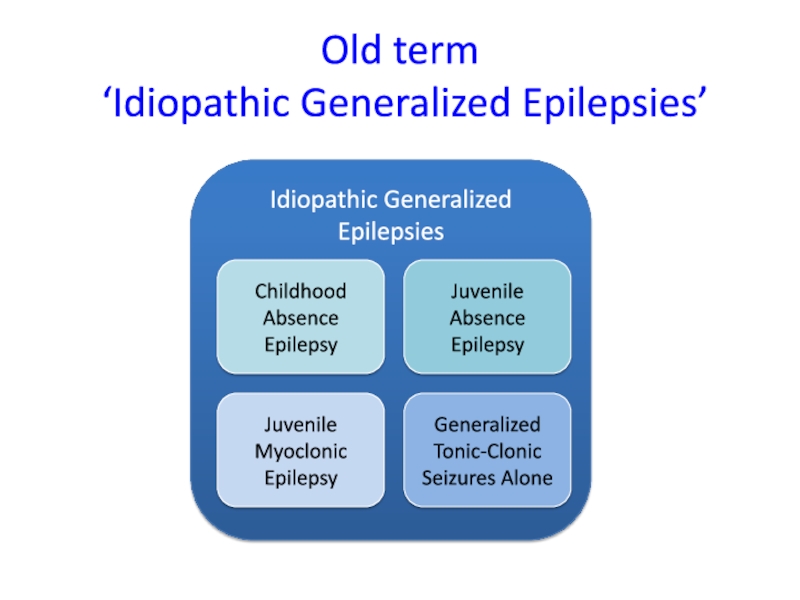
- 22. Old term ‘Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies’
- 23. Genetic versus idiopathic‘Idiopathic’ = presumed hereditary predispositionGenetic
- 24. Genetic ≠ Gene testingUsually the mutation is
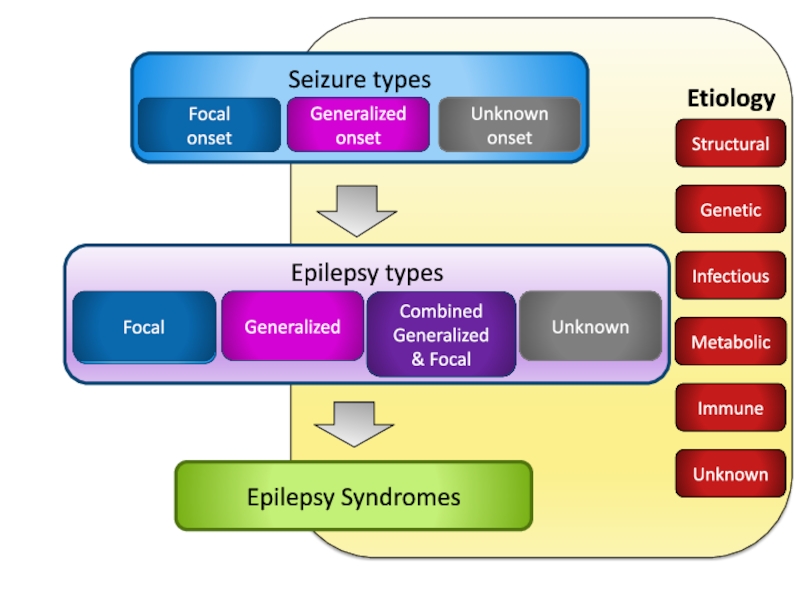
- 25. Co-morbiditiesEtiologyEpilepsy typesFocalGeneralizedCombinedGeneralized& FocalUnknownFocalEpilepsy SyndromesGeneralizedUnknownImmuneInfectiousStructuralMetabolicGeneticGenetic
- 26. Epilepsy syndromesThere are no approved ILAE epilepsy syndromes
- 27. https://www.epilepsydiagnosis.org
- 28. Слайд 28
- 29. Слайд 29
- 30. Слайд 30
- 31. Слайд 31
- 32. BenignMany epilepsies not benignCAE – psychosocial impactBECTS
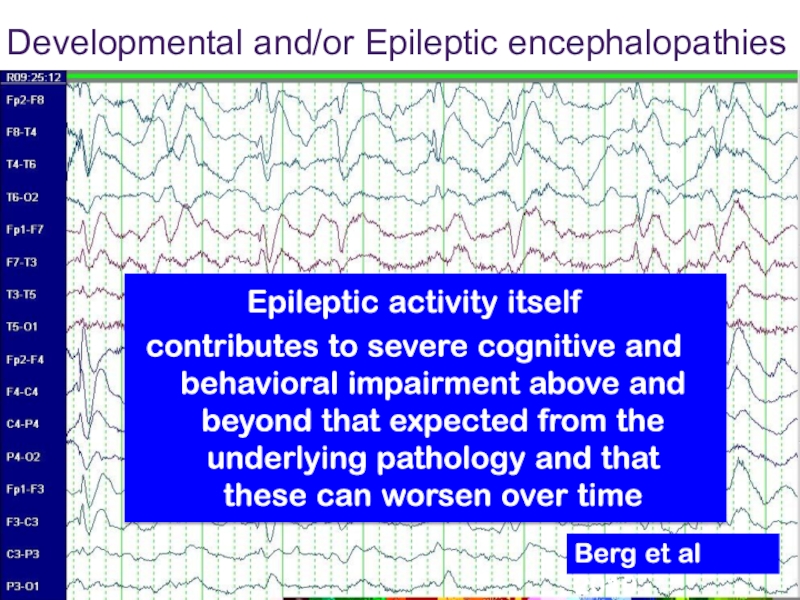
- 33. Epileptic activity itselfcontributes to severe cognitive and
- 34. Developmental and/or Epileptic EncephalopathyFor many encephalopathies, there
- 35. Developmental and/or Epileptic EncephalopathyDevelopmental encephalopathyMay begin in
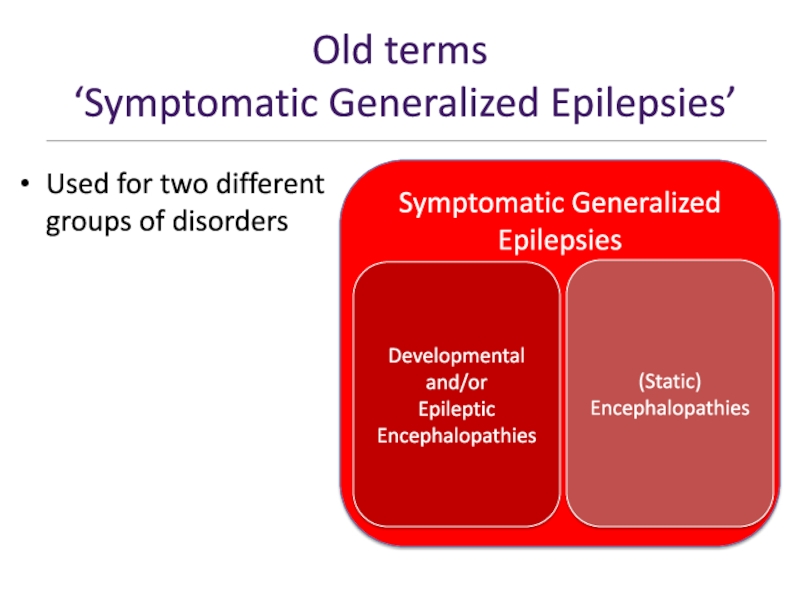
- 36. Old terms ‘Symptomatic Generalized Epilepsies’Used for two different groups of disordersSymptomatic Generalized EpilepsiesDevelopmentaland/orEpileptic Encephalopathies(Static)Encephalopathies
- 37. ILAE Classification of the EpilepsiesSimplified the frameworkEtiology
- 38. Impact on Clinical Care and PracticeNew classification
- 39. ILAE Classification Task Force 2013-7Torbjörn Tomson, Emilio
- 40. Скачать презентанцию
Classification of the EpilepsiesPurpose: for clinical diagnosisTransparent language: use words that mean what they say
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 2Classification of the Epilepsies
Purpose: for clinical diagnosis
Transparent language: use words
that mean what they say
Слайд 41. Seizure types
Certain that events are epileptic seizures – not
referring to distinguishing epileptic versus non-epileptic
In some settings classification
according to seizure type may be maximum level of diagnosis possibleIn other cases simply too little information to be able to make a higher level diagnosis
eg. when a patient has only had a single event
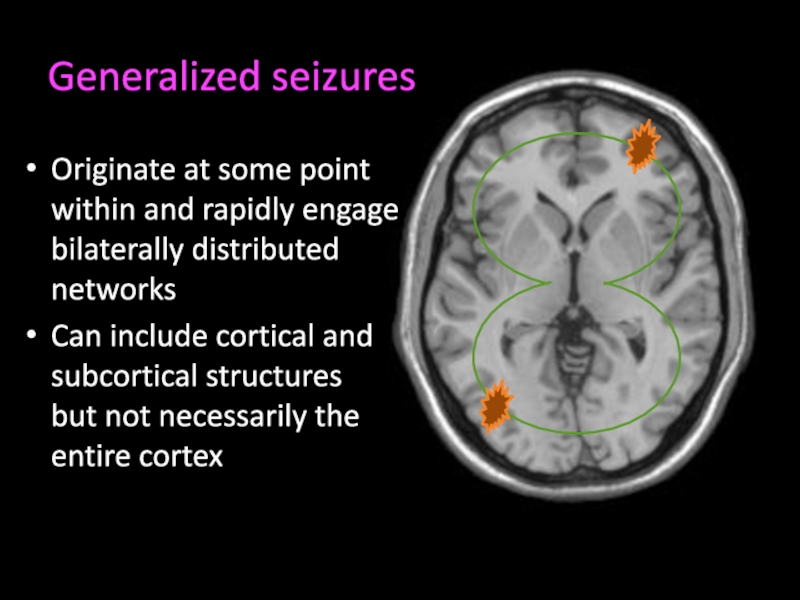
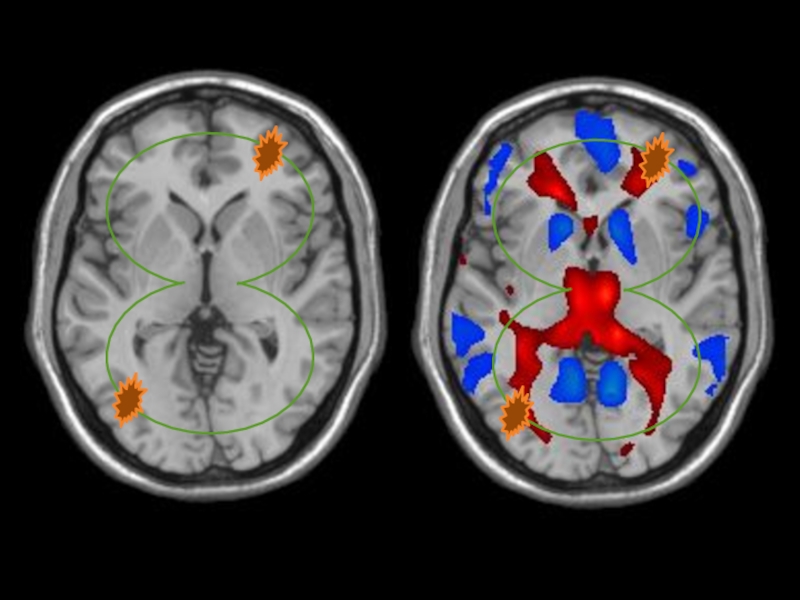
Слайд 6Generalized seizures
Originate at some point within and rapidly engage
bilaterally distributed networks
Can include cortical and subcortical structures
but not
necessarily the entire cortex Слайд 8Originate within networks limited to one hemisphere
May be discretely localized
or
more widely distributed.…
Focal seizures
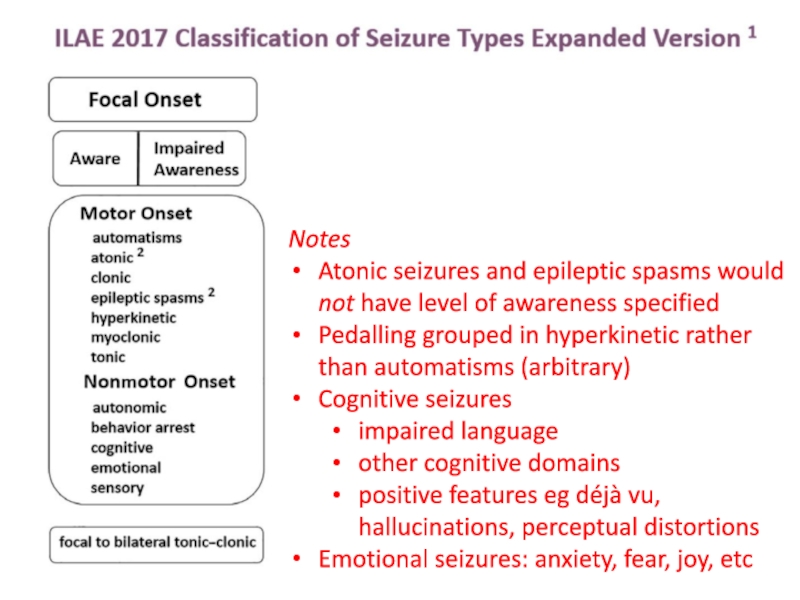
Слайд 10Notes
Atonic seizures and epileptic spasms would not have level of
awareness specified
Pedalling grouped in hyperkinetic rather than automatisms (arbitrary)
Cognitive seizures
impaired
languageother cognitive domains
positive features eg déjà vu, hallucinations, perceptual distortions
Emotional seizures: anxiety, fear, joy, etc
Слайд 13Note
When a seizure type begins with ”focal, generalized or absence”
then the word “onset” can be presumed
Слайд 14Terms no longer in use
Complex partial
Simple partial
Partial
Psychic
Dyscognitive
Secondarily generalized
tonic-clonic
Слайд 16Note
Clarify features of seizures but do not define unique seizure
types
Free text descriptors encouraged
Слайд 19Where unable to make an Epilepsy Syndrome diagnosis or a
diagnosis of Etiology
Many examples
Temporal lobe epilepsy
Generalized tonic-clonic seizures in a
5 year old with generalized spike-waveBoth focal impaired awareness seizures and absence seizures in a patient
Cannot tell if tonic-clonic seizure is focal or generalized
Слайд 20Generalized and Focal Epilepsies
Combined focal and generalized epilepsies
Examples
Dravet syndrome
What
do with
Multifocal epilepsies?
Hemispheric epilepsies?
focal
focal
Слайд 23Genetic versus idiopathic
‘Idiopathic’ = presumed hereditary predisposition
Genetic ≠ inherited
Importance of
de novo mutations in both
mild and severe epilepsies
Critical problem
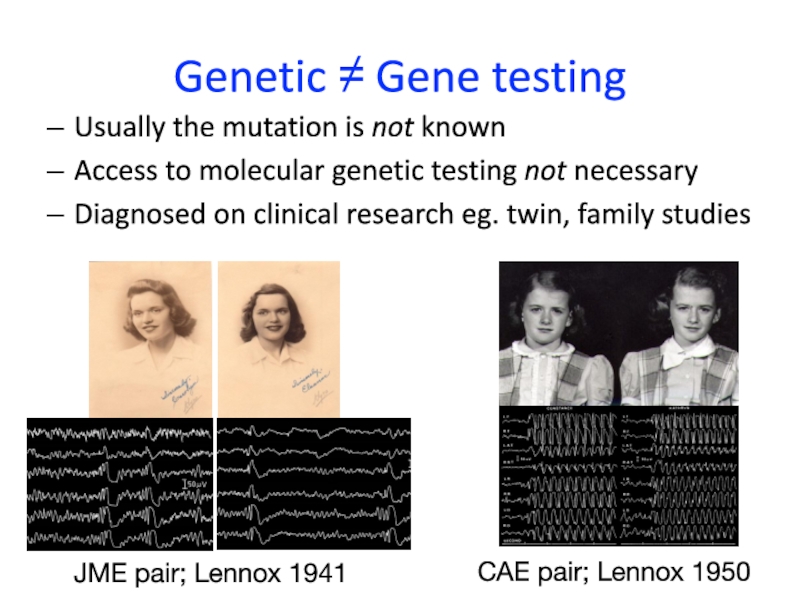
of stigma in some parts of the worldСлайд 24Genetic ≠ Gene testing
Usually the mutation is not known
Access
to molecular genetic testing not necessary
Diagnosed on clinical research eg.
twin, family studies
JME pair; Lennox 1941
CAE pair; Lennox 1950
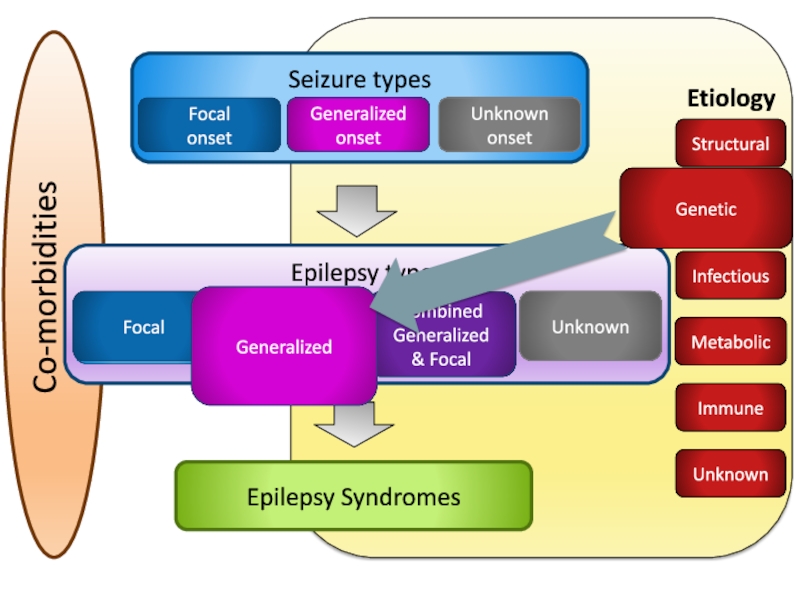
Слайд 25Co-morbidities
Etiology
Epilepsy types
Focal
Generalized
Combined
Generalized
& Focal
Unknown
Focal
Epilepsy Syndromes
Generalized
Unknown
Immune
Infectious
Structural
Metabolic
Genetic
Genetic
Слайд 32Benign
Many epilepsies not benign
CAE – psychosocial impact
BECTS – learning concerns
Replaced
by terms:
Self-limited
Pharmacoresponsive
No longer use
Malignant
Catastrophic
Слайд 33Epileptic activity itself
contributes to severe cognitive and behavioral impairment above
and beyond that expected from the underlying pathology and that
these can worsen over timeDevelopmental and/or Epileptic encephalopathies
Berg et al 2010
Слайд 34Developmental and/or Epileptic Encephalopathy
For many encephalopathies, there is a developmental
component independent of the epileptic encephalopathy
Developmental delay may precede seizure
onsetCo-morbidities eg. cerebral palsy, autism spectrum disorder, intellectual disability
Outcome poor even though seizures stop eg. KCNQ2, STXBP1 encephalopathies
Слайд 35Developmental and/or Epileptic Encephalopathy
Developmental encephalopathy
May begin in utero
Post birth
Epileptic encephalopathy
Can
occur at any age
May have remediable component – right vs
wrong AEDMove towards GENE encephalopathy
eg. CDKL5 encephalopathy, SCN2A encephalopathy
Слайд 36Old terms
‘Symptomatic Generalized Epilepsies’
Used for two different groups of
disorders
Symptomatic Generalized Epilepsies
Developmental
and/or
Epileptic
Encephalopathies
(Static)
Encephalopathies
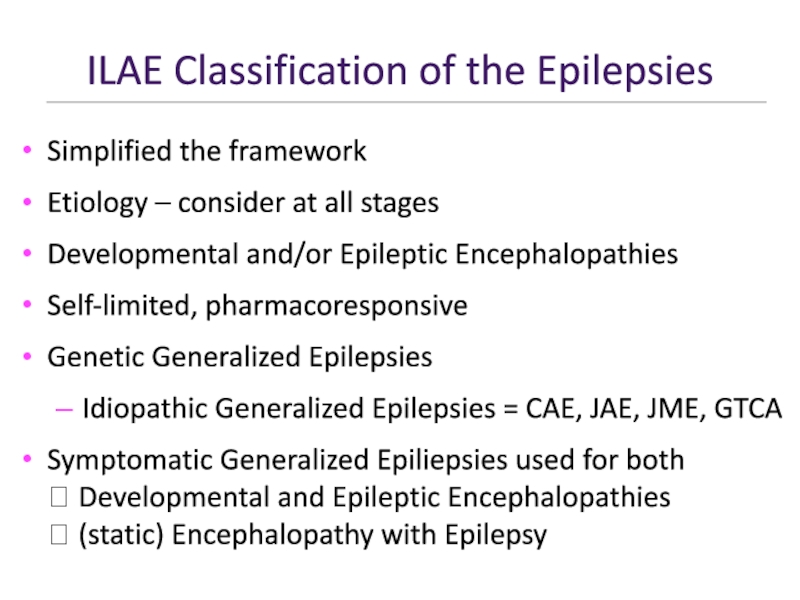
Слайд 37ILAE Classification of the Epilepsies
Simplified the framework
Etiology – consider at
all stages
Developmental and/or Epileptic Encephalopathies
Self-limited, pharmacoresponsive
Genetic Generalized Epilepsies
Idiopathic Generalized Epilepsies
= CAE, JAE, JME, GTCASymptomatic Generalized Epiliepsies used for both Developmental and Epileptic Encephalopathies (static) Encephalopathy with Epilepsy
Слайд 38Impact on Clinical Care and Practice
New classification framework will
Change the
approach to diagnosis in the clinic
Be applied to patients and
guide management Updates terminology to reflect current thinking
Scientific advances