Слайд 1Cloud and mobile technologies
Lecture #10
Слайд 3LECTURE PLAN
INTRODUCTION
WHAT IS CLOUD?
WHAT IS CLOUD COMPUTING?
CLOUD COMPUTING ARCHITECTURE
BASIC
CONCEPTS
DEPLOYMENT MODELS
SERVICE MODELS
INFRASTRUCTURE AS A SERVICE (IAAS)
PLATFORM AS
A SERVICE (PAAS)
SOFTWARE AS A SERVICE (SAAS)
ADVANTAGES, DISADVANTAGES
CLOUD STORAGE
MOTIVATION
WHAT IS MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING?
WHY IS MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING?
ARCHITECTURE
ADVANTAGES
APPLICATIONS
Слайд 4INTRODUCTION
Cloud Computing provides us a means by which we can
access the applications as utilities, over the Internet. It allows
us to create, configure, and customize applications online.
With Cloud Computing users can access database resources via the internet from anywhere for as long as they need without worrying about any maintenance or management of actual resources.
Слайд 5What is Cloud?
The term Cloud refers to a Network
or Internet.
In other words, we can say that Cloud
is something,
which is present at remote location.
Cloud can provide services over network, i.e.,
on public networks or on private networks, i.e.,
WAN, LAN or VPN.
Applications such as e-mail, web conferencing,
customer relationship management (CRM),
all run in cloud.
Слайд 6What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud Computing refers to manipulating,
configuring,
and accessing the applications online.
It offers online data storage,
infrastructure and application.
Cloud Computing is both a combination of software and hardware based computing resources delivered as a network service.
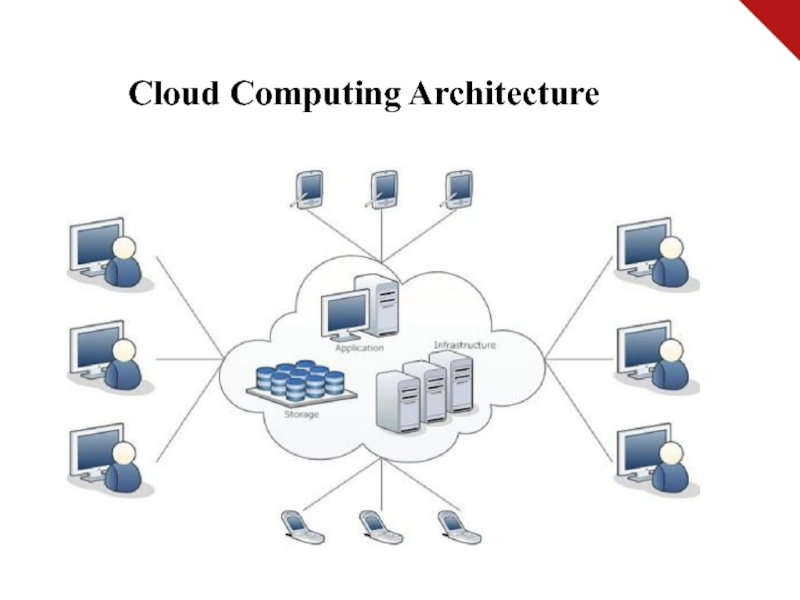
Слайд 7Cloud Computing Architecture
Слайд 8Basic Concepts
There are certain services and models working behind the
scene making the cloud computing feasible and accessible to end
users. Following are the working models for cloud computing:
1. Deployment Models
2. Service Models
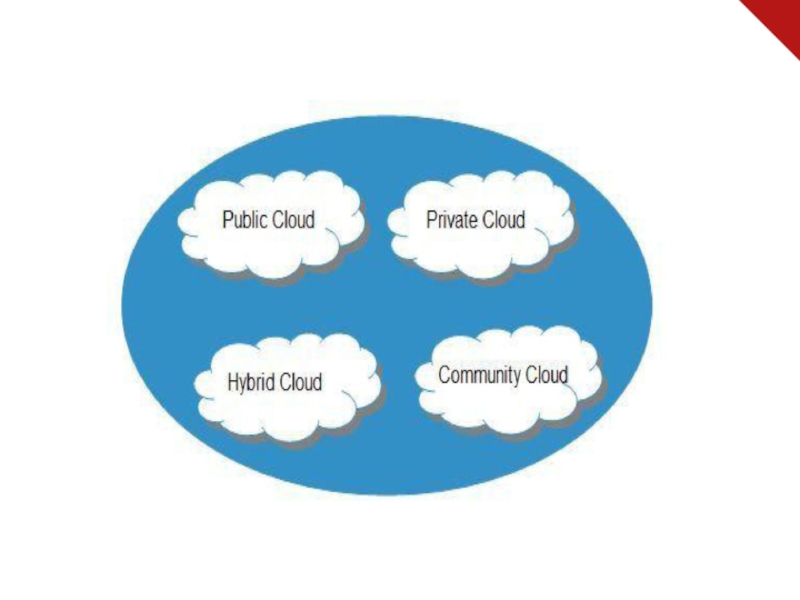
Слайд 9 Deployment Models
Deployment models define the type of access
to the cloud, i.e., how the cloud is located? Cloud
can have any of the four types of access: Public, Private, Hybrid and Community.
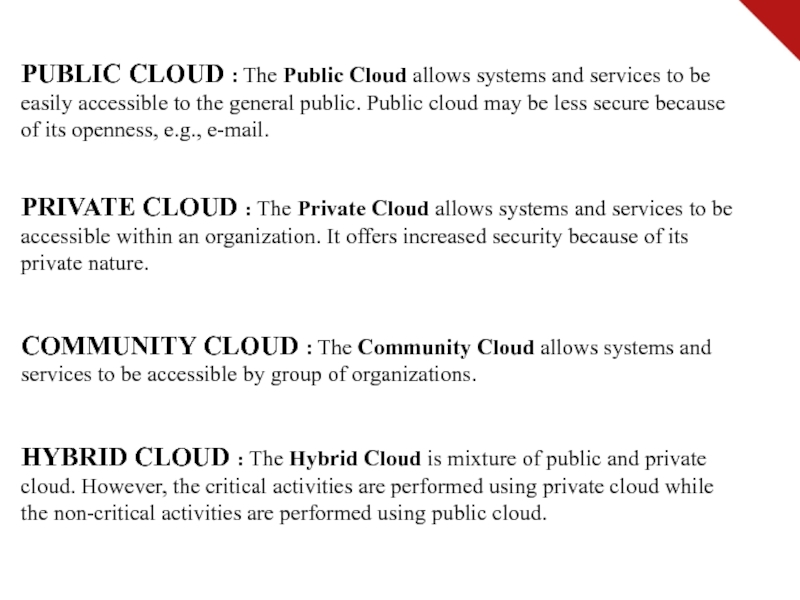
Слайд 11PUBLIC CLOUD : The Public Cloud allows systems and services
to be easily accessible to the general public. Public cloud
may be less secure because of its openness, e.g., e-mail.
PRIVATE CLOUD : The Private Cloud allows systems and services to be accessible within an organization. It offers increased security because of its private nature.
COMMUNITY CLOUD : The Community Cloud allows systems and services to be accessible by group of organizations.
HYBRID CLOUD : The Hybrid Cloud is mixture of public and private cloud. However, the critical activities are performed using private cloud while the non-critical activities are performed using public cloud.
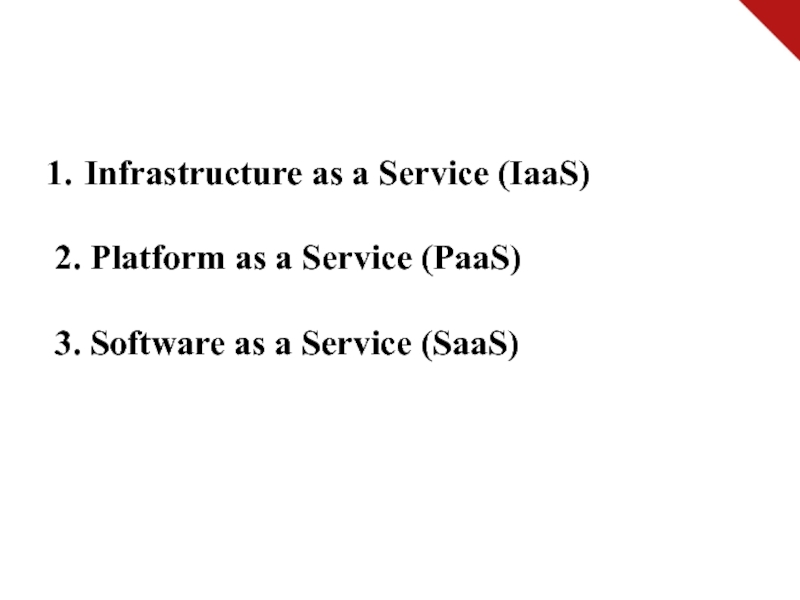
Слайд 12 Service Models
Service Models are the reference models on
which the Cloud Computing is based. These can be categorized
into three basic service models as listed below:
Слайд 13Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
2. Platform as a Service
(PaaS)
3. Software as a Service (SaaS)
Слайд 14Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
IaaS is the delivery of technology
infrastructure as an on demand scalable service.
IaaS provides access to
fundamental resources such as physical machines, virtual machines, virtual storage, etc.
Usually billed based on usage
Usually multi tenant virtualized environment
Can be coupled with Managed Services for OS and application support
Слайд 16Platform as a Service (PaaS)
PaaS provides the runtime environment for
applications, development & deployment tools, etc.
PaaS provides all of
the facilities required to support the complete life cycle of building and delivering web applications and services entirely from the Internet.
Typically applications must be developed with a particular platform in mind
Multi tenant environments
Highly scalable multi tier architecture
Слайд 18Software as a Service (SaaS)
SaaS model allows to use software
applications as a service to end users.
SaaS is a software
delivery methodology that provides licensed multi-tenant access to software and its functions remotely as a Web-based service.
Usually billed based on usage
Usually multi tenant environment
Highly scalable architecture
Слайд 20 Advantages
Lower computer costs
Improved performance:
Reduced software costs
Instant software updates
Improved document
format compatibility
Unlimited storage capacity
Increased data reliability
Universal document access
Latest version availability
Easier
group collaboration
Device independence
Слайд 21 Disadvantages
Requires a constant Internet connection
Does not work well with
low-speed connections
Features might be limited
Can be slow
Stored data can be
lost
Stored data might not be secure
Слайд 22 Cloud Storage
Create an Account User name and password.
Content lives
with the account in the cloud.
Log onto any computer with
Wi-Fi to find your content
Слайд 24MOTIVATION
In human life Mobile devices e.g., smartphone, tablet pcs, etc)
become an essential part of
Dream of “Information at your fingertips
anywhere anytime”,
When compared to conventional information processing devices these Mobile devices are lack in resources.
Mobile Cloud Computing (MCC)
Motivation
Soultion
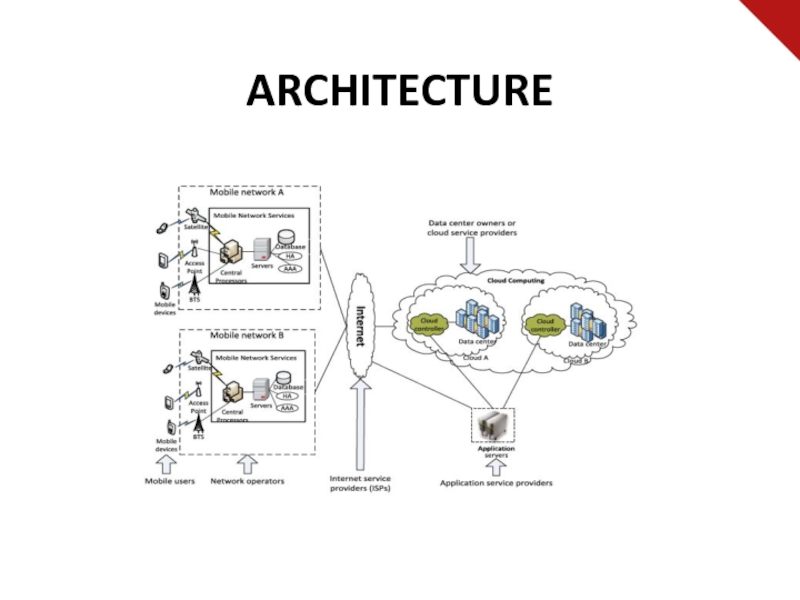
Слайд 25WHAT IS MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING?
MCC refers to an infrastructure where
both the data storage and data processing happen outside of
the mobile device.
Mobile cloud applications move the computing power and data storage away from the mobile devices and into powerful and centralized computing platforms located in clouds, which are then accessed over the wireless connection based on a thin native client.
MOBILE CLOUD COMPUTING = MOBILE COMPUTING + CLOUD COMPUTING
Слайд 26WHY DO WE NEED MCC?
Mobile devices face many resource challenges
(battery life, storage, bandwidth etc.)
Cloud computing offers advantages to users
by allowing them to use infrastructure, platforms and software by cloud providers at low cost and elastically in an on-demand fashion.
Mobile cloud computing provides mobile users with data storage and processing services in clouds, obviating the need to have a powerful device configuration (e.g. CPU speed, memory capacity etc), as all resource-intensive computing can be performed in the cloud.
Слайд 28APPLICATIONS
Mobile Commerce.
Mobile HealthCare.
Mobile Learning.
Mobile Gaming.
Слайд 29ADVANTAGES
Extending battery lifetime
Improving data storage capacity and processing power
Improving reliability
and availability
Dynamic provisioning
Scalability
Multi-tenancy
Ease of Integration