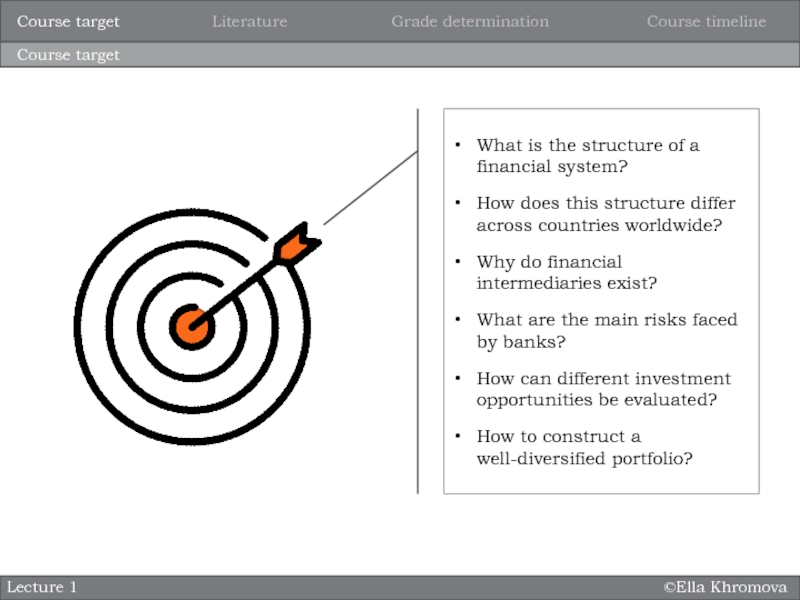
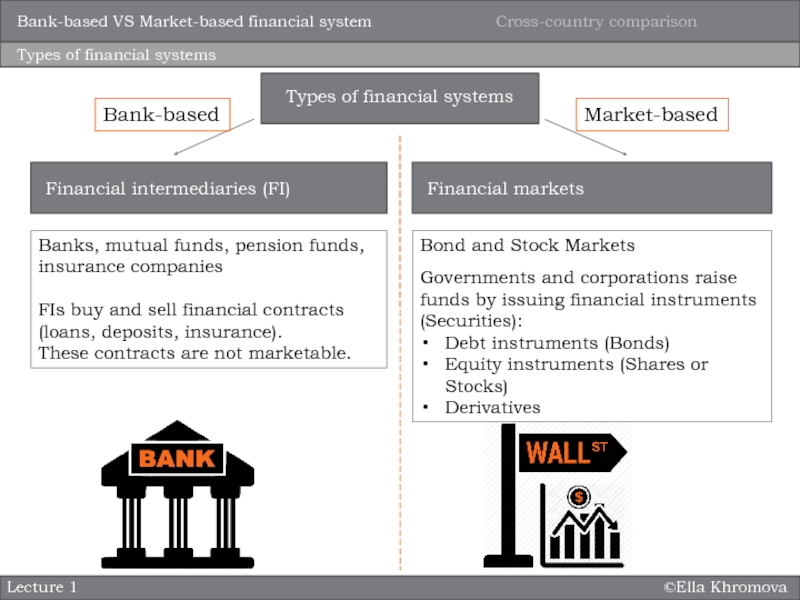
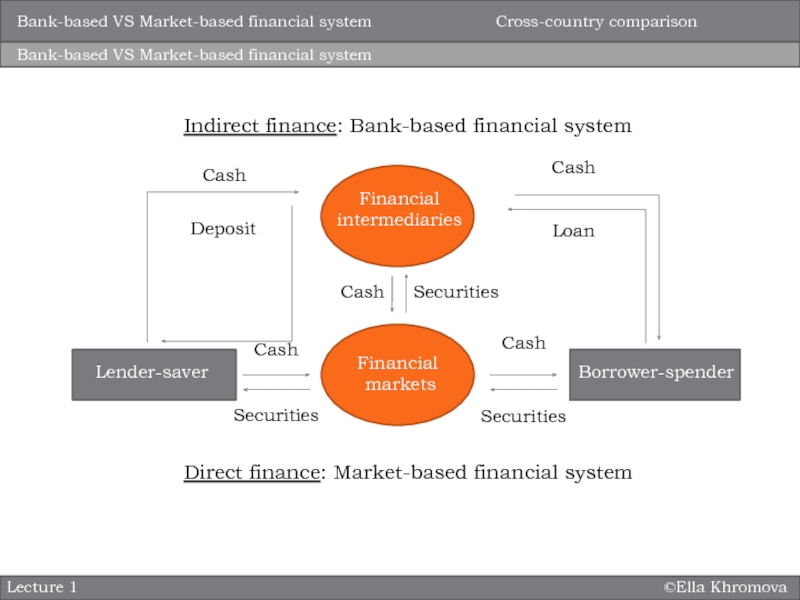
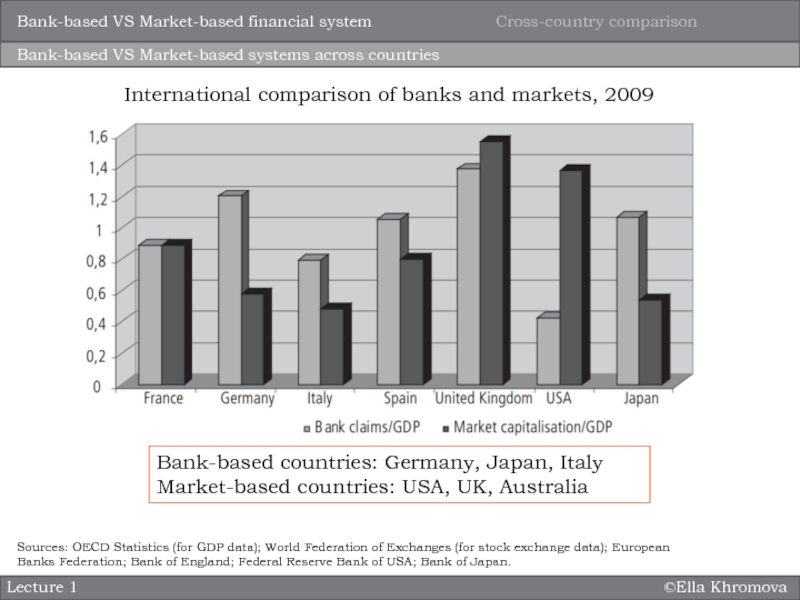
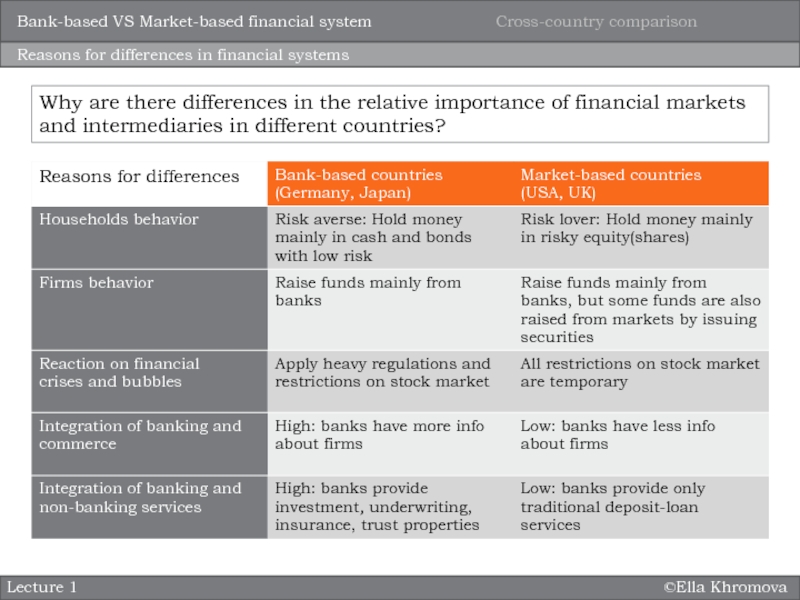
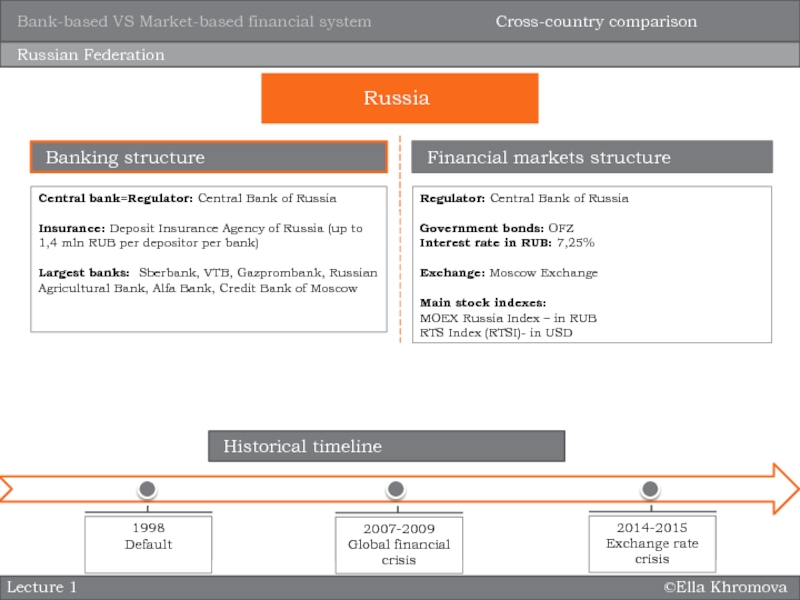
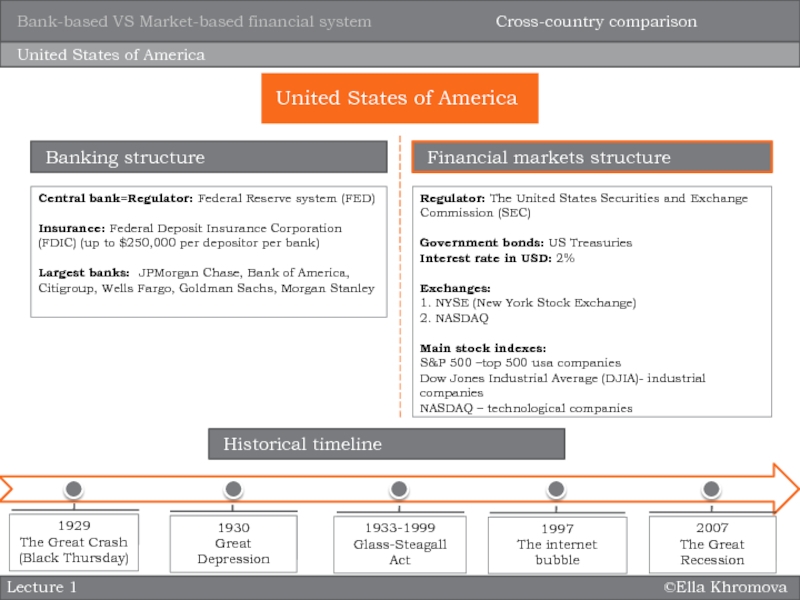
system?
How does this structure differ across countries worldwide?
Why do financial
intermediaries exist? What are the main risks faced by banks?
How can different investment opportunities be evaluated?
How to construct a well-diversified portfolio?
Course target
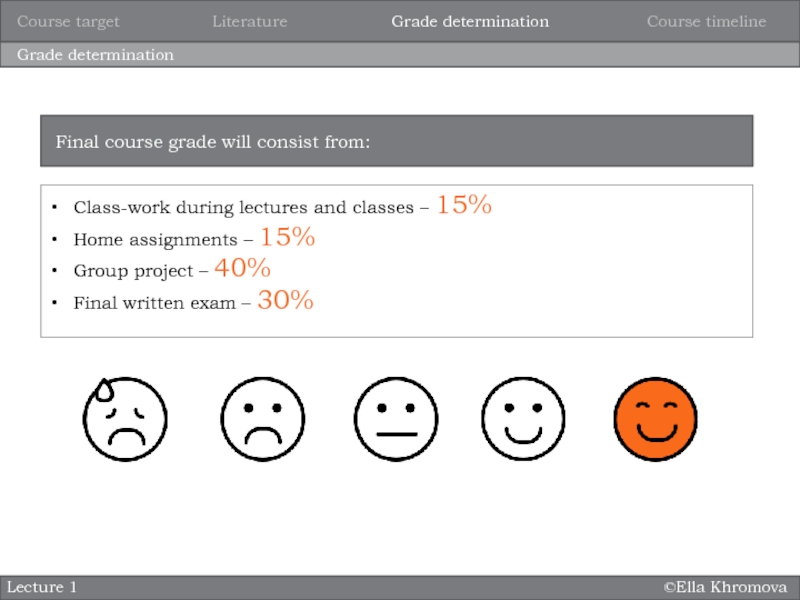
Grade determination
Literature
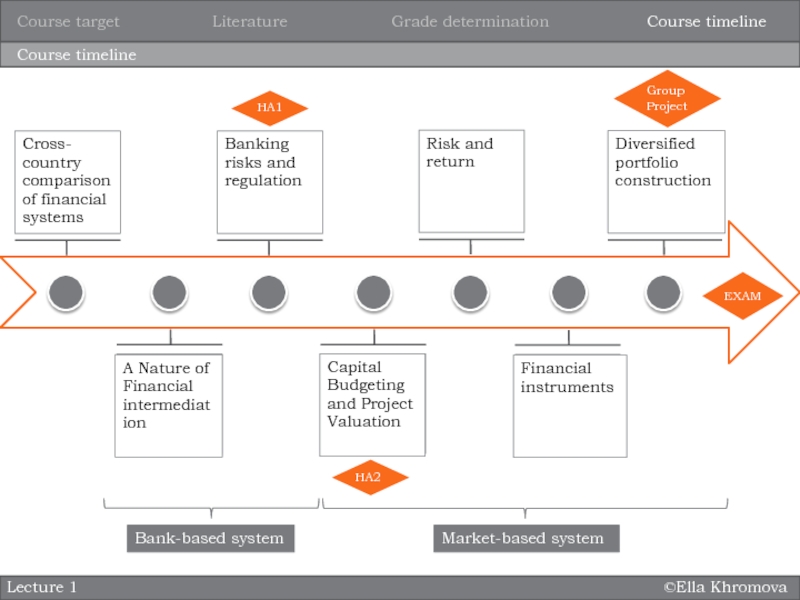
Course timeline