Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Crimean state medical University named after S. I. Georgievsky Submitted by
Содержание
- 1. Crimean state medical University named after S. I. Georgievsky Submitted by
- 2. Слайд 2
- 3. A population or group of populations whose
- 4. The diversity of species on Earth is
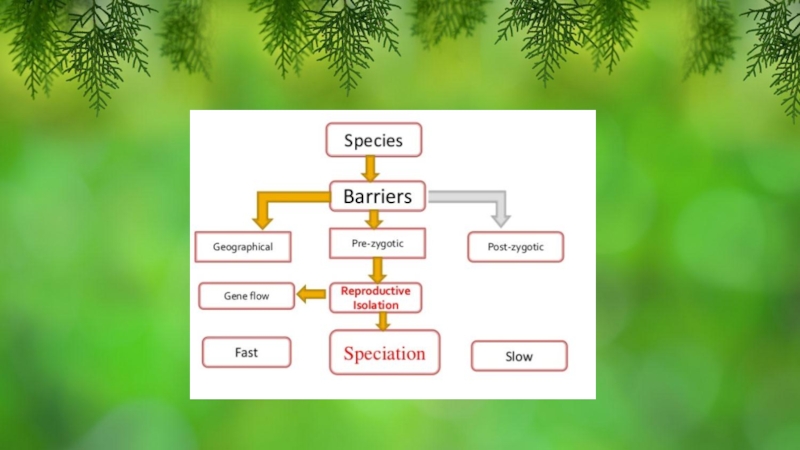
- 5. SpeciationSpeciation = formation of
- 6. Reproductive IsolationThe existence of biological factors (barriers)
- 7. Geographical isolation occurs when populations cannot mate
- 8. Слайд 8
- 9. Isolation mechanismIsolating mechanisms prevent interbreeding and
- 10. PRE-ZYGOTAIC BARRIERPre-zygotic barriers are obstacles that are
- 11. Ecological isolationEcological isolation occurs when potential mates
- 12. Temporal isolationTemporal isolation occurs when species can’t
- 13. Mechanical incompatibilityMechanical incompatibility occurs when species cannot
- 14. GAMETIC ISOLATIONSperm of one species may not
- 15. Behavioral isolationBehavioral isolation occurs when species can’t
- 16. POSTMATING ISOLATING MECHANISMIsolating mechanisms which operate after
- 17. HYBRID INVIABILITYThe term 'hybrid' refers to the
- 18. ABNORMALITIESSpecies mate and hybrid is viable but
- 19. Conclusion-(1)The reproductive isolation is quite difficult in
- 20. THANK YOU
- 21. Скачать презентанцию
A population or group of populations whose members have the ability to interbreed with one another under natural condition and produce fertile offspring and reproductively isolated from other species.In biology, a
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 3A population or group of populations whose members have the
ability to interbreed with one another under natural condition and
produce fertile offspring and reproductively isolated from other species.In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate sexes or mating types can produce fertile offspring, typically by sexual reproduction.
Слайд 4The diversity of species on Earth is simply astounding. Scientists
have identified about two million species and still do not
know how many species inhabit Earth. Scientists estimate as many as 30 million species may inhabit Earth.So, the big question is how did so many species form?
Слайд 5 Speciation
Speciation = formation of new species
Speciation
occurs when members of similar populations no longer interbreed to
produce fertile offspring within their natural environmentIt occurs when groups in a species become reproductively isolated and diverge
A single species can generate multiple species
HENCE IT LEAD TO A NEW IDEAS ABOUT EVOLUTION
Speciation is the origin of new species.
Speciation increases our planet’s biological diversity.
Therefore, speciation is an important part of the theory of evolution.
Many scientist have different ideas about it.
Слайд 6Reproductive Isolation
The existence of biological factors (barriers) that prevent two
individuals of a species from mating and producing viable and
fertile offspringA new species will form when reproductive isolation occurs
The mechanisms of reproductive isolation are a collection of evolutionary mechanisms, behaviours and physiological processes critical for speciation. They prevent members of different species from producing offspring, or ensure that any offspring are sterile. These barriers maintain the integrity of a species by reducing gene flow between related species
Слайд 7Geographical isolation occurs when populations cannot mate because of physical
barriers
Geographically separated populations aren’t necessarily distinct species.
Example: Northern Spotted
Owl and Mexican Spotted Owl.Geographical Isolation
Слайд 9 Isolation mechanism
Isolating mechanisms prevent interbreeding and maintain reproductive isolation.
Isolating
mechanisms can be divide in to two different types.
Isolating
mechanisms that occur before fertilization are called Prezygotic isolating mechanisms.Isolating mechanisms that occur after fertilization are called postzygotic isolating mechanisms.
Слайд 10PRE-ZYGOTAIC BARRIER
Pre-zygotic barriers are obstacles that are present before an
egg can be fertilized.
A zygote is an egg that
has been fertilized by a spermPremating isolating mechanisms include:
1) Ecological isolation.
2) Temporal isolation.
3) Behavioral isolation.
4) Mechanical incompatibility.
5) Gametic isolation
Слайд 11Ecological isolation
Ecological isolation occurs when potential mates never meet because
they live in different habitats.
Ex. The mountain bluebird lives at
high elevation while the eastern bluebird prefers low elevationСлайд 12Temporal isolation
Temporal isolation occurs when species can’t mate because they
breed at different times of year.
Ex: The Monterey Pine and
the Bishop pine have different pollination periods.Example Red and black sea urchins live in the same location, but release their gametes at different times of the year.
Слайд 13Mechanical incompatibility
Mechanical incompatibility occurs when species cannot mate because their
reproductive structures are incompatible
Closely related species may attempt to mate
but fail because they are anatomically incompatible and transfer of sperm is not possibleIn animals with internal fertilization, male and female sexual organs may not fit together
EX. snails of species whose shells have left handed spirals may be unable to successfully copulate with snails whose shells have right handed spirals
Слайд 14GAMETIC ISOLATION
Sperm of one species may not survive internal environment
of female reproductive tract in another species
For fertilization to occur,
the sperm must reach the ovum. For this to happen they usually attract each other through chemical means, but the chemicals might vary from one specie to another. In this case gametes won’t recognise each other and fertilization won’t take place.Слайд 15Behavioral isolation
Behavioral isolation occurs when species can’t mate because patterns
of courtship may be different to the extent that sexual
union is not achievedEx: Fireflies produce patterns of flashes that attract their mates. Over 2000 species of fireflies are isolated based on the patterns of flashes
Members of the two species will not mate with each other because they use different songs to attract mates. Eastern meadowlarks will not respond to western meadowlark songs, and vice versa.
Example: Eastern and Western Meadowlarks
Слайд 16POSTMATING ISOLATING MECHANISM
Isolating mechanisms which operate after fertilization
Prevents hybrid zygotes
from developing into viable, fertile adults
There are three likely cases
that will occur to ensure that the hybrid does not reproduce Postmating isolating mechanisms include:1. Hybrid inviability
2. Hybrid infertility
3. Hybrid breakdown
Слайд 17HYBRID INVIABILITY
The term 'hybrid' refers to the offspring between two
different species and 'inviability' refers to an organism that does
not thrive. In hybrid inviability, mating occurs and a hybrid is produced, but Hybrid very weak and can’t live outside the uterus.Ex. Several species of the frog live in the same habitats but hybrids do not complete development
If Sheep and goats mate then Hybrid zygotes Die before birth
The creation of an unsuccessful hybrid is also a form of post- zygotic barrier.