Слайд 1Definition of evidence-based medicine. The history of the development of
evidence-based medicine. World experience of development. Clinical epidemiology: definition, history
of development, the basic principles and methods of research.
Department of Health Policy and Management,
Associate Professor, Faculty, MD
Turdalieva Botagoz Saitovna
Слайд 2"... All knowledge, which is not weighed in the balance
of the mind, is not reliable and therefore not a
true knowledge"
Abu Ali Ibn Sina,
"Danish - nama" ("Book of Knowledge").
Слайд 3Evidence-based medicine
Evidence-based medicine - is fair, accurate and meaningful use
of the best results of clinical trials for the treatment
of a specific patient selection. This is a new technology of gathering, critical analysis, synthesis and interpretation of scientific information.
Слайд 4Evidence-based medicine
it is a way of medical practice, but:
not
"science"
not "epidemiology"
not "statistics",
not the way to research
V.V.Vlasov
Слайд 5Terminology
For the first time in 1990 by a group of
Canadian researchers from McMaster University has proposed to integrate the
best research evidence with clinical expertise and the patient's individual preferences in a separate branch of medicine.
This scientific and practical section provides an accessible, concise and objective information on the best and most reliable results of clinical trials conducted worldwide and objectively prove the benefits of a treatment or drug and was named the "Evidence-Based Medicine" (EBM).
Слайд 6BACKGROUND of the EBM
More than 4 million articles per year
More than 20,000 medical journals
Exchange of the information about
health is increasing with the development of the telecommunication networks: doubles every 2 years
Rapid obsolescence of knowledge
Inconsistency of the results and conclusions of clinical research
Слайд 7Background for use of evidence
We are remember not typical cases
better than outstanding situation
To the assessment influence personal experience, our
knowledge, beliefs and preferences.
We find what we are looking for, and hear what we are waiting to hear, do not notice what you do not want to notice
You can never be sure that the recovery of the patient is due to this interference, and not a coincidence, or other reasons unknown to us
The number of observed patients are often too little to make far-reaching conclusions
Слайд 8Where is the wisdom we have lost in knowledge, where
is the knowledge we have lost in information?
TS
Eliot
Слайд 9Basic approaches of physicians in the decision (not EBM)
Decision-making based
on a short story (anecdotal medicine)
Decision-making by clippings of
articles
Decision-making based on expert opinion (medicine based on celebrities)
Decision-making based on cost minimization
Слайд 10Key aspects of EBM
Translate the needs information into the questions
that you can find the answer
Identify the best based
information to answer these questions
Critically evaluate evidence-based information for validity and usefulness
Implement the results of this evaluation in clinical practice
Evaluate the results of the done work
Слайд 11Systems definition of evidence interventions:
Effectiveness is proven - interventions whose
effectiveness is well documented; while the expected harm is smaller
than the benefits;
Efficiency is assumed - the intervention of proven effectiveness is less convincing than the this interventions;
Слайд 12continued
Advantages and disadvantages of comparable - before use of such
interventions doctor and patient must weigh the value of the
expected benefits and harms to the particular situation;
Efficiency is not installed - evidence of effectiveness is not enough, or they are not completely reliable;
Слайд 13continued
Efficiency is unlikely - the evidence of inefficiency intervention less
convincing than for the following interventions;
Inefficiency or damage proved
- interference, inefficiency or damage which conclusively proved.
Слайд 14Algorithms use in EBM
Evidence-based medicine – it is a medical
information technology, which allows you to receive evidence-based solutions for
the prevention, diagnosis, treatment of diseases and health organizations. The algorithm using evidence-based medicine is as follows:
Слайд 154 steps to take action
Formulation of the problem
Seek information
- literature data in this research
Evaluation of scientific evidence
(confidence) and the usefulness of the information
Application in practice and / or distribution (publication) of the results obtained in three main areas: the development of clinical guidelines, formation of databases of systematic reviews of randomized controlled trials, the publication of specialized training and background paper and electronic journals, manuals, books and the Internet - resources
Слайд 16Step 1: Formulation of the problem
What is the probability of
re-sharpening and the prognosis of the patient ?, or
What diagnostic
models are optimal for this pathology?, or
What is the efficiency or safety of different treatment options?
Слайд 17Examples of unreasonable traditional approaches to the use of common
drugs
The use of antimicrobial agents (antibiotics, sulfonamides) in acute respiratory
viral infection treatment;
Parenteral administration of vitamin preparations with the purpose of auxiliary treatment of diseases of the internal organs;
Purpose means the metabolic correction of energy metabolism of ischemic myocardium and insufficient;
The use of so-called for the treatment of hepatic cirrhosis;
The use of clonidine and combined antihypertensive drugs in the early stages of treatment of hypertension;
Unwarranted use of infusion therapy for various diseases
Слайд 18Step 2: Search for data on the problem
3 reading level
for physicians in primary care (David Jewell)
Scrolling in which
flick through the pages in search of material;
Reading for information, search for the answer to a specific question, usually associated with an actual problem for the reader;
Reading - test that is carried out a targeted search for the formation of a comprehensive view of knowledge
Слайд 19Sources of scientific evidence
The Cochrane Library database in Russia on
discs or (www.cochrane.ru)
Internet DARE, MEDLINE www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Entrez/medline.html, EMBASE
Publication in
the periodic medical press including "J. international medical practice", «Evidence-based medicine"
Слайд 20EBM KazNMU named after S.Asfendiyarov
In 1992, the Oxford center was
opened, which was named Cochrane and in the same year
John. Chalmers was organized by the Association of Cochran, which acts as a network of interconnected centers in different countries.
In the structure of the Association organized multidisciplinary teams for analysis and synthesis of a variety of clinical sections (eg, stroke), regions (eg, pediatrics), methodological approaches (eg, statistical methods). There is a department coordination of the various survey of interest groups and networks (eg, the consumer network).
The purpose of the Association: Based on an exhaustive register of all randomized clinical trials to prepare systematic reviews.
In September 29, 2009 established the Center for Evidence-Based Medicine on the basis of KazNMU.
Слайд 21Basic base of EBM
Database Medline: created and maintained by the
National Library of Medicine, USA. It proindeksovano 4000 journals published
in more than 70 countries around the world, 3 versions available information:
Print (Index Medicus, hand pointer, which is updated every year, on the basis of which are electronic versions);
Online version (the whole database, since 1966., Accessible via the Internet);
CD - ROM (entire database consists of 10-18 discs depending on the manufacturer).
The Cochrane Library contains many hundreds of systematic reviews and hundreds of thousands of peer-reviewed abstracts of randomized trials kontrliruemyh. The Cochrane Collaboration has identified about 60,000 research incorrectly identified in Medline
Слайд 22Clinical Epidemiology
Clinical epidemiology (clinical epidemiology) (CE) – it is a
science that develops methods of clinical studies that allow us
to make a fair conclusion of controlling the effect of systematic and random errors.
CE – it is a science that allows for prediction for each patient based on a study of the clinical course of the disease in similar cases by using rigorous scientific methods to study groups of patients to ensure the accuracy of weather forecasts.
Слайд 23Clinical Epidemiology
The purpose of CE - development and application of
methods of clinical observations that allow us to make fair
conclusions, avoiding the influence of systematic and random errors
Слайд 24The main provisions of Clinical Epidemiology
In the most cases, the
diagnosis, prognosis and treatment outcomes for a particular patient is
not uniquely defined, and therefore must be expressed in terms of probabilities;
These probabilities for the individual patient is best assessed on the basis of previous experience gained in relation to the groups of similar patients;
Because clinical observations are carried out on the free in the behavior of patients and physicians make these observations with different skills and personal opinion, the results may be subject to systematic errors, leading to wrong conclusions;
Any observations, including clinical, influenced by chance;
To avoid false conclusions, doctors must rely on research based on scientific principles, using techniques to minimize systematic errors and random errors account
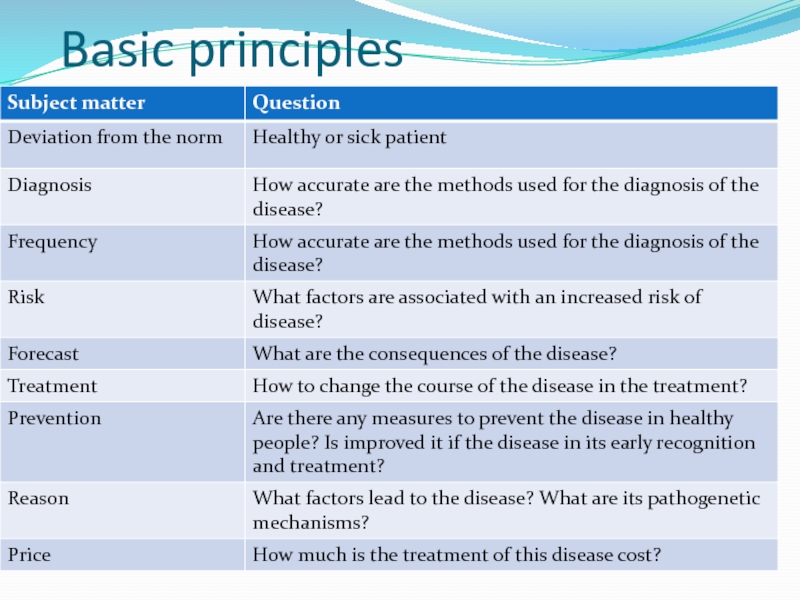
Слайд 26Basic principles
Clinical outcomes
Слайд 27basic principles
quantitative Approach
Population and sampling
Population (population) - a
large group of people living in a particular geographic region
or have some indication.
Sample (sample) - part of the population, obtained by selection
Слайд 28basic principles
Systematic error (offset, bias) - the systematic deviation of
the results from the true values
The most susceptible to
systematic errors are clinical studies (trust doctors certain drugs, emotions, behavior, individual characteristics of patients)
Слайд 29basic principles
Random error - deviation of the result of observation
in the sample from the true values in the population
Diseases studied in a sample of patients, and not the general population all individuals with the disease in question . Application of statistics helps minimize the random error by selection of optimal methods of investigation data Analysis
Слайд 30basic principles
The accuracy (internal validity) of research is defined by
the extent to which the results are valid with respect
to the sample.
Generalizability (external validity, or generalizability) - external characteristic, which is determined by the extent to which the results of this study are applicable to other groups of patients.