Разделы презентаций
- Разное
- Английский язык
- Астрономия
- Алгебра
- Биология
- География
- Геометрия
- Детские презентации
- Информатика
- История
- Литература
- Математика
- Медицина
- Менеджмент
- Музыка
- МХК
- Немецкий язык
- ОБЖ
- Обществознание
- Окружающий мир
- Педагогика
- Русский язык
- Технология
- Физика
- Философия
- Химия
- Шаблоны, картинки для презентаций
- Экология
- Экономика
- Юриспруденция
Evidence of Evolution
Содержание
- 1. Evidence of Evolution
- 2. The evidence for evolution
- 3. learning Objectiveanalyze the evidence for evolution
- 4. Success criteria 1. Name at least three
- 5. Terminology Microevolution, macroevolution, population, fossil record, comparative
- 6. Evolution …In biology, evolution is the change
- 7. What is natural selection?Individuals with characteristics best
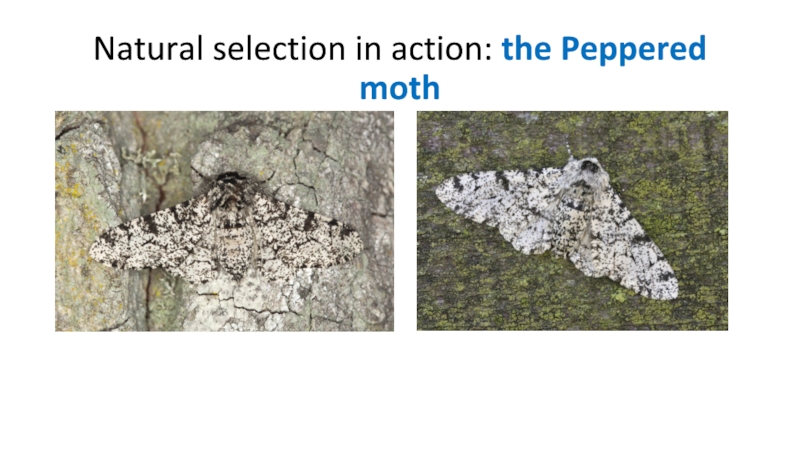
- 8. Natural selection in action: the Peppered moth
- 9. EvolutionMicroevolution is the change in allele frequencies
- 10. Слайд 10
- 11. Evidence of Evolutionfossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology, comparative biochemistry, molecular biology, biogeography
- 12. Слайд 12
- 13. Слайд 13
- 14. Fossil recordThe fossil reveals the existence of
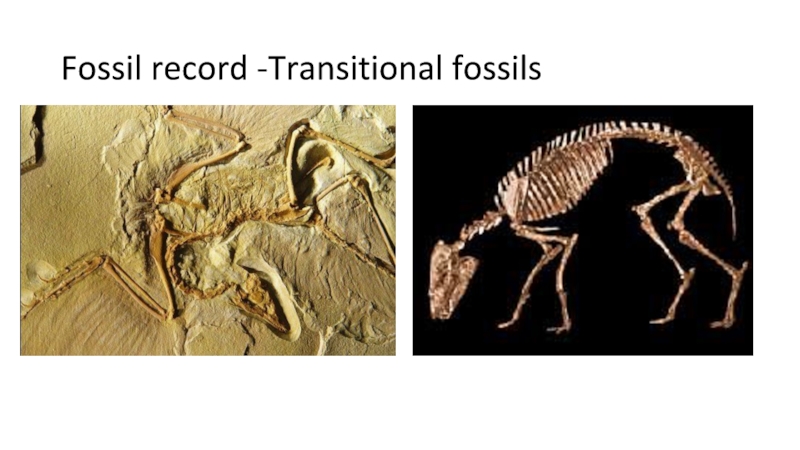
- 15. Fossil record -Transitional fossils
- 16. Comparative anatomyOrganisms that have similar anatomical structures
- 17. Comparative anatomyHomologous structure Bat wings, the lateral
- 18. Homologous structure
- 19. Comparative embryologyClosely related organisms go through similar
- 20. Слайд 20
- 21. Molecular biology (DNA, protein and enzyme system)Since
- 22. Number of amino acid differences in β chain of heamoglobin
- 23. Comparative biochemistryOrganisms that have a common ancestor
- 24. BiogeographyThe theory of continental drift (Pangaea).Supercontinent Pangaea
- 25. Слайд 25
- 26. Скачать презентанцию
Слайды и текст этой презентации
Слайд 4Success criteria
1. Name at least three examples which are
evolution evidences and comment two examples against reliability.
out research and analysis of results and make report on the performed work.Слайд 5Terminology
Microevolution, macroevolution, population, fossil record, comparative anatomy, comparative embryology,
comparative biochemistry, molecular embryology, biogeography, homologous structures, analogous structures, vestigial
structures, paleontology, protein sequence data, variations in heamoglobin molecules, cytochrome c, immunological, mitochondrial DNA, continental drift, Drug-Resistant Bacteria, evolutionary tree, convergent evolution.Слайд 6Evolution …
In biology, evolution is the change in the characteristics
of a species over several generations and relies on the
process of natural selection.The theory of evolution is based on the idea that all species are related and gradually change over time.
Evolution relies on there being genetic variation in a population which affects the physical characteristics (phenotype) of an organism.
Слайд 7What is natural selection?
Individuals with characteristics best suited to their
environment are more likely to survive, finding food, avoiding predators
and resisting disease. These individuals are more likely to reproduce and pass their genes on to their children.As a consequence those individuals most suited to their environment survive and, given enough time, the species will gradually evolve.
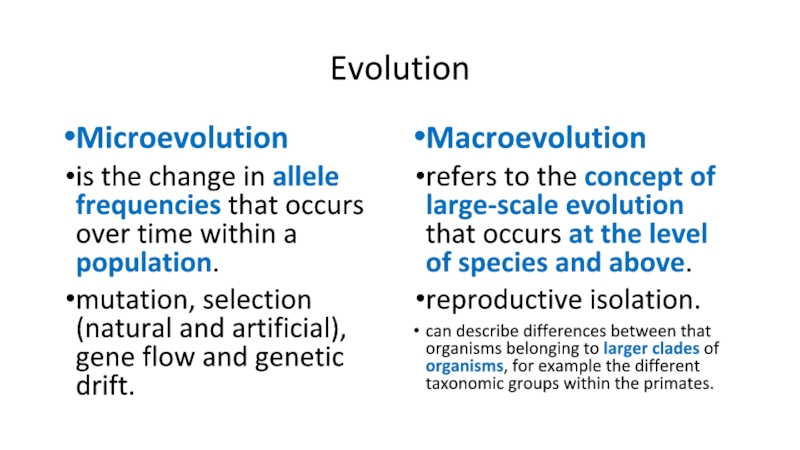
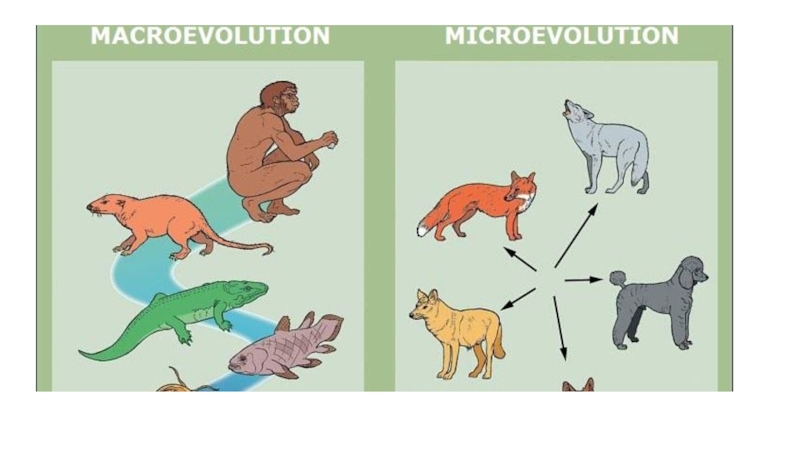
Слайд 9Evolution
Microevolution
is the change in allele frequencies that occurs over
time within a population.
mutation, selection (natural and artificial), gene flow
and genetic drift.Macroevolution
refers to the concept of large-scale evolution that occurs at the level of species and above.
reproductive isolation.
can describe differences between that organisms belonging to larger clades of organisms, for example the different taxonomic groups within the primates.
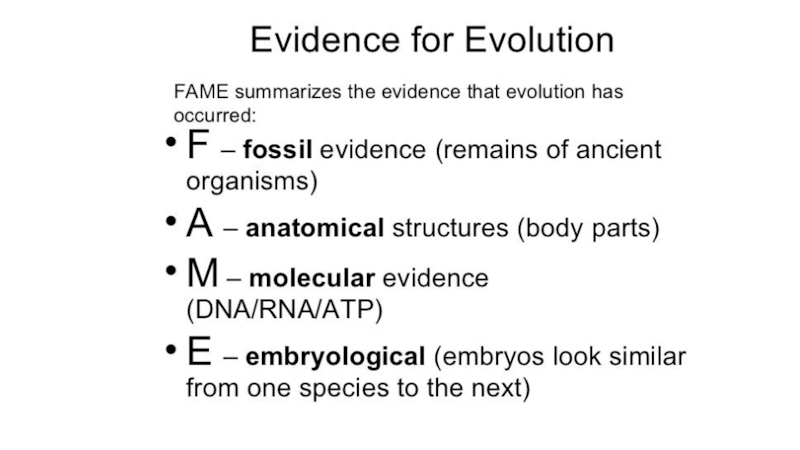
Слайд 11Evidence of Evolution
fossil record,
comparative anatomy,
comparative embryology,
comparative biochemistry,
molecular biology,
biogeography
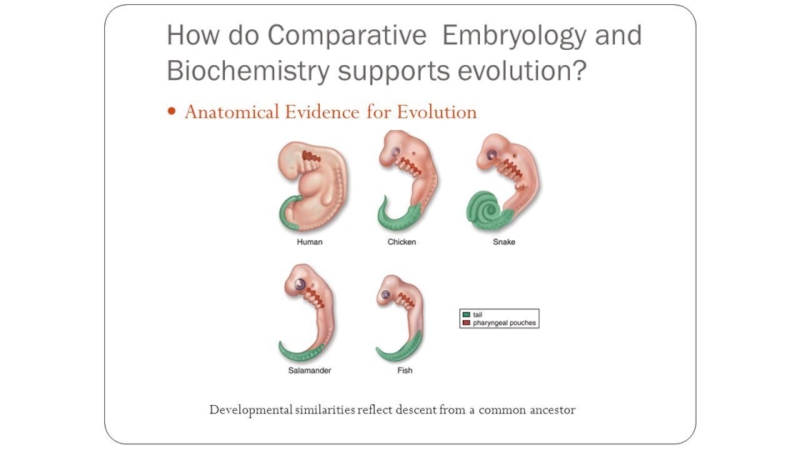
Слайд 14Fossil record
The fossil reveals the existence of species that have
become extinct or have evolved into other species. The fossil
record shows there important facts:99% of all organisms now extinct.
The radioactive dating and half-life, we know that Earth is about 4,6 billion years ago.
Prokaryotic cells are the oldest fossils and the first organisms to develop on Earth.
Transitional fossils that link older extinct fossils to modern species.
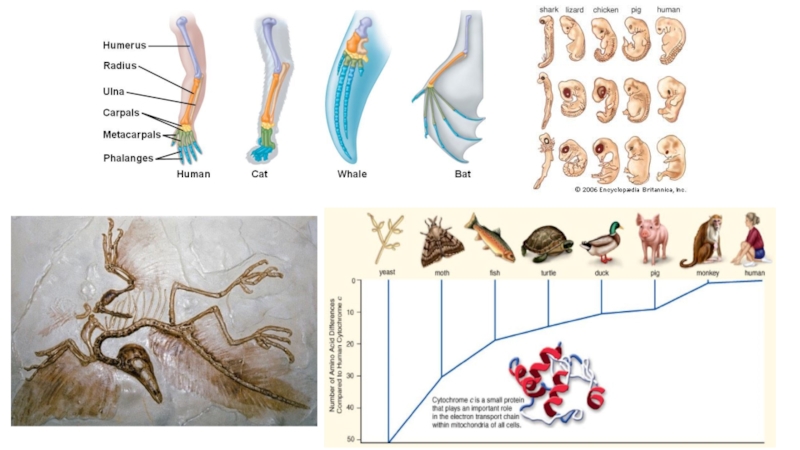
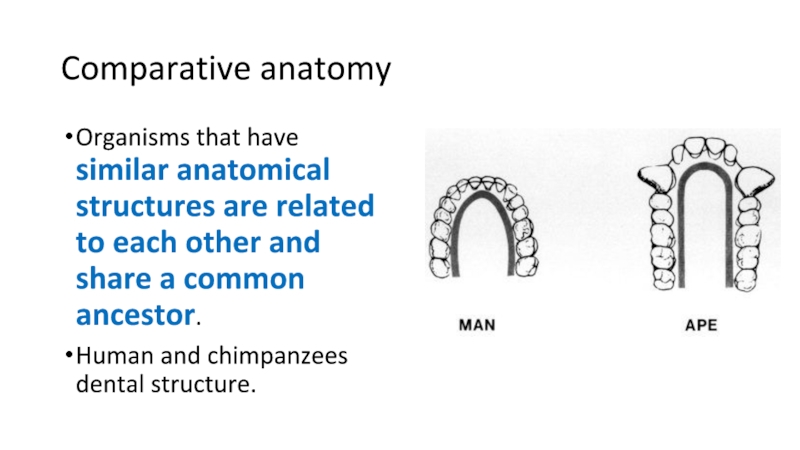
Слайд 16Comparative anatomy
Organisms that have similar anatomical structures are related to
each other and share a common ancestor.
Human and chimpanzees dental
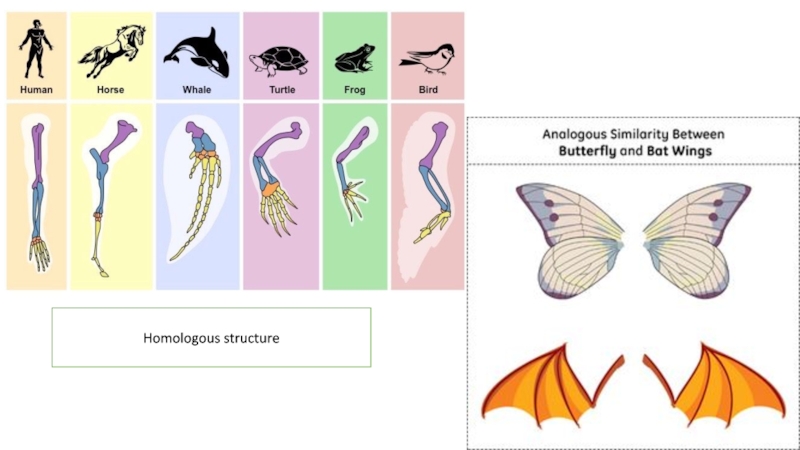
structure.Слайд 17Comparative anatomy
Homologous structure
Bat wings, the lateral fin of the
whale, human arm and etc.
Although the function of each varies,
they all have the same internal bone structure.Divergent evolution.
Analogous structure
Bat’s wings and a fly’s wings, have same function but not the same underlying structure.
Convergent evolution.
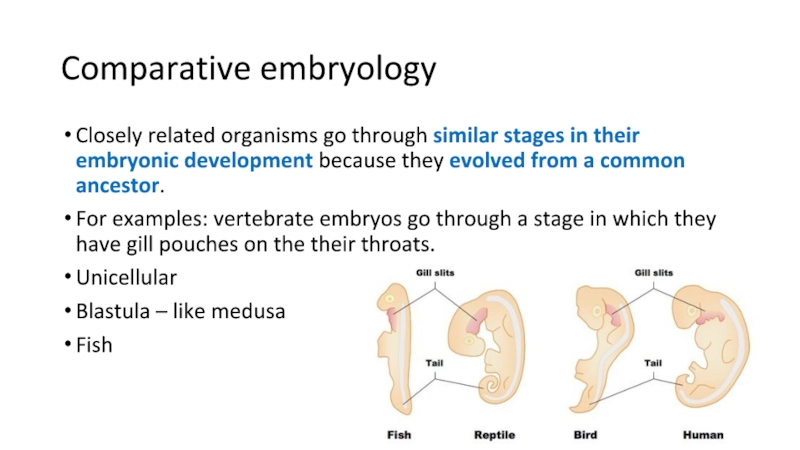
Слайд 19Comparative embryology
Closely related organisms go through similar stages in their
embryonic development because they evolved from a common ancestor.
For examples:
vertebrate embryos go through a stage in which they have gill pouches on the their throats.Unicellular
Blastula – like medusa
Fish
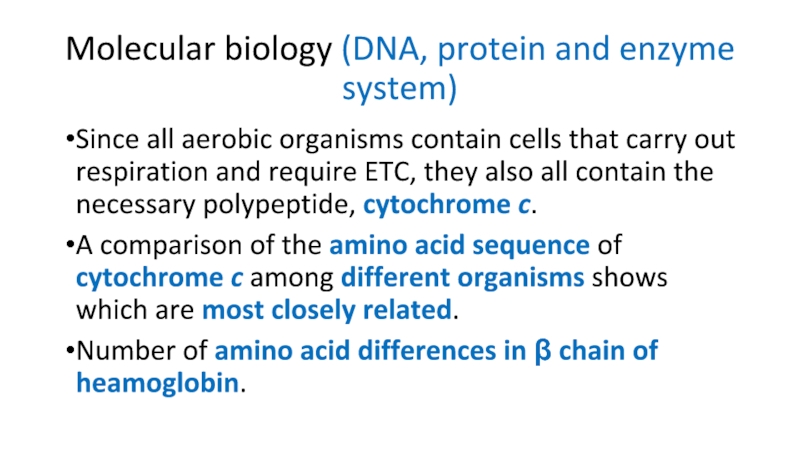
Слайд 21Molecular biology (DNA, protein and enzyme system)
Since all aerobic organisms
contain cells that carry out respiration and require ETC, they
also all contain the necessary polypeptide, cytochrome c.A comparison of the amino acid sequence of cytochrome c among different organisms shows which are most closely related.
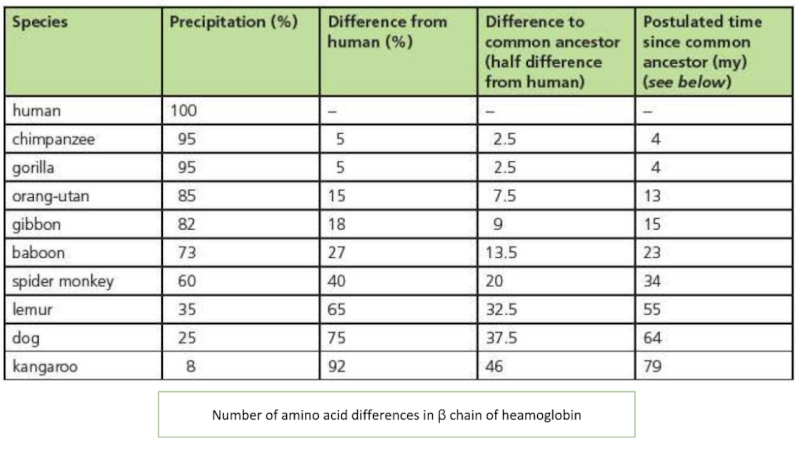
Number of amino acid differences in β chain of heamoglobin.
Слайд 23Comparative biochemistry
Organisms that have a common ancestor will have common
biochemical pathway.
The more closely related organisms are to each other,
the more similar their biochemistry is.For examples: human and mice are both mammals.
Immunological studies (reaction): serum and antibodyes.
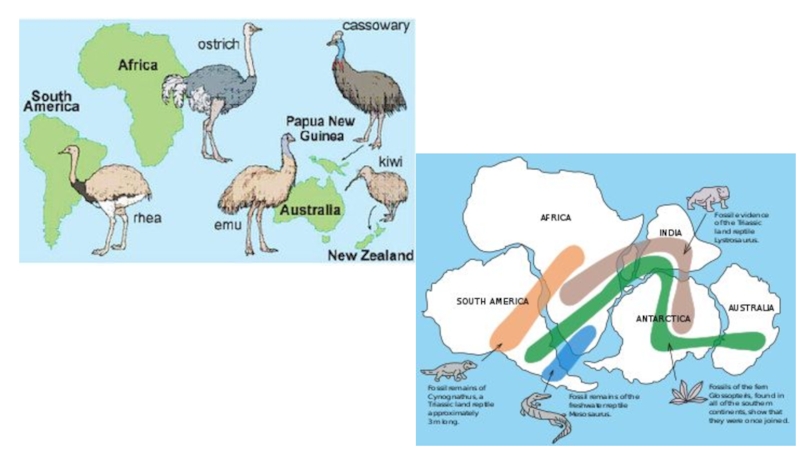
Слайд 24Biogeography
The theory of continental drift (Pangaea).
Supercontinent Pangaea slowly separated into
7 continents.
Isolation (most of the workd’s marsupials are isolated in
Australia).Endemic species –The ring-tailed lemur in Madagascar.
North America and Eurasia floras and faunas similar.