Слайд 1
Explaining democracy:
economic and cultural determinants
Слайд 2Modernization and democracy
“The more well-to-do a nation, the greater the
chances that it will sustain democracy” (Lipset 1959, Some Social
Requisites of Democracy, p. 75).
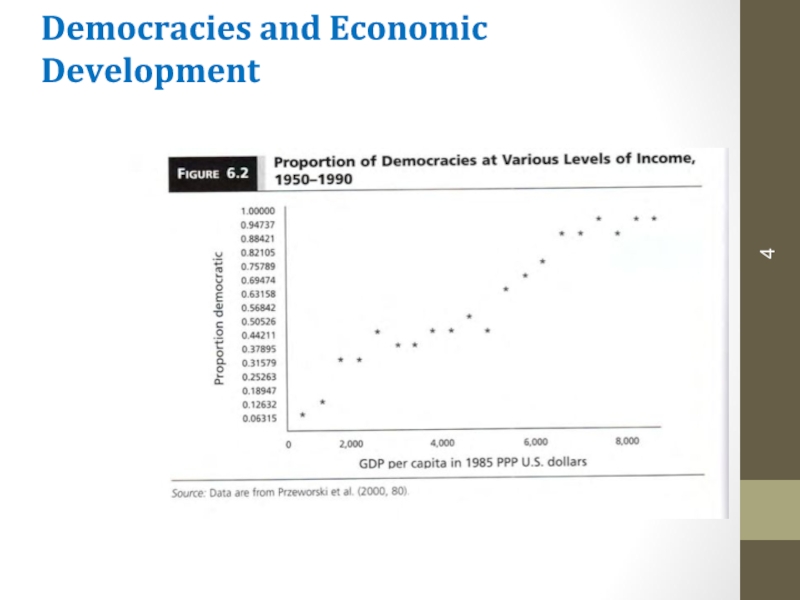
Democracy is more common in rich countries than in poor countries.
Transitions to dictatorship become less likely as wealth increases.
The importance of the middle class as a necessary condition: “No bourgeoisie, no democracy" (Moore 1966).
Empirical studies in disagreement: is there really a causal relationship between development and democracy?
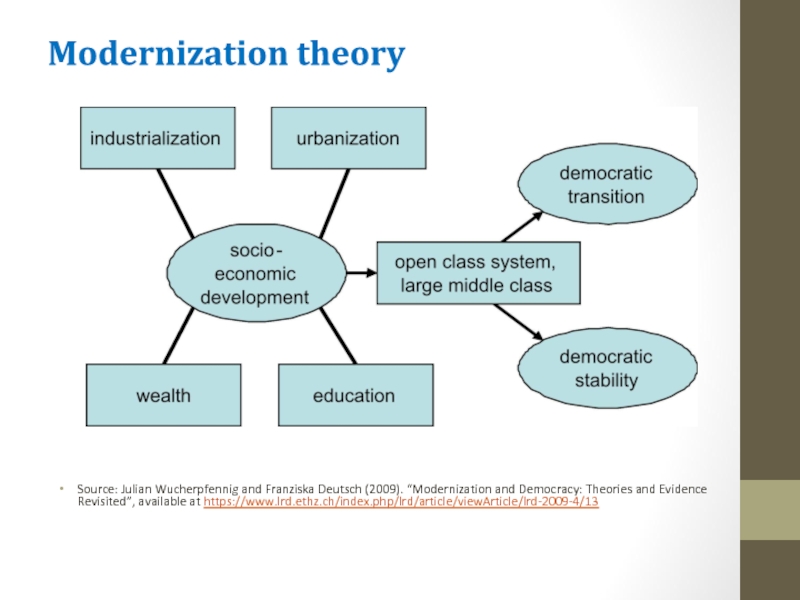
Слайд 3Modernization theory
Source: Julian Wucherpfennig and Franziska Deutsch (2009). “Modernization and Democracy:
Theories and Evidence Revisited”, available at https://www.lrd.ethz.ch/index.php/lrd/article/viewArticle/lrd-2009-4/13
Слайд 4Democracies and Economic Development
Слайд 5Survival Story
Modern variants: which way is the link? (Przeworski et
al. 2000)
Does development bring about democracy?
Does development sustain already
established democracies?
Wealth increases survival of democracy, but does not affect emergence of democracy (Przeworski et al. 2000)
Under democracy the wealthy are afraid to be left out of a small wealthy circle under dictatorship ->support democracy
Under democracy the poor are already poor and have nothing to lose ->will gamble for autocracy
Слайд 6Modernization Theory and Survival Story
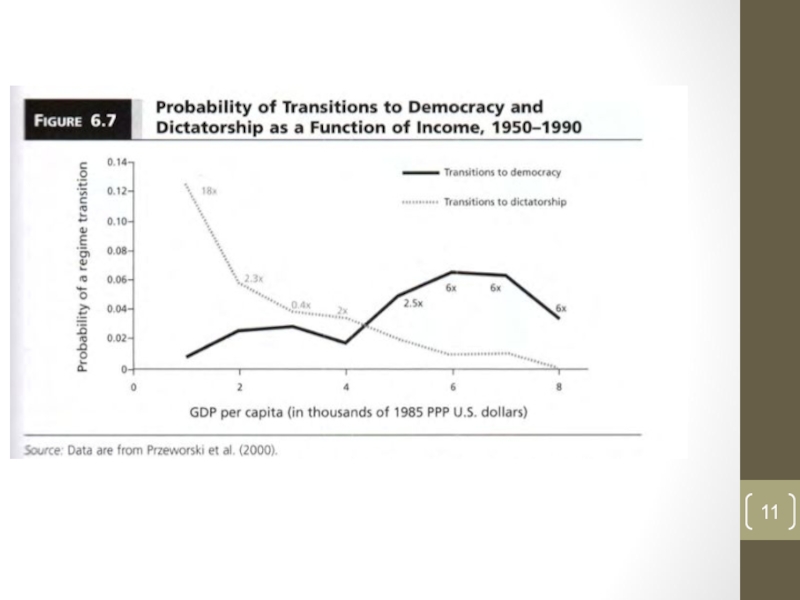
Слайд 8Democracy emergence or survival?
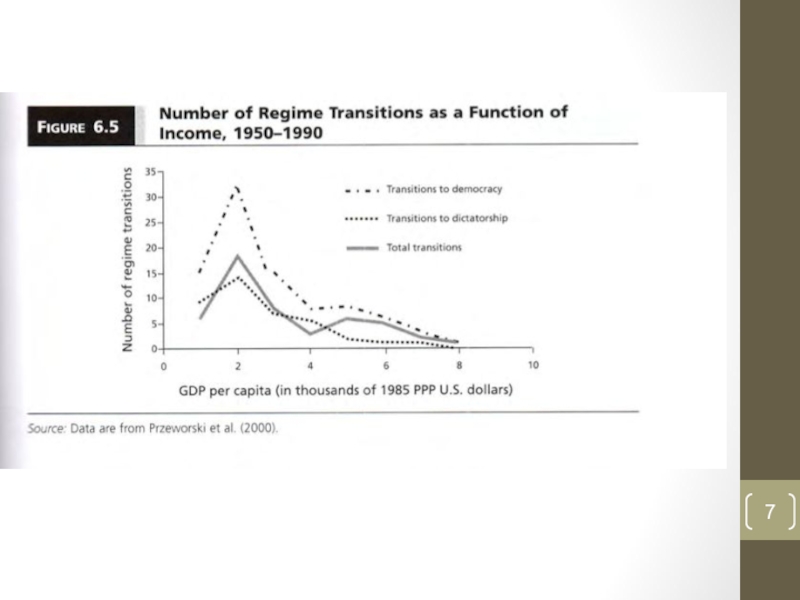
Poor countries – higher number of transitions
But:
different number of democracies and autocracies; poor and rich
Слайд 9Democracy emergence or survival?
Слайд 12Democracy emergence or survival?
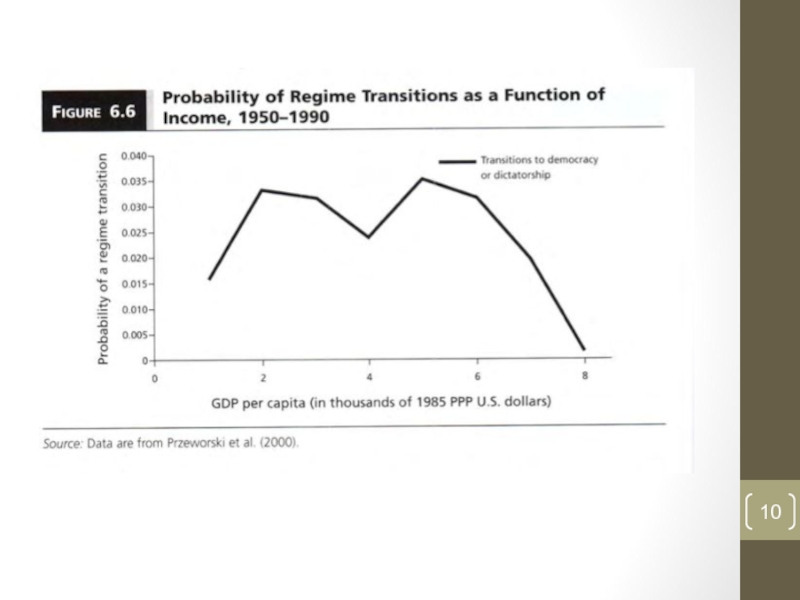
Empirical evidence shows that countries are more
likely to emerge and survive as they become wealthier
BUT WHY?
Слайд 13Strategic bargain and democracy
Democracy as a solution to a credible
commitment problem.
Credible commitment problem - when one promises smth,
but there is no way to check whether she will keep the promise
The latter arises when:
An actor who makes a promise today may have an incentive to renege on that promise in the future
Power is in the hands of the actor who makes the promise and not in the hands of those expected to benefit from the promise’. Clark et al. (2012, p.187)
Слайд 14Strategic bargain and democracy
England in the 17th century (similar story
in North and Weingast, 1989)
Modernization -> from agriculture to wool
production -> mobile assets (you can’t hide fields, but you can hide sheep!) -> production owners can escape taxes
The Crown needs to borrow resources (e.g., taxes) from gentry (e.g., to fund wars)
The Crown fails to credibly commit to pay back (how do we know?)
Gentry demands stronger parliament vis-à-vis the Crown that will make sure the Crown keeps its promises
Слайд 15Strategic bargain and democracy
When authoritarian elites have to bargain:
High level
of wealth inequality -> people demand wealth redistribution (but! Elites
will fight to retain autocracy)
When they fear revolution
When the cost of repression is too high
Acemoglu and Robinson, 2006
Слайд 16The resource curse and democracy
Explains many exceptions to Modernization Theory
Focuses
on the relationship between natural resource wealth (such as oil,
gas, minerals) and political regime type.
Rentier state theory: Leaders controlling large natural resource wealth can operate autonomously from societal interests and are more likely to be autocratic.
Rent availability: Authoritarian leaders with readily available resource revenue can use it for both repression and cooptation.
Taxation: Since leaders are not dependent on tax money from citizens, they can deny representation and ignore political demands.
Class structure: Natural resources usually prevent economic diversification and the formation of a large middle class who can demand democratization.
Exit options: Since natural resources are not mobile, if leaders give up power they will not be able to take these assets with them.
Слайд 17Culture and democracy
The idea that democracy is a culture emerging
from historical, religious, and philosophical foundations.
Culture and political regime are
better to be aligned
Two general hypotheses:
Democracy is more common in some cultures (for example, western cultures) – which support democratic values such as individual liberty, freedom of expression, equality – than in others (for example, Islam, Confucianism).
Economic development does not directly cause democracy, but rather economic development leads to cultural change and the emergence of a civic culture, which in turn leads to democracy.
Is every culture conducive to democracy?
Слайд 18Culture as a Barrier to Democracy
Lipset (1959): God’s word cannot
be disputed -> Catholicism incompatible with democracy
Huntington (1996: 114): Protestanism
is more receptive to democracy than Islam, due to “the inhospital nature of Islamic culture and society to Western liberal concepts”.
Huntington (1991) also argued that Confucianism contradicts with the main tenants of democracy, since it emphasizes “group over the individual, authority over liberty, and responsibilities over rights”. [Fukuyama 1995 disagrees with this view].
Слайд 19Culture as a Sustainer of Democracy
Almond and Verba (1963) -
Civic Culture
A belief that individuals can influence political decisions
High
support for the existing political system
High levels of interpersonal trust
Preference for gradual societal change.
Слайд 20Empirical Evidence
Religion fails to explain democracy
There are democratic countries with
a Muslim majority e.g., Albania, Bangladesh, Indonesia, Senegal and Turkey
Correlation
changes over time (Catholic countries are democratic)
Civic culture has more explanatory power
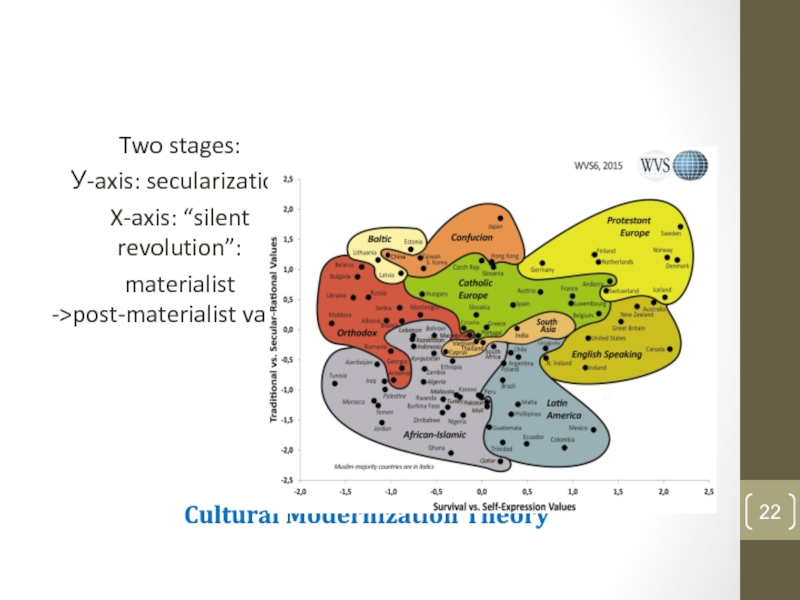
Слайд 21Inglehart-Welzel cultural map
According to Ronald Inglehart and Christian Welzel, there
are two major dimensions of cross cultural variation in the
world:
Traditional values vs. Secular-rational values
Survival values vs. Self-expression values
The explanations of values (from http://www.worldvaluessurvey.org/WVSContents.jsp)
Traditional values emphasize the importance of religion, parent-child ties, deference to authority and traditional family values. People who embrace these values also reject divorce, abortion, euthanasia and suicide. These societies have high levels of national pride and a nationalistic outlook.
Secular-rational values have the opposite preferences to the traditional values. These societies place less emphasis on religion, traditional family values and authority. Divorce, abortion, euthanasia and suicide are seen as relatively acceptable. (Suicide is not necessarily more common.)
Survival values place emphasis on economic and physical security. It is linked with a relatively ethnocentric outlook and low levels of trust and tolerance.
Self-expression values give high priority to environmental protection, growing tolerance of foreigners, gays and lesbians and gender equality, and rising demands for participation in decision-making in economic and political life.

Слайд 22Cultural Modernization Theory
Two stages:
У-axis: secularization
X-axis: “silent revolution”:
materialist ->post-materialist values
Слайд 23Cultural Modernization
“Modernization leads to and sustains democracy but only because
it changes cultural values and beliefs, not because of the
rise in wealth per se.”
Deterministic
Fails to offer a specific mechanism